Macrotomoderus similis, Telnov, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2022.797.1667 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8DF57743-9C53-4265-BCB5-743276A3A16C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6317955 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6E0B08FA-F336-4902-9E72-767D78C5FA95 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:6E0B08FA-F336-4902-9E72-767D78C5FA95 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Macrotomoderus similis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Macrotomoderus similis sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:6E0B08FA-F336-4902-9E72-767D78C5FA95
Differential diagnosis
This species appears similar to Macrotomoderus truncatulus sp. nov. (see description below) primarily due to the similar modification present at the anterior pronotal margin. However, the head base is stronger truncate with the obtuse but well-visible temporal angles in M. truncatulus sp. nov., the setae of the upper margin of the anterior wall of the antero-median pronotal impression are distinctly curved and pointed anteriad (not or slightly curved in M. similis sp. nov.), the pronotal constriction dorsally with a track of the longitudinal median carina (not observed in M. similis sp. nov.), and the lateral margins of the antero-median pronotal impression are stronger raised, slightly denticulate in dorsal view (not or almost not raised, not denticulate-like produced in M. similis sp. nov.). Also see key to species below.
Etymology
Named from the Latin ‘similis’ (‘similar’) to highlight its morphological similarity with Macrotomoderus truncatulus sp. nov. (see description below).
Type material
Holotype CHINA • ♂; “CHINA, Yunnan, SSE Shuangjiang Town , 2540 m, 22.vi.2011 Belousov, Kabak, Korolev leg. // 23°22′22″N 99°54′47″E ”; ZIN. GoogleMaps
Description
MEASUREMENTS. Holotype, total body length 3.35 mm; head 0.8 mm long, across eyes 0.75 mm broad, pronotum 0.9 mm long, maximum width 0.7 mm, minimum width 0.4 mm, elytra 1.65 mm long, 1.5 mm combined wide.
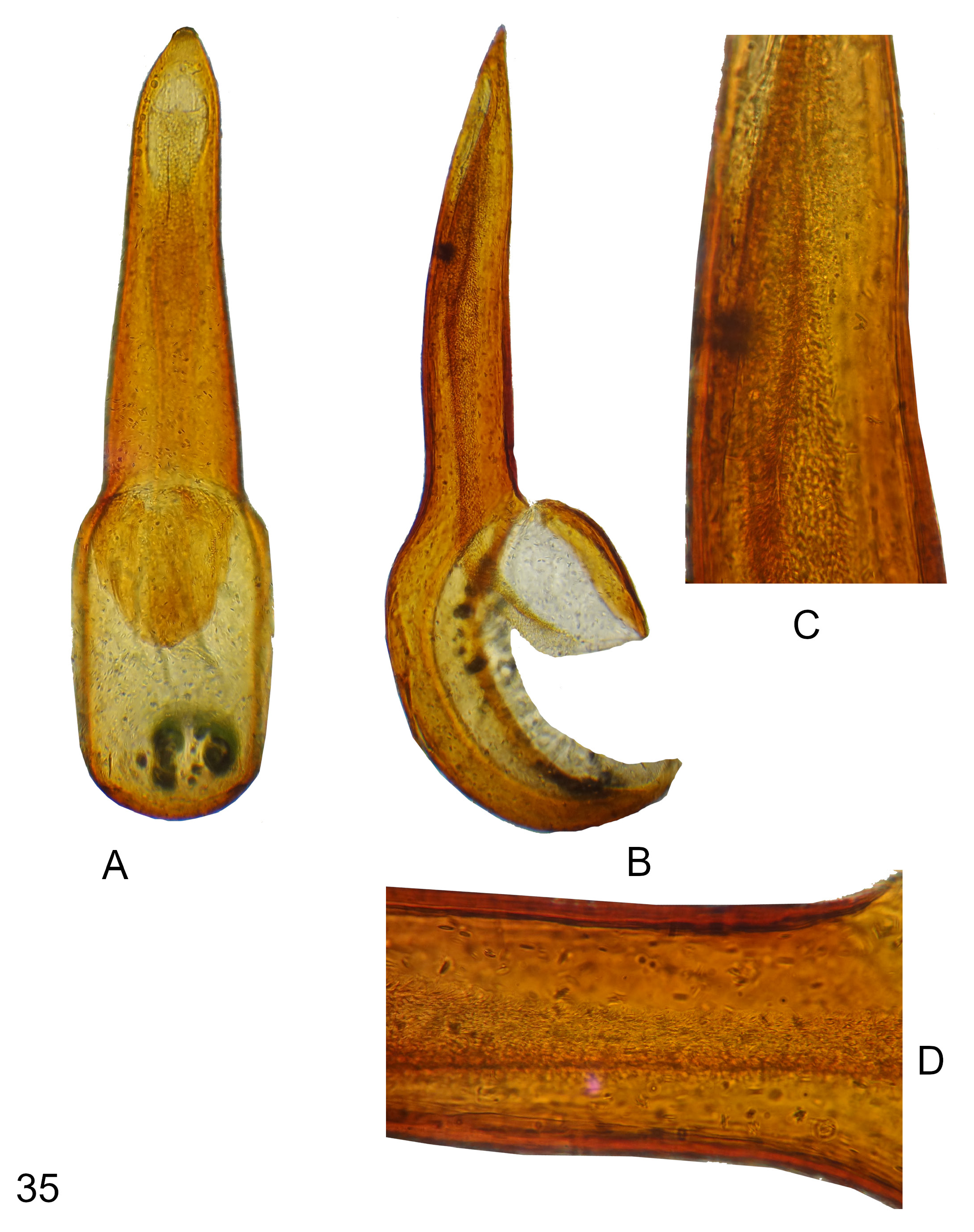
Dorsum and venter uniformly pale brown. Mouthparts, antennae, palps and legs yellowish-brown. Head ovoid with small, ovoid compound eyes, which are not or slightly protruding beyond head outline laterally. Tempora rounded and converging towards head base, temporal angles broadly rounded. Head base subtruncate; occiput somewhat declivous posteroventrally above insertion of cranial neck (in posterodorsal view head base appear medially truncate). Head dorsal punctures minute and inconspicuous. Head dorsal setae inconspicuous, sparse. Antennae extending towards base of pronotum. Antennomere three nearly same length as antennomere two, antennomeres 8–10 transverse, of them 9–10 strongly transverse. Terminal antennomere shortly triangular with obtusely pointed apex, about 2.1–2.2 × as long as penultimate antennomere. Terminal maxillary palpomere securiform. Pronotum with broad and medially shortly notched postmedian lateral constriction. Front margin of anterior lobe broadly rounded, in male shallowly and broadly impressed mesally opposite median part of head base; anterolateral margins of this impression not or almost not raised in dorsal aspect, not produced into denticles ( Fig. 34B–C View Fig ). Anterior edge of pronotum in front of anterior impression in male with thin, moderately high and short median wall that is provided with few golden, short, in part anteriadpointing setae ( Fig. 34C View Fig ). Lateral angles of this wall on each side with a few long, apically curved erect setae; both groups of lateral setae are meeting apically over the wall in П-shaped arc ( Fig. 34B View Fig ). Pronotum dorsally with narrow anterior rim. Anterior and posterior lobe slightly convex in lateral view ( Fig. 34C View Fig ). Lateral constriction continues onto disc in lateral view, shallow ( Fig. 34C View Fig ). Lateral pronotal fovea moderately broad at lower external margin of pronotum, widens upwards towards pronotal disc in lateral view, external margins protruding into a pair of strongly obtuse (in lateral view), moderately widely separated denticles (in lateral view). Cavity in lateral wall of pronotum between lateral denticles not studied due to the blocking position of anterior legs. In dorsal view, lateral pronotal fovea narrow, anterior and posterior pair of denticles small, appear obtusely angulate, glabrous, poorly visible from above since partially concealed by setae from adjoining portions of pronotum ( Fig. 34B View Fig ). Pronotal punctures minute on disc; lateral constriction dorsally somewhat denser and coarser punctured than anterior lobe. Dorsal pronotal setae rather long, appressed, at least in part concealing disc of posterior pronotal lobe. Scutellar shield small, apically rounded. Elytra dorsally elongate elliptical, slightly convex in lateral view, widened laterally around midlength and broadly rounded at lateral margins, shoulders obsolete (apterous species). Elytral punctures moderately large and deep, sparse, becoming smaller and shallower towards apices. Intervening spaces on basal half of elytra about 2–4 × as large as punctures. Elytral setae long and sparse, suberect. Male tergite and morphological sternite VII broadly rounded at posterior margin. Aedeagus as in Fig. 35 View Fig , large and elongate, basale hook-shaped. Gonopore armature very delicate, arranged into tube-enclosed ‘garland’, constituting pieces elongate and narrow, spine-like, closed attached to one another in apical portion of apicale, becoming smaller near apex of aedeagus.
Sexual dimorphism
Female is unknown.
Ecology
Collected at 2540 m elevation.
Distribution
Known only from southern part of Yunnan Province, SW China.
| ZIN |
Russian Academy of Sciences, Zoological Institute, Zoological Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |