Macrophthalmus depressus, Ruppell, 1830
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2022.2093679 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7015557 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2549A250-A833-FFAE-15A2-09BEEA0234B8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Macrophthalmus depressus |
| status |
|
Macrophthalmus depressus View in CoL
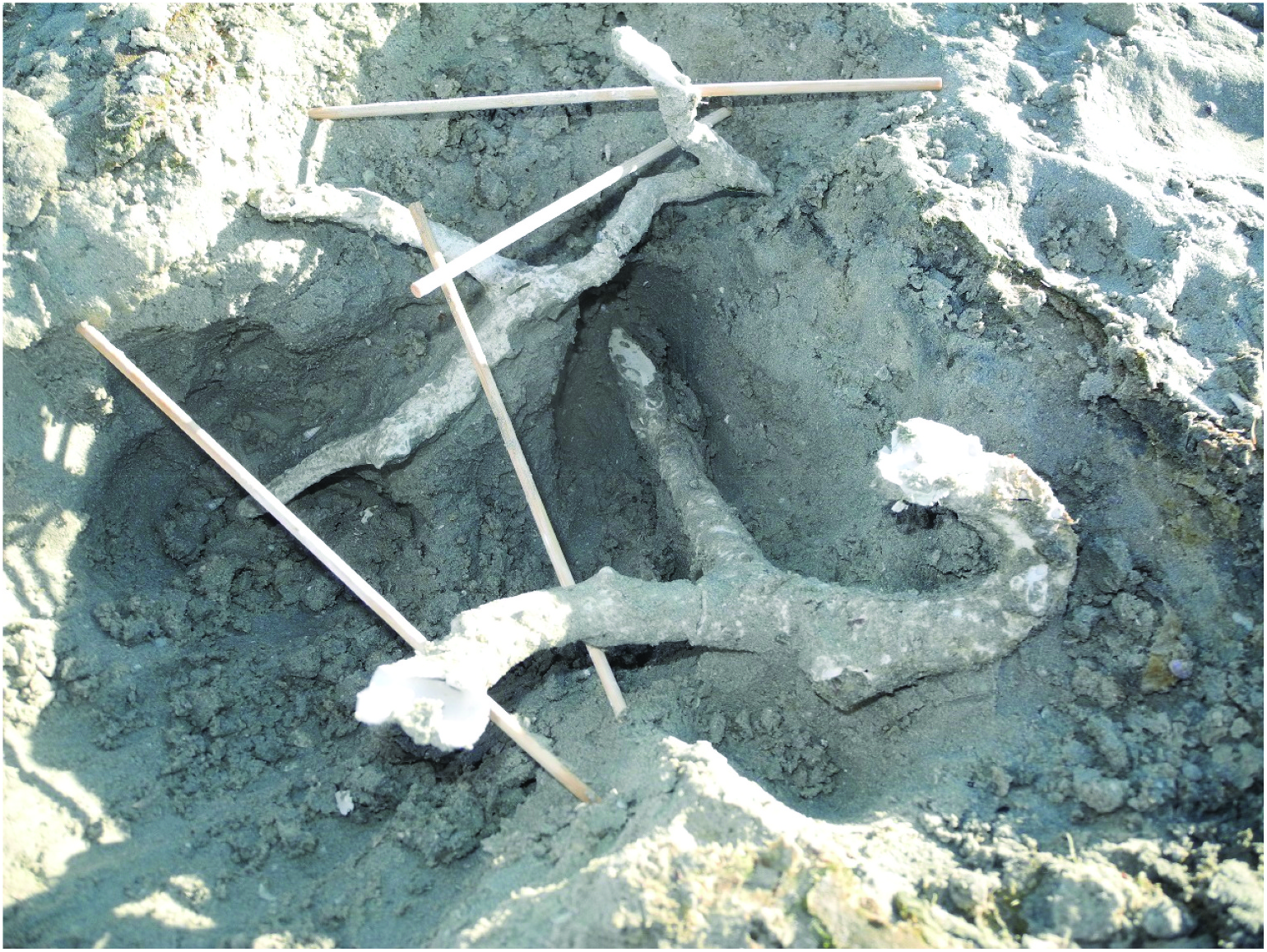
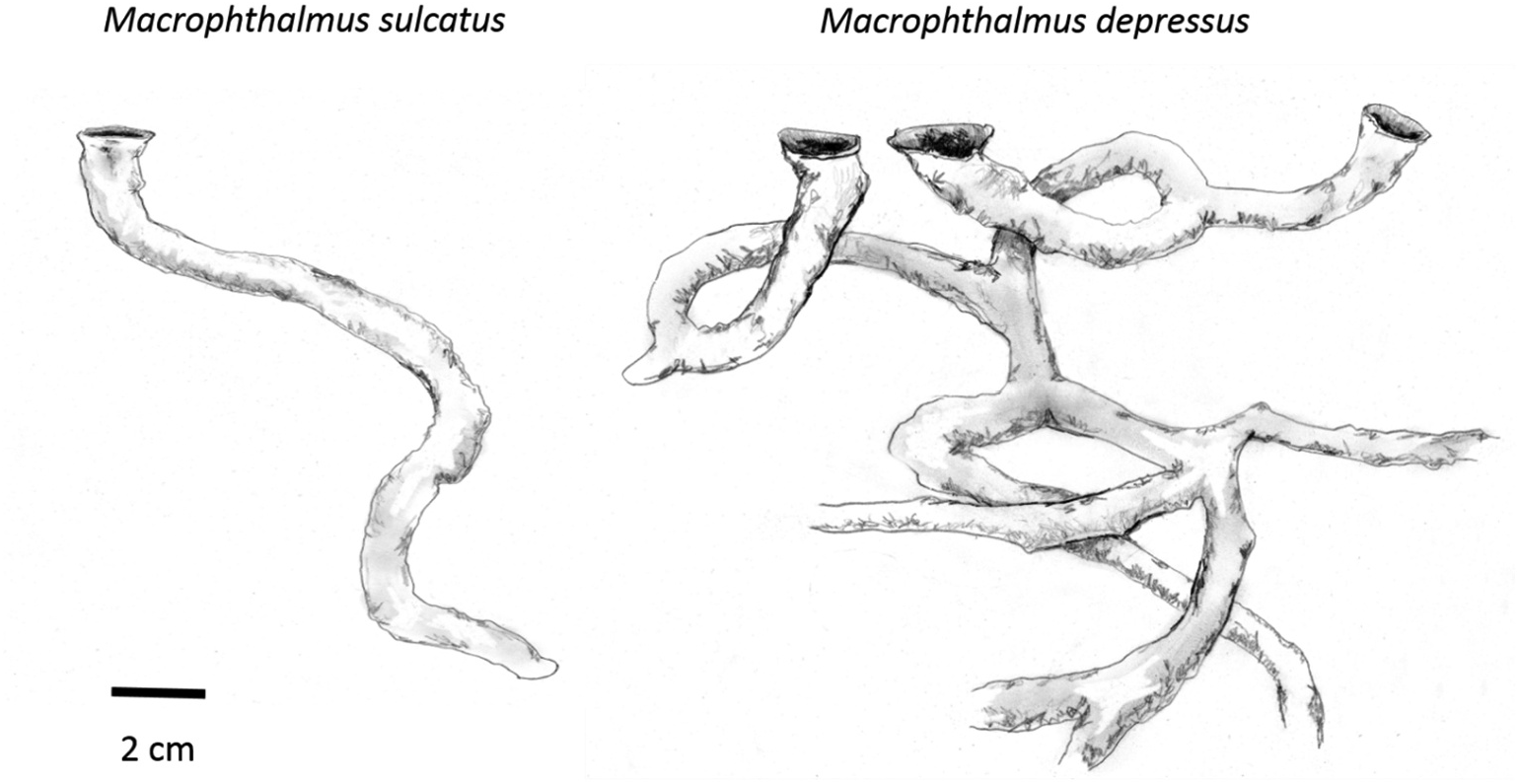
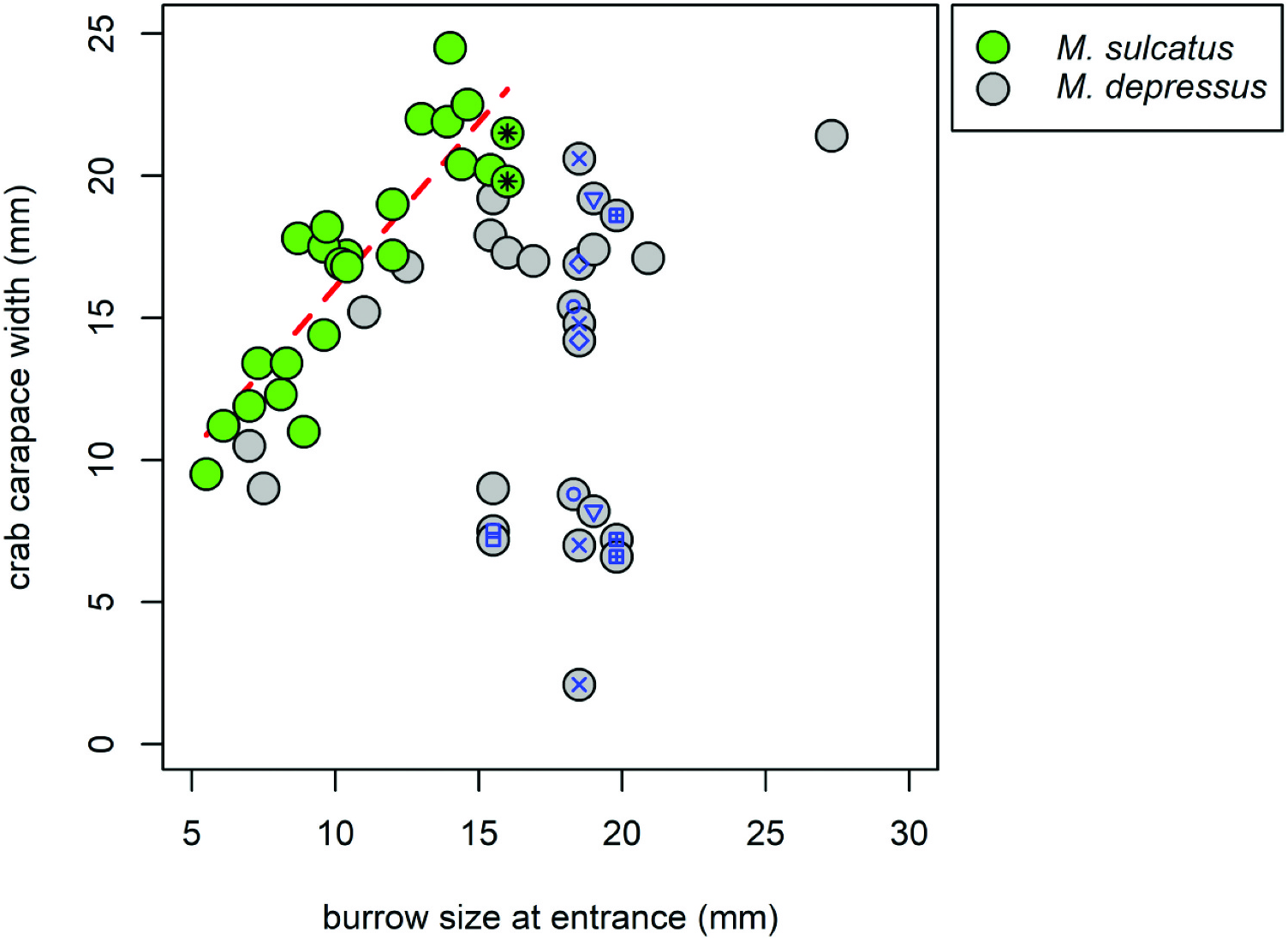
The casted burrows of M. depressus were complex, with multiple entrances and branches ( Figures 2 View Figure 2 and 3 View Figure 3 ). In fact, we never managed to make a complete cast of an entire burrow as the tunnels always continued after where the plaster stopped. One burrow appeared to have five entrances and another had two entrances (the 10 burrow entrances into which plaster was poured ultimately proved to belong to five burrows). Branches were observed leading in every direction and tunnels had various slopes and angles. The maximum depth of a cast was 35 cm, at which the water level was reached. In two casted burrows a single crab was found. In the three other burrows the crabs were probably able to escape, as the burrows were more extensive than our casts. The 16 excavated burrows were similarly complex as the casted burrows. In six of the 16 excavated burrows more than one crab per burrow was encountered (up to four crabs per burrow; Figure 4 View Figure 4 ). In total 27 crabs were captured, of which we identified seven as males and eight as females. Sex could not be convincingly determined in 12 smaller individuals. There was no relationship between burrow size at entrance and crab size (t = 1.109, P = 0.28, R2 = 0.01; Figure 4 View Figure 4 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |