Eurotocus australis Steyskal
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3853/j.0067-1975.64.2012.1582 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/887387E2-FF91-FFAA-FE85-FDBB927C6B90 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Eurotocus australis Steyskal |
| status |
|
Eurotocus australis Steyskal View in CoL
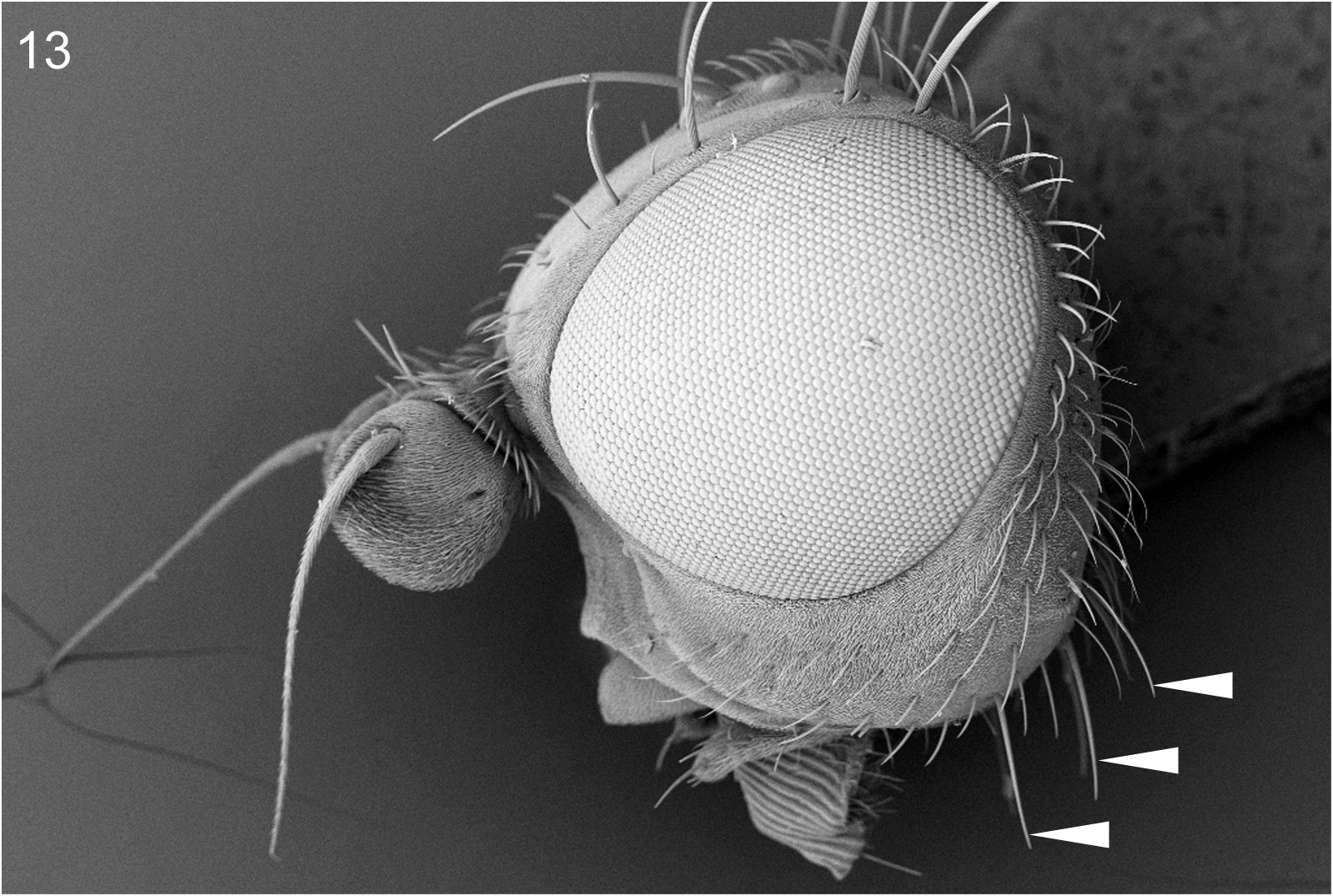
Fig. 13 View Figure 13
Eurotocus australis Steyskal , in Steyskal & Knutson, 1979: 728–730, figs 1, 3–6, 28–33, 38, 39 (not figs 36, 37 as listed by Steyskal); Barnes, 1981: 53–54, figs 7, 8.
Type material (re-examined D.K.M.). Holotype ♂. Victoria: Mount Baw Baw, near Tanjilbren , 4400 ft [c. 1340 m], 30.xi.1964, G.L.B.–64132 ( AM K264608 ) . Postabdomen in micro-vial on pin . Allotype ♀. Victoria: same data as holotype ( AM) . Paratypes. South Australia and Victoria: see list of Steyskal and Knutson (1979) ( AM, SAM) .
Other material examined (localities only given). Victoria: Lake Mountain ( MV); Mount Donna Buang, near summit ( AM). New South Wales: 5.6 km W of Perisher Valley, Kosciuszko National Park ( AM).
Distribution. Victoria: mainly mountainous areas. South Australia: Adelaide and southeastern districts. New South Wales: Snowy Mountains district.
Notes
Steyskal and Knutson (1979) described the puparium of this species, and recorded the larvae as found in agaric fungi at Adelaide by Adolfo Lutz in 1892, perhaps during a brief stop-over by that Brazilian entomologist.
| AM |
Australian Museum |
| SAM |
South African Museum |
| MV |
University of Montana Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.