Calomicrus jungchangi Lee and Beenen
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1649/072.066.0207 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7F4B87FB-FF7F-D535-7EAC-088CFCFA6A8D |
|
treatment provided by |
Diego |
|
scientific name |
Calomicrus jungchangi Lee and Beenen |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Calomicrus jungchangi Lee and Beenen , new species
Diagnosis. Calomicrus jungchangi is an entirely yellowish brown species. Other entirely yellow or yellowish brown species from Asia are Calomicrus fulvus Kimoto, 1977 from Bhutan, Calomicrus persimilis Kimoto, 1989 from Laos and Vietnam, and Calomicrus kimotoi Warchałowski, 1991 from Myanmar. Only C. fulvus is approximately of the same length as C. jungchangi . The other species are 5–7 mm in length. Calomicrus fulvus differs in the relative length of the antennal segments: the third segment is slightly longer than the second, the fourth one and half times the third. In C. jungchangi , the third segment is equal to the second, and the fourth is twice as long as the third segment. Calomicrus ochraceus from China (Sichuan) is also a yellow species, but differs by its length (5.5–6.0 mm) and black head. Furthermore, the median lobe of the aedaeagus in C. ochraceus is wide and abruptly curved at its apex. Calomicrus jungchangi may be confused with Monolepta when the size of the basi-metatarsus is disregarded. It is most similar to M. rufofulva with respect to the yellowish brown or reddish brown color and the evenly convex pronotum. Monolepta rufofulva differs by its broadly oval body, the sexually dimorphic antenna, and the reddish brown color.
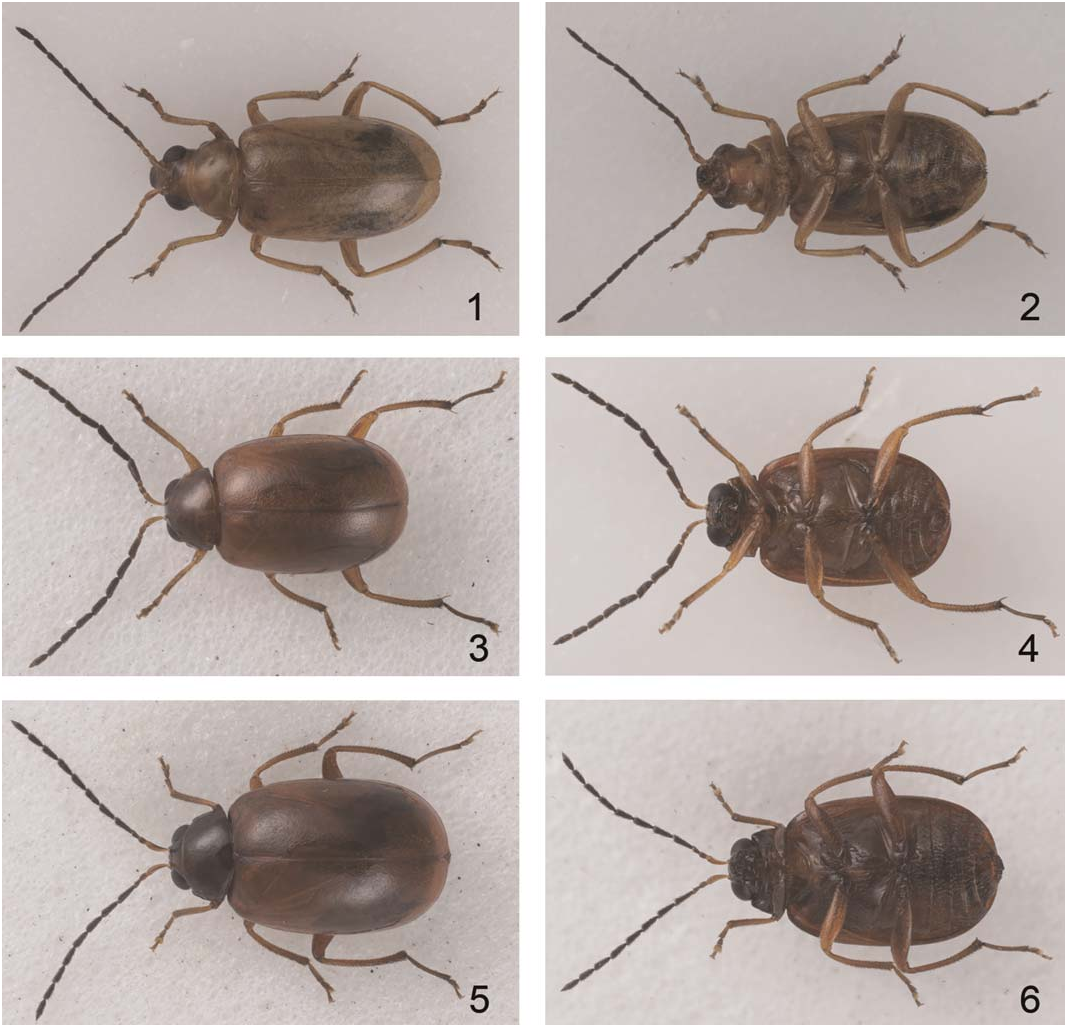
Description. Elongate oval. Total length 3.8– 4.1 mm. Greatest width across both elytra 2.0– 2.4 mm. Macropterous. General color ( Figs. 1–2 View Figs ) yellowish brown, antenna black or blackish brown except basal 2–3 antennomeres, labrum dark brown. Head: Maximum width of head across eyes 0.9 mm. Vertex impunctate, shiny with microscopic reticulation. Frontal tubercles transverse, shiny. Antennal formula 10-4-6-10-10-10-9-9-9-9-9; Length ratio of antennomeres II to III 0.96–1.00 ( Fig. 12 View Figs ); antennomeres III to IVabout 0.48–0.53; antennomeres IV-VII about 2.9 times longer than broad at apex; VIII-X relatively slender ( Fig. 7 View Figs ). Labrum square, with straight apical margin. Pronotum: Pronotal length to width ratio 0.63–0.66. Greatest width just before middle. Sides rounded. Front corners with calli, hind corners obtuse. Anterior border immarginate; lateral borders and posterior border with fine margin. Upper surface with fine reticulation and punctures, shiny. Scutellum: Triangular, impunctate, shiny. Elytra: Base broader than pronotum; ovate with greatest width just behind middle; maximum width of elytra to length of elytra 0.63–0.65. Humerus prominent; surface with shallow punctures on a reticulate surface; shiny with velvet sheen. Short erect hairs sparsely distributed on apical fifth of elytral surface. Elytral epipleuron even, wider from base to anterior margin of metasternum, then abruptly narrowing towards posterior margin of metasternum, then gradually narrowing towards apex. Legs: Slender. Hind tibia with large apical spine. Length ratio of basi-metatarsus to metatibia 0.33–0.34. Basi-metatarsus small, shorter than other tarsomeres combined. Tarsal claws appendiculate. Ventral surface: Procoxal cavities open posteriorly. Sexual dimorphism: Last abdominal sternite of male trilobed with central lobe almost square with straight margin; first segment of protarsus in male wider than in female. Male genitalia: Median lobe ( Fig. 8 View Figs ) slender, subparallel; apex rounded; ventral surface well-sclerotized; weakly curved in lateral view ( Fig. 9 View Figs ). Tectum apically acute and short, about 0.2X as long as median lobe. Endophallus in dorsal view ( Fig. 10 View Figs ) with 1 pair of small spiculae near apex, 4–5 hornlike spiculae at middle, basal spicula with 1 pair of slender sclerites curved towards apex; in ventral view ( Fig. 11 View Figs ), with 1 pair of flattened, wide, horn-like spiculae near apex, and in the middle part 2 pairs of spiculae: 1 pair of large horn-like spiculae with row of teeth along inner margin and 1 pair of curved spiculae composed of tiny teeth near basal part. Female genitalia: Spermathecal cornu ( Fig. 13 View Figs ) slender, apically strongly curved, abruptly widened near nodulus; nodulus spherical, large; spermathecal duct extremely wide at base, short. Dorsal part of bursa-sclerites ( Fig. 14 View Figs ) with 1 row of 7 teeth, 3–4 small teeth scattered near teeth; ventral part relatively long ( Fig. 15 View Figs ), with 1 row of 7 teeth.
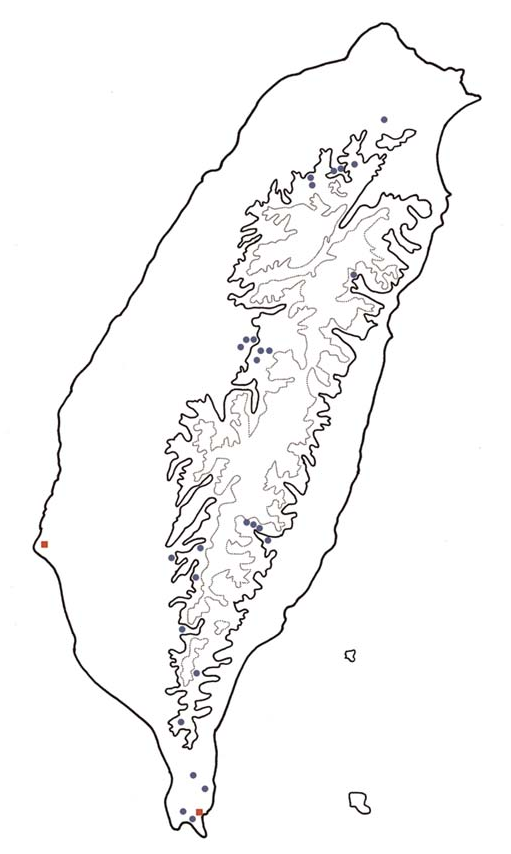
Distribution. Calomicrus jungchangi is found along marine shores in southern Taiwan (Tainan and Pingtung Counties; Fig. 16 View Fig ).
Type Series. Holotype ♂: “ Taiwan: Pingtung Manchou , 29.VI.2011, leg. J.-C. Chen ( TARI) . Paratypes: 2♂♂ 5♀♀, same data as holotype (2♀♀ in TARI; 2♂♂ 3♀♀ in RBCN) ; 12♂♂, 13♀♀: “ Taiwan: Tainan Chiku C01131, 20.III.2010, leg. T.- H. Lin ” ( TARI) .
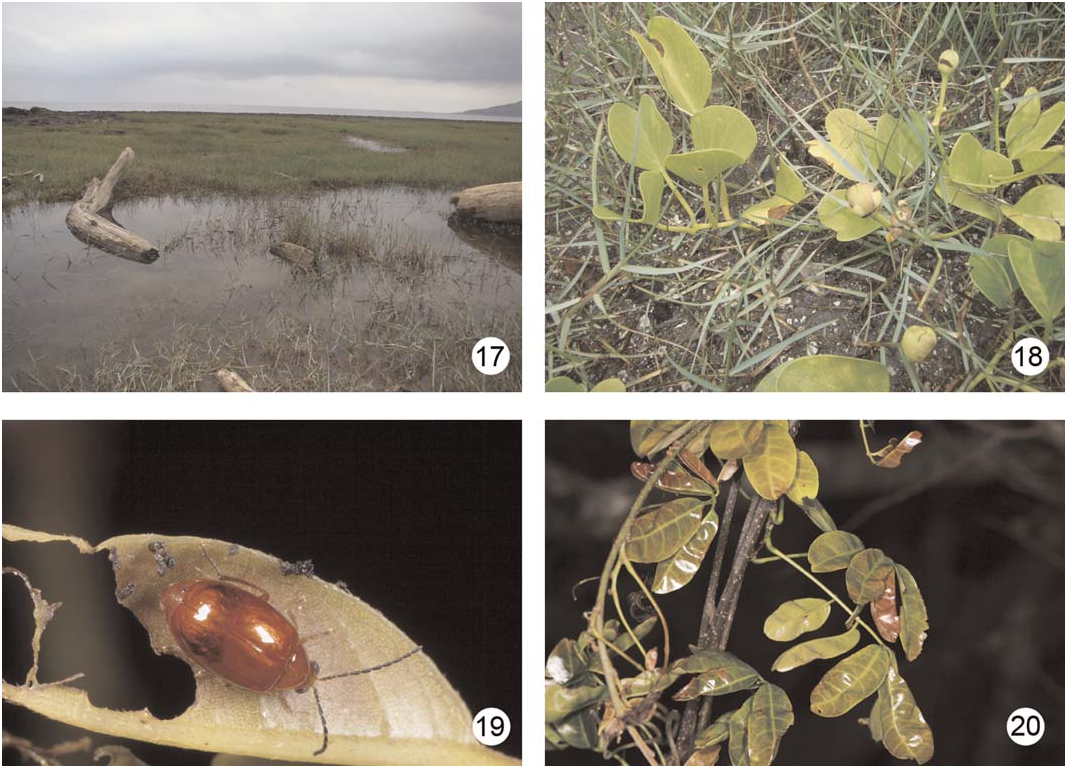
Type Locality. Marine shore near Manchou, Pingtung County ( Fig. 17 View Figs ).
Etymology. This new species is named in honor of Mr. Jung-Chang Chen, who discovered this new species and documented its ecology.
Plant Association. Leaves of I. pes-caprae ssp. brasiliensis (Convolvulaceae) .
Notes. Calomicrus jungchangi occurs on marine shorelines ( Fig. 17 View Figs ) presumably because of its apparent association with I. pes-caprae ssp. brasiliensis ( Fig. 18 View Figs ), a member of the shoreline floral community. In addition, specimens were collected with pitfall traps in Chiku.
| TARI |
Taiwan Agricultural Research Institute |
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |