Eutobrilus longicaudatoides, Gagarin, Vladimir G. & Naumova, Tatyana V., 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.203363 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5621710 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/486687B9-FFED-9E5A-FF5E-FFC3FB5DF901 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Eutobrilus longicaudatoides |
| status |
sp. nov. |
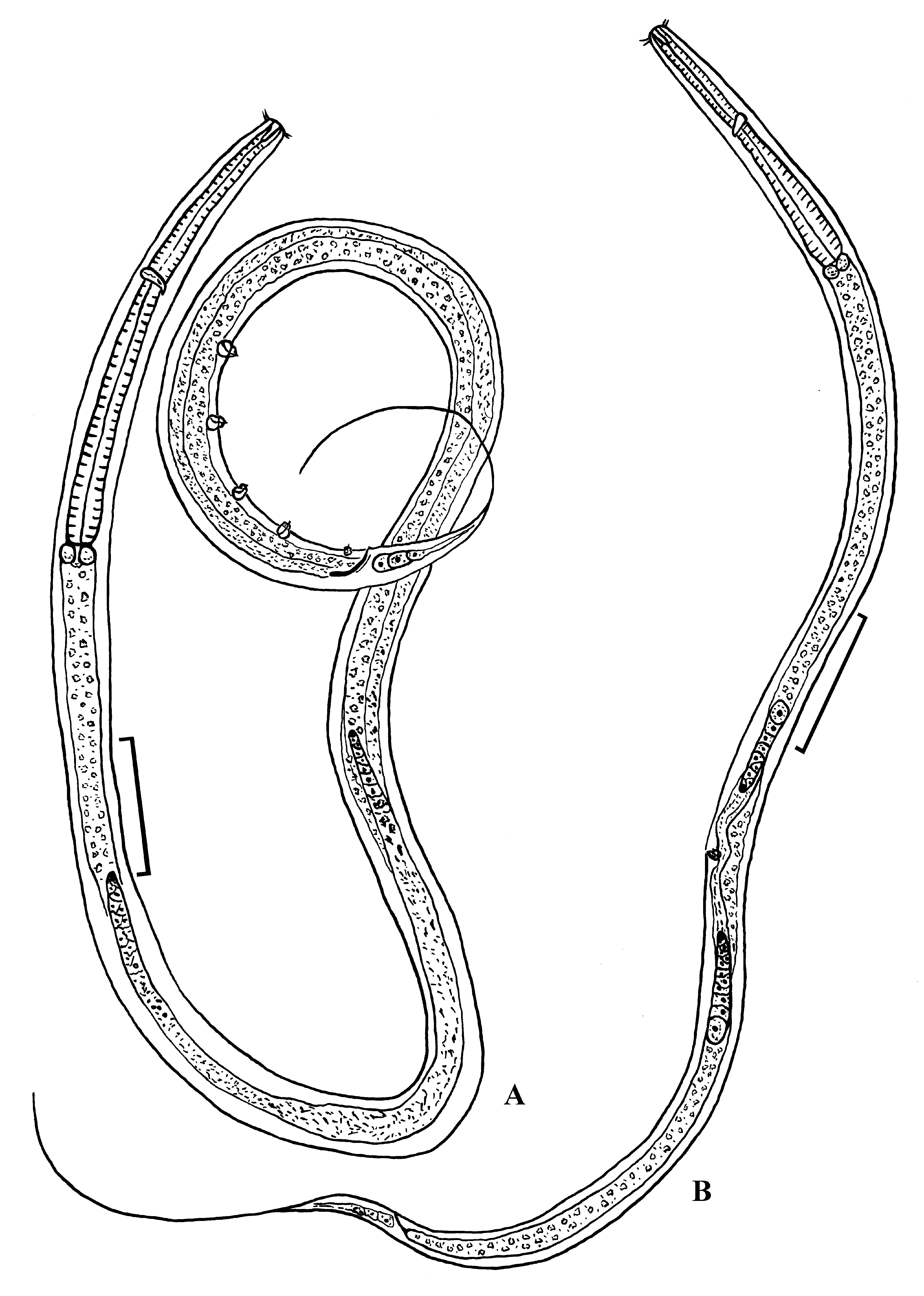
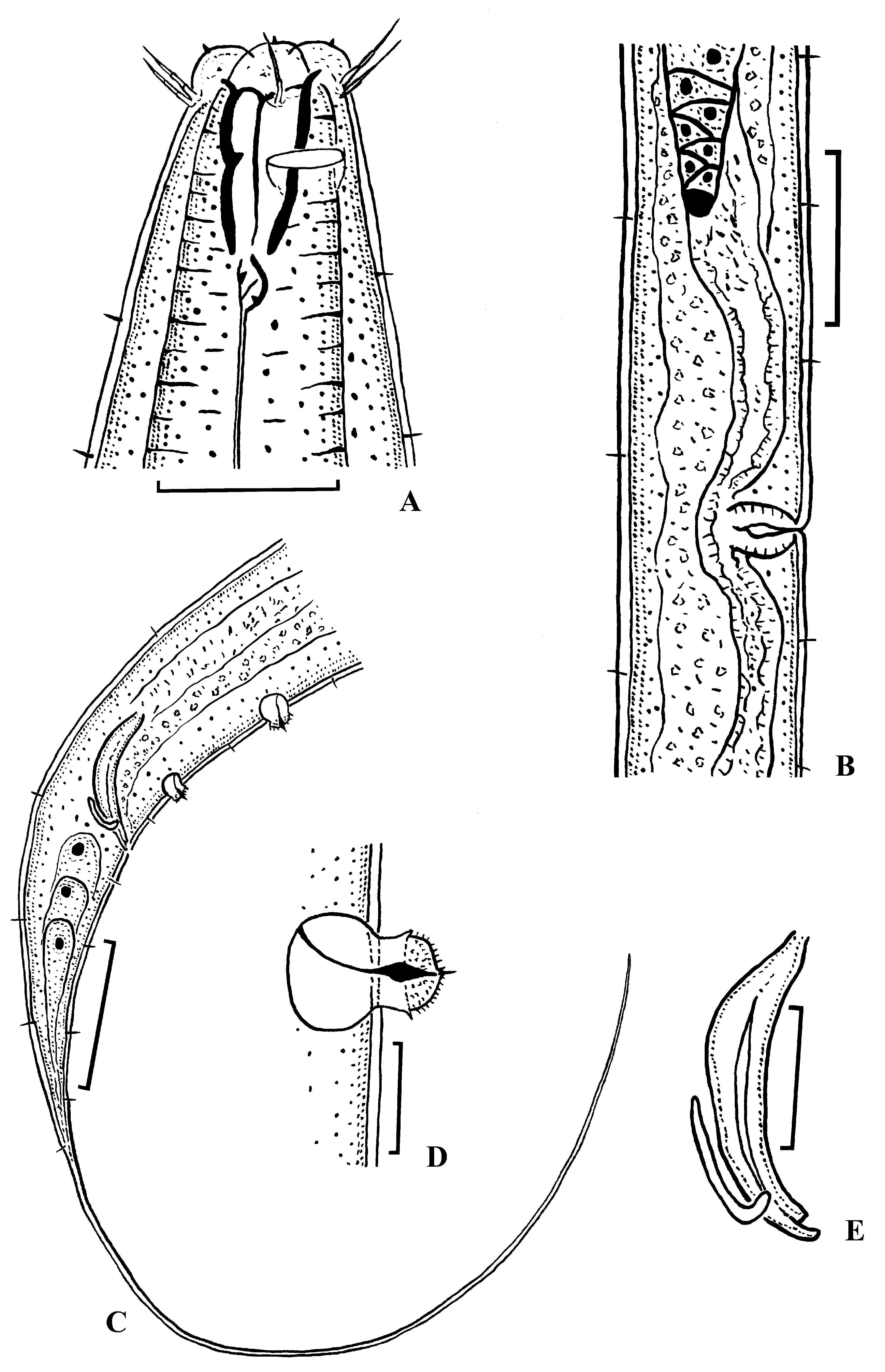
Eutobrilus longicaudatoides sp. n. ( Triplonchida : Tobrilidae )
( Figs 3–5 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 )
Type material. Holotype male, slide reference number 278, deposited in the collection of the Limnological Institute, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Irkutsk, Russia).
Paratypes. One male and three females deposited in the collection of the Limnological Institute, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Irkutsk, Russia).
Measurements. Table 3 View TABLE 3 .
Type locality. Academical Ridge. Lake Baikal, Siberia, Russia, depth 389 m, silt. Collected on 3 October 2009.
Etymology. The species name means “long-tailed”.
Description. Male. Body cylindrical, tapering toward both extremities. Cuticle finely annulated, 1.3–1.7 µm thick at mid-body. Crystalloids absent. Somatic setae 4–5 µm long. Lips well developed, high. Inner labial sensilla papilliform. Outer labial sensilla and cephalic sensilla setiform in shape, thin and articulated, arranged in a single circle. Six outer labial sensillae 10 µm long, 48–52 % of labial region width. Cephalic sensilla 7–8 µm long. Cheilostom spacious; remaining buccal cavity narrow, funnel-shaped, 18–20 µm long. Dorsal pocket and dorsal tooth not visible. Both subventral pockets overlapping each other. Stoma 31–32 µm long, equal to 1.5–1.7 labial region diameters in length. Amphidial fovea cup-shaped, amphid aperture located at the level of buccal cavity. Cervical setae absent. Pharynx muscular, comparatively long, expanding gradually towards its base. Nerve ring encircles pharynx at 40–45% of pharyngeal length. Cardia small, surrounded by 3 oval glands. Renette, renette canal, ampula and excretory pore not observed. Testes paired, opposed, situated to the left of intestine, anterior testis outstretched, posterior testis reflexed. Vas deferens well developed. Spicules 1.4–1.5 times as long as the cloacal body diameter, robust, slightly ventrally curved, without capitulum. Apical end of spicules bifurcated. Gubernaculum comparatively short, 20–22 µm long, with apical bend. Precloacal supplementary organs echinate, 5 in number. Supplement ampulla spacious, spherical, its content is concentrated in the upper portion of ampulla. Supplement pads armed with small thorns (approximately 40–50 in number) and one longer and thicker thorn. Posteriormost supplement is smaller than the other and is situated at the level of spicules. Row of supplements is 182–210 µm long. Tail slender, very long, with proximal conical and distal cylindrical portions, gradually merging into one another. Distal portion of the tail is 2.6–2.8 times longer than its proximal portion. Caudal setae 5–7 µm long, arranged in 4–5 subventral and 3–4 subdorsal pairs. Three caudal glands present, opening through short spinneret. Tail terminus without subterminal setae.
Female. General morphology is similar to that of males in structure of cuticle and anterior body end. Cuticle finely annulated. Somatic setae short and scarce. Crystalloids and cervical setae absent. Labial region comparatively wide. Lips well developed, high. Inner labial sensilla papilliform. Six outer labial sensilla and four cephalic sensilla setiform in shape, thin and articulate, arranged in a single circle. Outer labial sensilla are longer than cephalic sensilla; outer labial sensilla are as long as 45–50 % of labial region diameter. Cheilostom is comparatively small. Remaining of the buccal cavity narrow, funnel-shaped; somewhat longer than the labial region diameter. Dorsal pocket and dorsal tooth not visible. Both subventral pockets overlapping each other. Teeth in the pockets are comparatively small. Amphidial fovea cup-shaped, amphidial opening located at the level of buccal cavity. Pharynx muscular, comparatively long, expanding gradually towards its base. Renette cell and canal, ampulla and excretory pore not observed. Rectum 0.9–1.2 times as long as the anal body diameter. Reproductive system didelphic, amphidelphic. Ovaries situated to the left of intestine, reflexed and comparatively short. Oocytes numerous. Vulva a transverse slit, situated slightly anterior to mid-body. Vulval lips not sclerotized and not protruding outside the body contour. Vulval glands not seen. Vagina spherical, with thick and muscular walls. Uterus containing numerous spindle-shaped spermatozoa. Tail very long, with proximal conical and distal cylindrical portions. Distal portion of the tail is 2.9–3.3 times longer than its proximal portion. Caudal glands and spinneret well developed. Subterminal setae absent.
Diagnosis. Body 2.07–2.14 mm long in male, 2.47–3.05 mm long in female. Cuticle finely annulated. Crystalloids absent. Outer labial sensilla and cephalic sensilla thin and articulate, arranged in single circle. Outer labial sensilla longer than cephalic sensilla and are as long as 45–52 % of labial region diameter. Cheilostom comparatively small. Buccal cavity narrow, funnel-shaped. Dorsal pocket absent. Subventral pockets overlapping, with small teeth. Vulva a transverse slit, situated slightly anterior to mid-body. Vagina spherical, with thick and muscular walls. Males with comparatively short, robust, slightly curved spicules and comparatively short gubernaculum with curved apical end. Precloacal supplements 5 in number, echinate. Posteriormost supplement smaller than the other and situated at the level of spicules. Tail very long, with proximal conical and distal cylindrical portions. Distal portion of the tail 2.6–3.3 times longer than its proximal portion. Subterminal setae at tail terminus absent.
Differential diagnosis. Eutobrilus longicaudatoides sp. n. differs from all species of the genus Eutobrilus by its very long and slender tail (c = 4.5–6.3, c ΄ = 11.4–16.7 versus c = 5.0–24.3, c ΄ = 2.5–12.0 in other species of the genus). The new species is similar to E. anguiculus ( Tsalolikhin, 1977b) in body size and stoma structure, but differs from it in the longer outer labial setae (9–10 µm long or 45–52 % of the labial region diameter versus 15–20 long or 50–60 % of the labial region diameter in E. anguiculus ), longer tail (males, c = 5.3–5.5, c ΄ = 11.4–11.8 females, c = 4.5–6.3, c ΄ = 15.1–16.7 versus males, c = 7.4–10.4, c ΄ = 8–9, females, c = 5.0–7.7, c ΄ = 10–12 in E. anguiculus ), smaller number of supplements (5 in number versus 6 in number in E. anguiculus ) and shorter spicules (47–53 µm long versus 66–68 µm long in E. anguiculus ( Tsalolikhin, 1983; Gagarin, 2009)).
TABLE 3. Morphometrics of Eutobrilus longicaudatoides sp. n. (all measurements are given in µm unless otherwise stated, except for the rations a, b, c, c ʹ, V, n. sup. and spic. cl.)
| Character | Holotype male | Paratype male | Paratype females (n = 3) range mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| L a b | 2071 56 6.6 | 2142 51 4.8 | 2473–3045 2693 44–55 49 6.0–7.3 6.6 |
| c cˏ V, % | 5.5 11.4 – | 5.3 11.8 – | 4.5–6.3 5.4 15.1–16.7 16.0 44.5–48.5 47.1 |
| diam. c. s. diam. midb. a. d. | 19 37 33 | 21 42 34 | 19–24 22 46–62 55 28–36 33 |
| o. l. s. c. s. st. l. | 10 8 32 | 10 7 31 | 9–10 9 6–8 7 33–38 36 |
| st. w. | 10 | 9 | 10–13 12 |
| am. w. dis. am. | 10 13 | 11 14 | 9–10 9 13–15 14 |
| ph. l. dis. ph. cl. dis. ph. v. | 313 1383 – | 443 1298 – | 350–511 412 – – 805–843 824 |
| dis. v. a. | – | – | 805–1208 950 |
| Q1 Q2 spic. spic. cl. gub. l. | – – 47 1.4 20 | – – 53 1.5 22 | 180–197 190 195–220 208 – – – – – – |
| n. sup. l. sup. r. t. l. | 5 210 375 | 5 182 401 | – – – – 468–570 507 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |