Quadrimaera quadrimana ( Dana, 1853 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4554.2.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:13B319F8-915A-4FE5-8E56-C8C61ECCF369 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3510982 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/894F3B29-FFF2-310F-7596-FF6A201AF9D3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Quadrimaera quadrimana ( Dana, 1853 ) |
| status |
|
Quadrimaera quadrimana ( Dana, 1853) View in CoL
[Japanese name: Kaku-sunnariyokoebi, new]
( Figs 16–20 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 View FIGURE 18 View FIGURE 19 View FIGURE 20 )
Gammarus quadrimanus Dana, 1853: 955 .— Dana, 1855: pl. 65, fig. 9.
Moera quadrimanus .— Bate, 1862: 194, pl. 35, fig. 5.
Maera quadrimana View in CoL .— Schellenberg, 1938: 45, figs 21–22.— J.L. Barnard, 1955, 13.— Nayar, 1959: 23, pl. 7, figs 6–15.— J.L. Barnard, 1965: 511, fig. 17.— Sivaprakasam, 1968: 101.— Ruffo, 1969: 25.— Sivaprakasam, 1970: 35.— J.L. Barnard, 1970: 152, figs 94–95.— J.L. Barnard, 1971: 84, figs 31, 38, 40.— Surya Rao, 1972: 196 (list).— Ledoyer, 1972: 229, fig. 45.— Ledoyer, 1978: 279.— Ortiz, 1978: 8 (list).— Ledoyer, 1979: 80. — Ledoyer, 1982: 542, fig. 206.— Berents, 1983: 128, fig. 22.— Myers, 1985: 116, fig. 91.— Myers, 1995: 38 (list).— Krapp, Marti & Ruffo, 1996: 48 (list).— Appadoo & Steele, 1998: 639 (list).— Ruffo, Krapp & Gable, 2000: 5, figs 1–3.— Varela, Ortiz & Lalana, 2003: 74 (list).— Ren, 2012: 249, fig. 109.
Quadrimaera quadrimana View in CoL .— Krapp-Schickel & Ruffo, 2000: 195 (list).— Lowry & Stoddart, 2003: 186.— Krapp-Schickel, 2008: 25 (list).— Krapp-Schickel, 2009: 629 View Cited Treatment , fig. 21.— Hughes, 2015b: 243 View Cited Treatment , fig. 41.
not Moera quadrimanus .— Thomson, 1882: 235, pl. 17, figs 4a–b. (= Maera tepuni J.L. Barnard, 1972 View in CoL ) [according to Ruffo, Krapp & Gable. (2000)]
not Maera quadrimana View in CoL .— Ledoyer, 1968: 275, fig. 17. (= Maeropsis View in CoL sp.) [according to Ledoyer (1972) and Ariyama (2018)].— Ledoyer, 1986: 190, fig. 11. (= Maera miranda Ruffo, Krapp & Gable, 2000 View in CoL ) [according to Ruffo, Krapp & Gable. (2000)]
Material examined. One male, 6.3 mm (OMNH-Ar-10736), Pacific Ocean, south of Yakushima Island in Kagoshima Prefecture, 29°47'50"N 130°22'14"E ( Fig. 1J View FIGURE 1 ), sandy mud bottom, 176 m depth, using dredge, 18 May 2018, coll. K. Tomikawa.
Type locality. Fiji Islands ( Dana 1853) .
Diagnosis. Gnathopod 1, coxa anteroventral corner rounded. Gnathopod 2, anterior margin of basis without robust setae, anterodistal corners of basis and ischium lobate on lateral and medial surfaces; propodus subrectangular, palm transverse, defined by large tooth, male palmar margin with two small rounded excavations in middle, posterior excavation present. Pereopods 5–7, bases subrectangular, posterior margins not setose. Uropod 3, outer ramus slightly shorter than inner ramus, about 1.6 times length of peduncle. Telson slightly wider than long, distal margins truncate, each lobe without inner distal tooth, bearing 5–6 robust setae, longest seta longer than telson.
Description. Based on male, 6.3 mm (OMNH-Ar-10736).
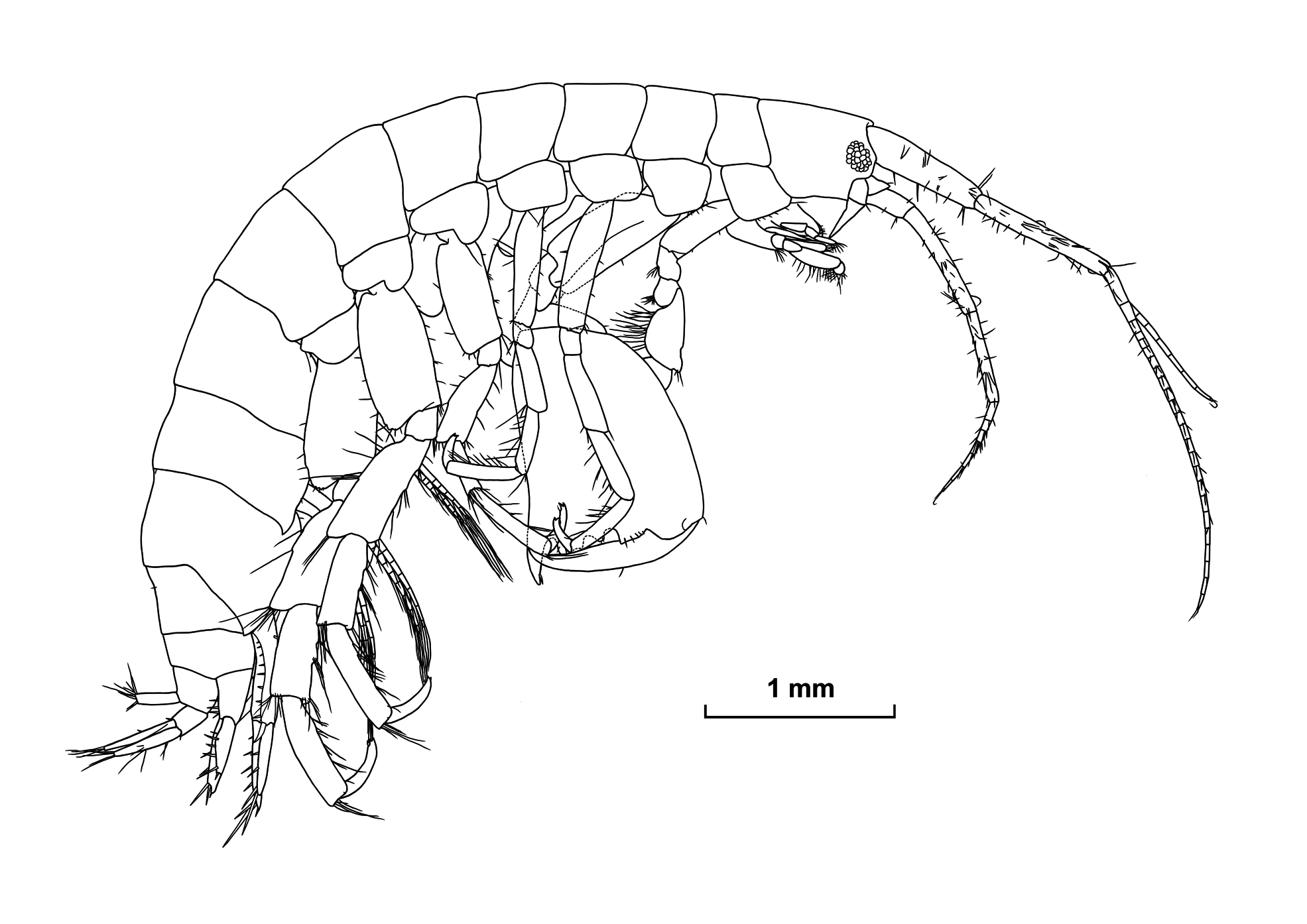
Head ( Figs 16–17 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 ). Anteroventral corner produced, eyes oval, about 0.2 times length of head. Antenna 1 about 0.55 times body length, setose; peduncle with ratio of lengths of articles 1–3 1:1.1:0.3, article 1 with 3 robust setae posteromedially; accessory flagellum with 8 articles, terminal article minute, length about 0.4 times of primary flagellum; primary flagellum with 23 articles. Antenna 2 about 0.6 times length of antenna 1, setose; peduncle with ratio of lengths of articles 3–5 1:3.9:3.1; flagellum with 8 articles, terminal article minute. Upper lip, ventral margin slightly produced, with short setae. Mandible, incisor bearing 3 and 2 cusps in left and right sides, respectively, both laciniae mobilis 3-dentate, number of accessory setae 5 on both sides, first setae wide; palp article length ratio 1:1.6:2.0, articles 2 – 3 heavily setose. Lower lip with inner lobes, distal margins of inner and outer lobes setose, mandibular processes small. Maxilla 1, inner plate bullet-shaped, with 3 long and 2 tiny apical setae, medial margin and dorsal surface with several feeble setae; distal margin of outer plate with 9 robust setae; palp article 1 bearing 2 long setae distolaterally, article 2 with 7 thick and 4 thin apical setae. Maxilla 2, outer plate larger than inner plate; medial margin of inner plate with several distal setae and many feeble setae. Maxilliped, distomedial corner of inner plate with 2 robust setae ventrally; outer plate with 14 long-to-short robust setae on distomedial margin; palp with 4 articles, article 4 with large apical robust seta.
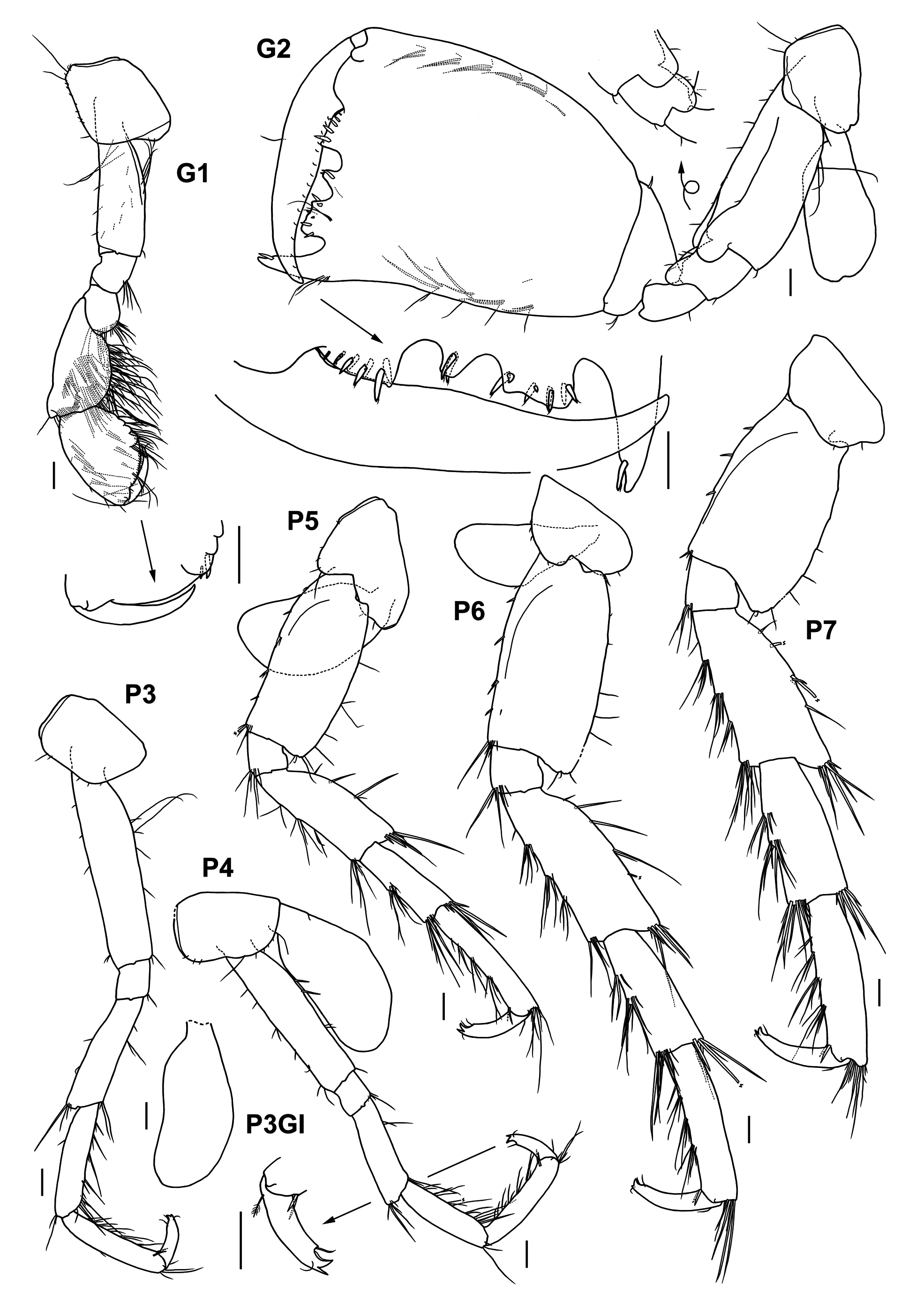
Pereon ( Fig. 18 View FIGURE 18 ). Gnathopod 1, coxa roundish trapezoidal, anteroventral corner rounded; basis bearing several long setae on posterior margin and medial surface; carpus with slight excavation on anterior margin; propodus palm defined by 2 short robust setae. Gnathopod 2, coxa subtrapezoidal; basis short, anterodistal corners on lateral and medial surfaces lobate, anterior margin without robust setae, posterior margin bearing 3 long setae; ischium, anterodistal corners on lateral and medial surfaces lobate; merus produced posterodistally; propodus subrectangular, slightly widened distally, length about 1.2 times width; palm transverse, defined by large tooth, palmar margin with 2 small rounded excavations in middle and small rounded excavation posteriorly, anterior lobe with 5 lateral and 4 medial robust setae, middle lobe with 1 lateral and 1 medial robust setae, posterior lobe bearing 4 lateral and 4 medial robust setae; dactylus, inner margin slightly swollen in middle.
Pereopods 3–4 subequal in shape, pereopod 3 about 1.1 times length of pereopod 4; coxae subrectangular; basis of pereopod 3 with 2 long setae posteriorly, basis of pereopod 4 bearing 2 robust setae. Pereopod 5 about 1.2 times length of pereopod 4; basis subrectangular, length about 2.0 times width, posterodistal lobe small, anterior margin with 4 short robust setae. Pereopod 6 about 115% length of pereopod 5; coxa with ventral robust seta on posterior lobe; basis subrectangular, length about 1.9 times width, posterodistal lobe small, anterior margin with 5 short robust setae, posterior margin with sparse short setae. Pereopod 7 almost same length as pereopod 6; coxa subtrapezoidal; basis roundish subrectangular, length about 1.7 times width, posterodistal lobe medium-sized, anterior margin with 3 short robust setae, posterior margin smooth.
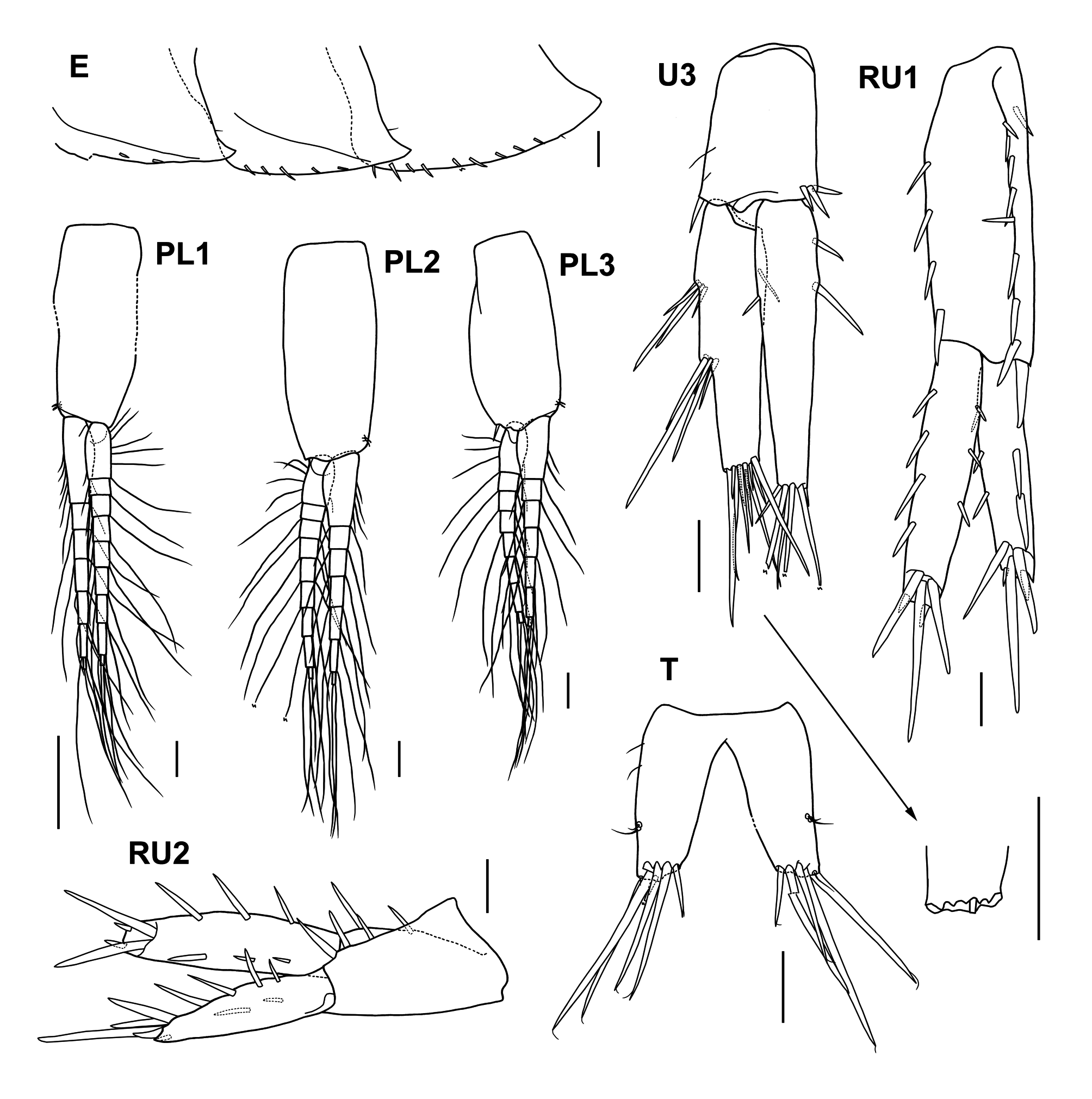
Pleon ( Fig. 19 View FIGURE 19 ). Epimera 1–3 slightly projected posteroventrally, epimera 1–2 each with minute seta posteriorly and oblique lateral ridge, ventral margins of epimera 1–3 with 2, 5, 9 robust setae, respectively. Pleopods 1–3, inner rami slightly longer than outer rami, each inner ramus with 7 articles and outer rami with 9, 9, 8 articles respectively; pleopod 3 shortest, peduncle bearing distal robust seta. Uropod 1, peduncle with 1 basofacial, 8 dorsolateral, 4 dorsomedial and 1 distolateral robust setae; outer ramus about 85% length of inner ramus, about 0.7 times length of peduncle, with 2 lateral, 3 medial and 5 terminal robust setae; inner ramus with 3 lateral, 4 medial and 5 terminal robust setae. Uropod 2 about 0.7 times length of uropod 1; peduncle bearing 4 dorsolateral and 1 dorsomedial robust setae; outer ramus about 85% length of inner ramus, almost same length as peduncle, with 4 lateral, 2 medial and 5 terminal robust setae; inner ramus with 3 lateral, 3 medial and 5 (1 lost) terminal robust setae. Uropod 3 about 85% length of uropod 2; distolateral and distomedial corners of peduncle with 1 and 3 robust setae, respectively; outer ramus about 1.6 times length of peduncle, about 95% length of inner ramus; outer ramus with 2 groups of robust setae laterally and single robust seta medially, distal margin with minute second article and many setae, longest distal seta about 0.6 times length of outer ramus; inner ramus with 1 and 2 robust setae on lateral and medial margins, respectively, distal margin bearing many setae. Telson slightly wider than long, distal margins truncate, inner distal corners without tooth; each lateral margin with 2 sensory setae, each distal margin bearing 4 long and 1–2 short robust setae and sensory seta, longest robust seta about 1.1 times of telson length.
Coloration in life ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 ). Eyes orange, other parts pale green and partly faint orange.
Remarks. Morphological characters of the present specimen agree well with those of Quadrimaera quadrimana (ex. J.L. Barnard 1970, Ledoyer 1982), although the bases of the pereopods 5–7 and the merus of the pereopod 5 are narrower in the specimen. This species is characterized by the transverse palm of the gnathopod 2 having 3 excavations.
Habitat in Japan. Sandy mud bottom, 176 m depth.
Distribution. Pacific Ocean (including marginal seas). Japan: south of Yakushima Island in Kagoshima Prefecture (present study); China: Taiwan, Hong Kong, Hainan Island ( Ren 2012); Nansha Islands ( Ren 2012); Micronesia: Caroline Islands ( J.L. Barnard 1965, Myers 1995), Marshall Islands ( J.L. Barnard 1965), Gilbert Islands ( Schellenberg 1938); Melanesia: Fiji ( Dana 1853, Schellenberg 1938, Myers 1985); Polynesia: Hawaii ( Schellenberg 1938, J.L. Barnard 1955, 1970); Australia: Great Barrier Reef ( Berents 1983, Krapp-Schickel 2009), Torres Strait, One Tree Island, North Stradbroke Island, Solitary Islands ( Hughes 2015b). Indian Ocean. Australia: Kimberley, Ningaloo Reef, Cape Leveque ( Hughes 2015b); Cocos Islands ( Hughes 2015b); India: Madras coast ( Nayar 1959, Sivaprakasam 1968, 1970), Palk Bay ( Sivaprakasam 1968), Gulf of Manner ( Sivaprakasam 1968, 1970), Bay of Bengal ( Surya Rao 1972); Red Sea ( Ruffo 1969); Mauritius ( Ledoyer 1978, Appadoo & Steele 1998); Madagascar ( Ledoyer 1972, 1979, 1982). Caribbean Sea. Cuba ( Ortiz 1978, Varela et al. 2003). Atlantic Ocean. Bermuda ( Ruffo et al. 2000).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Quadrimaera quadrimana ( Dana, 1853 )
| Ariyama, Hiroyuki 2019 |
Quadrimaera quadrimana
| Hughes, L. 2015: 243 |
| Krapp-Schickel, T. 2009: 629 |
| Krapp-Schickel, T. 2008: 25 |
| Lowry, J. K. & Stoddart, H. E. 2003: 186 |
| Krapp-Schickel, T. & Ruffo, S. 2000: 195 |
Maera quadrimana
| Ren, X. 2012: 249 |
| Varela, C. & Ortiz, M. & Lalana, R. 2003: 74 |
| Ruffo, S. & Krapp, T. & Gable, M. F. 2000: 5 |
| Appadoo, C. & Steele, D. H. 1998: 639 |
| Krapp, T. & Marti, A. & Ruffo, S. 1996: 48 |
| Myers, A. A. 1995: 38 |
| Myers, A. A. 1985: 116 |
| Berents, P. B. 1983: 128 |
| Ledoyer, M. 1982: 542 |
| Ledoyer, M. 1979: 80 |
| Ledoyer, M. 1978: 279 |
| Ortiz, M. 1978: 8 |
| Surya Rao, K. V. 1972: 196 |
| Ledoyer, M. 1972: 229 |
| Barnard, J. L. 1971: 84 |
| Sivaprakasam, T. E. 1970: 35 |
| Barnard, J. L. 1970: 152 |
| Ruffo, S. 1969: 25 |
| Sivaprakasam, T. E. 1968: 101 |
| Barnard, J. L. 1965: 511 |
| Nayar, K. N. 1959: 23 |
| Schellenberg, A. 1938: 45 |
Moera quadrimanus
| Thomson, G. M. 1882: 235 |
Moera quadrimanus
| Bate, C. S. 1862: 194 |
Gammarus quadrimanus
| Dana, J. D. 1853: 955 |