Begonia pachypoda L. Kollmann & Peixoto, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.15553/c2013v681a13 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6302209 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2F162D2A-FF82-6041-0B4D-33356D36FCB1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Begonia pachypoda L. Kollmann & Peixoto |
| status |
sp. nov. |
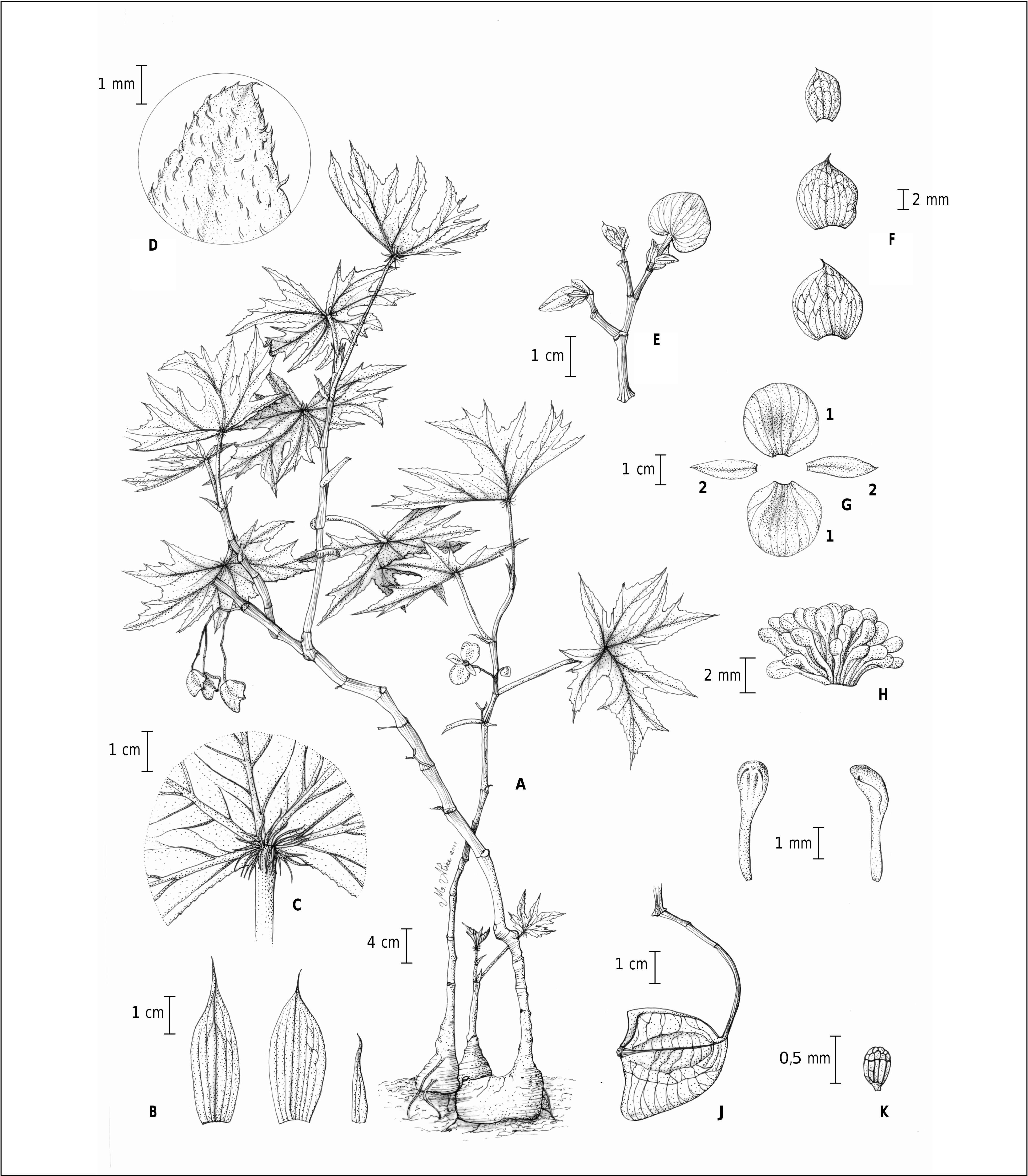
1. Begonia pachypoda L. Kollmann & Peixoto View in CoL , spec. nova
( Fig. 1 View Fig ).
Typus: BRAZIL. Espírito Santo: Alegre, Pedra Severina base, 300 m, 20°40’19”S 41°28’35”O, 16.VI.2009, fl., fr., L.Kollmann, E.Leme & D. Couto 1 1670 (holo-: MBML ; iso-: RB, US, P).
Begonia pachypoda is closely related to B. aconitifolia and B. platanifolia in its swollen stem base, flower size (3.4- 6.5 cm diam.), two placentae per locule and ovules on both sides of placentae, but can be distinguished by a ring of trichomes at the petiole apex, lamina deeply 4-5 lobed, each lobe usually further divided and cut.
Suffrutescent herbs 1.5-2 m tall, saxicolous to rupicolous, glands and simple trichomes. Stems swollen at base, 10-20 × 5-10 cm, brown, internodes 1.2-9(-20) cm long, green, brown when old. Stipules deciduous, 2.4-3.7 × 1-1.7 cm, greenish to reddish, translucent, asymmetrical, slightly falcate, lenticellate, apex mucronate, margins entire, abaxial face carinate, nerves brownish to reddish. Petioles 5-15.5 × 0.8 cm, red, lenticellate, glabrous with a ring of white, dense, thick, trichomes ca. 1 cm long at the apex. Laminae 18-23.5 × 21-37 cm, asymmetrical, palmatifid, deeply 4-5 lobed, each lobe usually further divided and cut, transversely ovate, base cordate, apex acute, margins serrulate, ciliate, venation actinodromous, 4-6 veins at base, red, the midvein making an angle with the petiole, prominent abaxially, adaxial face setose, green, with shining silver-streak near the veins when in shade, abaxial face glabrous, with crystal-like glands, stomata solitary. Inflorescences with 2-3-dichotomous cymes, 4.5- 6 cm long, red, glandular; bracts deciduous, 0.7-1.3 × 0.6- 0.9 cm, greenish with red veins, translucent, ovate to obovate, apex acute, glabrous. Flowers fragrant, occasionally closed up at night. Staminate flowers with pedicels 2.5-3.6(-4.5) cm long, reddish, glabrous; sepals 2, 2.4-2.6(-3.2) × 2-2.3(-3.1) cm, white-pinkish with green margins at base, ovate, base rounded, apex acute to obtuse, margins serrulate; petals 2, 1.8-2(-2.7) × 0.6-0.65(-1.1) cm, white-pinkish, elliptical, base cuneate, apex obtuse, margins entire; stamens 49-52, yellow, filaments 2-2.5 mm long, anthers ca. 2 mm long, obovate, connective not projecting, rimose, apex obtuse to rounded. Pistillate flowers with pedicels 2-2.4 cm long, red, glabrous to glandular; sepals 2, 1.9-2.8 × 1.5-2 cm, white-pinkish, ovate, apex acute, margins serrulate; petals 3, 1.5-2.5 × 0.7- 1.4 cm, white-pinkish, unequal, elliptic to obovate or falcate, apex acute, margins serrulate; ovary 3-locular, placentation axile, two placentae per locule, ovules on both sides of placentae; styles 3, ca. 3.7 mm long, yellow, united at base, each bifurcate, branches flattened, each kidney-shaped with a band of marginal stigmatic papillae. Capsules 1.65-2.5 × 0.9- 1.5 cm, basally dehiscent, wings 3, rounded, larger one 2-3 × 2-2.5 cm, smaller two 1.9-3 × 0.5-0.7 cm. Seeds 0.3-0.4 × 0.25 mm, cylindrical, apex obtuse to rounded.
Habitat, distribution and phenology. – Begonia pachypoda grows in leaf litter and humus on rocks in dry forests of the Atlantic Forest (seasonally semideciduous forests) at ca. 250 m. It is also found on open rocky outcrops. It is presently known only from the type locality in Alegre County in the state of Espírito Santo, Brazil. The type locality is very disturbed by anthropic activities from cattle farming. Flowers were observed from December to June; fruits from June to September.
Etymology. – The specific epithet derives from the latin «pachy» (thick) and «poda» (foot) in reference to the swollen stem base.
Conservation status. – Due to the apparent endemic distribution of B. pachypoda , with extent of occurrence estimated to be less than 10 km 2, it would seem prudent to include this species on the Critically Endangered (CR) (B2ab(iii)) list according to the IUCN (2001).
Paratypes. – BRAZIL. Espírito Santo: Alegre, São João do Norte, base da Pedra Severina , 26.VI.2008, fr., L. Kollmann 11069 ( MBML) ; Alegre, São João do Norte, base da Pedra Severina , 10.VI.2009, fl., V. C. Manhães & al. 230 ( MBML).
Additional material examined. – Cultivated material: plant grown from seed sent from Brazil by Dr. Handro and received by Sylvia Leatherman in 1957, cult. Marge Lee, San Diego, O’Reilly 22 (private herbarium of Kolz Begonia Research Center, duplicate US 2953909 and US 2953910, not seen).
Taxonomical notes. – Begonia pachypoda is part of sect. Knesebeckia (Klotzsch) A. DC. characterized by their two placentae per locule and ovules on both sides of placentae, anthers obovate and shorter than or rarely about as long as the filaments.
Begonia pachypoda resembles B.aconitifolia A. DC. and B. platanifolia Schott. in its swollen stem base, flower size (3.4-6.5 cm diam.), two placentae per locule with ovules on both sides of the placentae. Nevertheless, it can be distinguished from B.platanifolia by the new growth sprouting on the caudex (vs. growth sprouting beside the base of the caudex), lamina with 4-5 deeply divided lobes, each lobe usually further divided and cut (lobes note deeply 4-5 divided with each lobe usually further divided and cut) and with a ring of trichomes at the petiole apex (petiole without a ring of trichomes). It can be distinguished from B. aconitifolia by the staminate flower with 2 petals (vs. without petals) and a ring of trichomes on the petiole apex (vs. petiole without a ring of trichomes) ( Table 1 View Table1 ).
Begonia pachypoda resembles B. leathermaniae O’Reilly & Kareg. by its palmate leaves, ring of trichomes at the petiole apex, and flower size, but it can be distinguished by its suffrutescent habit (vs. rhizomatous), swollen stem base (vs. nonswollen stem base), leaves straight (vs. oblique), shorter inflorescences (4.5-6 vs. 40-50 cm long), and larger capsule wing (2 × 1.4 vs. 0.8-1.6 × 2.9-3.3 cm) ( Table 1 View Table1 ).
Begonia pachypoda is a very singular species that can be distinguished by the caudex at the base of the stem, which can be large, ca. 20 × 10 cm, with new growth generally sprouting on it. B. aconitifolia and B. platanifolia have a swollen stem base, 4-6 cm diam., and growth sprouting beside the stem base, forming a new swollen stem base every year. The leaves of B. pachypoda are green with a shiny silvery white streak along the nerves due to muricate cells where the upper side of the upper epidermis is flattened, reflecting light and causing shiny-streaked areas. When the plant is in a sunlit place the leaf is green, and when it is in a shady place the leaves have the silvery white streak.
The plant is dormant during the dry season, in winter, and sheds its leaves. The inflorescence is short with few, large, white flowers. The flowers have the fragrance of «sweet violet» ( Viola odorata L. ) and occasionally close at night, which is rare in begonia flowers.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |