Lamelloramus rhombiformis, Frederiksen, Sara B., 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3694.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AEFE8AE1-4B6A-4BC2-8D08-9CFF6087E2A4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6161317 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/456F277E-C468-1A07-FF0B-FE70FD4F334D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lamelloramus rhombiformis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Lamelloramus rhombiformis View in CoL n.sp.
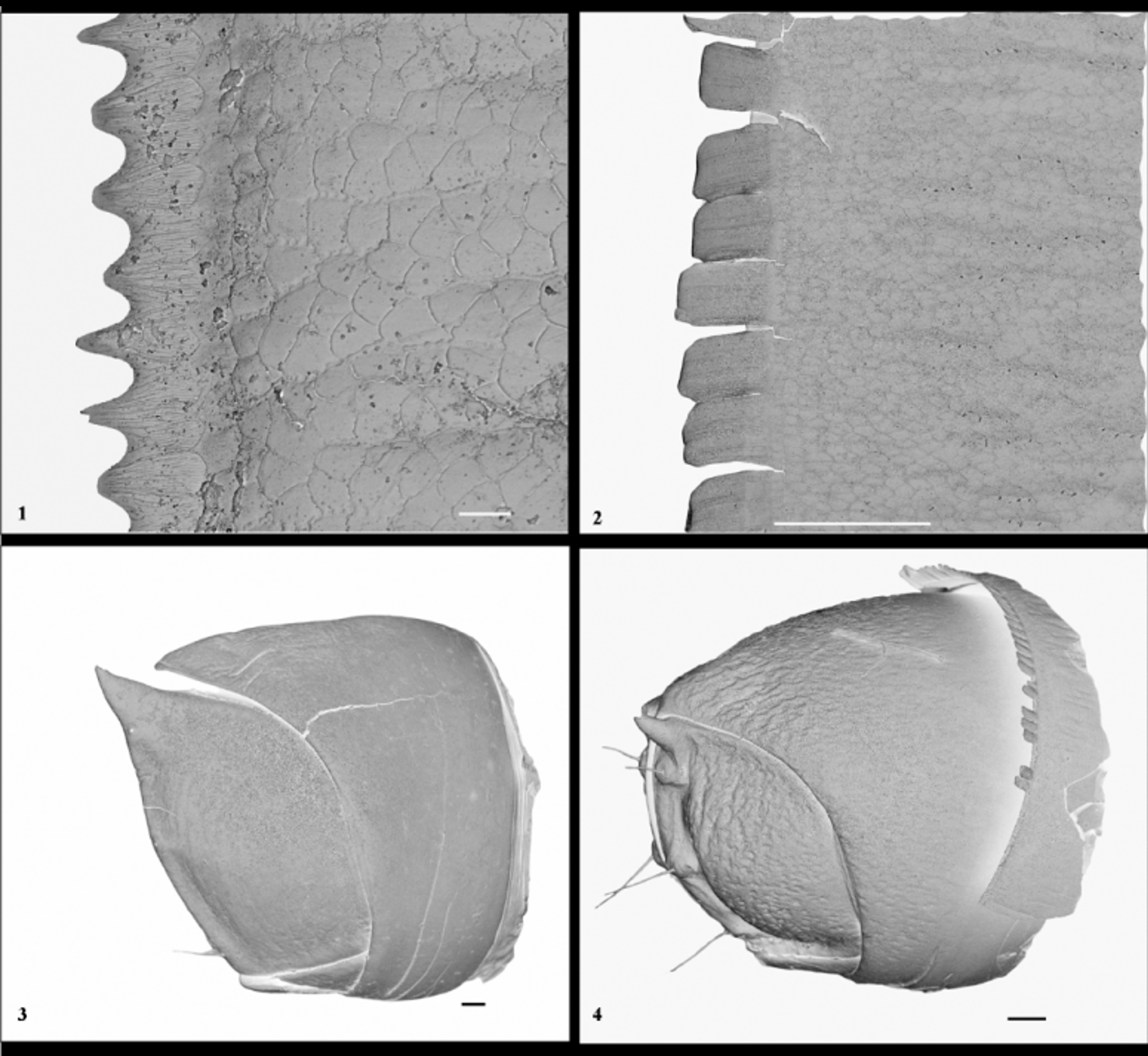
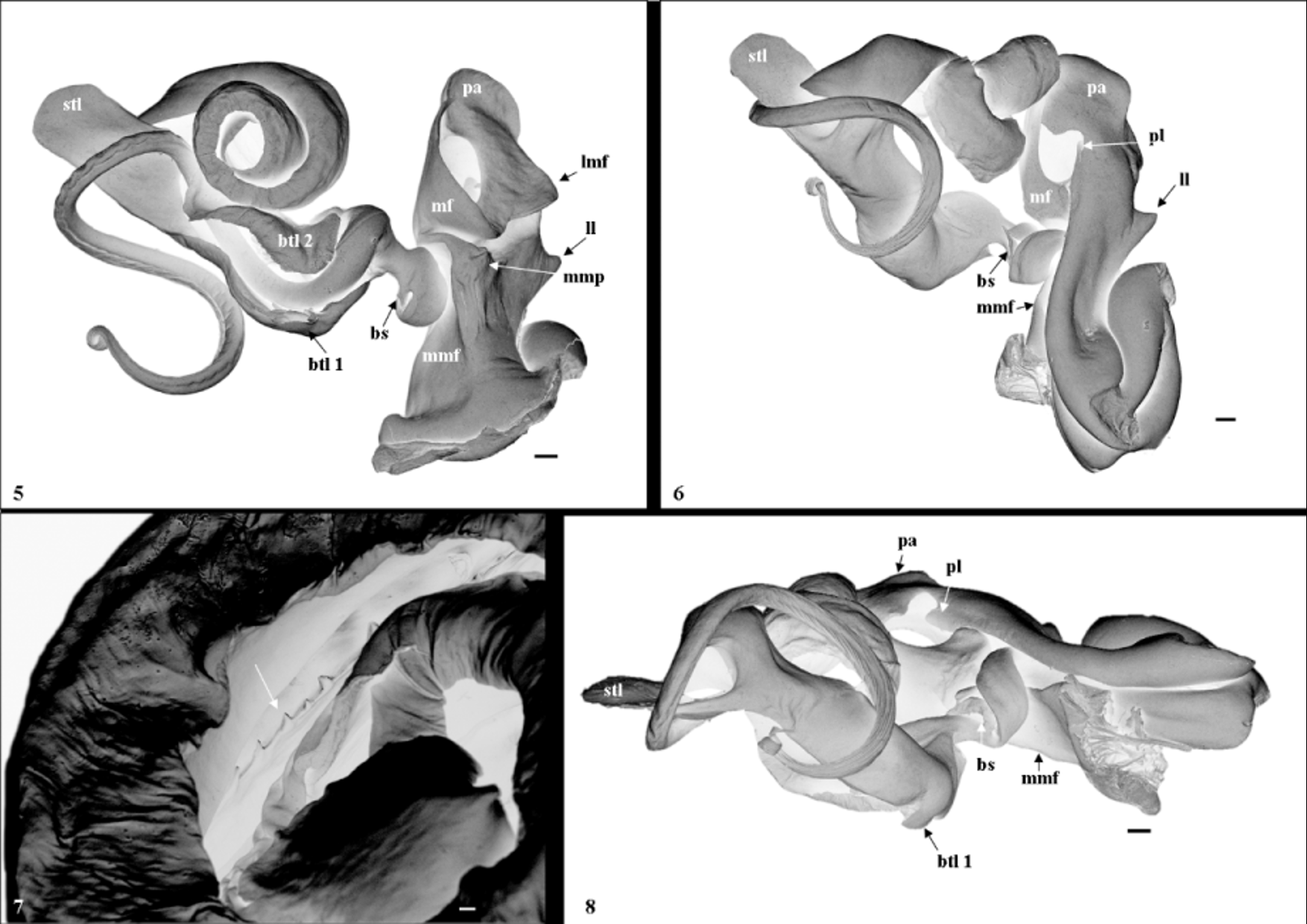
Fig.1 View FIGURE 1 – 4. 1 , 5–8 View FIGURE 5 – 8 .
Material: Holotype male: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani, 29/VI/1985, R. Jacobsen leg. (ZMUC 00020514). Paratype male: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani, 8/IV/1985, T. Nielsen leg. (ZMUC 00020515). 3 males: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani, 500 m, 07/II/1977, H. Enghoff, O. Lomholdt. O. Martin leg. (ZMUC 00020512, ZMUC 00020513, ZMUC 00020509). Male: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani, 1000 m, 05° 07`S, 38° 34`E, 10/II/1997. P. Bjørn. L. Sørensen leg. (ZMUC 00020520). Male: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani, 1000 m, 26/VII/1974, I.B. & H. Enghoff leg. (ZMUC 00020510). Male: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani, 1000 m, 02/II/1977, H. Enghoff, O. Lomholdt. O. Martin leg. (ZMUC 00020519). Male: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani, 950 m, 05° 05,7`S, 38° 38`E, 27/X–9/XI/1995. C.E. Griswold, N. Scharff, D. Ubick leg. (ZMUC 00020522). Male: TANZANIA, East Usambara Mts., Amani Nature Reserve, Tanga region, Muheza + Korogwe destrict, 05° 06`04,7” S, 38° 37`43,3” E, 25/V/2011. S. Frederiksen leg. (ZMUC 00020525).
Diagnosis: Differs from L. triangularis by the coxa. Whereas the coxal apex of L. rhombiformis is diamondshaped, that of L. triangularis is triangular. Also the median metaplical flange of L. triangularis does not reach as high apically as that of L. rhombiformis does, but instead reaches further lateral basally (it reaches beyond metaplical process which metaplical flange of L. rhombiformis does not). Also, the side-branching lamella of L. triangularis is triangular instead of square. L. rhombiformis has a serration running along the centre of the telomere, where L. triangularis only has a straight-edged ridge.
Etymology: Named after the diamond-shaped (a rhombe) coxal apex.
Description (based on all specimens): Body length 45–50 mm, diameter 3,1–3,8 mm, 51–56 podous body rings.
For head, body and colouration see genus description. Telson more yellow than brown.
Gonopods (fig. 5–8): Coxa with a lateral lobe (ll) about half way towards apex, mesal metaplical flange (mmf) small. Proplica ending in a distad proplical lobe (pl) on median side. Above, proplical lobe reaches the large flat diamond-shaped proplical apex (pa) overreaching metaplica. Medially to proplical lobe metaplical lamella (ml) curves outwards and up, flat and triangular, with the flat side turned 90° compared to proplical apex. Median metaplical lamella starting on anterior side of coxa curving around medially to the posterior side. Metaplica continues curving into a small posteriad lateral metaplical flange (lmf), metaplica further continues curving up to merge with the proplical apex on the posterior side, giving the coxa an overall apical sickle-shaped appearance posteriorly. Median metaplical flange merges anteriorly into a lobular median metaplical process (mmp) which is "roofing" the position of the telopodite arculus. Metaplical process continues basoposteriorly curving around to accommodate telopodite arculus. Telopodite: basomere with a torsotope and a posttorsal narrowing, between torsotope and narrowing a posttorsal basomeric spine (bs) is situated appressed to basomere. Telomere long and ribbon-shaped, the last 2/3 curled up completely with serration running the length of it centrally. Telomere turning apically at a 90° angle. At the base of telomere a small telomeric lamella (btl1) is closely appressed, ending in a round, dark sclerotization, sometimes superficially resembling a spine. At the base of telomere on the opposite side of the small telomeric lamella a big elongate telomeric lamella (btl2) is folded over telomere and solenomere. Just before the telomere curls a big, square ended lamella side branches (stl). Solenomere long and whip-like, protruding from telomere just basally to side-branching telomeric lamella, and with a small loop and strong striation at apex. Efferent grove clearly visible.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |