Poeciloterpa mangkas Crispolon et Yap, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4608.2.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:57BB0265-12E2-438A-804B-9897182A6541 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5931916 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6A34A87C-AA07-0F3A-FF2E-FD23FE47FA70 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Poeciloterpa mangkas Crispolon et Yap |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Poeciloterpa mangkas Crispolon et Yap sp. nov
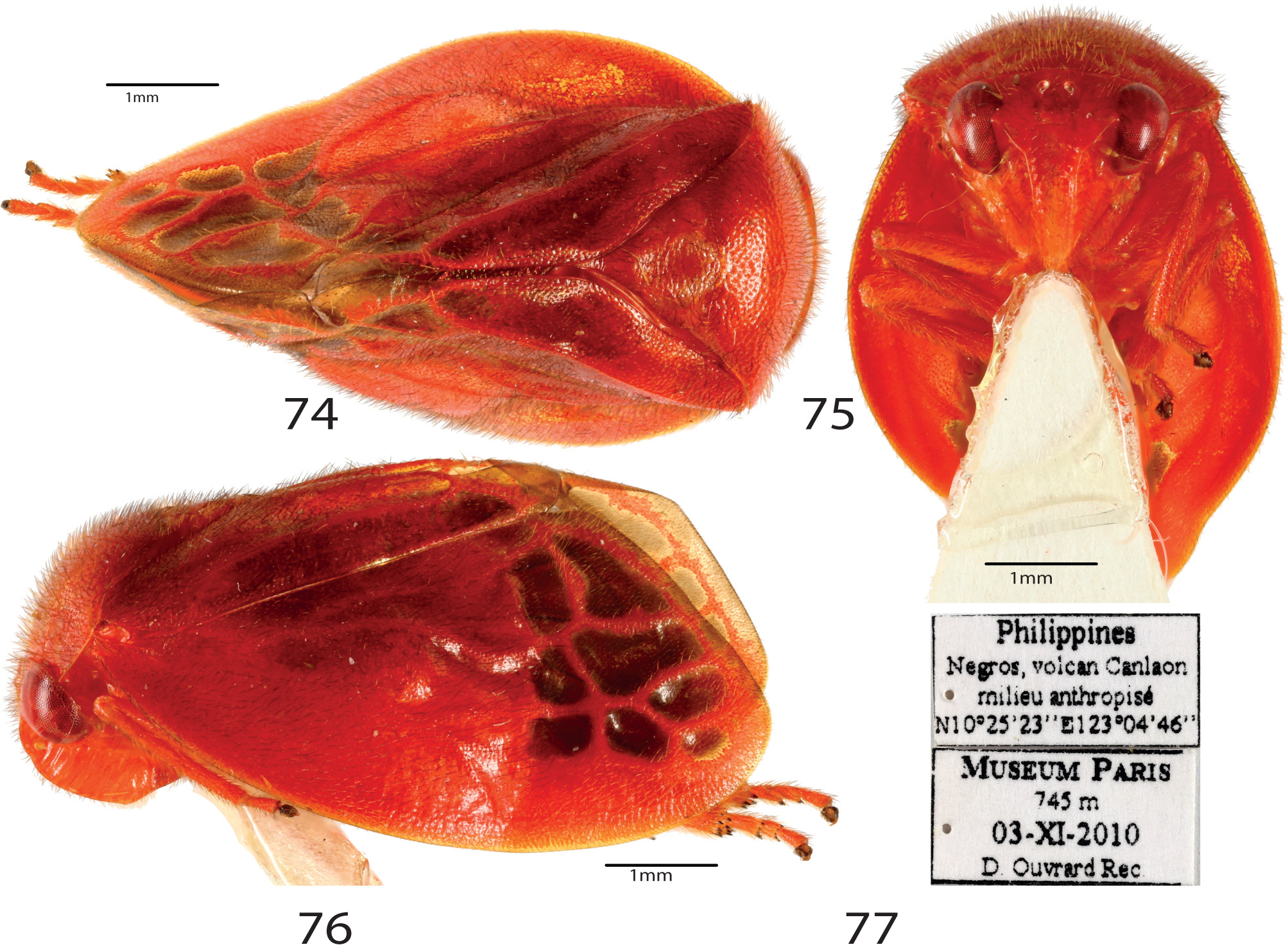
( Figs 74–83 View FIGURES 74–77 View FIGURES 78–83 )
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
Type Material. Holotype ♂: [ Philippines, Negros , volcan Canlaon, milieu anthropisé, N 10 ° 25’. 23’’ E 123 ° 04.46 ’’], [ MUSEUM PARIS, 745 m, 31-X-2010, D Ouvrard Rec.], MNHN ( EH) 2363 ( MNHN). GoogleMaps
Paratypes. [ Philippines: Negros, volcan Canlaon, forêt], [ MUSEUM PARIS piège lumineux], 1098 m asl , N 10 ° 25’.19’’ E 123 ° 04.36 ’’, 27-X-2010; 932 m asl N 10 ° 25’.29’’ E 123 ° 05.23 ’’, 28-X-2010; 1050 m asl N 10 ° 25’.29’’ E 123 ° 05.36 ’’, 28-X-2010; N 10 ° 25’ 31’’ E 123 ° 05.40 ’’, 1098 m asl, 29-X-2010; N 10 ° 25’ 20’’ E 123 ° 05.19 ’’, 02- XI-2010; N 10 ° 25’ 36’’ E 123 ° 05.37 ’’, 03-XI-2010; A Soulier-Perkins and D. Ouvrard. 6♂ 2♀ MNHN ( EH) 23643, 24390–24397 ( MNHN), 1♂ 1♀ UPLBMNH HEM 05046–05047 ( MNH-UPLB) .
Labels. Photographed by Laurent Fauvre © 2017 MNHN.
Type Locality. Philippines: Visayas, Negros Occidental, Mount Kanlaon.
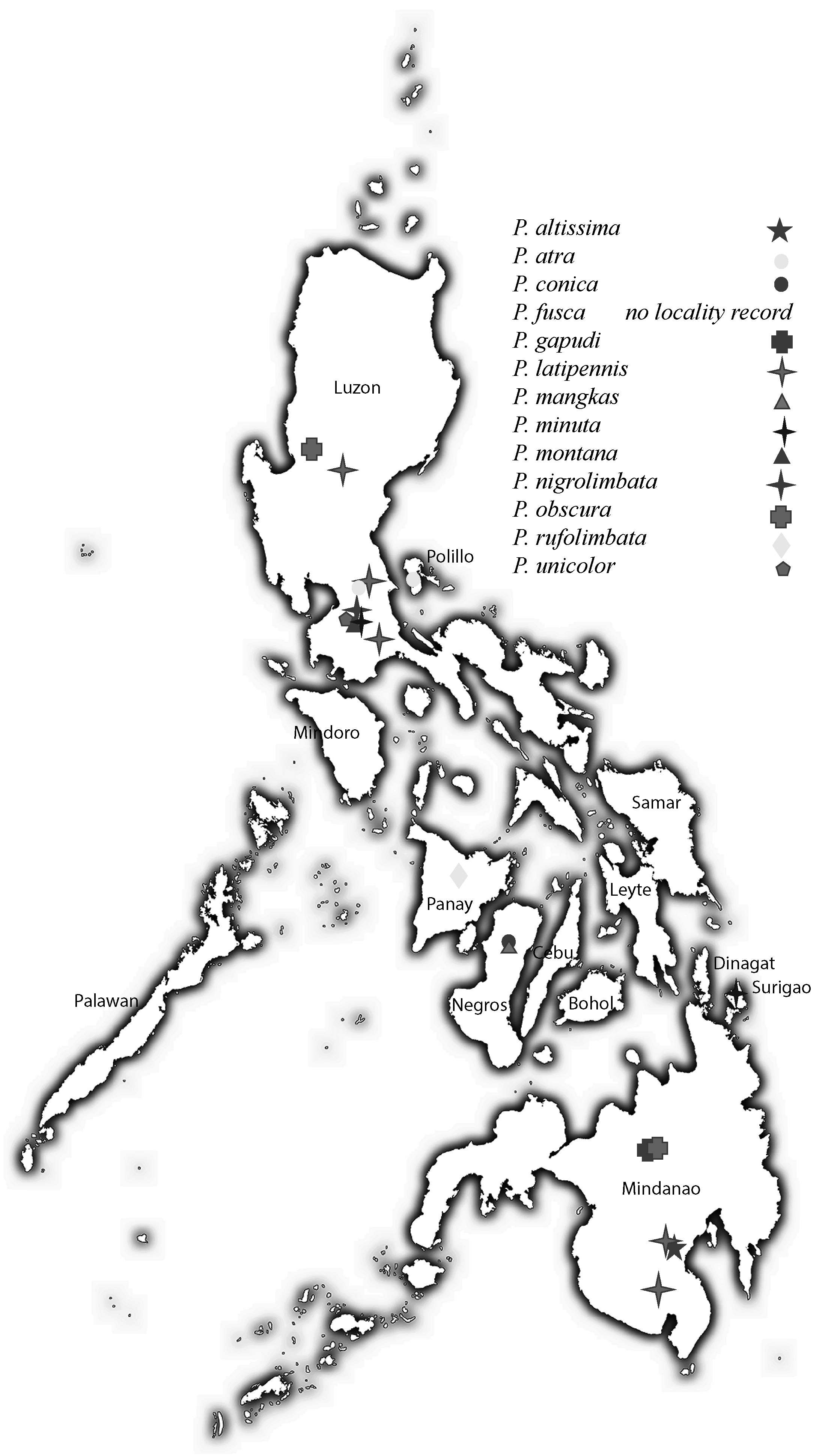
Distribution. Philippines: Visayas, Negros Island ( Fig. 148 View FIGURES 148 ).
Diagnosis. P. mangkas , P. gapudi and P. altissima have a common general tegmina pattern, red with brown to dark brown apical cells. However, P. mangkas is the only one with the radial vein not reaching the costal margin.
Description. Body length 7mm (including tegmina), width 4 mm.
Head. In dorsal view, head slightly narrower than pronotum and concealed in pronotum. Distance between ocelli equals two times ocellar diameter, ocelli closer to each other than from compound eyes. Eyes, 1.26 times longer than wide. Two vertex grooves extending from posterior to anterior margins and forming a narrow rectangular area, arina absent on frons and vertex. Pedicel of antennae with short and sparse hairs, flagellum with arista, short relative to pedicel. Postclypeus angular and not receding in lateral view, smooth and furrowed medially forming two narrow longitudinal carinae with lateral grooves on both sides. Rostrum long, reaching posterior margin of metacoxae. In dorsal view, pronotum bearing 6 notches, ornamented with hairs anteriorly. Pronotum wider than head and finely punctuated, anterior margin curving, anterolateral margin convex and smaller than half of anterior margin, humeral angle rounded, posterior margin slightly grooved, in lateral view, pronotum convex. Scutellum finely punctuated, slightly wider than long, large median depression and spiniform tip not depressed. Tegmina ( Fig. 83 View FIGURES 78–83 ) length 6.5 mm, R forking at half of tegmina length, Cu and M forking before mid-length. Apical reticulation reduced. No vein reaching costal margin outlining a wide area without any vein. Metafemur with apical spine in inner margin, metatibiae with 1 lateral spine, metatarsus with third segment bearing triangular subungueal process and first and second segments bearing a crown of spines.
Male terminalia ( Fig. 78 View FIGURES 78–83 ). In lateral view, pygofer ( Fig. 79 View FIGURES 78–83 ) with dorsal margin almost straight on 2/3 of its length, posterior margin with dorsal half concave, ventral half almost straight and a clear hump in middle. Dorsal margin of subgenital plate slightly undulated, curing dorsally just apically, ventral margin almost straight most of its length curving dorsally at apex ( Fig. 80 View FIGURES 78–83 ), subgenital plate almost straight finishing with sharp apex oriented dorsally, covered with hair from base to apex, lateral plate roughly shaped as an isosceles triangle pointing anteroventrally. Paramere ( Fig. 81 View FIGURES 78–83 ) largely rounded on dorsal and ventral margins, dorsal margin concave subapically, set of setae located on roundest dorsal and ventral area of paramere and oriented dorso posteriorly, tip of hairs not reaching posterior tip of paramere. Sharp posterodorsal and posteroventral angles. Aedeagus ( Fig. 82 View FIGURES 78–83 ) in lateral view, dorsal margin curving gently ventrally then dorsally more abruptly then curved without any drastic break, posterior end finishing in an apical extension curling posteriorly and slightly ventrally, apex not very sharp and tip pointing posteroventrally, posterior prostrusion narrowing at the base, then roughly subcylindrical and finishing by a comma shaped apex after a strong constriction, posteroventral protrusion present. Ventral margin of aedeagus curving down and anteriorly at the anterior base then curving regularly posteriorly then dorsally.
Colour. Body covered with yellowish to brownish hairs. Head including postclypeus and rostrum red, ocelli glassy white, eye red with darker marks. Antennae yellowish brown. Pronotum and scutellum red. Tegmina red, with apical cells dark brown. Legs red with tarsal claws and tip of spines black. Abdomen red.
Etymology. The species refers to the old name of the type locality, La Carlota which is Mangkas. It is treated as a noun in apposition.
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |