Ginkgoites abaniensis (Kostina) A.Frolov, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.567.1.4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7143312 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/780E87A4-7200-124F-FF41-FE73958EFB1A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ginkgoites abaniensis (Kostina) A.Frolov |
| status |
comb. nov. |
Ginkgoites abaniensis (Kostina) A.Frolov comb. nov.
Fig. 1 View FIGURE , 3–5 View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE
Synonyms
2004. Ginkgo abaniensis: Kostina View in CoL , p. 52, Pl. XXVIII, fig. 1–8; Fig. 14.
2005. Ginkgo abaniensis: Kiritchkova et al. View in CoL , p. 94, Pl. XXIX, fig. 1–8; Pl. XXX, fig. 1–7; Pl. XXIV, fig. 1–7; Fig. 27.
Holotype: — RUSSIA, Eastern Siberia: Kansk Coal Basin , N 56°37’9”.700, E 96°54’49”.576, well 8400, depth 115– 119. 7 m, Kamala Formation , lower Middle Jurassic (Aalenian) (holotype no. 4844/374- 76 in Kostina, 2004: 52, Pl. XXVIII, fig. 1–8; Fig. 14; in this paper–fig. 1; Geological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences) GoogleMaps .
Epitype: — RUSSIA, Eastern Siberia: Mura-Kova interfluve, Bratsk – Kodinsk highway, 6 km from the bridge over the Tazeu I river, N 57°47’34”.015, E 99°49’37”.769, Mura Formation, Middle Jurassic (conventionally,Aalenian– Bajocian) (Epitype no. 9Т/81-12, Fig. 3 A View FIGURE ; 4 A, E–L View FIGURE ; 5 A, B, D, E, F View FIGURE ; Institute of the Earth’s Crust Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences).
Emended diagnosis. Leaves wedge-shaped to half-round, stalked. Median incision does not reach petiole. Lobes lanceolate-linear with subacute, sinuate or shallowly incised apices. Rare fusiform secretory channels between veins. Leaves amphistomatic. Cells of non-stomatal bands elongate, rectangular or spindle-like, some of them with flat papillae. Cells of stomatal bands short, isodiametric. Periclinal walls of some cells with small papillae or rarely with short rounded trichomes. Rows formed by cells with anisometric outlines (cell width is longer than length) characteristic of both leaf surfaces.
Cell walls straight or, rarely, slightly curved. Stomatal complexes in disordered in upper epidermis, in interrupted rows in lower epidermis. Stomatal complexes monocyclic, rounded or widely oval with irregular contour. Subsidiary cells identical with ordinary cells in degree of cutinization. The stomatal pit covered by marginal papillae.
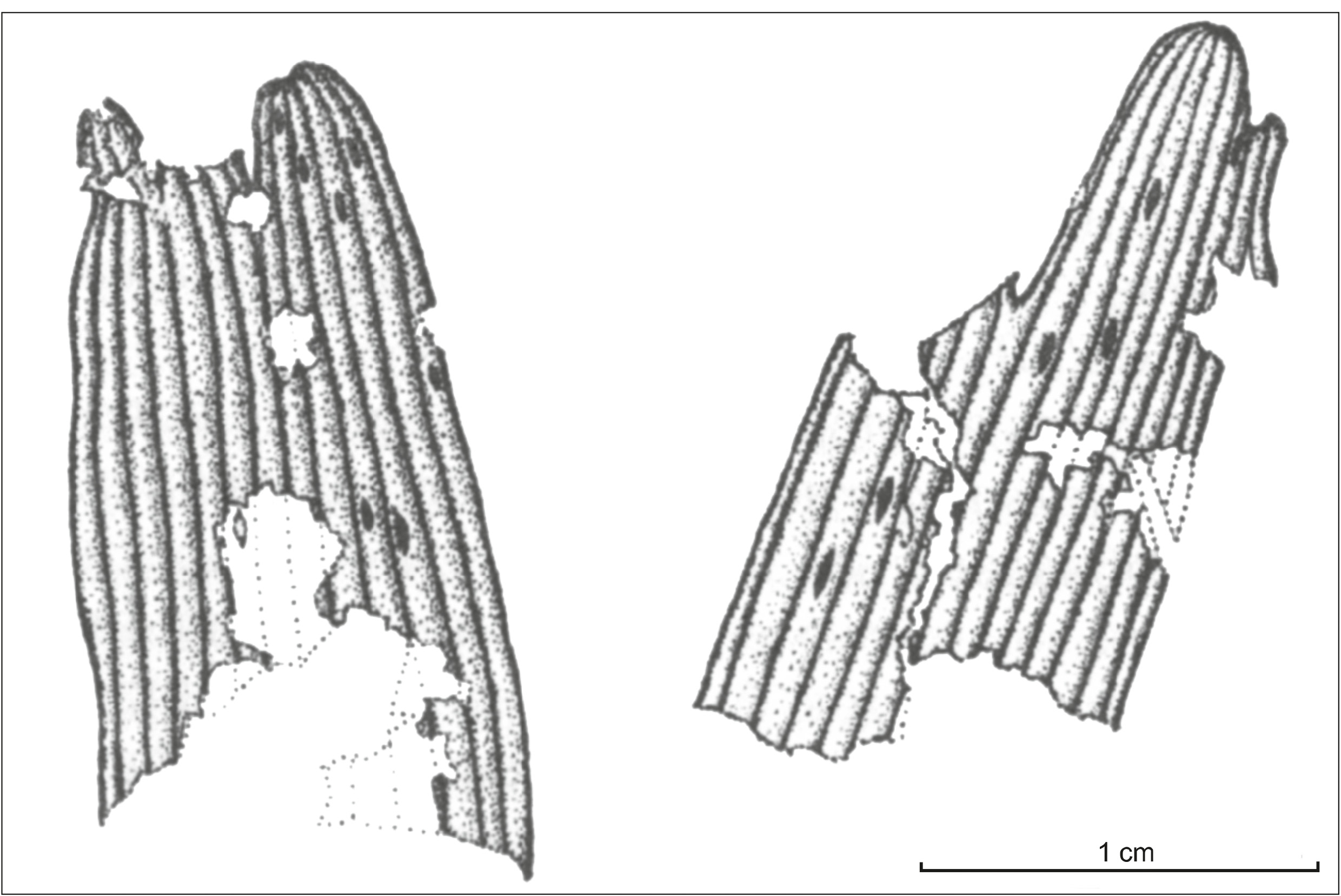
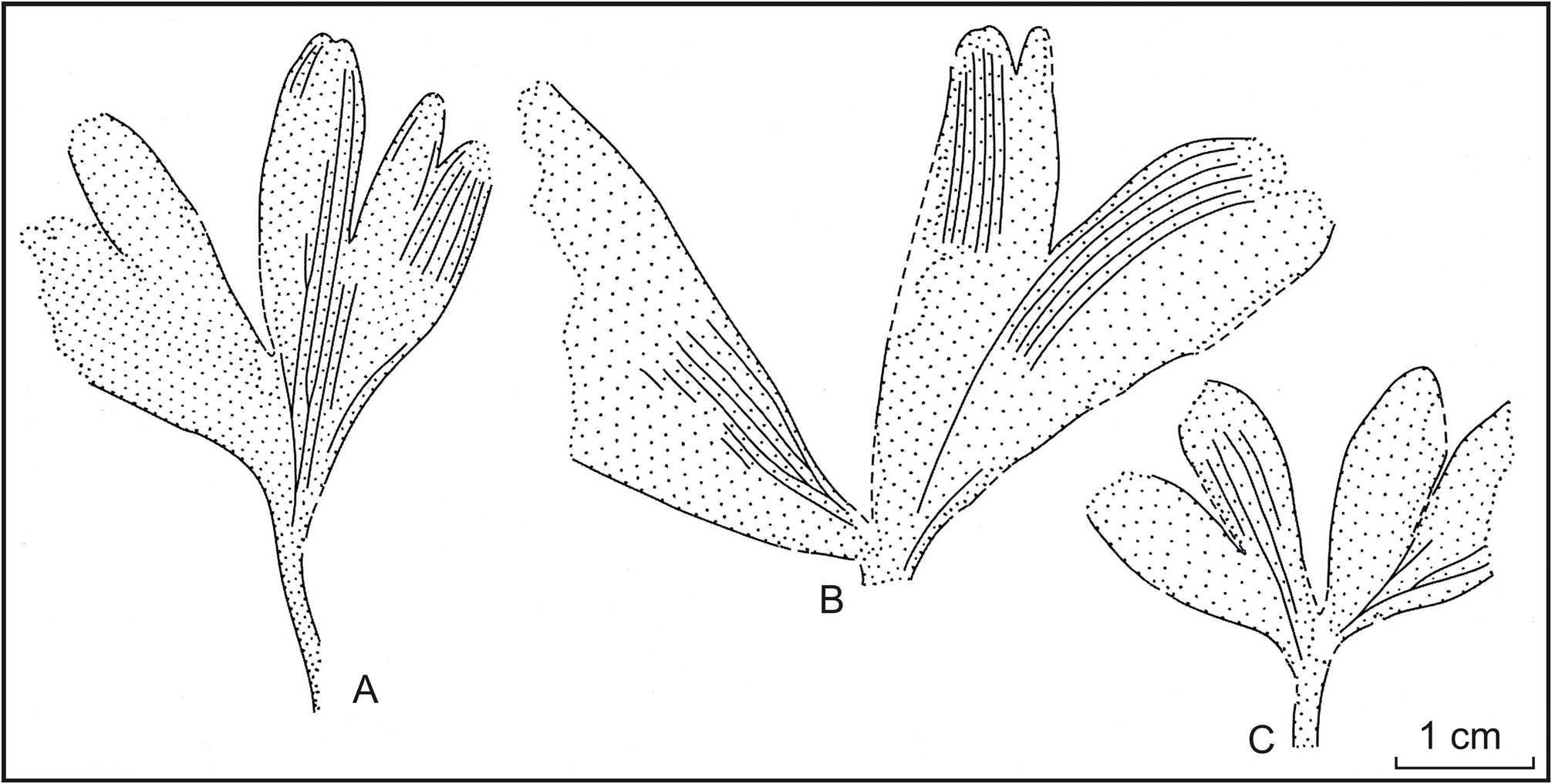
Description. The studied collection contains two impressions of larger leaves, an impression of a smaller leaf, and numerous fragments of compressions. Leaves are wedge-shaped in outline or almost rounded and stalked ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE ; 4 A–C View FIGURE ).
The laminae of the larger leaves are 36–32×60– 35 mm and those of the smaller ones are 17× 25 mm. The median incision is the deepest; it does not reach the petiole, stopping 4–5 mm above it on the larger leaves and 10 mm on the smaller ones. Leaves are quadrilobate. Lobes in outline are linear-lanceolate with subacute, sinuate or slightly incised apices; their width in the middle part is 5.5–8 mm. Apparent length of petiole on impressions is 14 mm and its width is 1–1.5 mm. Near the base of lamina the petiole slightly widens up to 2 mm. Veins are dichotomous in the lower half of leaf; they are simple, parallel in lobes. There are up to 6 veins per 5 mm of the lobe width. Rare spindle-like secretory channels are present between the veins ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE , D).
Leaves are amphistomatic. Stomatal and non-stomatal bands of the upper epidermis are less distinct than on the lower surface. Cells of non-stomatal bands are oblong, rectangular ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE , F). Sometimes their periclinal walls bear moderate-sized papillae, and seldomly have flat papillae. Single short trichomes are present in non-stomatal bands ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE , H). Anticlinal walls of cells are straight, smooth (rarely – slightly curved), uniformly thickened.
Cells of stomatal bands are short, isodiametric, multiangular with straight, uniformly thickened anticlinal walls. Small papillae, and rarely flat papillae are present on periclinal walls of some cells. Scattered, short, rounded trichomes occur on cells of stomatal bands. Rarely, rows formed by cells with anisometric outlines (cell width is longer than length) are present on the lower epidermis ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE , G). Stomatal complexes in bands are located randomly.
Lower epidermis is differentiated into well expressed stomatal (width 250–300 µm) and non-stomatal (width 150 µm) bands ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE , A–C). Non-stomatal bands are composed of strongly elongated spindle-like cells. Their anticlinal walls are straight, smooth or slightly curved, uniformly thickened. Small papillae occur on periclinal walls. Rare trichomes with a rounded apex are confined to non-stomatal bands. However, single trichomes are also found on the cells of the stomatal bands. The length of the trichomes ranges from 15 to 45 µm, but more often it is 19–30 µm.
Stomatal bands are composed of isodiametric cells. Anticlinal walls of cells are straight, or slightly curved, uniformly thickened. Small papillae are present on periclinal walls of some cells of stomatal bands.
Stomatal complexes in bands form interrupted rows and are oriented parallel to the long axis of leaf or at an angle to it ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE , A–D). There are 4–5 stomata per the stomatal band width. They are monocyclic; in outline they are oval with broken contour. The five subsidiary cells do not differ from the ordinary cells of lower epidermis in the degree of cutinization. They bear well-developed marginal papillae, which cover the stomatal pit. In some subsidiary cells, papillae may be longer, trichome-like, or less developed ( Fig. 4 J–L View FIGURE ; 5 E–G View FIGURE ). Guard cells of stomata are slightly sunken.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |