Ceriana brunettii (Shannon, 1927)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4196.2.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:68A88A77-E760-4293-BE95-AA2785DE3C0C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6084067 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3D0E232F-FFA2-5932-7AAA-FDEE7276FE1A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ceriana brunettii (Shannon, 1927) |
| status |
|
Ceriana brunettii (Shannon, 1927) View in CoL
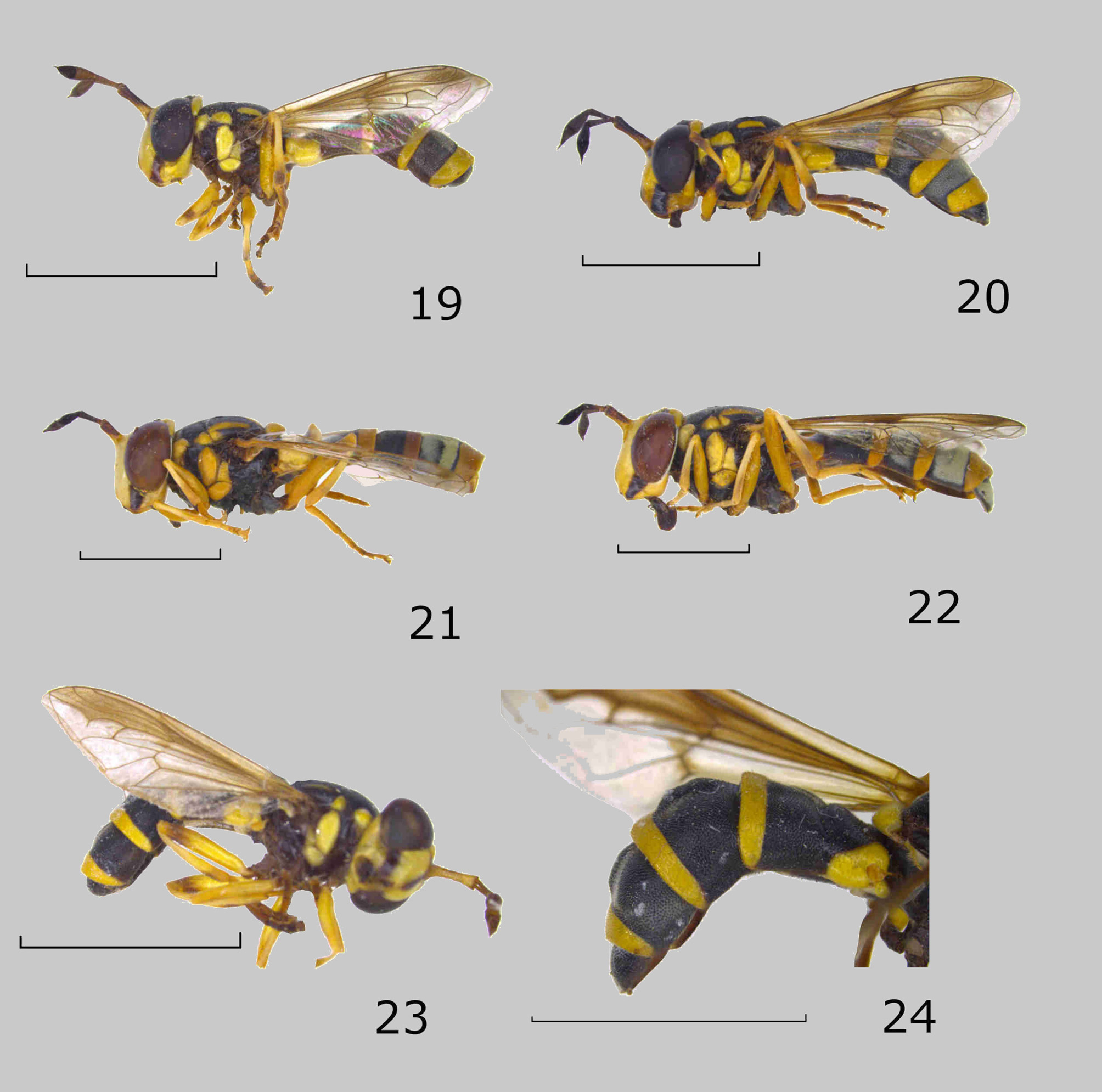
Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1 – 6 , 19, 20 View FIGURES 19 – 24 , 37 View FIGURES 37 – 48 , 56–58 View FIGURES 56 – 58 , 64 View FIGURES 64 – 70 , 166 View FIGURES 166 – 168
Tenthredomyia brunettii Shannon, 1927b: 45 View in CoL . Type locality: Pakistan [HT ♂, AT ♀, NHM]. Ceriana brunettii: Violovitsh (1974) View in CoL comb. nov.
Redescription. MALE ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 – 6 , 19 View FIGURES 19 – 24 ). Body length: 9.1–11.5 mm; wing length: 6.3–7.8 mm. Head ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 37 – 48 ). Face slightly protruding antero-ventrally, with a weakly demarcated tubercle and slightly concave below antennae. Head 2.1–2.2 times wider than face just below the antennae; eye contiguity 0.59–0.67 times as long as length of frons; angle of eyes at eye contiguity 115–125o. Face with a rectangular vitta from eye margin to mouth edge, a short medial vitta on tubercle and an upside down turned V-shaped black macula at level of the frontal prominence. Vertical triangle, dorsal surface of head capsule and a squarish macula on the area of the dorsal surface of head capsule posterior to the ocelli black (the reminder yellow). Frontal prominence 5.0–5.8 times longer than wide; relative length of pedicel is as 1.0–1.1: 1: 0.71–0.83. Antenna and frontal prominence brownish yellow to black; arista with white pile.
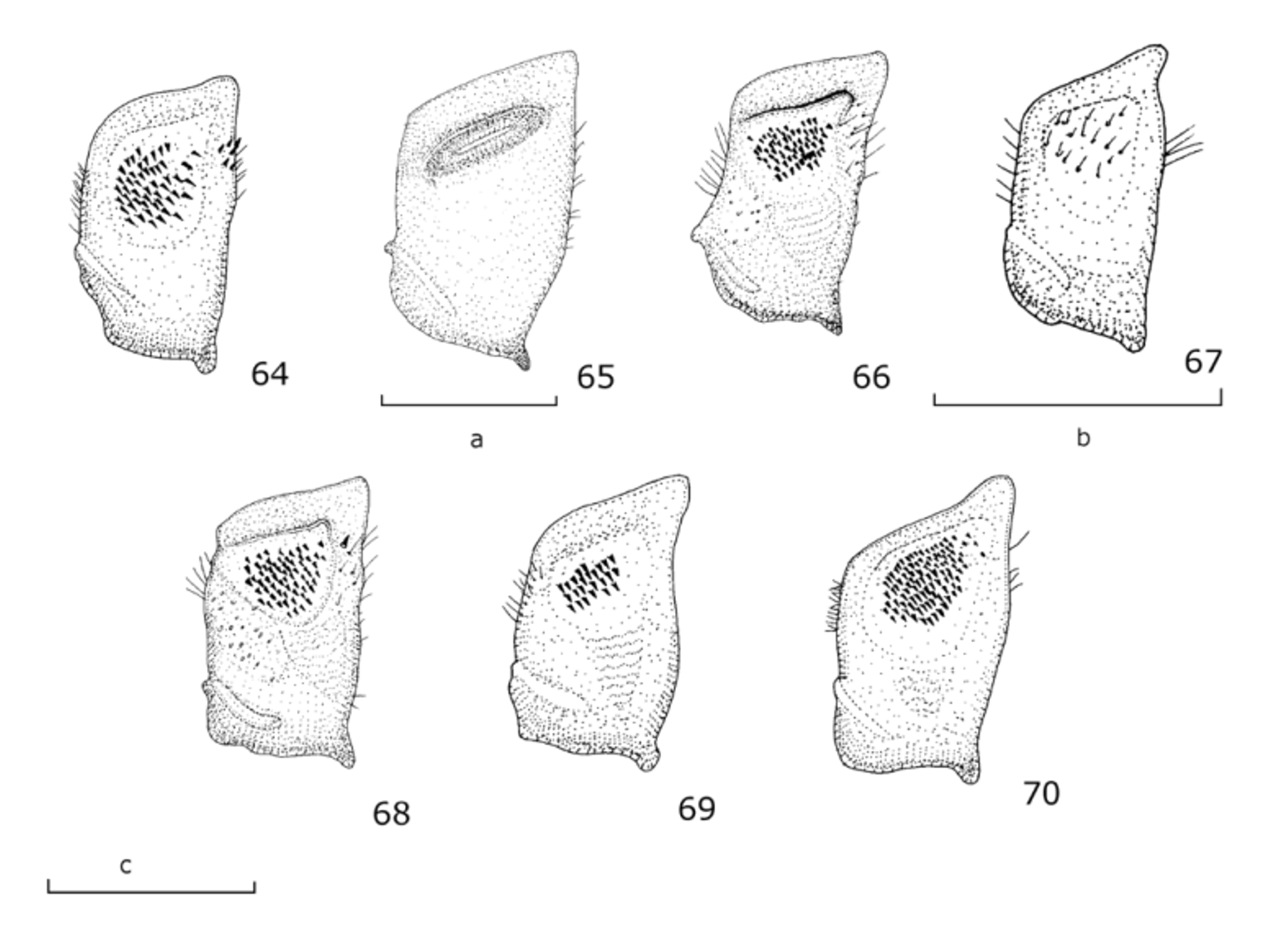
Thorax. Scutum black; yellow maculae on postpronotum and notopleuron connected by a broad yellow vitta. Scutum with a lateral, oval, yellow macula between postalar callus and transverse suture, sometimes without macula. Scutum with white pollinose maculae medially to the transverse suture and two vague white-grey vittae along antero-medial margin. Pleuron black except for the yellow 1/2–3/5 of posterior anepisternum posteriorly, 1/ 3–1/4 of katepisternum dorsally and nearly the entire anepimeron. Metasternum with short pile and a low, rounded elevation medially on antero-ventral part. Scutellum entirely yellow. Legs. Colour yellow with black; coxa black; trochanter yellow; apical 1/8–1/6 of profemur black; apical 1/6–1/5 of meso- and metafemur black; apical 1/4–1/3 of pro- and mesotibia black; apical 1/5–1/3 of metatibia black; tarsus dark-brown to black, sometimes first 2 tarsomeres of pro- and mesotarsus brown-yellow to yellow. Metatrochanter with dense black setulae medially and scattered black setulae posteriorly ( Fig. 64 View FIGURES 64 – 70 ). Mesofemur without flattened area antero-basally; metatrochanter with a weak sulcus and a narrow rim laterally. Metatibia without an appendix; metafemur elongate and slightly curved. Wing. Hyaline except for anterior 1/2, along vein R4+5, and along spurious vein. Loop of vein R4+5 deep, with a short appendix. Cross-vein r-m slightly curved. Wing microtrichose, except for the basal half of cell br, area posterior to vena spuria and along apical half of cell bm. Alula microtrichose, more sparsely on the posterior half; alula 2.4–2.7 times longer than wide.
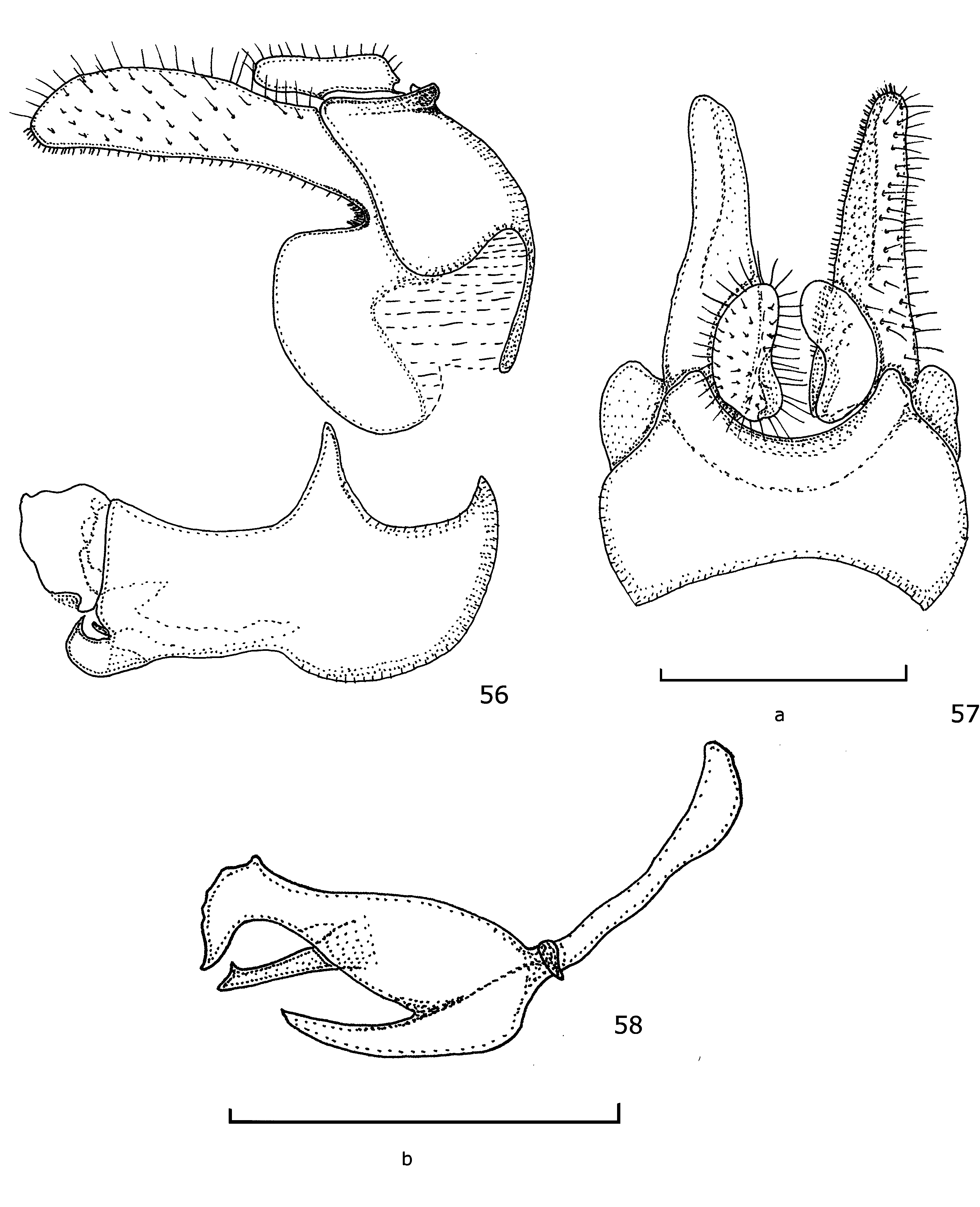
Abdomen. Length of tergite I: II: III: IV is as 1: 1.5–1.6: 1.7–1.8: 1.5–1.6. Width of yellow fascia medially: length of tergite of respectively tergite II, III and IV as 1: 3.3–3.7, 1: 3.5–4.1 and 1: 2.4–2.6. Tergite II wider than long, although anterior margin narrower than posterior margin; length of tergite II: width of tergite II at respectively anterior: posterior as 1: 1.0–1.1: 1.1–1.4. Tergite I with a large triangular yellow macula on each antero-lateral corner (maculae separated by a short distance). Posterior margin of tergites II–IV with a broad, yellow fascia tapering abruptly just before lateral margin of tergite; lateral margin of tergite IV black and very narrowly emarginated. Tergite I with a low medial elevation. Tergites III and IV medially with a very inconspicuous longitudinal elevation. Tergites III and IV with variable amount of grey-white pollinosity mediolaterally (tergite IV entirely pollinose). Sternites I–III with narrow yellow posterior margin. Genitalia. Epandrium with rather narrowly emarginated ventral rim ( Figs 56, 57 View FIGURES 56 – 58 ); in dorsal view, cerci bean shaped ( Fig. 57 View FIGURES 56 – 58 ), with pile about as long as the width of cerci; surstylus bi-lobed, dorsal lobe elongate, ventral lobe circular ( Fig. 56 View FIGURES 56 – 58 ); surstylar apodeme separated in two triangular shaped sclerotized parts; superior lobe and lingula as in Fig. 56 View FIGURES 56 – 58 ; aedeagus with an elongated and apically pointed extension baso-ventrally; with an elongate extension, originating from the medial part of aedeagus, ventro-medially, with a triangular-shaped projection apically on dorsal margin; apex of aedeagus duck-head shaped ( Fig. 58 View FIGURES 56 – 58 ). FEMALE ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1 – 6 , 20 View FIGURES 19 – 24 ). Body length: 9.5–10.2 mm; wing length: 7.2–7.9 mm. Similar to male, except for normal sexual dimorphism and the following characters. Head. 2.0–2.1 times wider than face just below the antennae. Frontal prominence 5.2–5.9 times longer than wide; relative length of pedicel is as 1.0– 1.1: 1: 0.79–0.88. Frons with a yellow fascia from eye to eye; vertex black with a large, triangular, yellow macula medially; dorsal surface of head capsule yellow with a squarish black medial macula posterior to the ocellar triangle. Legs. Metatrochanter with black setulae medially. Wing. Alula broad, 2.3–2.5 times longer than wide. Abdomen. Length of tergite I: II: III: IV: V is as 1: 1.6–1.8: 2.1–2.4: 1.7–2.0: 0.5–0.7. Width of yellow fascia medially: length of tergite of respectively tergite II, III and IV as 1: 3.1–3.5, 1: 3.3–3.6 and 1: 2.1–2.3. Tergite II wider than long (anterior margin narrower than posterior); length of tergite II: width of tergite II at respectively anterior: posterior as 1: 1.1–1.2: 1.5–1.6. Tergites II–IV extensively pollinose.
Material examined. Holotype and allotype of Ceriana brunettii : 1 Ƌ, "Holo- / type " [round white label with red margin], "British Baluchistan / Quetta / July 1902 / Lt. Col. C.G. Nurse", " Quetta / 7.02.", " Tenthredomyia / brunettiii / Shannon " ( NHM) ; 1 ♀, "allo / Type " [round white label with red margin], "British Baluchistan / Quetta / July 1902 / Lt. Col. C.G. Nurse", " Quetta / 7.03." ( NHM) . Additional material: 26 Ƌ, 15 ♀ (NHM, MZLU, NBC, ZIN).
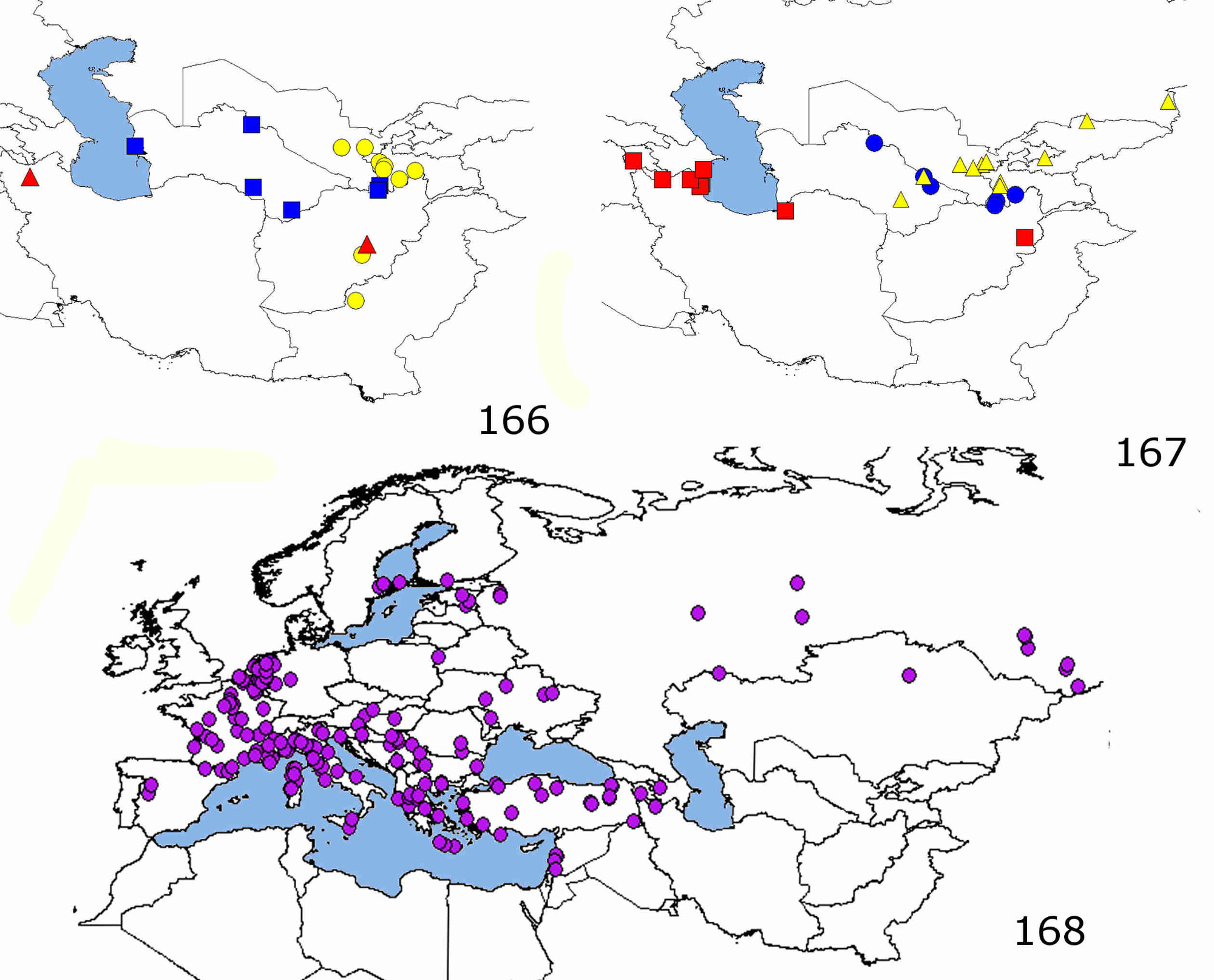
Distribution ( Fig. 166 View FIGURES 166 – 168 ). Afghanistan, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
Biology. Adults have been found visiting flowers of Matricaria chamomilla . They fly from late May to mid September, with an apparent peak in late August to early September. Larva unknown.
| NHM |
University of Nottingham |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.