Liobagrus hyeongsanensis, Kim, Su-Hwan, Kim, Hyeong-Su & Park, Jong-Young, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4007.2.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:60ABECAF-9687-4172-A309-D2222DFEC473 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5621746 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/492087BF-FFE3-7969-A7E8-F8EDFEA9C59A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Liobagrus hyeongsanensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Liobagrus hyeongsanensis View in CoL sp. nov.
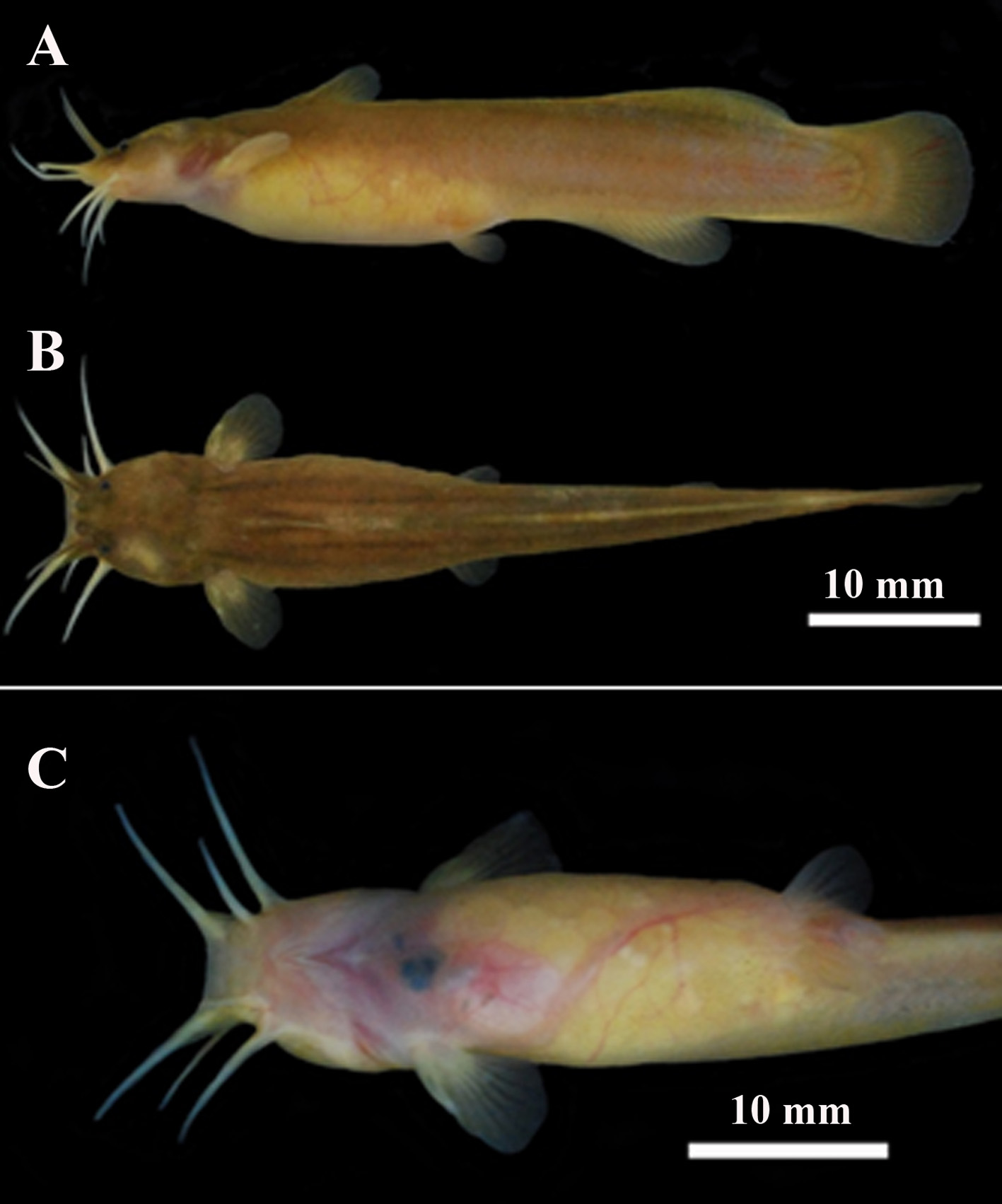
( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 )
Type material. Holotype: CNUC 38547, 84.1 mm standard length (SL); Hyeongsan River, Yangbuk-myeon, Gyeongju-si, South Korea, 35°49'58"N 129°24'41"E; J. Y. Park & S.H. Kim, 2 June 2013.
Paratypes: CNUC 38548–38567 (20), 57.1–84.1 mm SL; same data as holotype.
Nontypes: CNUC 38830–38854 (25), 41.8–67.8 mm SL; Bukcheon River, Hwangnyong-dong, Gyeongju-si, South Korea; J. Y. Park & S.H. Kim, 28 March 2010.
Diagnosis. Liobagrus hyeongsanensis is distinguished from all its congeners by a small size (a maximum of 90 mm SL, vs. 150–180 mm); a smaller number of eggs per gravid female (60–110 vs.130–210); and a smaller number of serrations on the pectoral fin (2–3, mostly 3, vs. 3–6 or 0–3, smaller or vestigial); a slenderer body width at pectoral-fin base (15.5–17.9 % SL, vs. 17.1–21.9%); a relatively short pectoral spine (3.7–6.5 % SL, vs. 6.8– 13.1%). The lower jaw is shorter than the upper jaw (vs. longer or equal), and the body and fins are entirely brownish yellow without any other markings (vs. a vertical broad yellowish crescent-shaped band on the caudal fin or black or whitish yellow outer margins of the dorsal and anal fins).
Description. Meristic and morphometric data are provided in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Asterisks indicate meristic values for holotype. Maximun size not exceeding 90 mm standard length. Body thin, compressed, and round; head depressed, caudal peduncle vertically depressed; dorsal and ventral profiles of body straight. Predorsal profile slightly sloping ventral from dorsal fin to occiput. Head depressed, broad. Eye small, dorsolateral, subcutaneous, ovoid. Snout rounded in dorsal view. Anterior nostril tubular, rim with fleshy flap forming short tube; posterior nostril porelike, rim posteriorly confluent with base of nasal barbel. Lateral line absent or vestigial.
Mouth terminal; lips thickened, papillate, premaxillary and mandibular toothpads curved, teeth small and ciliform or setiform, with upper jaw slightly longer than lower jaw. Four pairs of barbels: maxillary barbel longest, reaching base of pectoral spine; nasal barbel short, not reaching posterior margin of preoperculum; lateral mandibular barbel long, reaching posterior margin of pectoral-fin base; medial mandibular barbel shortest of the four pairs of barbels, about half length of outer mental barbel, reaching to gill membrane.
L. hyeongsanensis L. mediadiposalis Length from occiput to dorsal-fin origin 9.4 20 9.3–12.9 10.3 0.8 18 10.3–13.3 11.7 0.8 Dorsal fin with II, 6 rays; origin closer to snout tip than to anal-fin origin, its posterior margin convex. Dorsalfin spine a little shorter than pectoral-fin spine. Adipose fin base long, as long as or slightly exceeding anal-fin base length, confluent with caudal fin, its posterior margin convex. Pectoral fin with I, 7 rays, its origin anterior to vertical from posterior margin of operculum, partially covered by opercular membrane. Pectoral-fin spine sharp, short, with 2 (5), 3 (16) serrations on posterior edge. Pelvic fin with i, 5 rays; short, its origin located midway between dorsal and adipose fins, its tip not reaching base of anal fin. Anal fin with 15 (2), 16 (5), 17 (11), or 18 (3) rays, its distal margin rounded; anal fin short, origin slightly posterior to vertical through adipose-fin origin, posterior tip of anal fin not reaching beyond posterior margin of adipose fin. Caudal fin subtruncate, rounded. Vertebral column 38 (1), 39 (10), 40 (9), or 41 (1) post-Weberian elements. Gill rakers 6–8.
Coloration. See Figure 1 View FIGURE 1 for general appearance. In life ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ): body generally brownish yellow, fading to light yellow on ventral surface, without distinct markings. All barbels pale gray. All fins with similar color to body, without any other markings.
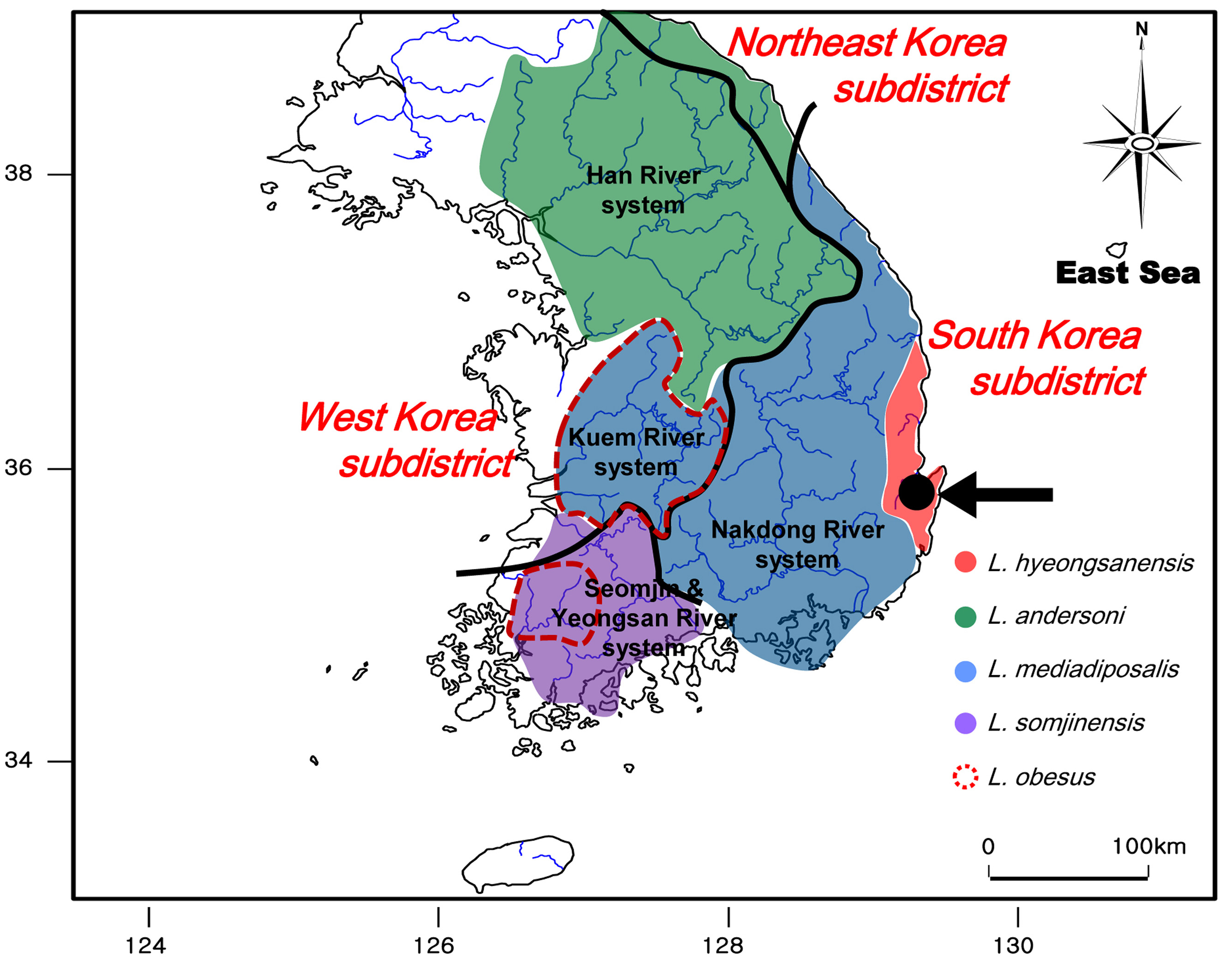
Distribution. Liobagrus hyeongsanensis is restricted to the rivers flowing to the eastern coast of Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea: Upper Hyeongsan and Taehwa Rivers ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
Sexual dimorphism. The adductor mandibulae in males is greatly expended during the spawning season, from late April to June.
Etymology. Named after the Hyeongsan River, the type locality. We propose the Korean name Donbang-Jagasari for this species.
Biology and habitat. Liobagrus hyeongsanensis is small, nocturnal and benthic. It inhabits the bottom stratum of running waters with moderately fast currents, in upper streams and valley streams. It is generally seen in shallow waters (0.3–0.8 m deep) with large or small stony or pebbly substrates. The spawning season is from late April to June. The adult females do not exceed 90.0 mm SL and lay a small number of eggs (60–110), 2.8–3.3 (3.1±0.2) mm in diameter.
TABLE 1. Morphometric and meristic data of Liobagrus hyeongsanensis (CNUC 38547 – 38567) and L. mediadiposalis (CNUC 37821 – 37838). H, holotype.
| H n | range | mean | SD | n | range mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard length (mm) | 84.1 20 | 57.1–84.1 | 68.9 | 6.0 | 18 | 73.5–100.3 85.4 | 7.7 |
| In percents of standard length | |||||||
| Preocciput length | 19.1 20 | 18.3–22.3 | 19.6 | 1.1 | 18 | 17.9–20.3 19.2 | 0.6 |
| Predorsal length | 28.2 20 | 27.8–31.3 | 29.4 | 1.1 | 18 | 28.4–31.4 30.3 | 0.8 |
| Prepectoral length | 18.7 20 | 18.7–21.4 | 19.9 | 0.7 | 18 | 20.6–23.3 22.0 | 0.8 |
| Prepelvic length | 45.8 20 | 45.4–51.4 | 47.4 | 1.6 | 18 | 44.2–49.0 46.0 | 1.2 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.