Xylota abiens Meigen, 1822
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4661.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:28EFDB26-4C37-4DA9-ABBB-122083EE396B |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5A219B24-3441-473E-FCED-FC4D98A216B6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2019-08-29 06:44:18, last updated 2024-11-26 22:04:21) |
|
scientific name |
Xylota abiens Meigen |
| status |
|
Xylota abiens Meigen View in CoL
(Korean name: cheong-lam-saeg-heo-ri-kkot-deung-e)
Figs 1P View FIGURE 1 , 2P View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 A–E, 8A–D, 13E
Xylota abiens Meigen, 1822: 218 View in CoL (type locality: Europe; type ♀, NMW); Hippa, 1968: 186 (taxonomic discussion); Hippa, 1978: 64 (taxonomic discussion); Violovitsh, 1986: 140, 142 (in Siberian key); Peck, 1988: 224 (in Palaearctic catalog); Kim J.I. et al., 1994a: 116 (fauna of Mt. Gwangdoksan); ESK & KASAE, 1994: 291 (in Korean checklist); Kim J.I., 1995b, 145 (fauna of Byonsan peninsula); Kim J.I., 1996: 178 (fauna of Mt. Bangtaesan); Park, 1998: 86 (Insects in Gangwon-do); Han et al., 1998: 152 (Korean catalog); Mutin & Barkalov, 1999: 495 (in species key); Speight, 1999: 216, 217 (in European key); Vujić & Milankov, 1999: 124, 126 (in key of Balkan peninsula); Han & Choi, 2001: 214 (in Korean catalog); Stubbs & Falk, 2002: 333, 340 (color illustration); Bartsch et al., 2009: 404, 406 (color illustration and diagnosis); Paek et al., 2010: 232 (in Korean checklist); Huang & Cheng, 2012: 669 (illustration and diagnosis); Han et al., 2014: 29 (in Korean catalog); Ohara et al., 2014: 522 (in Japanese catalog).
Musca semulator Harris, 1780: 112 (type locality: England; type lost).
Zelima subabiens Stackelberg, 1952: 326 View in CoL (type locality: Russia, Leningrad Prov.; holotype ♂, ZISP).
Zelima abiens: Sack, 1932: 373 (in Palaearctic key); Shiraki, 1930: 64, 71 (in key with description); Hokuryukan, 1965: 214 (description with color photograph); Kim C.W. & Nam, 1982b: 130 (fauna of Mt. Gyebangsan, Sogyebangsan and Gachilbong).
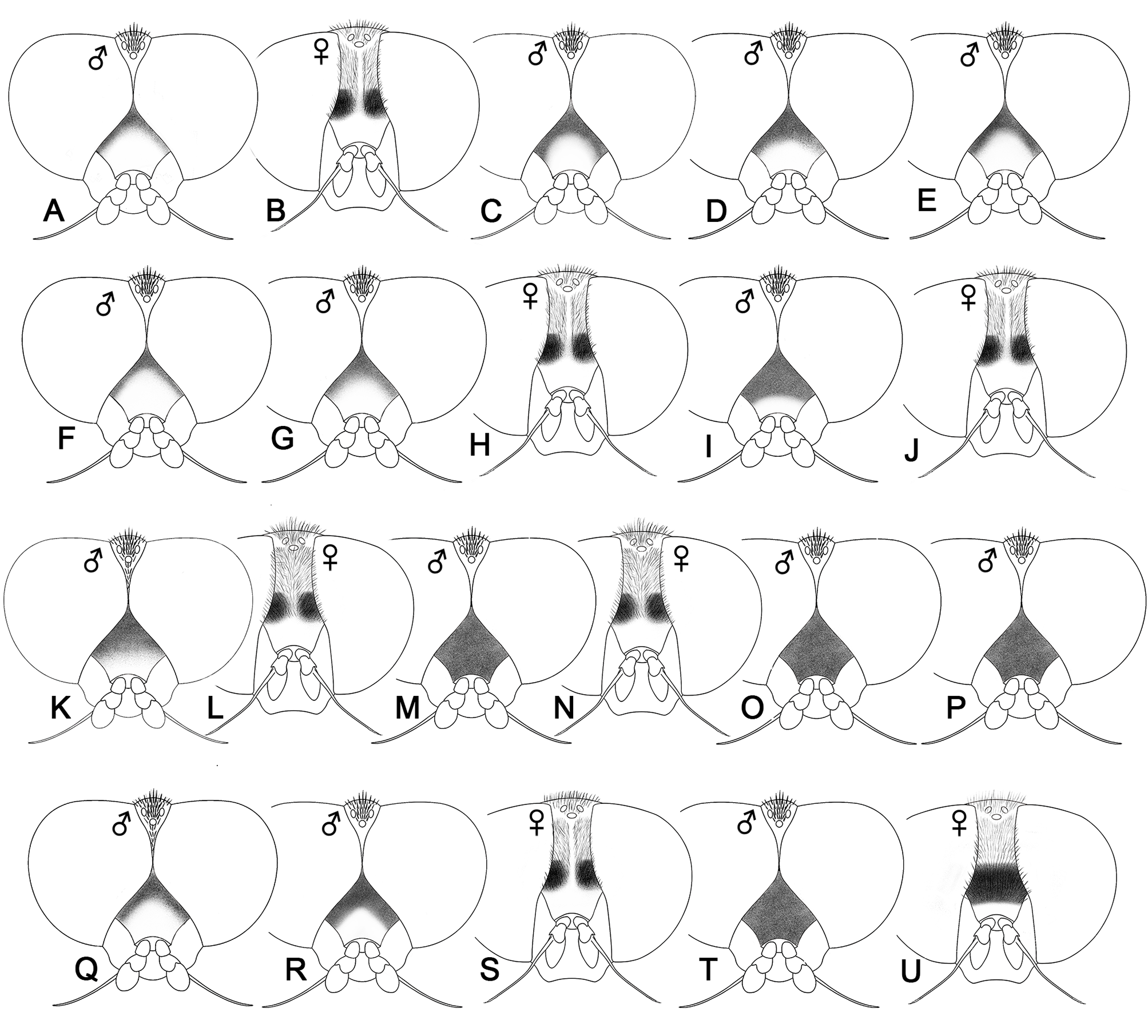
Diagnosis. In Korea, only X. abiens , X. orientiflorum sp. n. and X. tarda share a light colored abdominal pattern in dark background, by which they can be separated from any other Korean Xylota species: abdominal terga 2 and 3 each with a pair of orange-yellow maculae ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 P–S). Among these three species, the shape and size of maculae are species specific, and there is no problem distinguishing one another. Xylota tarda do have the largest maculae almost touching each other ( Figs 2R, S View FIGURE 2 , 6O, P View FIGURE 6 ). The other two species have smaller maculae, but maculae on tergite 3 are more or less square in X. abiens ( Figs 2P View FIGURE 2 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ) but widely rectangular in X. orientiflorum sp. n. ( Figs 2Q View FIGURE 2 , 5O View FIGURE 5 ). In addition, the latter species can be further separated by having the area anterior to ocellar triangle (vertical triangle anterior to ocellar triangle in male, and small area immediately anterior to ocellar triangle in female) covered with yellowish pile ( Fig. 1Q View FIGURE 1 ) while the other two species do not have pile on that area ( Fig. 1P View FIGURE 1 , R–U). The latter species also has black pile on scutal area anterior to wing base, while others have yellow pile.
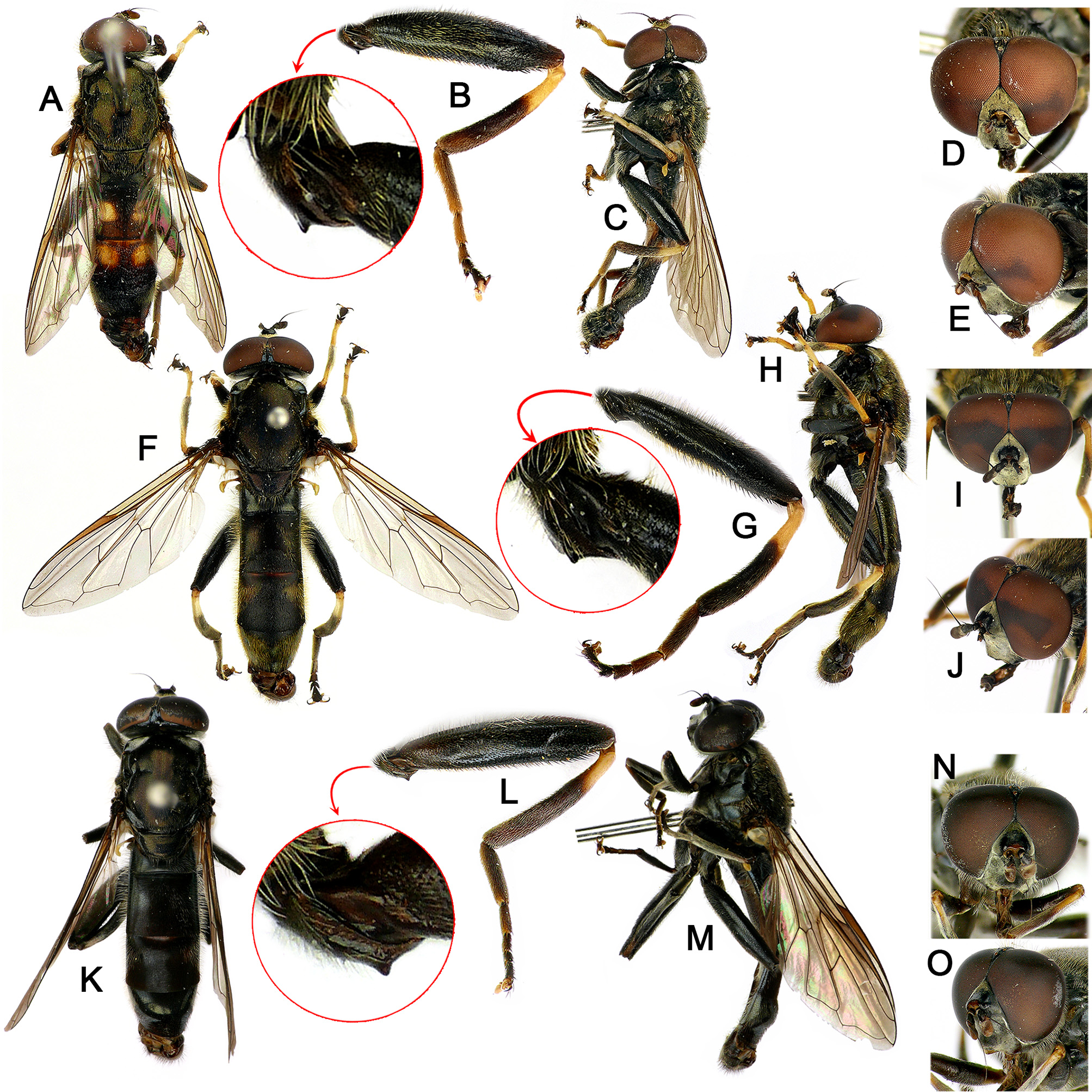
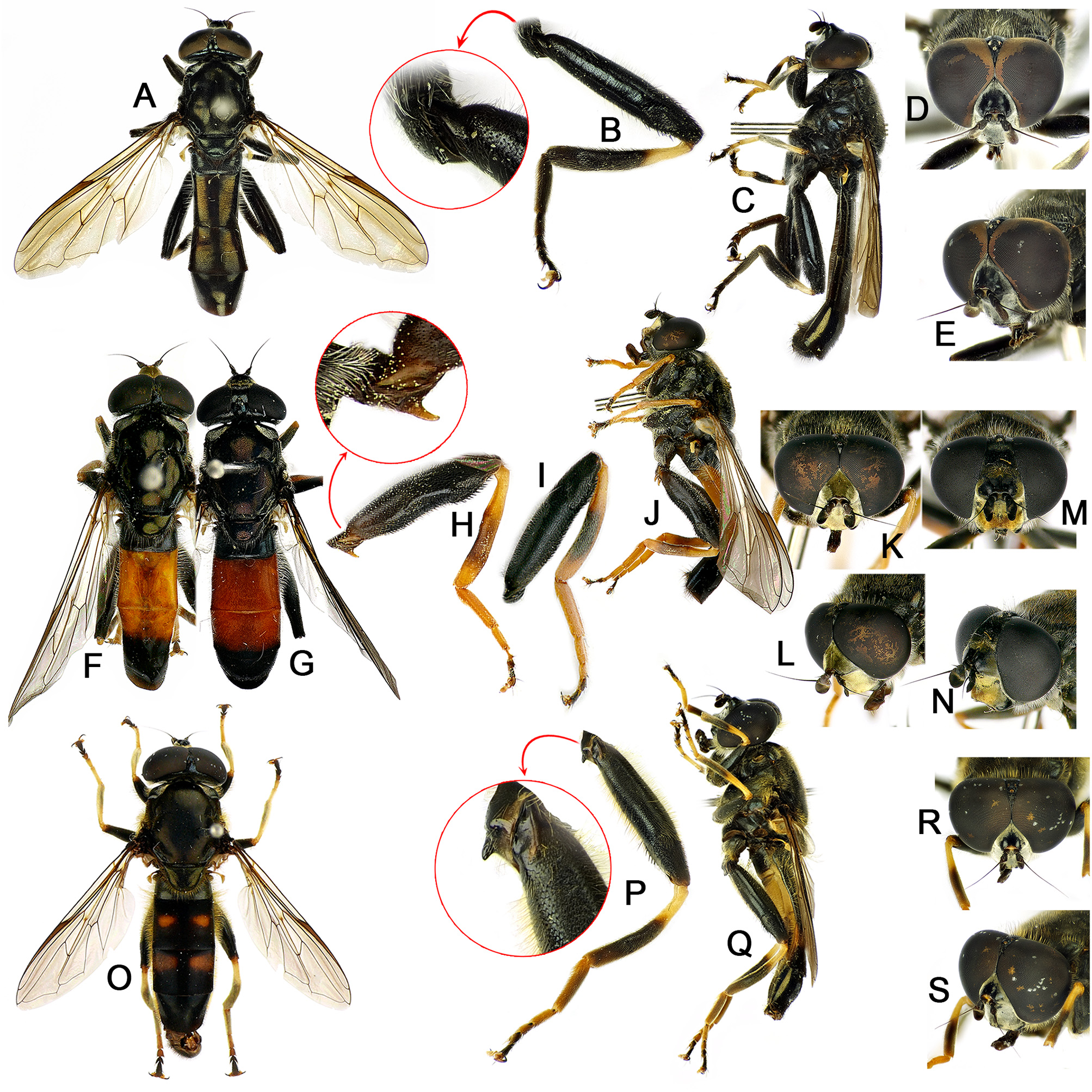
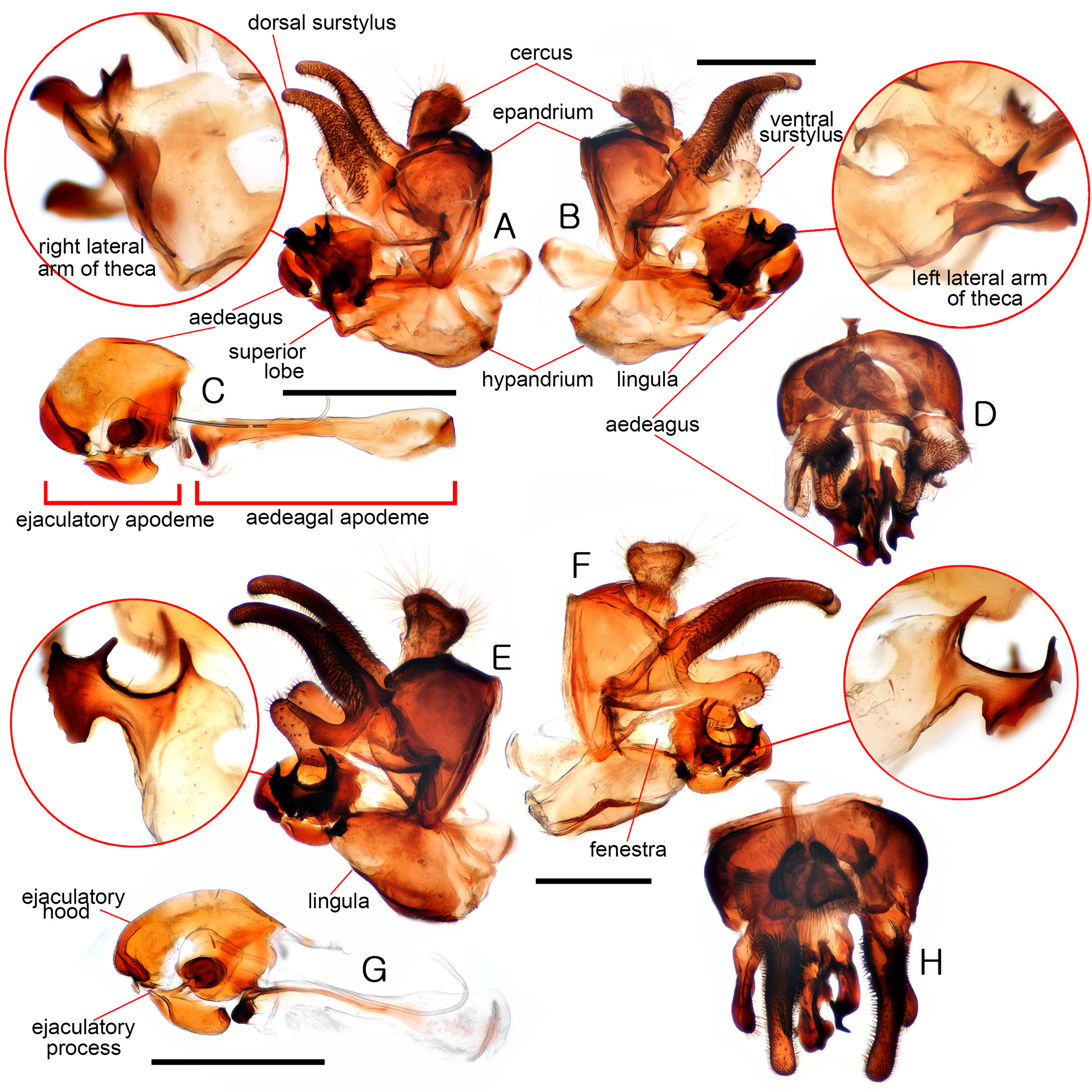
Description of Korean material. MALE. Body length 8.8–9.0mm; wing length 6.1–7.3mm; dark brown to black species with orange-yellow abdominal maculae ( Figs 2P View FIGURE 2 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Head black; face with dense yellow pollinosity ( Fig. 3D, E View FIGURE 3 ); frons anterior to eye contiguity with dense yellow pollinosity ( Figs 1P View FIGURE 1 , 3D, E View FIGURE 3 ); area anterior to ocellar triangle (vertical triangle anterior to ocellar triangle) bare but posterior area covered with yellow pile ( Fig. 1P View FIGURE 1 ). Thorax entirely black; scutum subshiny black with appressed short yellow pile, but posterior half sparsely with longer erect yellow pile mixed with short pile; anterior anepisternum covered with yellowish white pollinosity; posterior anepisternum with yellow pile and yellowish white pollinosity; anepimeron covered with yellow pile; katepisternum moderately covered with yellowish white pollinosity, dorsal posterior area with yellow pile; notopleuron with yellow pile; scutal area anterior to wing base with yellow pile; postalar callus with yellow pile; metasternum bare with white pollinosity. Wing hyaline except for brown pterostigma ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ); halter yellowish white. Legs: femora almost entirely dark brown to black; pro- and mesotibiae yellow with subapico-ventral 3/5 dark brown; pro- and mesotaromeres 1–3 yellow; pro- and mesotaromeres 4 and 5 brown; metatrochanter ventrally with short calcar (subequal to basal width) ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ); apico-ventral 1/3 of metafemur with two carinae covered with spinose setulae, remaining ventral area with few spinose setae, antero-dorsally and postero-ventrally with long yellowish white pile, apico-dorsal 1/3 with short black pile; basal 1/3 of metatibia yellow ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ); metataromeres 1–3 dark brown and 4 and 5 black ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ). Abdomen about 2.5x longer than wide ( Figs 2P View FIGURE 2 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ); terga 2 and 3 more or less parallel-sided; preabdominal terga dark brown in ground color; tergum 2 medially with a pair of orange-yellow and relatively small subrhombic maculae, separated from each other roughly by 1/3 of each macula width; tergum 3 with a pair of orange-yellow subsqure maculae, separated from each other by about 1/3 of each macula width ( Figs 2P View FIGURE 2 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Male genitalia ( Figs 8 View FIGURE 8 A–D, 13E): surstylus with dorsal lobe about twice as long as ventral lobe, long finger shaped and slightly bent ventrally in lateral view, densely covered with spinose setulae ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ); ventral lobe of surstylus widely bulged, apically with scattered short setulae ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ); cercus cordate in profile with long pale pile ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ); lingula indistinct ( Fig. 13E View FIGURE 13 ); fenestra small and elliptic in outline ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ); spur of superior lobe reduced ( Fig. 13E View FIGURE 13 ); superior lobe asymmetrical ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ); each lateral arm of theca apico-dorsally with 4 thorny projections ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ); aedeagus with ejaculatory hood medially with furrow in postero-ventral view, dorsally round in lateral view ( Fig. 8C View FIGURE 8 ); ejaculatory process short ( Fig. 8C View FIGURE 8 ); ejaculatory apodeme apically enlarged and bowl shaped.
FEMALE. Not examined. Bartsch et al. (2009) indicated that European female of this species has frons with a distinct pollinose fascia, the posterior margin of which is straight.
Material examined. SOUTH KOREA: Gangwon-do: 1♂, Inje-gun, Girin-myeon, Mt. Jeombongsan, Valley along Gangseon-ri, 7.VIII.1997, HY Han et al.; 1♂, Inje-gun, Sangnam-myeon, Bangdong-ri, Mt. Bangtaesan, north valley of Guryongduckbong, 1.VIII.1996, HY Han and HW Byun.
Distribution. Europe, Korea, Japan, Northeast China, Russia (From Urals to Sakhalin).
Bartsch, H., Binkiewicz, E., Klintbjer, A., Raden, A. & Nasibov, E. (2009) Nationalnyckeln till Sveriges flora och fauna. Tvavingar: Blomflugor: Eristalinae & Microdontinae. Diptera: Syrphidae: Eristalinae & Microdontinae. ArtDatabanken, SLU, Uppsala, 470 pp. [in Swedish]
Han, H. Y., Choi, D. S., Kim, J. I. & Byun, H. W. (1998) A catalog of the Syrphidae (Insecta: Diptera) of Korea. Insecta Koreana, 15, 95 - 166.
Han, H. Y. & Choi, D. S. (2001) Family Syrphidae. Economic Insects of Korea 15. Insecta Koreana, 22 (Supplement), 1 - 224. [in Korean]
Han, H. Y., Suk, S. W., Lee, Y. B. & Lee, H. S. (2014) National List of Species of Korea, Insect (Diptera II). National Institute of Biological Resources, Incheon, 268 pp. [in Korean]
Hippa, H. (1968) Classification of the Palaearctic species of the genera Xylota Meigen and Xylotomima Shannon (Dipt., Syrphidae). Annales Entomologicae Fennicae, 34, 179 - 197.
Hippa, H. (1978) Classification of Xylotini (Diptera, Syrphidae). Acta zoological fennica, 156, 1 - 153.
Hokuryukan, Co. (1965) Iconographia Insectorum Japonicorum, Colore Naturali Edita. Vol. III. Hokuryukan, Tokyo, 358 pp., 156 colour pls. [in Japanese]
Huang, C. & Cheng, X. (2012) Fauna Sinica: Diptera Syrphidae. Vol. 50. Insecta. Science press, Beijing, 852 pp. [in Chinese]
Meigen, J. W. (1822) Systematische Beschreibung der bekannten Europaischen zweiflugeligen Insekten. Dritter Theil. Schultz- Wundermann, Hamm, x + 416 pp., pls. 22 - 32.
Mutin, V. A. & Barkalov, A. V. (1999) 62. Family Syrphidae. In: Lehr, P. A. (Ed.), Key to the insects of Russian Far East. Vol. 6. Diptera and Siphonaptera. Part 1. Dal'nauka, Vladivostok, pp. 342 - 500. [in Russian]
Ohara, K., Ohishi, H. & Ichige, K. (2014) Catalog of the insects of Japan. Vol. 8. Part 1. Diptera (Nematocera-Brachycera Aschiza). Entomological society of Japan, Touka Shobo, Fukuoka, xxxii + 539 pp. [in Japanese]
Paek, M. K., Hwang, J. M., Jung, K. S., Kim, T. W., Kim, M. C., Lee, Y. J., Cho, Y. B., Park, S. W., Lee, H. S., Ku, D. S., Jeong, J. C., Kim, K. G., Choi, D. S., Shin, E. H., Hwang, J. H, Lee, J. S., Kim, S. S. & Bae, Y. S. (2010) Checklist of Korean insects. In: Peak, M. K. & Cho, Y. K. (Eds.), Nature & Ecology Academics. Series 2, Nature & Ecology, Seoul, pp. 1 - 598.
Park, K. T. (1998) Insects in Kangwon-do. Center for Insect Systematics and Institute for Biodiversity Research, Kangwon University, Chuncheon, 155. [in Korean]
Peck, L. V. (1988) Family Syrphidae. In: Soos, A. (Ed.), Catalogue of Palaearctic Diptera. Vol. 8. Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, pp. 11 - 230.
Sack, P. (1932) 31. Syrphidae. In: Lindner, E. (Ed.), Die Fliegen der Palaearktischen Region. Band IV / 6. E. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart, pp. 1 - 451. [in German]
Shiraki, T. (1930) Die Syrphiden des Japanischen Kaiserreichs, mit Berucksichtigung benachbarter Gebiete. Memoirs of the Faculty of Science and Agriculture, Taihoku Imperial University, 1, 1 - 446.
Speight, M. C. D. (1999) A key to European Xylotini (Dip.: Syrphidae). Entomologist's Record, 111, 211 - 218.
Stackelberg, A. A. (1952) Brief review of palaearctic species of the genus Zelima Mg. (Diptea, Syrphidae). Entomologiceskoe obozrenie, 32, 316 - 328. [in Russian]
Stubbs, A. E. & Falk, S. (2002) British hoverflies, an illustrated identification guide. Second edition. British Entomological and Natural History Society, Penzance, Cornwall, 253 pp., 13 pls., supplement I-XV.
Violovitsh, N. A. (1986) Siberian Syrphidae (Diptera) (Sirfidy Sibiri) Novosibirsk, 1983. Verslagen en Technische Gegevens Instituut voor Taxonomische Zoologie (Zoologische Museum) Universiteit van Amsterdam, No. 43, 1 - 228. [English translation of Violovitsh (1983)]
Vujic, A. & Milankov, V. (1999) New data for the tribes Milesiini and Xylotini (Diptera, Syrphidae) on the Balkan peninsula. Dipteron, 2, 113 - 132.
FIGURE 1. Schematic drawings showing head pilosity and pollinosity in Xylota species, dorsal view (A, B) Xylota umbrosa; (C) X. amaculata; (D) X. filipjevi; (E) X. atricoloris; (F) X. hauseri sp. n.; (G, H) X. xanthotarsis sp. n.; (I, J) X. pseudiognava; (K, L) X. coquilletti; (M) X. spurivulgaris; (N) either X. spurivulgaris or X. fo; (O) X. fo; (P) X. abiens; (Q) X. orientiflorum sp. n.; (R, S) X. tarda; (T, U) X. ignava. Areas of pollinosity shown by darkened areas are actually silvery white to yellowish white.
FIGURE 2. Pattern of abdominal terga in Xylota species, dorsal view (A, B) X. umbrosa; (C) X. amaculata; (D) X. filipjevi; (E) X. atricoloris; (F) X. hauseri sp. n.; (G, H) X. xanthotarsis sp. n.; (I, J) X. pseudiognava; (K, L) X. coquilletti; (M) X. spurivulgaris; (N) either X. spurivulgaris or X. fo; (O) X. fo; (P) X. abiens; (Q) X. orientiflorum sp. n.; (R, S) X. tarda; (T, U) X. ignava. (A–O) Grainy areas represent same colored patterns that can be distinguished by having differently oriented and (or) colored pile. These patterns can be best viewed by turning a specimen under a microscope. (P–U) Lighter areas represent lighter colored patterns.
FIGURE 3. Leg, head and body of Xylota species. A–E. X. abiens: (A dorsal view, C antero-lateral view) male body; (B) male left metafemur, anterior view; (D dorsal view, E antero-lateral view) male head. 3F–J. X. amaculata: (F, H) male body; (G) male left metafemur, anterior view; (I, J) male head. 3K–O. X. atricoloris: (K, M) male body; (L) female left metafemur, anterior view; (N, O) male head.
FIGURE 5. Leg, head and body of Xylota species. A–E. X. hauseri sp. n.: (A dorsal view, C lateral view) male body; (B) male left metafemur, anterior view; (D dorsal view, E antero-lateral view) male head. 5F–N. X. ignava: (F, J) male body; (G) female body; (H) male left metafemur, anterior view; (I) female left metafemur, anterior view; (K, L) male head; (M, N) female head. 5O–S. X. orientiflorum sp. n.: (O, Q) male body; (P) male left metafemur, anterior view; (R, S) male head.
FIGURE 6. Leg, head and body of Xylota speices. A–E. X. pseudoignava: (A dorsal view, E lateral view) male body; (B) female body; (C) male left metafemur, anterior view; (D) female left metafemur, anterior view; (F dorsal view, G antero-lateral view) male head; (H, I) female head. 6J–N. X. spurivulgaris: (J, L) male body; (K) male left metafemur anterior view; (M, N) male head; see Fig, 4 for presumed female photos. 6O–W. X. tarda: (O, S) male body; (P) female body; (Q) male left metafemur, anterior view; (R) female left metafemur, anterior view; (T, U) male head; (V, W) female head.
FIGURE 8. Male genitalia of Xylota species, D, H dorsal view, B, F left lateral view, A, E right lateral view, G aedeagus lateral view: (A–D) Xylota abiens; (E–H) X. amaculata. Scale bar: 0.5mm. Enlargement showing apical part of superior lobe (lateral arms of theca).
FIGURE 13. Male genitalia of Xylota species, ventral view with aedeagus removed. (A) Xylota umbrosa; (B) X. amaculata; (C) X. atricoloris; (D) X. hauseri sp. n.; (E) X. abiens; (F) X. orientiflorum sp. n.; (G) X. filipjevi; (H) X. tarda; (I) X. xanthotarsis sp. n.; (J) X. pseudoignava; (K) X. ignava; (L) X. coquilletti; (M) X. spurivulgaris; (N) X. fo. The pictures are arbitrarily arranged based on three morphological groups (A–H; I–K; L–N). Scale bar: 0.5mm.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Xylota abiens Meigen
| Jeong, Soo-Hyun & Han, Ho-Yeon 2019 |
Zelima subabiens
| Stackelberg, A. A. 1952: 326 |
Zelima abiens: Sack, 1932: 373
| Hokuryukan, Co. 1965: 214 |
| Sack, P. 1932: 373 |
| Shiraki, T. 1930: 64 |
Xylota abiens
| Han, H. Y. & Suk, S. W. & Lee, Y. B. & Lee, H. S. 2014: 29 |
| Ohara, K. & Ohishi, H. & Ichige, K. 2014: 522 |
| Huang, C. & Cheng, X. 2012: 669 |
| Paek, M. K. & Hwang, J. M. & Jung, K. S. & Kim, T. W. & Kim, M. C. & Lee, Y. J. & Cho, Y. B. & Park, S. W. & Lee, H. S. & Ku, D. S. & Jeong, J. C. & Kim, K. G. & Choi, D. S. & Shin, E. H. & Hwang, J. & Lee, J. S. & Kim, S. S. & Bae, Y. S. 2010: 232 |
| Bartsch, H. & Binkiewicz, E. & Klintbjer, A. & Raden, A. & Nasibov, E. 2009: 404 |
| Stubbs, A. E. & Falk, S. 2002: 333 |
| Han, H. Y. & Choi, D. S. 2001: 214 |
| Mutin, V. A. & Barkalov, A. V. 1999: 495 |
| Speight, M. C. D. 1999: 216 |
| Vujic, A. & Milankov, V. 1999: 124 |
| Park, K. T. 1998: 86 |
| Han, H. Y. & Choi, D. S. & Kim, J. I. & Byun, H. W. 1998: 152 |
| Peck, L. V. 1988: 224 |
| Violovitsh, N. A. 1986: 140 |
| Hippa, H. 1978: 64 |
| Hippa, H. 1968: 186 |
| Meigen, J. W. 1822: 218 |
1 (by plazi, 2019-08-29 06:44:18)
2 (by plazi, 2019-09-19 10:43:35)
3 (by plazi, 2019-09-19 10:44:10)
4 (by ExternalLinkService, 2019-09-19 10:55:06)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2019-09-19 11:29:34)
6 (by veselin, 2019-09-30 14:03:02)
7 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-01-29 12:33:41)
8 (by plazi, 2023-10-30 18:37:13)