Thliboclivinina, Balkenohl, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5190.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:41EE357A-9577-4C46-AA9A-980C6E4534C1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7126091 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/803E6543-FFD1-9922-FF4D-F966FB90FBBD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Thliboclivinina |
| status |
|
Subtribe Thliboclivinina subtr. nov.
Type genus Thliboclivina Kult, 1959 View in CoL
Taxa included:
microphthalma (Burgeon, 1937) diophthalmica (Basilewsky, 1955)
Eoclivina Kult 1959: 176 stat. nov.
Physoclivina Kult 1959: 214 stat. nov.
Sulciclivina gen. nov.
Subtribe diagnosis. General appearance similar to a small- to medium-sized subcylindrical Clivina . Head with clypeus bisinuate anteriorly in most of the species or more or less straight, in some species fused with clypeal wing; wing small; supraantennal plate conspicuously widened and conspicuously elongated posteriorly, in most of the species as wide as the eye, partially or completely continued over the eye and separating the eye either anteriorly or completely into two parts; frons separated from clypeus by a carina or a sulcus in form of a flat inverted V; frons in some species with second carina in form of an inverted V or with small depression; with two pairs of supraorbital and one pair of clypeal setae; labrum five- or six-setose; eye small, reduced in many species, separated partially or completely into two parts by lateral carina of supraantennal plate; mandible moderately short, flattened, scrobe small, asetose; antennomeres four to ten moniliform or submoniliform. Pronotum with lateral margin running basally in a regular curve up to base, with two lateral setae, base narrow. Proepisternum tumid laterally, visible dorsally. Elytron with striae 1-3 free at base, intervals asetose. Mesotibia dorsally with two distinct parallel rows of short protuberances furnished with robust seta each, laterally with row of strong setae, medially with up to five fine setae. All sterna punctured, but to a different degree among the groups. Last visible sternum with the two apical setigerous punctures separated. Female genitalia very small in comparison to body size, with gonocoxite foliform, monomeric, flattened dorsally and ventrally, less sclerotized to hyaline, with few setae; the coxites are medially not attached but separate; epipleurite semi-rectangular and asetose, the median joint is replaced by a broadly angulated and more or less widened flat rod.
Differential diagnosis. Distinguished from all other Clivinini by the outstanding external female genitalia, the elongated and widened form of the supraantennal plates separating the eyes anteriorly or completely into two parts, the small pronotal base, and the tuberculate mesotibia.
Habitat preference. Ecological data are not published. However, among the 640 specimens checked (MRACT, RBINS, CMBB), there were not seldom ecological data noted on the labels. According to these data, Physoclivina , Eoclivina , and African species of Thliboclivina were collected in detritus from vegetation and in humus of swamp forests, whereas the single Oriental Thliboclivina species was found in an open rice field. For the Oriental genus Sulciclivina gen. nov., data indicate the same habitats but also cultivated areas (bamboo forest, swamp forest, garden, plantation, zebu dung, ground vegetation covered by litter). In summary, the subtribe seems to populate humus underground in shaded humid and wet areas.
Remarks. Clivina arunachalensis Saha & Biswas, 1985 may possibly belong into the subtribe as well. It is tentatively not included because some key characters are not mentioned in the description nor visible on the ink drawing, giving space for interpretation of the position. In the description, a close relationship to members of the genus Pseudoclivina is emphasized. The type material has not been seen or investigated after the description. Inquiries to the place of deposition of the type material remained unanswered.
Identification key to the genera of the subtribe Thliboclivinina subtr. nov.
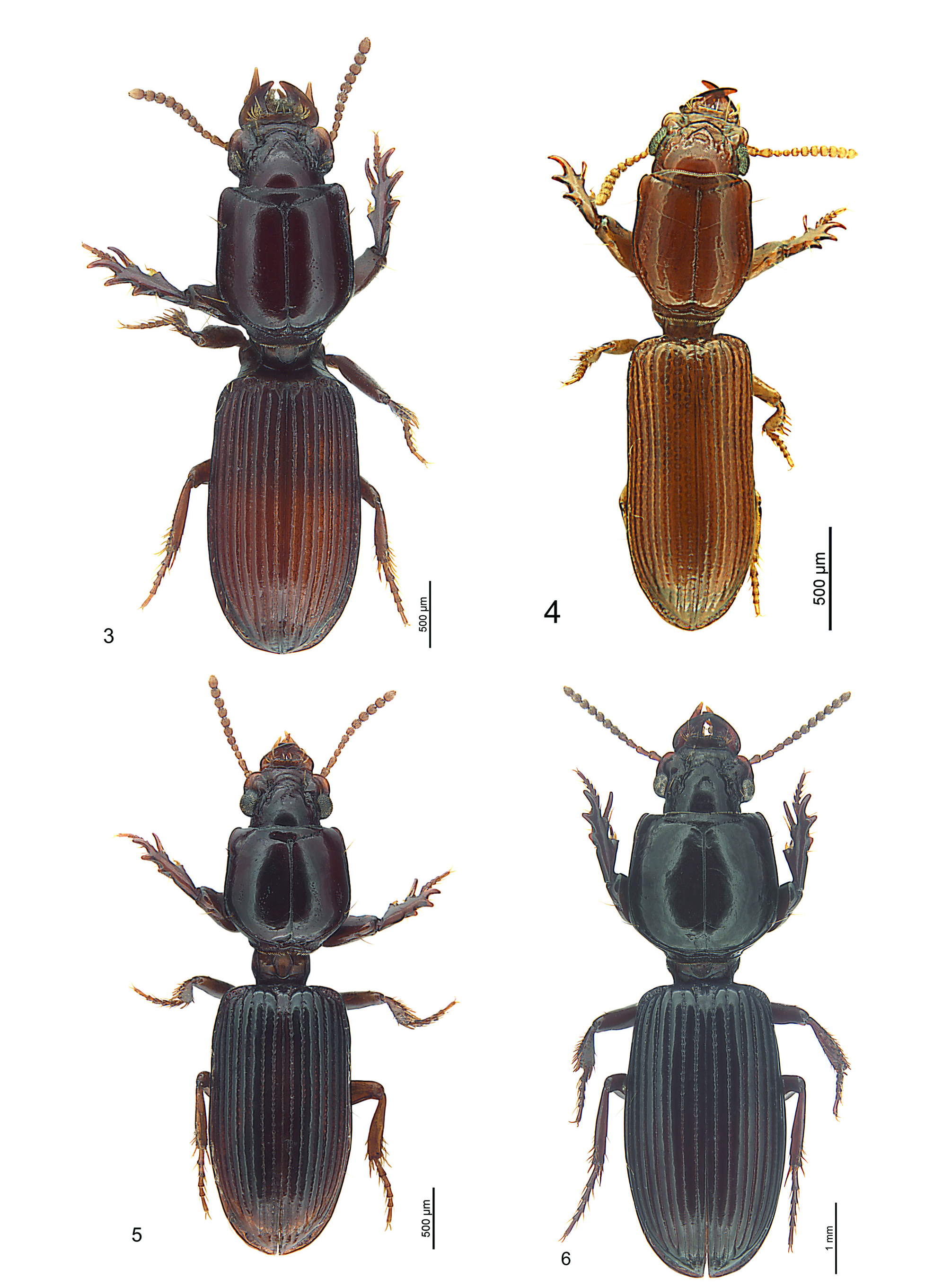
1 Habitus distinctly cylindrical; clypeus excised, more or less straight at middle; pronotum distinctly longer than wide (ratio LP/WP 1.21), long narrowed posteriorly, maximum width at middle, regularly long-convex from middle to base; epipleura distinctly visible in dorsal view; interval eight of elytron convex at apex; colour fuscous; fully winged; body length 2.3-3.5 mm; Africa; Fig. 4 View FIGURES 3-6 .................................................................. Physoclivina Kult stat. nov.
- Habitus subcylindrical or long oval; clypeus bilobed; pronotum as long as wide or moderately longer than wide (ratio LP/WP 1.0- 1.15), moderately narrowed posteriorly, maximum width at posterior third, convex or abruptly convex to base; epipleura slightly visible in dorsal view; interval eight of elytron carinate at apex; colour piceous; wings fully developed or reduced... ................................................................................................... 2
2 Supraantennal plate conspicuously elongated, overtopping by half or completely the eye; eye reduced or separated by the supraantennal plate into two parts; size of gena one third of eye; antenna with segments five to ten distinctly wider than long (L/W around 0.8); shape of elytra parallel; wings reduced; body length 3.9-5.6 mm; Africa, Asia; Fig. 3 View FIGURES 3-6 ... Thliboclivina Kult View in CoL
- Supraantennal plate as long as wide, about as long as eye, reaching by 20-25% over the eye; eye of moderately small size, transverse semicircular or oval; size of gena one fifth or one sixth of eye; antenna with segments five to ten as long as wide or slightly longer than wide; shape of elytra long oval........................................................... 3
3 Frons of the head with a carina forming an inverted V; elytra with a row of umbilical setigerous punctures in the lateral marginal channel interrupted at middle by a gap of two to three punctures; eye somewhat small, oval; size of genae one fifth of eye; mesotibia with 5 tubercles latero-dorsally, with a row of 7 strong setae laterally; ratio WP/WB around 4.6; fully winged; body length 3.5-5.2 mm; Africa; Fig. 5 View FIGURES 3-6 ..................................................................... Eoclivina Kult stat. nov.
- Frons of the head with the inverted V formed by a sulcus; elytra with a row of umbilical setigerous punctures in the lateral marginal channel uninterrupted; eye large; size of genae one sixth of eye; mesotibia with 10 tubercles latero-dorsally, with a row of 12 strong setae laterally; ratio WP/WB around 3.8; specimens with reduced and fully developed wings; body length 5.4-9.5 mm; Asia; Fig. 6 View FIGURES 3-6 ...................................................................................... Sulciclivina gen. nov.
Thliboclivina and Physoclivina have been intensively characterised recently on a species and group level ( Dostal 2015, Balkenohl 2001, 2018c). Eoclivina has been characterised by Kult (1959).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Thliboclivinina
| Balkenohl, Michael 2022 |
Eoclivina
| Kult, K. 1959: 176 |
Physoclivina
| Kult, K. 1959: 214 |