Craspedomerus beckeri Bernhauer, 1934
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.195931 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6195819 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8709583B-FFDA-185E-FF03-6B0A6387FAAB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Craspedomerus beckeri Bernhauer, 1934 |
| status |
|
4. Craspedomerus beckeri Bernhauer, 1934 View in CoL
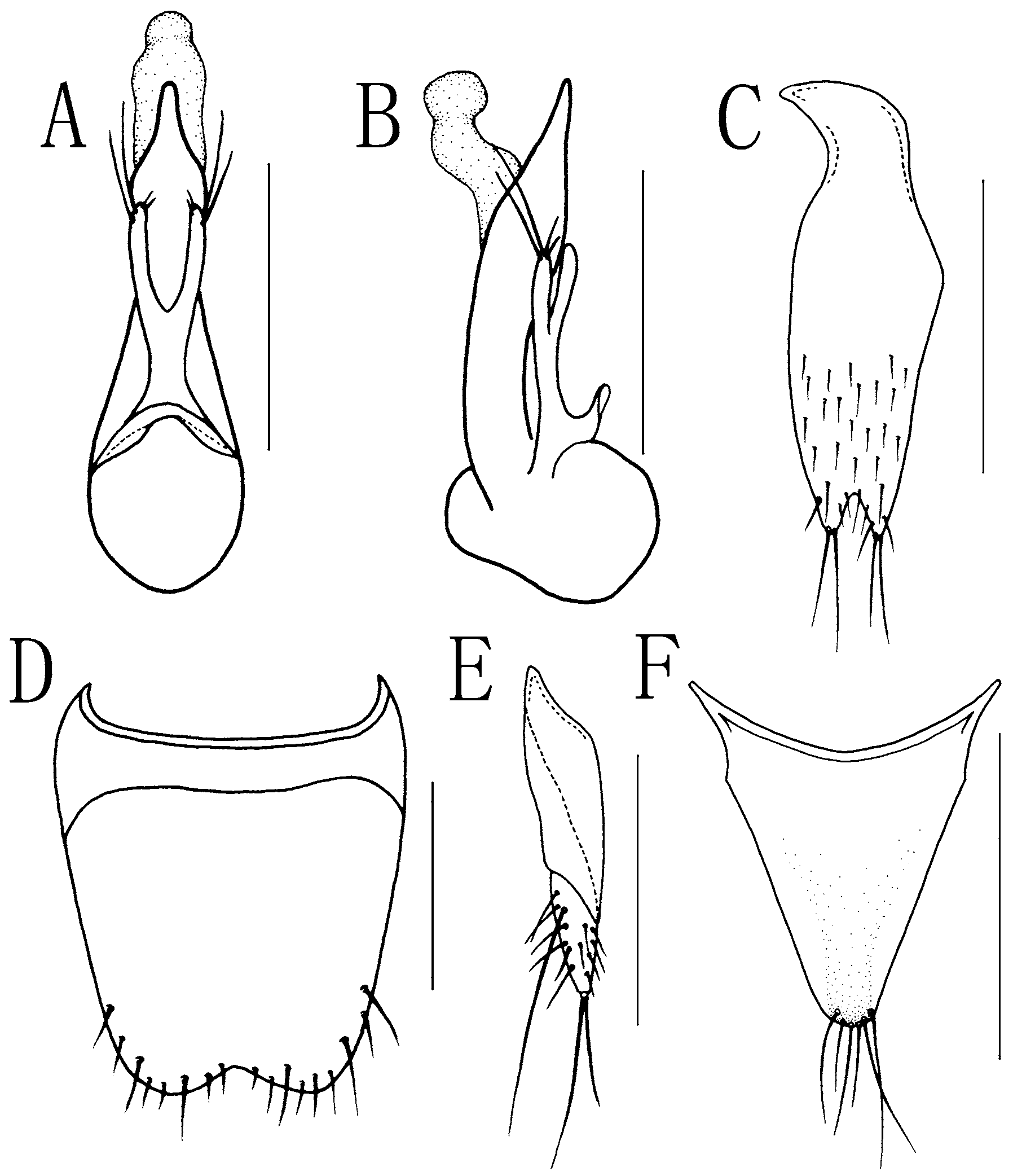
( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 A–F, 12C)
Bernhauer, 1934: 11 ( Craspedomerus , type locality: Kinfushan, China); Scheerpeltz, 1976b: 150 ( Craspedomerus , characters); Herman, 2001: 2582 ( Craspedomerus , world catalog); Smetana, 2004: 632 ( Craspedomerus , catalog for Palaearctic region).
Material examined. CHINA: Sichuan: 5ɗɗ, 3ΨΨ, Wolong (31°46´N, 103°36´E), 2650 m, 6–9.V.2004, Yu Xiaodong collected (IZ-CAS); 6ɗɗ, 7ΨΨ, Baoxing (30°36´N, 102°49´E), 2498 m, 6 June 1997, Zhou Haisheng collected (IZ-CAS); 7ɗɗ, 9ΨΨ, Baoxing (30°36´N, 102°49´E), 1796 m, 12.VIII.2003, Wu Jie collected (IZ-CAS); Ψ, Jinfo Shan (29°01´N, 107°14´E), 1750 m, 26.VI.1998, A. Smetana collected (CSO).
Description. Head and pronotum black with slightly bronze-greenish reflex. Antennae black-brown with 8th–11th segments yellow, sometimes last segment dark. Elytra fusco-testaceous. Scutellum black. Abdomen black with strongly iridescent reflex, posterior 1/2–4/5 portion of tergite VII and entire tergites VIII–X reddish-yellow. Mandibles dark brown. Maxillary and labial palpi and legs reddish-brown.
Body large, 13.8–16.9 mm long (HPL = 4.82–5.14 mm). Head of rounded quadrangular shape, 1.96–2.20 mm long, 2.20–2.53 mm wide, slightly wider than long (HW:HL = 1.10–1.30). Tempora 0.81–0.98 mm long, almost evenly rounded, densely and coarsely punctate, setiferous. Eyes moderately large, slightly protruded, 0.65–0.74 mm long, 0.67–0.82 times as long as tempora. Dorsal surface of head with moderately numerous, large setiferous punctures, becoming sparser toward vertex, vertex largely impunctate; entire head with distinct and profound microsculpture of transverse waves.
Pronotum subquadrate, slightly narrowed anteriad, 2.53–2.69 mm long, 2.37–2.53 mm wide, slightly wider than head (PW:HW = 1.03–1.11), densely and finely punctate, punctures separated by 3–5 times their diameter, narrowly impunctate along midline; surface with distinct and profound microsculpture of obliquely, long waves.
Elytra 3.10–3.27 mm long, 3.27–3.51 mm wide, 1.21–1.29 times as long as pronotum, densely and finely punctate, punctures separated by 2–3 times their diameter. Scutellum large, triangular, densely and finely punctate.
Abdomen a little narrowed posteriad, widest 2.86–2.94 mm, tergites densely and finely punctate, at base punctures separated by 1–2 times their diameter, gradually becoming sparser toward apex of each tergite, surface between punctures with dense and fine microsculpture of transverse striae; elevated area between basal lines of tergites III–V almost without punctures.
Male. Sternite VIII with moderately wide, obtusely triangular medio-apical emargination ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 D). Sternite IX with distinctly asymmetrical basal portion, apex deeply emarginate, each lobe bearing two long apical setae ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 C). Tergite X simple, triangular, subrounded at apex, with variable number of apical setae ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 F).
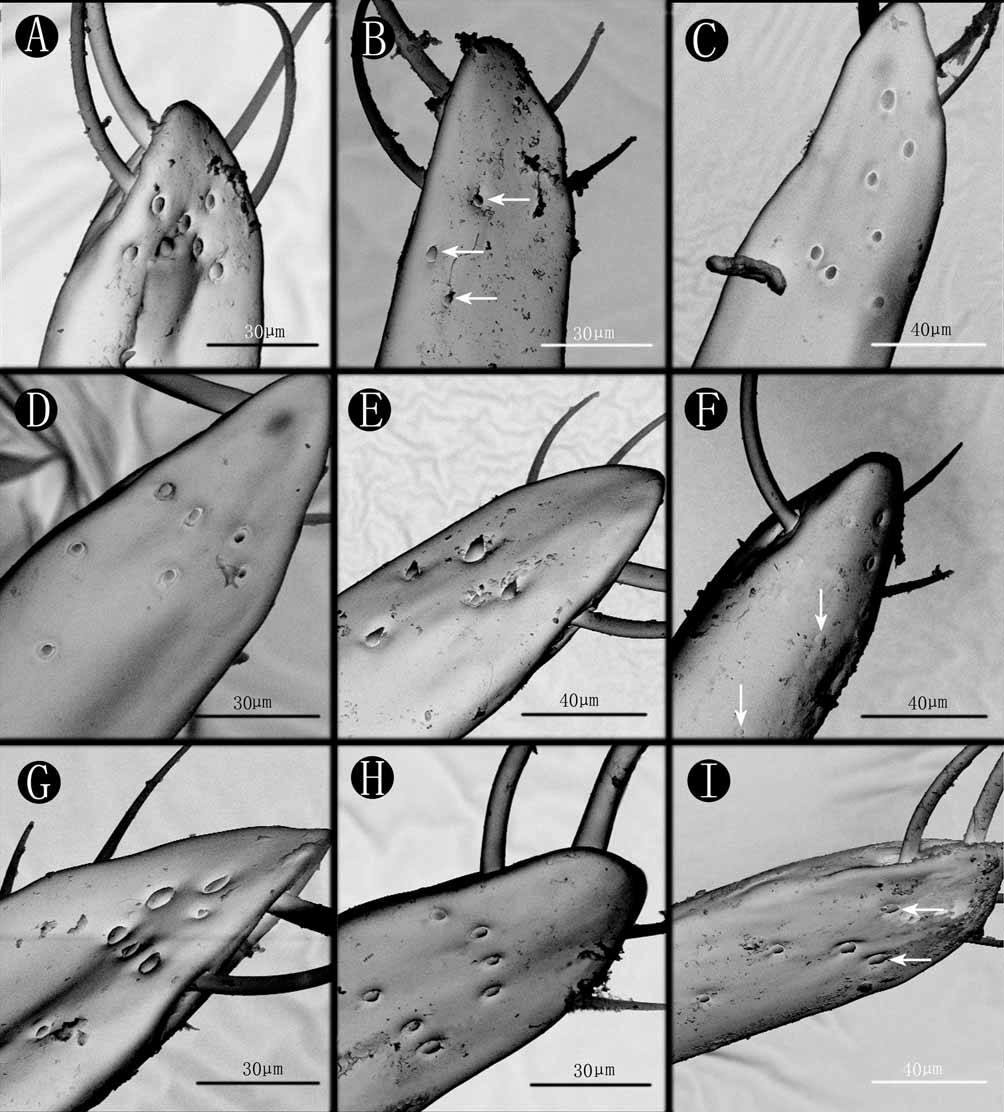
Aedeagus as ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 A–B); underside of each branch of paramere with very small, flat sensory peg setae arranged at subapical portion ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 C).
Female. Sternite VIII without medio-apical emargination. Gonocoxites moderately developed, second gonocoxites each with minute stylus bearing two long apical setae ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 E). Tergite X similar to that of male.
Remarks. Bernhauer (1934) described this species from Sichuan. Craspedomerus beckeri is similar to C. bernhaueri Cameron, 1926 , C. glenoides , C. nepalensis Scheerpeltz, 1976 b, C. birmanus Scheerpeltz, 1965 , C. tricoloricornis ( Coiffait, 1977a) and C. ganeshensis in having fusco-testaceous elytra. Craspedomerus beckeri can be easily distinguished from those species by antennae with last four segments yellow. Distribution. China (Sichuan).
5. Craspedomerus cyanipennis Scheerpeltz, 1976 b, first record from China ( Figs. 7 View FIGURE 7 A–E, 12I)
Scheerpeltz, 1976b: 144 ( Craspedomerus , type locality: Thodung, Nepal); Coiffait, 1982a: 32 ( Craspedomerus , Nepal); 1982b: 233 ( Craspedomerus , Nepal); Herman, 2001: 2582 ( Craspedomerus , world catalog); Smetana, 2004: 632 ( Craspedomerus , catalog for Palaearctic region).
Material examined. CHINA: Yunnan: ɗ, Ψ, Baoshan (24°56´N, 98°45´E), 2300–2440 m, 26–31.X.1998, Liang Hongbin collected (IZ-CAS); Ψ, Baoshan (24°56´N, 98°45´E), 2440 m, 15.X.2003, Liang Hongbin collected (IZ-CAS); Ψ, Tengchong: Shangying (24°57´N, 98°44´E), 2200 m, 14.X.2003, Liang Hongbin collected (IZ-CAS); Ψ, Baoshan: Longyang (24°54´N, 98°45´E), 2350 m, 30.V.2005, Liang Hongbin collected (IZ-CAS); Ψ, Baoshan Pref., mountain range 14 km E Tengchong (25°00´N, 98°38´E), 1850 m, 1.VI.2007, secondary mixed forest, litter sifted, M. Schülke collected ( CSB).
Description. Head and pronotum black with strongly violaceous reflex. Antennae black with 8th–10th segments yellow. Elytra metallic blue or violaceous. Scutellum black. Abdomen black with strongly iridescent reflex, posterior 2/5-4/5 portion of tergite VII and entire tergites VIII–X reddish-yellow. Mandibles dark brown. Maxillary and labial palpi reddish-brown. Femora dark, tibae and tarsi reddish-brown.
Body 11.8–14.0 mm (HPL = 4.82–5.06 mm). Head of rounded quadrangular shape, 1.88–1.96 mm, 2.20– 2.37 mm wide, slightly wider than long (HW:HL = 1.13–1.22). Tempora 0.74–0.82 mm long, almost evenly rounded, densely and coarsely punctate, setiferous. Eyes moderately large, slightly protruded, 0.65 mm long, 0.80–0.89 times as long as tempora. Dorsal surface of head with moderately numerous, large setiferous punctures, becoming sparser toward vertex, vertex largely impunctate; entire head with distinct and profound microsculpture of transverse waves.
Pronotum subquadrate, slightly narrowed posteriad, 2.53–2.61 mm long, 2.45–2.61 mm wide, almost as wide as head (PW:HW = 0.97–1.14), sparsely and finely punctate, punctures separated by 4–6 times their diameter, narrowly impunctate along midline, microsculpture fine, similar to that on head.
Elytra 2.94–3.35 mm long, 3.10–3.43 mm wide, 1.13–1.28 times as long as pronotum, densely and finely punctate, punctures separated by 1–2 times their diameter. Scutellum large, triangular, densely and finely punctate.
Abdomen a little narrowed posteriad, widest 3.10–3.27 mm, tergites densely and finely punctate, at base punctures separated by 2–3 times their diameter, gradually becoming slightly sparser toward apex of each tergite, surface between punctures with dense and fine microsculpture of transverse striae; elevated area between basal lines of tergites III–V almost impunctate.
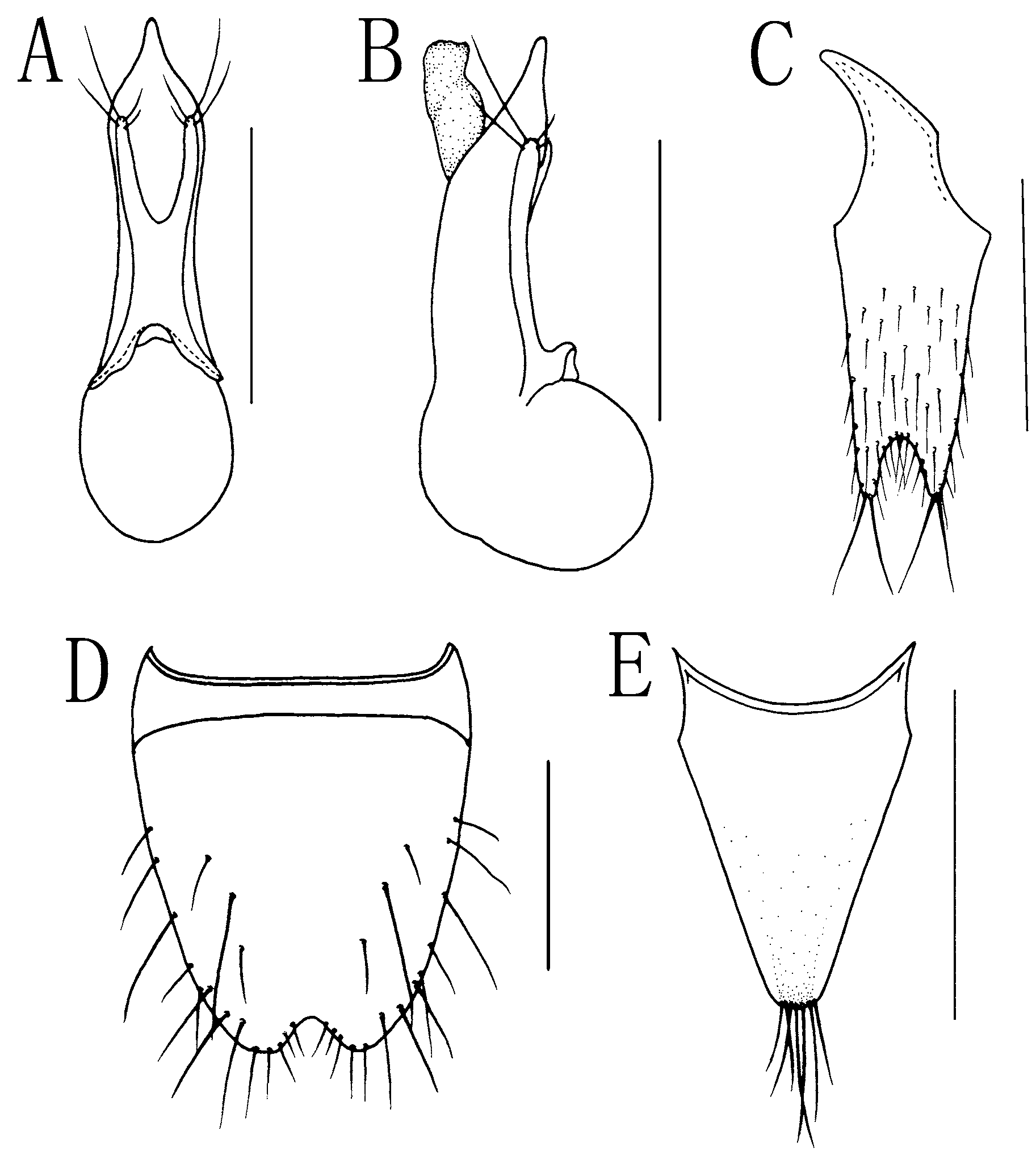
Male. Sternite VIII with moderately wide, obtusely triangular medio-apical emargination ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 D). Sternite IX with distinctly asymmetrical basal portion, apex deeply emarginate, each lobe bearing two long apical setae ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 C). Tergite X simple, triangular, subrounded at apex, with variable number of apical setae ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E).
Aedeagus as ( Figs. 7 View FIGURE 7 A–B); underside of each branch of paramere with very small, flat sensory peg setae irregularly arranged at subapical portion ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 I).
Female. Sternite VIII without medio-apical emargination. Gonocoxites moderately developed, second gonocoxites each with minute stylus bearing two long apical setae. Tergite X similar to that of male.
Remarks. Scheerpeltz (1976b) described C. cyanipennis from Nepal. Coiffait (1982ab) also reported it from Nepal. This species is similar to C. violaceipennis in having elytra metallic blue or violaceous and antennae black with 8th–10th segments yellow. Craspedomerus cyanipennis differs from C. violaceipennis by pronotum with distinctly violaceous reflex, femora dark and different number and arrangement of the sensory peg setae on the underside of paramere ( Figs. 12 View FIGURE 12 D, I) (pronotum with bronze-green reflex and femora reddishbrown in C. violaceipennis ). This species is recorded from China for the first time.
Distribution. China (Yunnan), Nepal.
| CSB |
St. John's University/College of Saint Benedict |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.