Sparsorythus nanjangudensis Muthukatturaja and Balasubramanian, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5040.3.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9CF39A34-15D0-4C8B-A9E8-F179D3EB39B4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5531556 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4D6987A8-7913-FFF4-28E3-14B7BB57852B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sparsorythus nanjangudensis Muthukatturaja and Balasubramanian |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Sparsorythus nanjangudensis Muthukatturaja and Balasubramanian sp. nov.
( Figs. 1–23 View FIGURES 1–2 View FIGURES 3–10 View FIGURES 11–20 View FIGURES 21–23 )
Diagnosis. The nymph of Sparsorythus nanjangudensis sp. nov. can be differentiated from other Sparsorythus by the following combination of characters: (i) segment III of labial palp pointed at apex; (ii) pronotum wider than head; (iii) fore claw slender, slightly curved with one prominent denticle and one or two minute denticles; (iv) subapical teeth on claws absent; (v) fore wing pads reaching the middle of abdominal segment III of final-instar larva; (vi) abdominal sternum VII with medial cleft. The male imago of Sparsorythus nanjangudensis sp. nov. can be differentiated from other known Oriental Sparsorythus by the following combination of characters: (i) forewing shaded with dark grey on C, Sc and R fields; (ii) forceps base broad, without tiny bristles; (iii) penis apex reaching approximately half of forceps segment II.
Type material ( ZSI) Holotype: male imago, India, Karnataka, Mysore district, Nanjangud, Kabini River , 12.121630 °N, 76.696019 °E; 652 m. a.s.l., 29.iii.2018, Muthukatturaja & Balasubramanian Cols. — Reg.No. ZSI – SRC/ I/E 594 GoogleMaps . Paratypes: two male imagoes— Reg.No. ZSI –SRC/ I/E 595 and five mature nymphs— Reg.No. ZSI –SRC/ I/E 596, same data as holotype GoogleMaps .
Additional material ( ZMTC): five male imago and ten mature nymphs, India, Karnataka, Mysore district, Nanjangud, Kabini River, 12.121630 °N, 76.696019 °E; 652 m. a.s.l., 29.iii.2018, Muthukatturaja & Balasubramanian Cols.
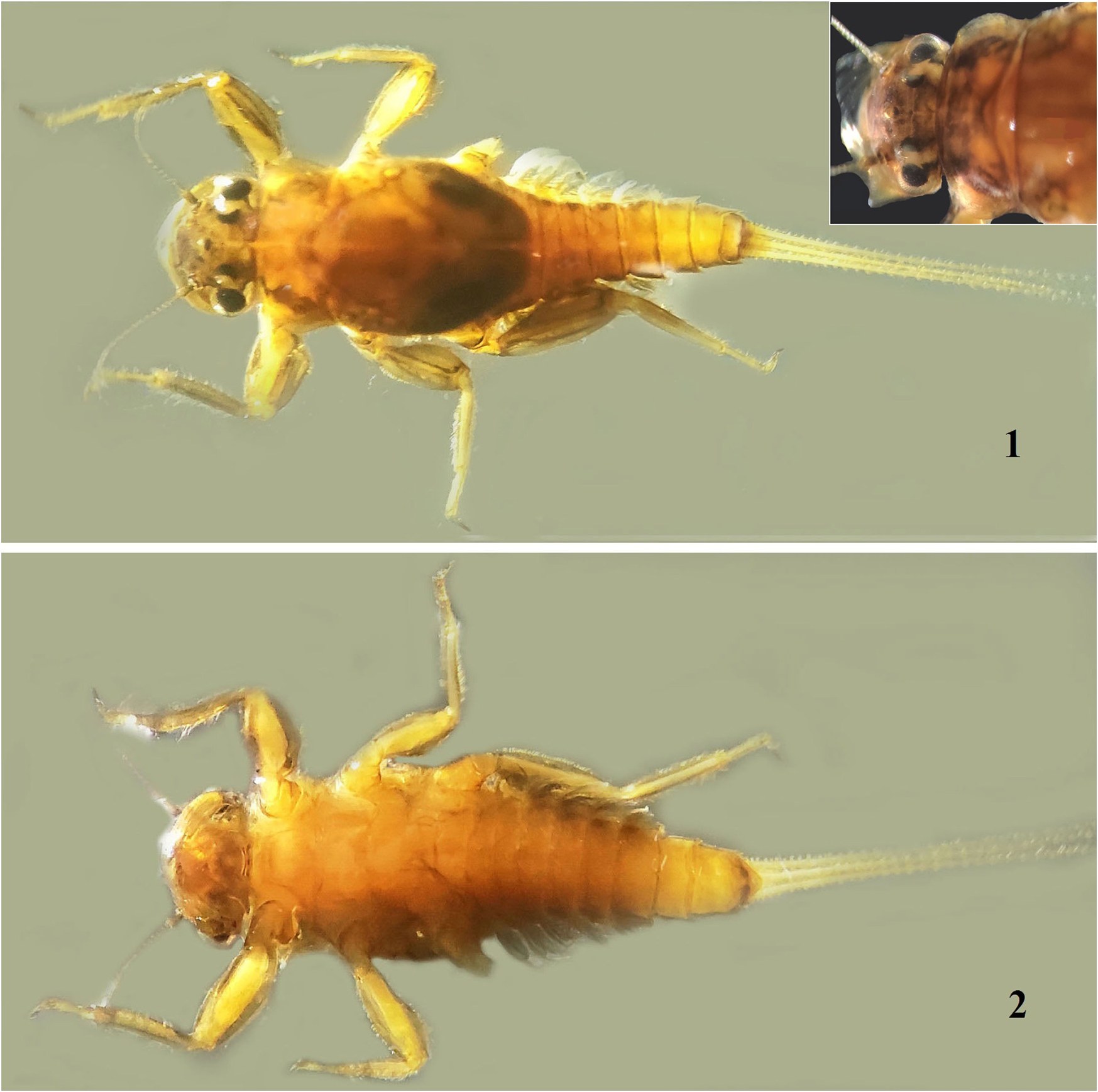
Mature Nymph ( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURES 1–2 ). Dimensions (mm): body length (excluding cerci) 5.3–5.6; cerci length 5.4–5.6; antennae length 1.8; width of compound eye 0.4; length of compound eye 0.3; distance between compound eyes 0.6. General body coloration brown to yellowish brown; legs brown to yellowish brown.
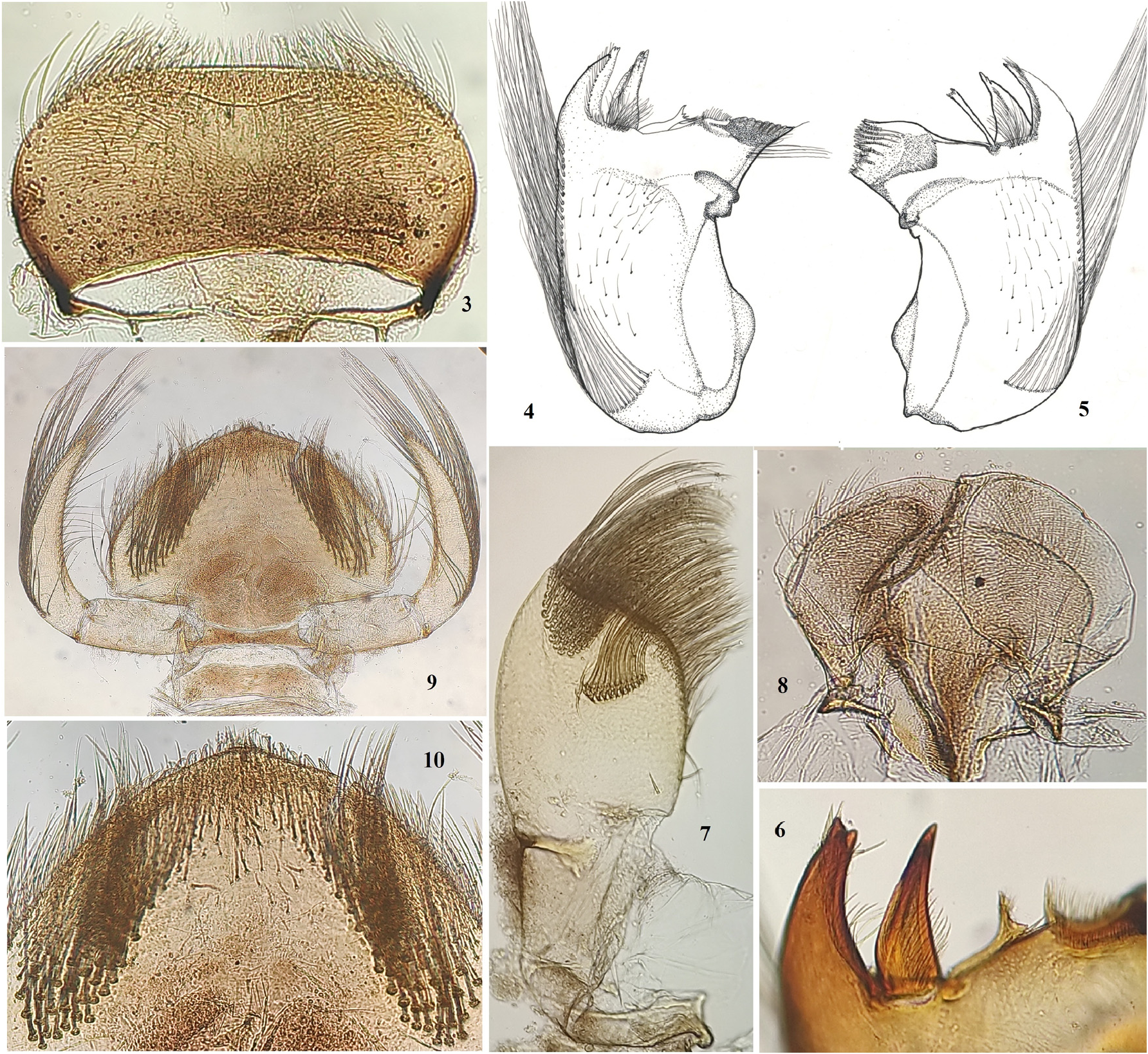
Head: two times wider than long, yellowish brown; scape and pedicel of antennae blackish brown, flagellum pale yellow to translucent; articulation in antennal segments with small, thin, hair-like setae. Compound eyes black. Upper portion of ocelli white, lower black. Mouthparts: Labrum ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 3–10 ) two times wider than long; dorsum covered with thin, long hair-like setae; anterior margin with numerous middle-sized, thin bristles; angular margin with few long, pectinate setae; dorsum with cluster of middle-sized, thin setae below angular margin. Mandibles ( Figs. 4–6 View FIGURES 3–10 ) with row of very long filtering setae on outer margin; mandibular body covered with small, thin, stout hair-like setae ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 3–10 ); outer incisor of both mandibles with three apical denticles and numerous thin bristles; inner incisors (kinetodontium) bifurcated; four to six long thin setae below mola of right mandible ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 3–10 ); apex of left mandibular prostheca ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 3–10 ) slightly wider apically with bluntly pointed teeth and four bristle-like processes at base; right mandibular prostheca notched ( Figs. 4, 6 View FIGURES 3–10 ),broadened apically with few pointed teeth. Maxillae ( Fig.7 View FIGURES 3–10 ) oblong shaped, truncate apically; two bunches of long, thin filtering setae at galea-lacinia; inner margin of lacinia with long, thin, fringed setae; maxillary palp absent. Hypopharyngeal superlingua triangular, covered with thin, stout spine-like setae at anterior margin; lingua membranous and translucent without setae ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 3–10 ). Labium ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 3–10 ): glossae and paraglossae fused ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 3–10 ), rounded; short, stout spines and numerous spine-like setae on anterior margin; cluster of long, thin, filtering setae below dorsal side of lateral margin; labial palp three-segmented; length of segment I ½ of segment II; segment III seven times shorter than segment II; 4/5 of outer margin of segment II with row of long, thin, sub marginal filtering setae; ¾ of inner margin of segment II with row of long, thin, sub marginal filtering setae; segment III very small, pointed at apex, without any setae.
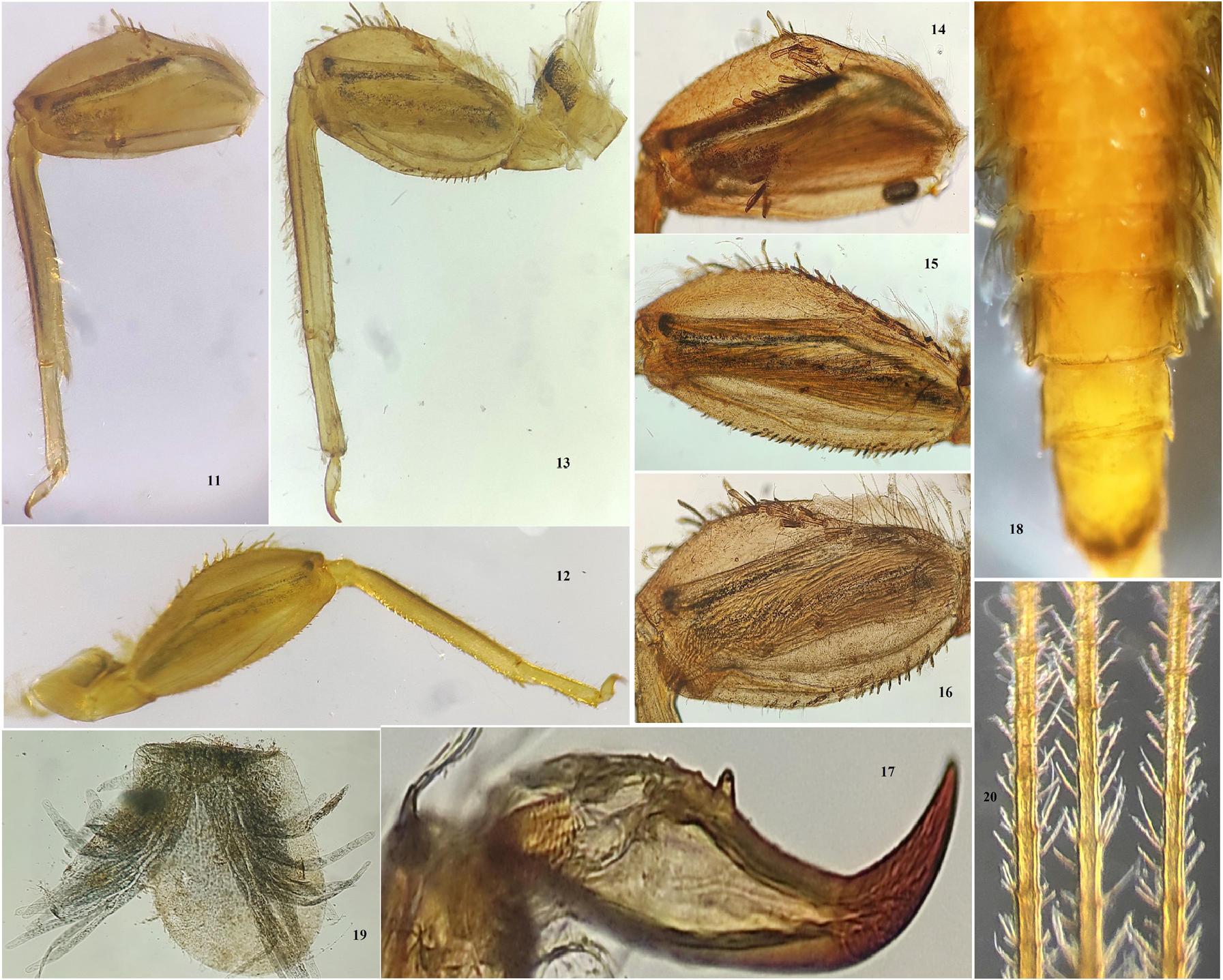
Thorax: brown; pronotum wider than head ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–2 ); fore wing pads reaching the middle of abdominal segment III. Foreleg ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11–20 ): length of femur: tibia: tarsus (mm) =1.1: 1.1: 0.5; coxa and trochanter with short, thin hairlike setae; femoral surface ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 11–20 ) with transverse row of long, cuneate-like setae and sparse, short hair-like setae; middle of outer margin with few cuneate-like setae; length of fore femoral setae about 5 to 6 times their width, spatulate; inner margin of tibia with row of thin, spike-like setae; surface of tibia with few long, thin bristles and numerous long, thin hair-like setae; surface of tarsi with long, thin hair-like setae; claw slender, strongly curved with denticles (one prominent and one or two minute denticles); lateral sub apical teeth absent ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 11–20 ). Middle leg ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11–20 ): length of femur: tibia: tarsus (mm) =1.1: 1.0: 0.45; coxa and trochanter similar to foreleg; femoral surface ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 11–20 ) with sparse, short hair-like setae and sparse, short cuneate-like setae; outer margin of femora with row of long, cuneate-like setae; proximal half of outer margin of femora with long, thin bristles; proximal half of inner margin with rows of short, cuneate-like setae and a row of cuneate-like setae along inner margin; tibia with row of middle-sized, cuneate-like setae at inner margin; surface of tibia with few long, thin bristles and numerous long, thin hair-like setae; tarsi and claw similar to foreleg. Hindleg ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 11–20 ): length of femur: tibia: tarsus (mm) = 1.4: 1.4: 0.5; coxa and trochanter similar to foreleg; femora broader than fore and middle legs; femoral surface ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 11–20 ) with sparse, short hair-like setae and sparse, short cuneate-like setae; outer margin of femora with row of long, cuneatelike setae and with long, thin bristles; basal half of inner margin with rows of short, cuneate-like setae and a row of cuneate-like setae along inner margin; tibia with row of long and middle-sized, cuneate-like setae at outer margin; inner margin with row of middle-sized, cuneate-like setae; surface of tibia with few long, thin bristles and numerous long, thin hair-like setae; inner margin of tarsi with row of short, stout spine-like setae; claw slender, strongly curved with two denticles (one prominent and one minute); lateral sub apical teeth absent.
Abdomen: brown to yellowish brown; terga I–X with grey smudge on sub lateral margin; terga I–VII brown; terga VIII–X yellowish brown; posterior margin of terga with row of thin setae; posterolateral spines on terga VII–IX short, pointed; sterna I– VI brown; sterna VII–X yellowish brown; posterior margin of sterna VII black and with medial cleft ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 11–20 ). Gills: present on segment II– VI; dorsal lamella grayish, with short, hair-like setae on margins; ventral lamella with two branches with numerous fringed filaments ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 11–20 ). Caudal filaments ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 11–20 ): pale yellow; cerci subequal in length to paracercus; lateral margins with spiky setae as long as 1/3 of the length of segment. Long spiky setae present on both sides of caudal filaments.
Male imago ( Figs. 22–23 View FIGURES 21–23 ). Dimensions (mm): body length (excluding cerci) 4.0–4.4; length of fore wing 4.3–4.7; width of fore wing 1.7–2.1; length of antenna 0.7; length of cerci 12–14; length of terminal filament 13–15.General coloration dark brown to yellowish brown.
Head: length 1.13, tan brown, anterior margin darker; antennae with scape and pedicel blackish brown, flagellum translucent; dorsal diameter of eye, 0.2; distance between compound eyes 0.4.
Thorax: dark brown. Legs: length of segments in foreleg (mm) femur: tibia: tarsus = 0.8: 0.9: 0.4; coxa and trochanter dark brown at base; fore femora dark brown to yellowish brown; tibia and tarsus paler; fore tibia slightly longer than femur; mid tibia shorter than femur; hind femur and tibia equal in length; foreleg with two rounded claws, middle and hind legs with one claw rounded and the other pointed. Wings: hyaline with dark grey shading in C, Sc and R sectors ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 21–23 ); pterostigmatic region faint grey, usually no discernible cross veins in costal space; venation mostly grey; C, Sc and R grey; CuA and CuP reaching the wing margin; cross veins of CuP and analis frequently not visible along their entire length.
Abdomen: tergum brown to yellowish brown and sternum paler; tergum with grey smudges on lateral margin; dorsomedial line paler. Genitalia ( Fig.23 View FIGURES 21–23 ): sub genital plate entire; forceps two segmented; distal segment slightly longer than basal segment, length (mm) = 0.20: 0.27; forceps base broad, without tiny bristles; inner margin of segment two of forceps covered with numerous short, leaf-shaped attachment structures; penis lobes simple, straight and tubular, slightly bent in dorsal direction (live specimen); penis apex reaching approximately half of second forceps segment; apex of penis rounded with distinct medial emargination, bisecting penial apex. Caudal filaments: translucent, base of each segment black; three times longer than body length, cerci glabrous.
Male subimago ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 21–23 ). Similar to imago, except wings uniformly grayish and with microtrichiae on surface and margins; tarsus of fore leg with pair of rounded claws; fore femur slightly shorter than tibia, length (mm) 0.9: 1.0; caudal filaments longer than body (coloration as in imago) and with numerous whorls of setae; male genitalia almost as in imago, but forceps segment I stouter.
Female imago. unknown.
Etymology. Species name nanjangudensis refers to the locality Nanjangud, Mysore district, where the new species was collected.
Distribution. The species is so far only known from the type locality, Kabini River, Nanjangud, Karnataka, India.
Ecology. Nymphs were collected in March 2018 in Kabini River, Nanjangud, Mysore district, Karnataka, India. The River presented a width of 90 m and a mean water depth of 0.65 m at time of collection. The water velocity was 0.5 m /s, substratum with cobbles, pebbles and boulders, canopy cover about 5%. Water pH ranged 7.5–7.8; water temperature was 28 ±2°C and air temperature 30 ±2°C. The new species was associated with other mayfly genera including Caenis Stephens, 1835 (Caenidae) , Teloganodes Eaton, 1882 (Teloganodidae) , Notophlebia Peters & Edmunds, 1970 and Choroterpes Eaton, 1881 (Leptophlebiidae) , Baetis Leach, 1815 and Nigrobaetis Kazlauskas (in Novikova & Kluge), 1987 ( Baetidae ).
| VI |
Mykotektet, National Veterinary Institute |
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |