Neochlamisus bebbianae ( Brown, 1943 ) IV
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2007.00343.x |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/862A87D5-FFBB-FFEB-00F7-FC34FB352A91 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Neochlamisus bebbianae ( Brown, 1943 ) IV |
| status |
|
Neochlamisus bebbianae ( Brown, 1943) IV :
Acer rubrum host form ( Figs 9 View Figure 9 , 10 View Figure 10 )
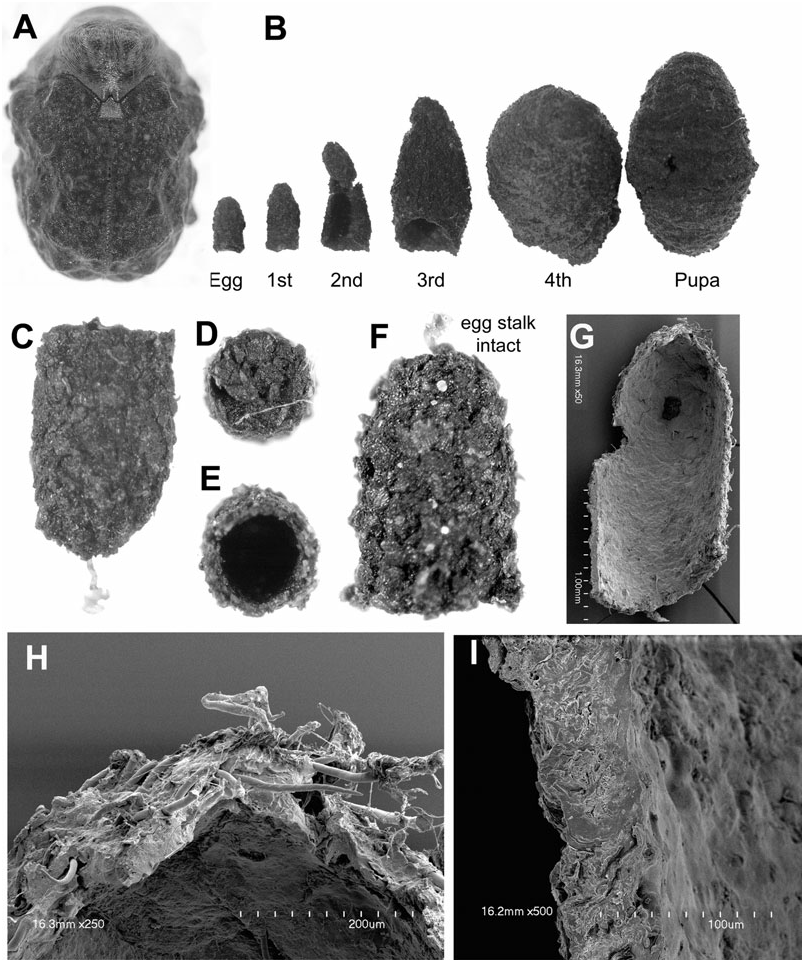
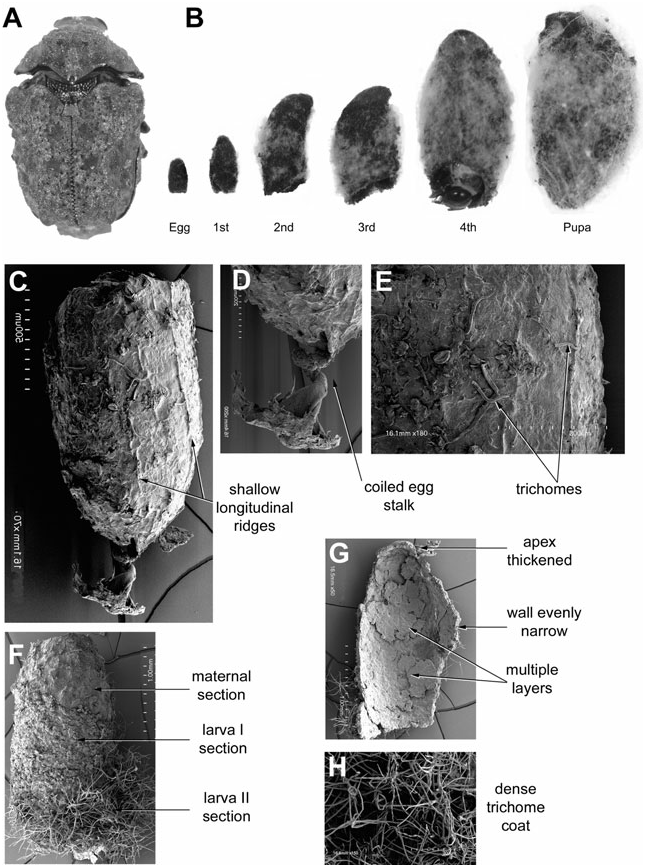
Egg case ( Fig. 9B–E View Figure 9 ): Size (N = 6): L, 1.68–1.87 mm; W at roof, 0.95–1.05 mm. Colour: unevenly brownishblack. Shape: bell-like; symmetrical in lateral aspect; apex rounded; egg stalk present, slender, translucent, one-third of the length of case, lacking coiling. External surface: coarse, with pine cone-like appearance; faeces arranged as overlapping plates, dorsal margin of plates exposed, surface protuberant, producing pine cone-like appearance; plates at apex of case project vertically; longitudinal ridges absent. Roof: transverse, coarse, slightly concave; flange: narrow. Internal surface: smoother than external surface; plates and ridges not apparent. Walls: evenly narrow. Trichomes: present, simple, sparse, deeply embedded into faecal matrix.
Larva-I case ( Fig. 9B, F–I View Figure 9 ): Size (N = 11): L, 1.47– 1.79 mm; W at base opening, 0.94–0.99 mm. Colour: uneven brownish black, larval section grey-black. Shape: bell-like, symmetrical to asymmetrical according to age; egg case generally intact; egg stalk present or absent; base opening transverse. External surface: coarse, larval section with dark fine transverse faecal rows. Internal surface: lacking apparent plates and ridges ( Fig. 9G View Figure 9 ). Walls: evenly narrow ( Fig. 9H, I View Figure 9 ). Trichomes: apparent, deeply embedded into matrix, not protuberant, lacking furry appearance.
Larva-II case ( Figs 9B View Figure 9 , 10A, B View Figure 10 ): Size (N = 8): L, 2.05– 2.21 mm; W at base opening, 1.34–1.36 mm. Colour: uneven dark brownish-black, larval sections greyishbrown, younger sections grey. Shape: tubular, asymmetrical; ventral, lateral, and dorsal surfaces apparent; ventral wall shorter than dorsal wall; apex dome-like. Egg case: apparent; shape, position, and texture generally intact; egg stalk absent. Ventral surface: with ventral suture and triangular insertion extending subapically to margin; insertion protuberant, occupying half of the total ventral surface. External surface: rough; larval sections with fine parallel rows of faecal deposit. Base opening: transverse, margin simple. Walls and apex: generally narrow, slightly thicker in larval section. Internal surface texture of larval section: smoother than external surface; egg section partially papered over with faecal layer. Trichomes: apparent, sparse, deeply embedded into matrix, decumbent.
Larva-III case ( Figs 9B View Figure 9 , 10C–F View Figure 10 ): Size (N = 4): L, 4.45– 5.44 mm, W at base opening, 2.6–3.25 mm. Shape: tubular; ventral, lateral, and dorsal walls apparent. Egg case: apparent, position inclined ventrad, shape distorted by ventral insertion of faecal field. External surface: rough, faeces in fine rows ( Fig. 10C, D View Figure 10 ); plates and ridges absent. Anterior surface with transverse faecal rows; lateral surface with obliquely transverse faecal rows; posterior surface with longitudinal faecal rows and medial ventral suture; ventral suture extending from apex through egg case to basal margin. Base opening: transverse, dorsal wall longer than ventral wall; margin simple. Internal surface: smooth; rows, projections, and plates not apparent; walls evenly thick, broader than in egg case. Trichomes: present, sparse, deeply embedded in matrix, decumbent.
Larva-IV case ( Fig. 9B View Figure 9 ): Size (N = 4): L, 6.49– 6.81 mm; W at base opening, 4.40–4.64 mm. Colour: brownish-black. Shape: tubular, asymmetrical in lateral view, ventral surface somewhat flattened. Egg case: apparent, distorted with ventral insertion of faeces, position inclined ventrad. External surface: rough, striated appearance with faecal rows orientated longitudinally on ventral surface, obliquely transverse laterally and transverse dorsally. Base opening: transverse, margin simple. Internal surface: smooth, walls evenly thick; rows, ridges, and plates not apparent. Trichomes: present, deeply embedded in faecal matrix.
Pupal case ( Figs 9B View Figure 9 , 10H View Figure 10 ): Size (N = 9): L, 6.98– 7.23 mm; W at base opening, 4.74–5.20 mm. Colour: brownish-black. Shape: bean-shaped, asymmetrical in lateral view; ventral, lateral, and dorsal walls apparent. Egg case: not easily discernible, split hemispherically by ventral suture and faecal insertions, each hemisphere shifted laterad and ventrad. Ventral wall: somewhat flattened, texture coarse with fine faecal rows; faecal rows orientated longitudinally, faecal insertion occupying most of wall; ventral suture extending medially from apex to base. Lateral walls: bulging medially, tapering centrad apically and basally. Base: transverse, margin simple. Internal surface: smooth; plates, rows, and ridges absent. Trichomes: present, deeply embedded in faecal matrix, not forming furry surface.
Neochlamisus bimaculatus Karren, 1972 :
host plant Rubus spp . ( Fig. 11 View Figure 11 )
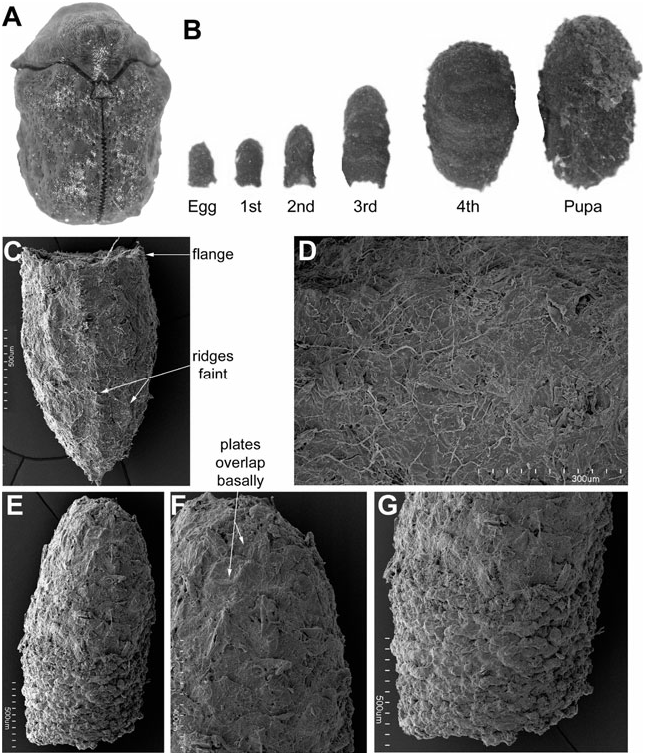
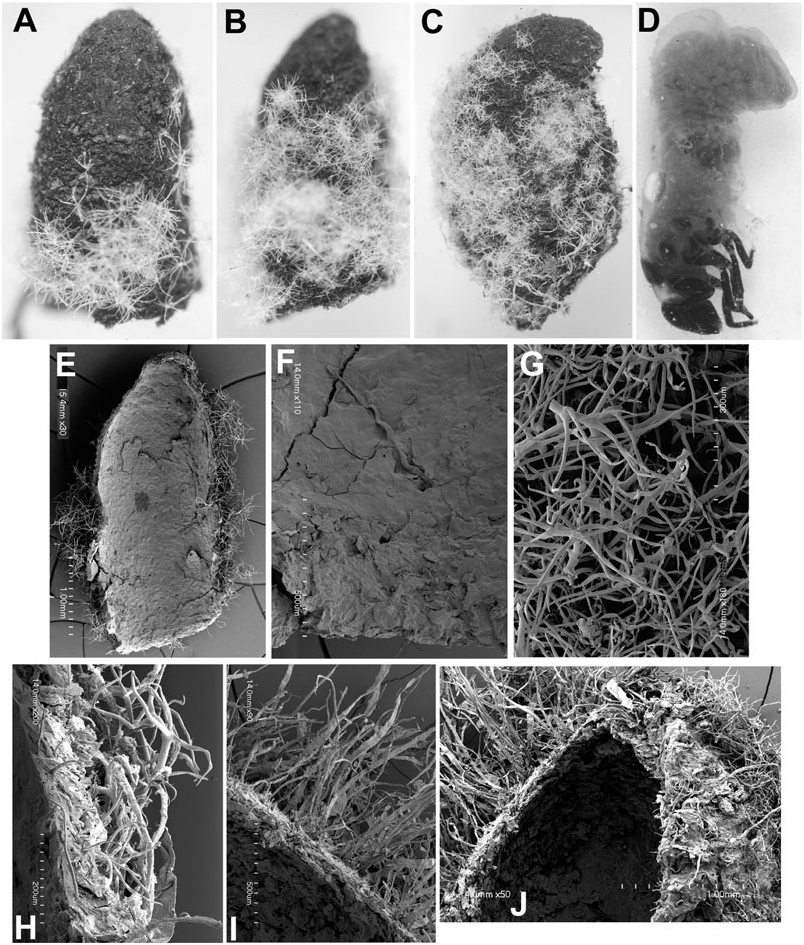
Egg case ( Fig. 11B–E View Figure 11 ): Size (N = 10): L, 1.27–1.61; W at roof, 0.97–1.18 mm. Colour: unevenly brownish black. Shape: bell-like; symmetrical in lateral aspect; flange narrow. Egg stalk: present, short, not coiled. External surface: coarse; faeces arranged as flattened plates; plates rounded to quadriform, some slightly protuberant medially, overlapping basally with apical margin exposed; longitudinal ridges absent. Roof: transverse; surface shallowly concave and texture coarse. Internal surface: smooth, scale outline sometimes apparent. Trichomes: present, sparse, deeply embedded in faecal matrix.
Larva-I case ( Fig. 11B View Figure 11 ): Size (N = 8): L, 2.37–3.37 mm; W at base opening, 1.46–1.62 mm. Young cases: shape, colour, and texture the same as in egg case. Older cases: asymmetrical in lateral view; dorsal, ventral, and lateral surfaces distinct; egg section occupying half of the total case length; apex rounded; egg stalk present or absent. Larval section: with fine faecal rows extending longitudinally on ventral surface and transversely on other surfaces. Ventral suture: slightly protuberant, extending subapically to base. Base opening: transverse, basal margin continuous with lateral walls; flange of egg case slightly discernible. Internal surface: smooth, internal surface of egg case as original, larval surface lacking discernible patterns of plates, rows, or ridges. Wall thickness: evenly narrow. Trichomes: present, very sparse.
Larva-II case ( Fig. 11B, F View Figure 11 ): Size (N = 8): L, 3.47– 5.06 mm; W at base opening, 1.7–2.40 mm. Colour: unevenly dark brownish-black. Shape: asymmetrical in lateral view; egg case apparent, inclined ventrad; apex rounded; attachment stalk absent. External surface: coarse; dorsal surface with faeces in transverse rows; ventral surface with larval section roughly triangular, occupying half of the total surface area, and comprising longitudinal rows; ventral suture extending subapically to base. Base opening: slightly transverse. Internal surface: smooth; rows, plates, or ridges absent. Walls: evenly thin. Trichomes: present, sparse, deeply embedded in faecal matrix.
Larva-III case ( Fig. 11B View Figure 11 ): Size (N = 9): L, 5.12– 5.99 mm; W at base opening, 2.43–3.62 mm. Colour: uneven brownish-black, with striated appearance. Shape: asymmetrical; dorsal, lateral, and ventral surfaces apparent; apex rounded, apical margin continuous with lateral walls; diameter widest in basal third. Egg case: apparent, shape distorted, split into two hemispheres by larval insertion; inclined ventrad, appearing as nipple-like dome. External surface: coarse; longitudinal ridges absent. Ventral surface: with larval insertion occupying more than half of the total surface area; ventral suture extending from apex to base, dissecting egg case. Base opening: transverse. Internal surface: smoothened. Wall: thickness, surface, and trichome density as in case II.
Larva-IV case ( Fig. 11B, G–I View Figure 11 ): Size (N = 9): L, 7.27– 7.78 mm; W at base opening, 4.96–5.12 mm. Shape, colour, surface texture, and trichome density and distribution, as in case III. Older cases: barrel-shaped, being widest in basal third; egg case distorted, inclined ventrad; base opening transverse. Internal surface ( Fig. 11H View Figure 11 ): smoothened. Walls: with layers of faeces ( Fig. 11I View Figure 11 ).
Pupal case ( Fig. 11B View Figure 11 ): Size (N = 7): L, 7.98–785 mm; W at base, 4.96–5.12 mm. Shape, colour, texture, trichome pattern as in case IV; ventral wall shorter than dorsal wall.
Neochlamisus chamaedaphnes ( Brown, 1943)
( Figs 12 View Figure 12 , 13 View Figure 13 ): host plant Chamaedaphnae calyculata
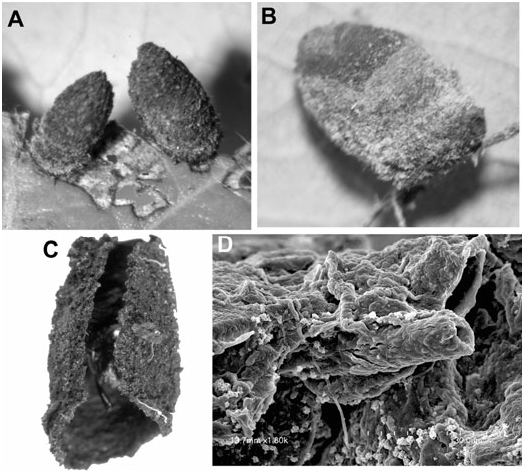
Egg case ( Fig. 12B–D View Figure 12 ): Size (N = 18): L, 1.55– 2.35 mm; W at roof, 0.84–1.24 mm. Colour: uneven, medium to dark brown. Shape: elongate bell-shape; symmetrical in lateral aspect; apex rounded; flange narrow. Egg stalk: slender, translucent, broadly coiled. External surface: coarse, wall comprised of faecal plates; plates somewhat flattened, triangular to quadriform, overlapping basally, apical margin exposed; apical plates project vertically; plate surface slightly protuberant medially, projections forming overall effect of slight, irregular longitudinal rows. Roof: surface rough, shallowly concave; flange narrow, thin, unevenly flared. Trichomes: present, sparse. Internal surface: smooth; plate outline slightly discernible; space between egg and wall narrow.
Larva-I case ( Fig. 12E–G View Figure 12 ): Size (N = 9): L, 1.46– 2.00 mm; W at base opening, 0.81–0.87 mm. Colour: unevenly dark brown, larval section darker. Shape: bell-like, similar to egg case; apex rounded; apical faecal plates projecting slightly; egg stalk absent. External surface of larval section: rough, faeces arranged as fine horizontal rows, not pellets. Base opening: transverse; margin slightly flared. Ventral surface: apparent in older cases; ventral suture terminating subapically. Internal surface: smooth; wall of larval section slightly thicker than wall of egg case. Trichomes: present, sparse.
Larva-II case ( Fig. 13A–C View Figure 13 ): Size (N = 4): L, 2.34– 2.91 mm; W at base opening, 1.39–1.72 mm. Shape: elongate tube, twice as long as base width; slightly asymmetrical in lateral view with anterior margin slightly longer than posterior margin. Apex: rounded; egg stalk absent. Egg case: generally intact, distorted ventrally by insertion of ventral suture and faecal wedge. Larval sections: darker brown than egg case; boundary between instar-I section and instar-II section marked by light-brown colour; surface texture scabrous. Ventral surface: with triangular faecal wedge occupying half the surface; surface slightly projecting, lateral margins with irregular projections. Ventral suture: terminating subapically. Base opening: slightly oblique in lateral view; margin simple, not flared. Internal surface: smooth, egg case surface intact, larval sections with rows not apparent. Wall of larval section: slightly thicker than in egg case.
Larva-III case: Size (N = 4): L, 3.84–4.09 mm; W at base opening, 1.84–1.87 mm. Shape: elongate tube, widest medially and slightly narrowed basally; asymmetrical in lateral view with dorsal wall longer than ventral wall; apex rounded. Egg case: split hemispherically by ventral suture, hemispheres connected apically; egg stalk absent. Larval section-III surface texture: coarser and lighter brown than previous sections. Base opening and margin: as in case II. Internal surface: smooth, external pattern of plates and rows not apparent; wall, evenly narrow. Trichomes: present, sparse, unevenly distributed, decumbent.
Larva-IV case ( Fig. 13D View Figure 13 ): Size (N = 5): younger cases, L, 4.20–4.68 mm, W at base opening, 2.26–2.74 mm; older cases, L, 4.65–4.91 mm, W, 3.39 mm. Colour: light to dark brown, striated appearance, thick coloured bands marking some instar sections. Shape: ovoid to conical, widest in apical half, narrowed by half at base; apex rounded. External surface: granulose; section IV and posterior wall scabrous. Ventral surface: entirely comprised of longitudinal rows and suture; ventral suture slightly protuberant, extending from apex to base opening. Base opening and margin: as in case III. Trichomes: absent. Internal surface: smooth, without apparent patterns (no subunits, ridges, or rows); striated colour patterning apparent.
Pupal case ( Fig. 13E–G View Figure 13 ): Size (N = 1): L, 5.82 mm; W at base, 3.37 mm. Colour: striated, medium to light brown. Shape: ovoid, asymmetrical lateral views, dorsal surface longer than ventral surface; egg case forming nipple-like projection at apex. Case: as in larval instar IV, similar in colour, striation, and faecal arrangement; diameter widest in basal section. Egg case: distorted, protuberant, and inclined ventrad. Base: circular in apical view, transverse in lateral view, margin thickened; disc-like seal, coarse.
Neochlamisus comptoniae ( Brown, 1943) ( Fig. 14 View Figure ): host plant Myrica asplenifolia View in CoL
Egg case ( Fig. 14B–E View Figure ): Size (N = 10): L, 1.4–1.53 mm; W at roof, 0.89–0.92 mm. Colour: unevenly brownishblack. Shape: bell-like; symmetrical in lateral aspect; apex rounded or pointed; flange present, narrow; dorsal, ventral, and lateral walls not distinguishable; egg stalk present, short, not coiled, forming flattened disc at substrate. Roof: transverse, external texture coarse. External surface of walls: rough, faeces arranged in plates; plates rounded to quadriform, fitted together apically, overlapping with basal margin exposed; longitudinal ridges very weakly developed. Internal surface: smoothened; case walls evenly thin, external plate pattern not distinct. Trichomes: not apparent.
Larva-I case ( Fig. 14F, G View Figure ): Size (N = 7): L, 0.99– 1.35 mm; W at base opening, 1.65–2.46 mm. Young phase of case with shape, colour, texture, and symmetry as in egg case. Apex: rounded; lateral margins subparallel; base opening transverse. Flange of egg case: apparent. Larval case section: darker than egg case, with fine faecal rows. Older case: with insertion of ventral suture and development of dorsal, lateral, and ventral walls; suture terminating subapically. Internal surface: as in egg case, larval section darker and wall thicker. Trichomes: present, very sparse, deeply embedded in faecal matrix, evenly distributed.
Larva-II case ( Fig. 14H, I View Figure ): Size (N = 7): L, 2.54– 2.57 mm; W at base opening, 1.39–1.50 mm. Colour: uneven, egg case dark brown; sections of instars I–II darker, boundary between I and II marked by fine light-brown line. Shape: tubular, asymmetrical in lateral aspect, margins subparallel. Apex: rounded; egg case split ventrally by ventral suture and faecal insertion; flange of egg case apparent in some cases; egg stalk absent. External surface: coarse; larva I–II sections with faeces arranged in fine rows. Ventral surface: with protuberant triangular wedge, longitudinal faecal rows occupying half surface; ventral suture slightly protuberant, terminating subapically. Base opening: transverse, margin simple. Internal surface: rough, lacking any plates, ridges, or row patterns; colour and texture of egg case intact; larval section evenly darker; wall thickness evenly narrow. Trichomes: sparse, evenly distributed, and deeply embedded in faecal matrix.
Larva-III case ( Fig. 14B, J View Figure ): Size (N = 10): L, 4.15– 4.58 mm; W at base opening, 1.88–2.00 mm. Colour of larval sections: dark-brown/black. Shape: tubular, asymmetrical in lateral aspect. Egg case: occupying 1/8th of case length, split into two hemispheres, forming basal cap, position not markedly inclined ventrad. Ventral wall: with triangular wedge occupying two-thirds of the surface; ventral suture terminating subapically; walls with faeces arranged in rows. Internal surface: smooth, external patterning not apparent. Trichomes: apparent, sparse, evenly distributed, deeply embedded into faecal matrix.
Larva-IV case ( Fig. 14B View Figure ): Size (N = 9): L, 5.17– 5.18 mm; W at base opening, 2.86–3.00 mm. Shape: tubular, ovoid, widest in basal half. Egg case: distinguishable by lighter brown coloration, granular texture, and lack of colour striations; larval section darker, blackish, striated in appearance; surface texture granular in early stages, coarser in later phases; faecal rows unevenly ridged and coarse. Boundaries between subsequent larval phases distinguishable by texture changes, indentations, and sometimes coloration; indentation especially apparent on anterior wall between the instar I–II boundary. Base opening: transverse in lateral aspect, ventral wall shorter than dorsal wall; basal margin simple. Ventral surface: with broad faecal insertion occupying most of wall; ventral suture protuberant, terminating subapically. Internal surface: smooth; plates, ridges, and rows not apparent; wall evenly narrow. Trichome: density and distribution as in younger cases.
Pupal case ( Fig. 14B View Figure ): Size (N = 12): L, 5.40–5.42 mm; W at base opening, 3.26–3.32 mm. Colour, texture, and trichomes: as in larval case IV. Shape: somewhat barrel-shaped, apex and base inclined ventrad; ventral wall flattened. Egg case: split into two hemispheres, inclined ventrad. Base: obliquely transverse in lateral aspect; coarse seal texture, margin sometimes with irregular projections.
Neochlamisus cribripennis (LeConte, 1878)
( Figs 15 View Figure 15 , 16 View Figure 16 ): host plant Vaccinum spp .
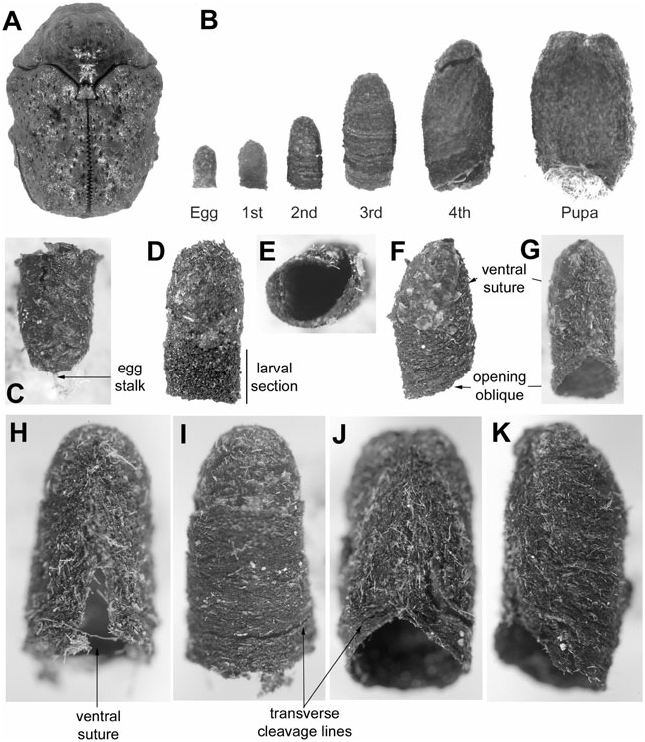
Egg case ( Fig. 15B–D View Figure 15 ): Size (N = 9): L, 1.48–1.56 mm; W at roof, 0.99–1.04 mm. Colour: unevenly dark brown. Shape: bell-like, symmetrical in lateral aspect; apex arcuate; egg stalk present, short, not coiled; flange slight. External surface: with faeces arranged in rounded plates; plates: protuberant medially, giving uneven surface texture, contiguous, not overlapping; longitudinal ridges absent. Trichomes: not apparent.
Larva-I case ( Fig. 15B View Figure 15 ): Size (N = 5): L, 1.57–1.73 mm; W at base opening, 1.08–1.36 mm. Colour: background dark brown. Shape: conical, symmetrical in lateral view; apex arcuate; egg stalk present; flange of egg case distinct. External surface: flattened and rough; egg case with faecal plates fitted together, not overlapping; section I with faeces in horizontal rows, not in plates. Faecal rows arranged horizontally on ventral, lateral, and dorsal surfaces; ventral suture apparent in older cases. Base opening: slightly oblique; margin simple, not flared or thickened. Trichomes: not apparent.
Larva-II case ( Fig. 15B View Figure 15 ): Size (N = 5): L, 2.53– 3.78 mm; W at base opening, 1.36–2.00 mm. Colour: unevenly dark brown; lighter brown marking boundaries between egg case and section I, and between sections I and II. Shape: generally conical, symmetrical in lateral view; apex rounded; egg stalk absent. Diameter of sections I and II similar, slightly wider than diameter of egg case at apical margin; remnants of flange of egg case apparent. External surface texture: scabrous with faecal rows. Ventral suture: present, terminating subapically, dissecting egg case. Base opening: oblique, basal margin simple, not thickened. Trichomes: present, sparse, irregularly arranged, deeply incorporated into wall matrix, some emergent and decumbent.
Larva-III case ( Figs 15E–G View Figure 15 , 16A View Figure 16 ): Size (N = 4): L, 4.31–4.36 mm; W at base opening, 1.63–2.23 mm. Colour: uneven dark brown, boundaries between egg case and section I, sections I–II and sections II–III marked by slightly lighter-brown coloration. Shape: conical, symmetrical in lateral view; apex rounded. External surface: rough. Ventral suture: extending from apex to base, dissecting egg case. Base opening: oblique; margin simple, uneven, not flared or thickened. Trichomes: as in case II.
Larva-IV case ( Figs 15B View Figure 15 , 16C, D View Figure 16 ): Size (N = 3): L, 4.31–4.86 mm; W at base opening, 2.61–2.8 mm. Colour: uneven dark brown; boundaries of sections distinct. Shape: barrel-like, symmetrical in lateral view; apex rounded. External surface: rough. Ventral suture: extended from apex to base, dissecting egg case. Base opening and margin: as in case III. Trichomes: as in cases IIand III.
Pupal case ( Figs 15B View Figure 15 , 16B View Figure 16 ): Size (N = 1): L, 5.47 mm; W at base opening, 3.28 mm. Shape, colour, texture, and trichomes as in instar IV. Apex: somewhat flattened; egg case discernible, inclined ventrad. Base opening: inclined at 45° to ventral wall, margins flared.
Neochlamisus eubati ( Brown, 1943) ( Fig. 17 View Figure 17 ):
Egg case ( Fig. 17B, C View Figure 17 ): Size (N = 10): L, 1.62– 1.76 mm; W at roof, 1.00– 1.12 mm. Colour: dark brown. Shape: bell-like, approximately twice as long as wide; symmetrical in lateral aspect; flange very slight. Apex: rounded; egg stalk present, short, narrow, tan-coloured. Faeces shaped into flattened triangular plates; plates overlap basally, apical margins free; scale pattern indistinct near apex. External surface: uneven with inclusions of trichomes; longitudinal ridges not apparent; wall thickness very narrow; internal surface smooth. Base opening: rounded; disc seal concave, texture uneven, rough. Trichomes: sparse, evenly distributed, and deeply incorporated into faecal material, some trichomes occasionally protuberant.
Larva-I case ( Fig. 17B View Figure 17 ): Size (N = 14): L, 1.58– 2.29 mm; W at base opening, 0.94–1.02 mm. Colour of larval addition: brownish-black. Shape, symmetry, texture, and colour of young cases: as in egg case. Older cases: double the length of egg case; ventral suture terminating subapically; lateral margins subparallel, evenly tapered. Egg case: intact except for ventral suture; egg stalk present or absent; flange of egg case sometimes apparent. Base opening: transverse in lateral aspect. Internal surface: smooth, thicker in larval section, external patterns of plates and rows not apparent internally.
Larva-II case ( Fig. 17F, G View Figure 17 ): Size (N = 10): L, 2.18– 2.6 mm; W at base opening, 1.16–1.39 mm. Shape, colour, symmetry, and texture: as in late larva case I. Ventral surface: with triangular wedge, inserted by larvae I–II; ventral suture not protuberant, terminating subapically, dissecting egg case. Wedge: distinguishable from adjacent case material by inclusion of trichomes and coarse surface texture. Case-II section: with trichome inclusions more dense than in case I. Case diameter evenly enlarged basad. Base opening: rounded, obliquely transverse in lateral aspect; margin not flared. Internal surface: texture smooth.
Larva-III case ( Fig. 17H, I View Figure 17 ): Size (N = 10): L, 3.22– 3.67 mm; W at base opening, 1.88–2.17 mm. Shape: tubular, as in case II. Egg case: completely split by ventral suture into two slightly protuberant lobes, and separated by triangular faecal wedge, inclined slightly ventrad. Larval insertions: with dense trichomes. Base opening: obliquely transverse in lateral view; lateral walls evenly tapered, widening basad. Internal surface: as in case II.
Larva-IV case ( Fig. 17J, K View Figure 17 ): Size (N = 8): L, 5.37– 6.52 mm; W at base opening, 2.80–3.89 mm. Colour, texture, and orientation of faecal rows: as in case III. Shape of young cases: tubular, as in case III. Older cases: ovoid or barrel-shaped, widest near base opening; egg case distorted, as in case III. Ventral wall: slightly protuberant near base. Base opening: strongly obliquely transverse in lateral view, margin simple.
Pupal case ( Fig. 17B View Figure 17 ): Size (N = 5): L, 5.76–6.82 mm; W at base, 4.13–4.67 mm. Shape: barrel-shaped, dorsal wall longer than ventral wall; apex somewhat flattened. Egg case: not easily discernible. Base: obliquely transverse; coarse seal texture. Internal surface: smooth, evenly thickened, multi-layered, layers parchment-like; apex thick, comprising many layers.
Neochlamisus platani (Brown, 1952) ( Figs 18 View Figure 18 , 19 View Figure 19 ): host plant Platanus occidentalis
Egg case ( Fig. 18B–E View Figure 18 ): Size (N = 11): L, 1.32– 1.56 mm; W at roof, 0.91–0.95 mm. Colour: unevenly dark brown. Shape: bell-like, symmetrical in lateral aspect; apex rounded; roof margin simple, flange absent; egg stalk present. Walls composed of faecal plates; plates faintly pentagonal, fitted together basally, and overlapping apically, some projecting vertically at case apex; plate surface protuberant centrally. Wall with fine longitudinal ridges, extending from apex to base, spanning multiple plates; ridges evenly spaced and slightly radially arranged. Trichomes: present, filamentous type, medium density, evenly distributed, deeply embedded in matrix. Internal surface: rough, external plates and ridges not apparent; wall evenly thin. Roof: transverse, seal unevenly flattened.
Larva-I case ( Fig. 18G, H View Figure 18 ): Size (N = 9): L, 2.13– 2.30 mm; W at base opening, 1.04–1.14 mm. Shape, colour, and symmetry of young case: as in egg case; larval section brownish-black; egg stalk sometimes present. Older cases: conical, asymmetrical in lateral aspect; dorsal, ventral, and lateral surfaces apparent. Ventral suture: terminating subapically; triangular faecal insertion not protuberant. Trichomes: present, stellate type, light to medium density. Internal surface: smooth. Wall of larval section: slightly thicker than in egg case. Base opening: obliquely transverse.
Larva-II case ( Figs 18B, F View Figure 18 , 19A View Figure 19 ): Size (N = 9): L, 3.94– 4.27 mm; W at base opening, 1.46–1.72 mm. Colour: uneven brown-black. Shape: tubular; egg case shape, position, and texture intact; ventral suture present ventrally, terminating subapically; apex evenly rounded; egg stalk lacking. Larval section with faeces as in instar I. Boundaries between egg case and larval-I case well demarcated; boundary between larval sections I and II obscured by trichomes. Internal surface: smooth. Base opening: obliquely transverse, anterior wall slightly longer than ventral wall. Trichomes: more dense than in case I, obscuring surface.
Larva-III case ( Figs 18B View Figure 18 , 19B View Figure 19 ): Size (N = 12): L, 4.97– 5.08 mm; W at base opening, 2.38–2.85 mm. Shape, colour, texture, and trichome arrangement: as in case II. Egg case: apparent, position inclined ventrad.
Larva-IV case ( Figs 18B View Figure 18 , 19G, H View Figure 19 ): Size (N = 8): L, 7.26–8.86 mm; W at base opening, 3.95–4.46 mm. Shape: tubular in young phase; barrel-like in older stage, widest in apical section. Asymmetry, colour, and trichome pattern: as in case III. Egg case: somewhat distorted, split into two hemispheres, inclined ventrad, diagnosable by lack of stellate trichomes.
Pupal case ( Figs 18B View Figure 18 , 19I, J View Figure 19 ): Size (N = 15): L, 7.33– 8.75 mm; W at base, 4.24–4.42 mm. Shape, colour, asymmetry, and trichome type and density: as in late case IV. Egg case: inclined ventrad, protuberant, overhanging ventral suture. Base: rough seal surface; trichomes present, medium density, incorporated into faecal matrix, not forming fuzz.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Neochlamisus bebbianae ( Brown, 1943 ) IV
| Chaboo, Caroline S., Brown, Christopher G. & Funk, Daniel J. 2008 |
Neochlamisus bimaculatus
| Karren 1972 |