Alloclubionoides solea, Kim & Kim, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2012.707246 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/712F900F-FF9B-FFAF-FDB8-FBFBFE3CFDAD |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Alloclubionoides solea |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Alloclubionoides solea sp. nov.
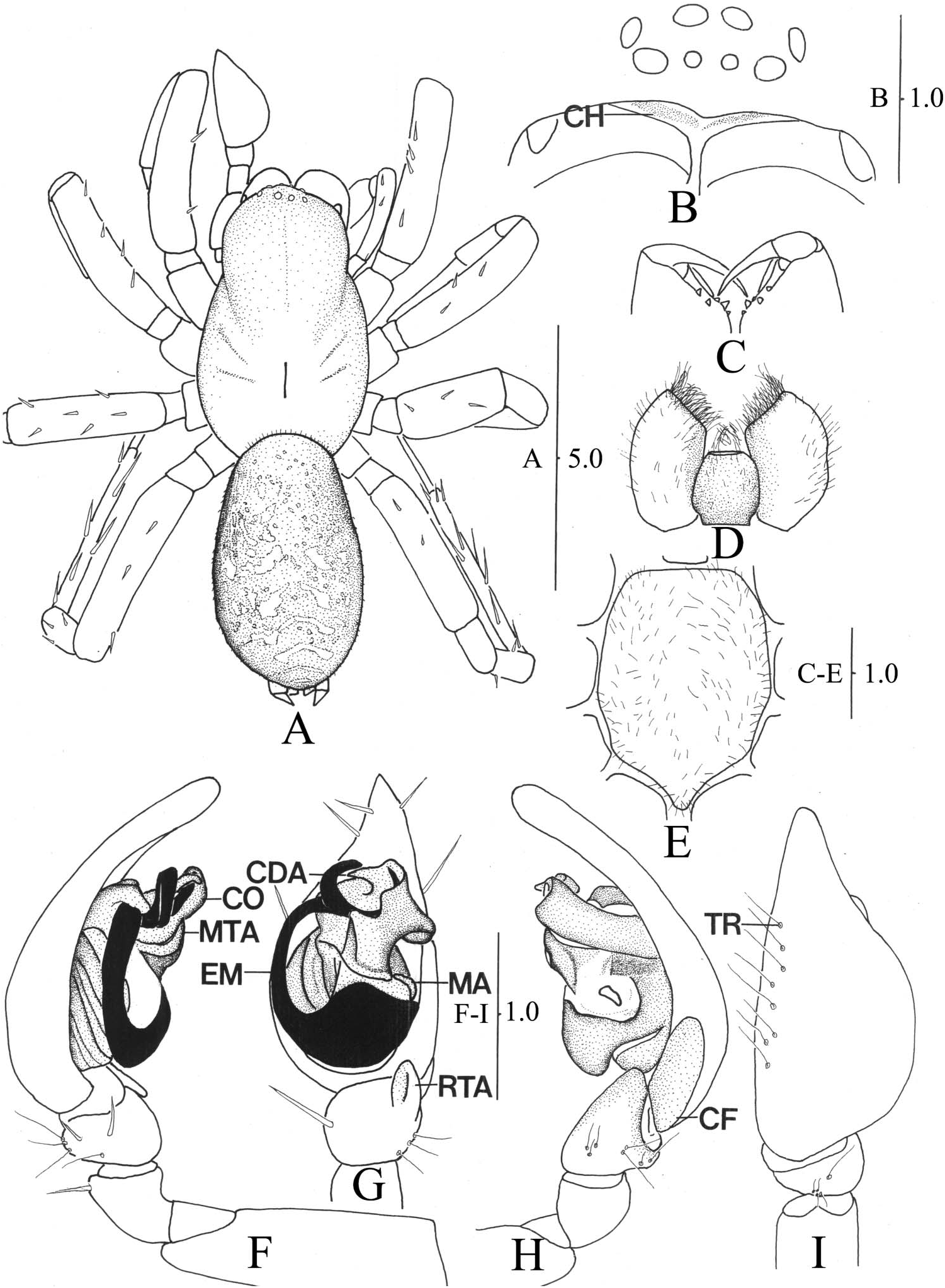
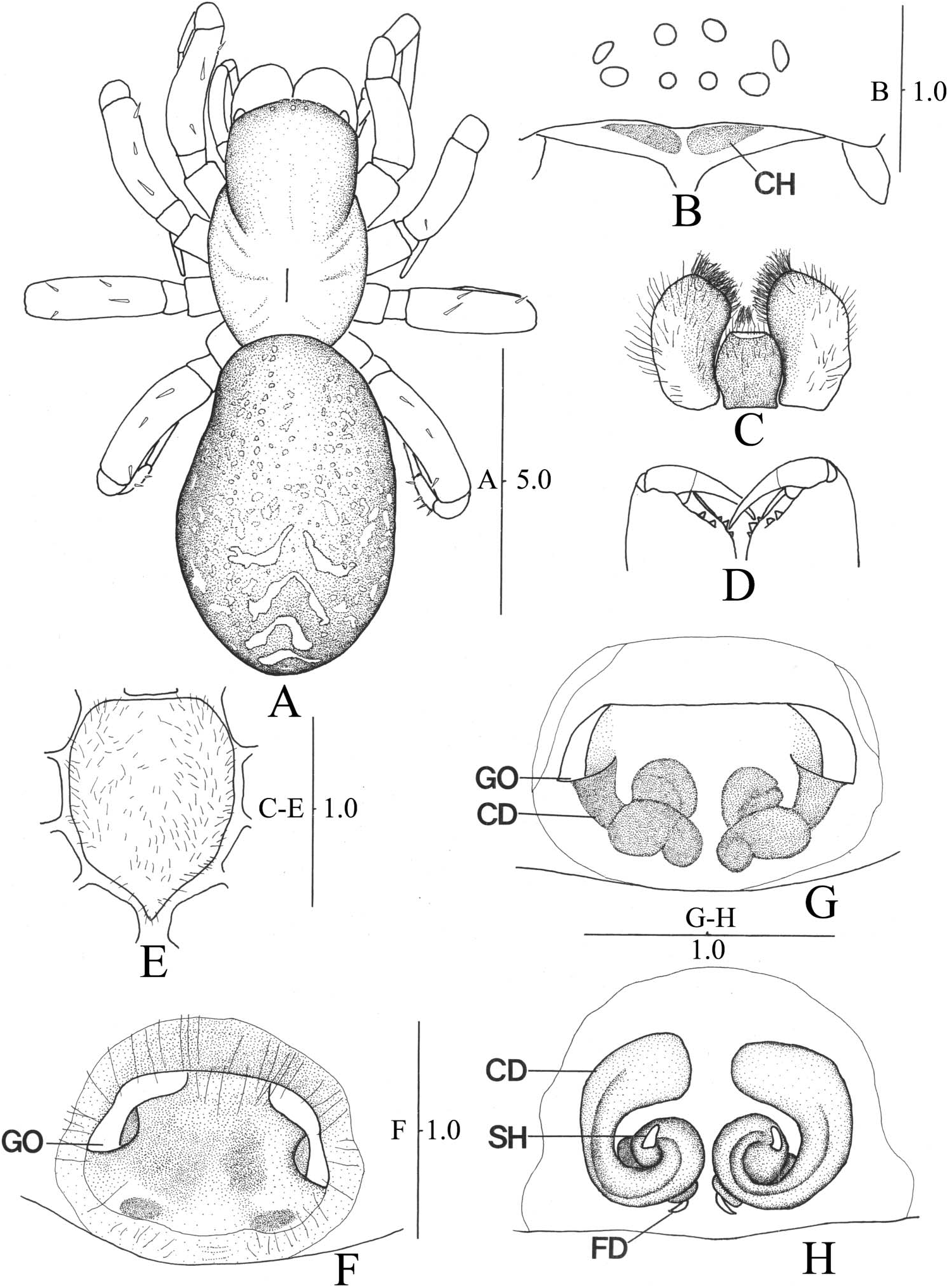
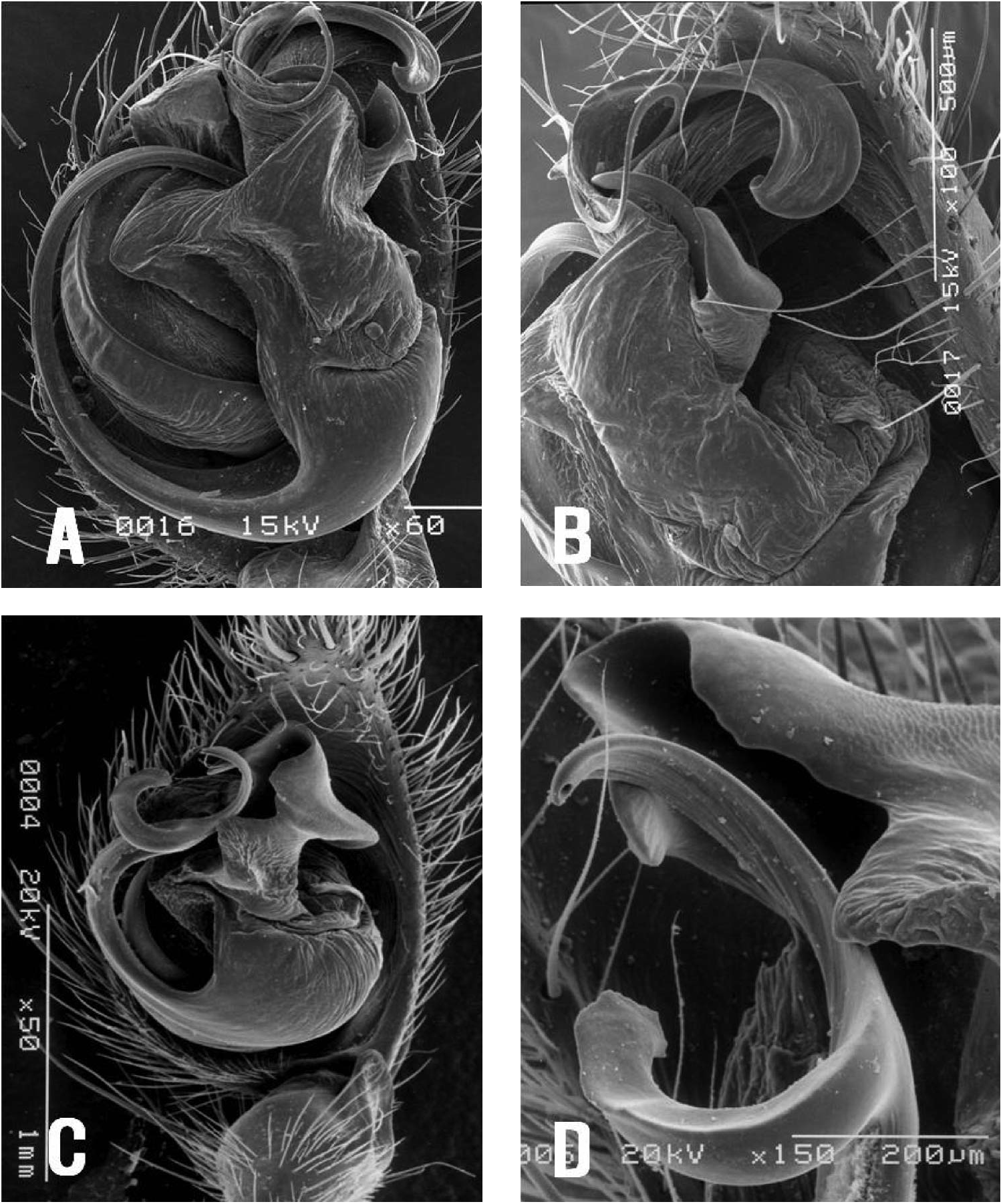
( Figures 3 View Figure 3 , 4 View Figure 4 , 5C,D View Figure 5 )
Type materials
Holotype. Male ( NPRI), Dolsan Island , Dadohaehaesang marine National Park, Korea, 26 February 2009, collected D.Y. Choi and B.W. Kim.
Paratypes. 1 ♀ ( NPRI), the same data as holotype ; 1 ♂ ( NPRI), the same collection, 13 October 2008, leg. B.W. Kim.
Diagnosis
This species is similar to A. napolovi Ovtchinnikov, 1999 , A. paiki Ovtchinnikov, 1999 and A. coreana ( Paik, 1992) in having male palpal organs with embolus not penetrating the tegulum and conductor surrounding the distal part of embolus and female epigynum with genital opening located on the lateral of atrium and without atrial septum and hood. The species can be distinguished by the presence of a median apophysis (absent in A. paiki ), embolus with a horseshoe-like bifurcated distal part (thickly linear in A. napolovi ); and in female by distinctly spiral copulatory duct (indistinctly wound in A. dimidiatus ), spermathecal head located on the inner side of copulatory duct (outer in A. coreana ).
Etymology
The specific name is derived from the special distal part (Latin, horseshoe) of embolus in male palpal organ.
Measurements (mm)
Male (female in parentheses). Habitus length 9.4 (10.7); cheliceral length 2.7 (2.5), cheliceral width 1.1 (1.3), cheliceral fang length 1.3 (1.3); clypeal height 0.3 (0.2); carapace length 5.0 (4.7), carapace width 3.2 (3.0), carapace height 2.9 (2.1); endite length 1.5 (1.5), endite width 0.9 (0.8); labium length 0.8 (0.9), labium width 0.7 (0.7); sternum length 2.6 (2.4), sternum width 1.8 (1.8); AER 0.9 (1.0), PER 1.1 (1.2), AME 0.1 (0.1), ALE 0.2 (0.2), PME 0.2 (0.2), PLE 0.2 (0.2). Eye formula ALE = PME = PLE = AME (PLE = ALE = PME = AME). Palp 5.1 (4.8) [1.8 (1.7), 0.6 (0.7), 0.4 (0.9), 2.3 (1.5)]. First leg 13.0 (10.4) [3.6 (3.1), 1.7 (1.5), 2.8 (2.3), 3.1 (2.3), 1.8 (1.2)], second leg 11.7 (9.4) [3.3 (2.7), 1.5 (1.5), 2.3 (1.9), 2.9 (2.3), 1.7 (1.2)], third leg 11.1 (9.1) [3.2 (2.5), 1.5 (1.4), 2.0 (1.7), 2.9 (2.3), 1.5 (1.2)], fourth leg 15.1 (12.5) [4.0 (3.4), 1.7 (1.7), 3.1 (2.6), 4.3 (3.4), 2.0 (1.4)]. Leg formula IV I II III (IV I II III). Abdomen length 4.8 (6.4), abdomen width 2.8 (4.0), abdomen height 2.9 (4.3).
Description
Male (holotype). Medium-sized spiders. Carapace elongate, 1.6 times as long as wide, moderately narrowed in eye area, with distinctly longitudinal fovea at middle ( Figure 3A View Figure 3 ). Eye: AER straight, PER slightly procurved in frontal view; AME smaller than other eyes, separated by slightly less than their diameter, eye ratio 34 ( Figure 3B View Figure 3 ). Clypeus: clypeal height three times as long as AME diameter, with pair of eyebrow-shaped chila ( Figure 3B View Figure 3 ). Chelicerae with numerous long setae, lateral condyle yellowish brown, with three promarginal teeth, middle one largest; two retromarginal teeth subequal in size ( Figure 3C View Figure 3 ). Endites reddish brown, widest at mid part; labium rectangular, slightly longer than wide ( Figure 3D View Figure 3 ). Sternum shield-shaped, widest at second coxae, slightly produced between fourth coxae ( Figure 3E View Figure 3 ).
Palp without claw; tibia with 13 trichobothria in three rows (5d-3r), tarsus eight (8d), femur with three spines, tibia three on prolateral, tarsus eight (8d). Legs yellowish brown; length of leg I (patella + tibia) always shorter than carapace length; trochanters not notched; tibiae with 18–25 trichobothria in four rows (6p-6d-6d-7r on leg I, 5p-6d- 5d-7r on II, 4p-4d-5d-5r on III, 5p-6d-6d-4r on IV), metatarsi five to nine in one row (six on leg I, seven on II, five on III, nine on IV), tarsi five to seven in one row (nine on leg I and IV, eight on II, five on III); tarsal organ situated close to distal end of tarsus, slightly anterior of distal trichobothrium; tarsi with three claws, upper claws with 8–11 side teeth (11 on leg I, 9 on II, 10 on III, 8 on IV), lower with one.
Leg spination: Leg I femur with four spines, tibia seven (one, 0-0-1 on prolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), metatarsus eight (two, 0-1-0-1 on prolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus without spine; leg II femur with four spines, tibia six with one small spine half as long as others on inner ventral (two, 0-1-1 on prolateral; four, 1-2-1 on ventral), metatarsus nine (three, 0-1-2 on prolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus without spine; leg III femur with six spines, tibia 10 (two, 1-1 on prolateral; two, 0-1-1 on retrolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), metatarsus 15 (five, 1-2-2 on prolateral; four, 1-1-2 on retrolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus three (two, 0-1-1 on prolateral; two, 0-1-1 on ventral); leg IV femur with four spines, tibia 10 (two, 1-1 on prolateral; two, 0-1-1 on retrolateral; six, 2-2-2a on ventral), metatarsus 16 (10, 1-2-2 on prolateral and retrolateral; six 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus six (0-1-1 on prolateral, retrolateral and ventral). Abdomen ovoid, with scattered brownish yellow spots ( Figure 3A View Figure 3 ). Cribellum absent.
Male palp ( Figures 3 View Figure 3 F–I, 5C,D): patellar apophysis absent; RTA modified without ITA; CFR, 30%, cymbial length (2.3 mm) 3.3 times as long as CF (0.7 mm); tegular sclerite weakly sclerotized and situated longitudinally on tegulum; conductor saddlelike, with large groove surrounding the distal embolus tip of the inner branch, located on the upper part of tegulum; CDA developed, a sharp projection; embolus long slen- der, broadly wound clockwise (left palp) and horseshoe-like, roundly bifurcate on the distal part; MA small, thin and semicircular.
Female (paratype). Medium-sized spider, found under stones and fallen leaves on the ground of forests. Carapace elongated, 1.6 times longer than wide, moderately narrowed in eye area, with distinctly longitudinal fovea at middle ( Figure 4A View Figure 4 ). Eyes: AER straight, PER slightly procurved in frontal view; AME smaller than other eyes, slightly separated by as much as their diameter, eye ratio 40 ( Figure 4B View Figure 4 ). Clypeus: clypeal height twice as long as AME diameter, with pair of eyebrow-shaped chila ( Figure 4B View Figure 4 ). Chelicerae with numerous long setae; lateral condyle yellowish brown; three promarginal teeth, middle one largest; two retromarginal teeth subequal in size ( Figure 4C View Figure 4 ). Endites reddish brown, widest at mid part; labium rectangular as long as wide ( Figure 4D View Figure 4 ). Sternum shield-shaped, widest at second coxae, 1.2 times as long as wide, and slightly produced between fourth coxae ( Figure 4E View Figure 4 ).
Palp bearing one claw with seven side teeth; tibia with 14 trichobothria in three rows (6d-6d-2r), tarsus six in one (6d), femur with three spines, tibia three (1-2 on prolateral), tarsus 15 (one, 1-0 on dorsal; 10, 2-2-1 on prolateral and retrolateral; four, 0-0-2-2 on ventral). Legs yellowish brown without ring patterns; length of leg I (patella + tibia) always shorter than carapace length; trochanters not notched; tibiae with 20–23 trichobothria in four rows (4p-6d-5d-6r on leg I, 5p-6d-5d-5r on II, 4p-6d- 5d-5 on III, 5p-7d-5d-6r on IV), metatarsi five to eight in one row (seven on leg I, five on II, six on III and IV), tarsi six to eight in one row (seven on leg I, II and III, eight on IV); tarsal organ situated close to distal end of tarsus, slightly anterior of distal trichobothrium; tarsi with three claws, upper claws with 9–12 side teeth (12 on leg I, 11 on II, nine on III and IV), lower with two (on all legs).
Leg spination: leg I femur with four spines, tibia seven (one, 0-0-1 on prolateral; 2-2-2 on ventral), metatarsus eight (two, 0-1-1 on prolateral; 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus without spine; leg II femur with three spines, tibia five (one, 0-0-1 on prolateral; four, 1-1-2 on ventral), metatarsus nine (three, 0-1-2 on prolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus without spine; leg III femur with four spines, tibia 10 (two, 1-1 on prolateral; two, 0-1-1 on retrolateral; six, 2-2-2a on ventral), metatarsus 16 (10, 1-2-2 on prolateral and retrolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus four (two, 0-1-1 on prolateral; two, 0-1-0 on retrolateral and ventral); leg IV femur with three spines, tibia 10 (four, 1-1 on prolateral and retrolateral; six, 2-2-2a on ventral), metatarsus 16 (10, 1-2-2 on prolateral and retrolateral; six, 2-2-2 on ventral), tarsus six (0-1-1 on prolateral, retrolateral and ventral). Abdomen ovoid with scattered brownish yellow spots, with distinct chevrons on dorsal side ( Figure 4A View Figure 4 ). Cribellum absent.
Female epigynum ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 F–H): epigynal teeth absent; GO oval-shaped located on the lateral part of atrium; ALR, 84%; atrium, 1.8 times as wide as long (length 0.73 mm, width 1.33 mm); atrial septum absent; copulatory pore deep, situated at lateral part of atrium; without atrial hood; CDs broadly spiral counterclockwise to epigynal furrow (left), not adjoined from each other; SHs small fingerstall-like processes, situated at the upper end of spermathecae; spermathecae largely spherical, with indistinctive bases; FDs small, arising from posterior spermathecae.
Distribution
Korea (Dolsan Island)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |