Pericelis cata Marcus & Marcus 1968
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3873.5.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:687DC4E0-9B78-4AF0-9DD2-8B868E3B8EB5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6143908 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/927D87F1-FFC8-321C-FF78-7F346891FE7F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pericelis cata Marcus & Marcus 1968 |
| status |
|
Pericelis cata Marcus & Marcus 1968 View in CoL
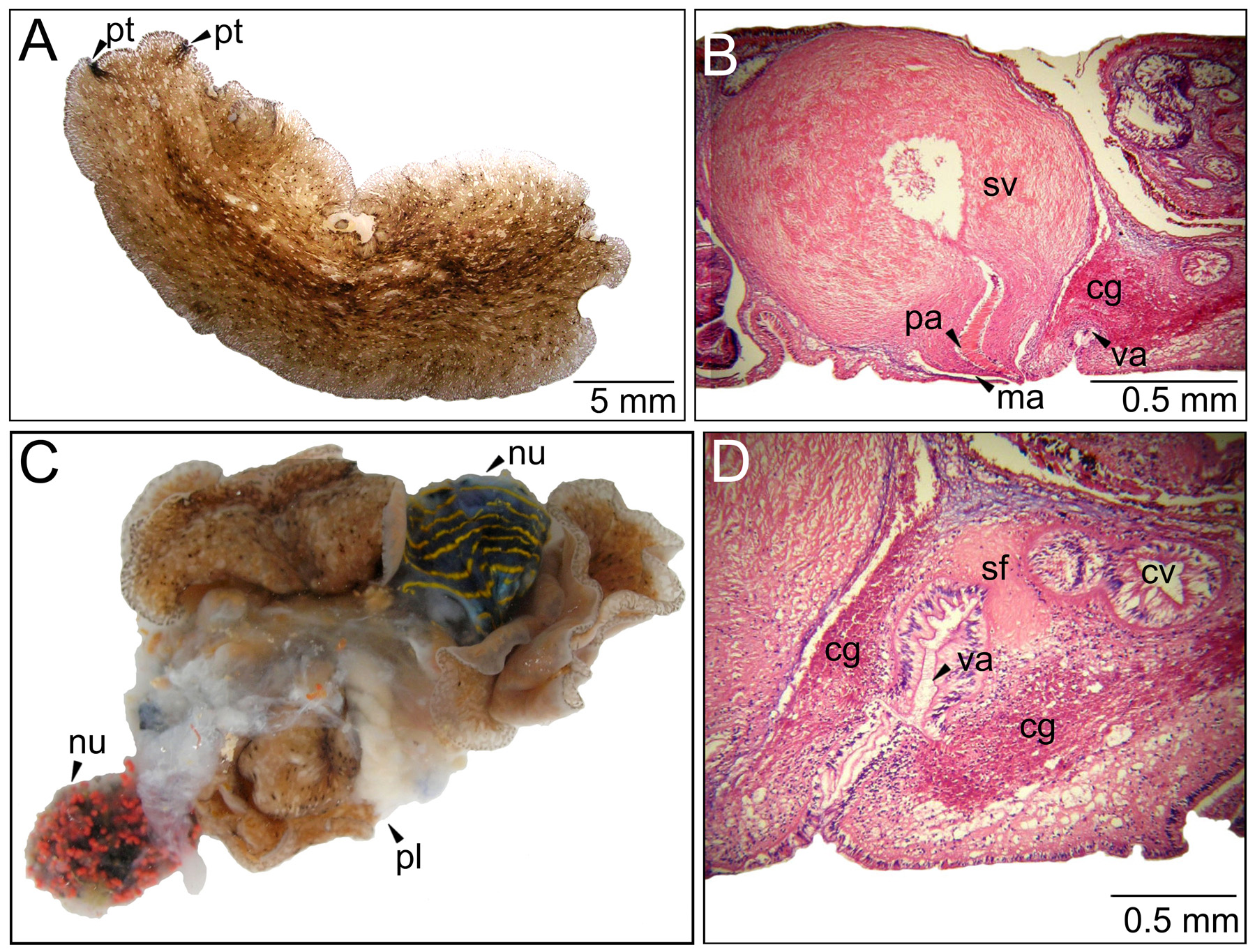
( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Material examined. One specimen (MNRJ-PLAT 24, 23 x 22 mm) as sagittal sections of reproductive structures (23 slides), rest of the animal in ethanol 70%. Collected 0 3.08.2008 at Enseada do Mimi, Ilha do Papagaio, Cabo Frio, Brazil ( 22°53'30.85"S; 41°59'9.52"W). Depth: 6 m.
Distribution. This species was recorded from Curaçao ( type locality; Marcus & Marcus 1968), Colombian Caribbean ( Quiroga et al. 2004b), Cabo Frio ( Bahia & Padula 2009) and Bahia, Brazil ( Queiroz et al. 2013). At Cabo Frio P. c a t a seems to occur only at the sublittoral, as no specimen was found at the intertidal zone, but instead at 6 to 10 m depth, and only at Ilha do Papagaio.
Diagnosis. Pattern of coloration mottled with dark beige coloration combined with black spots; marginal tentacles distant from each other; marginal, pre-cerebral and cerebral eyespots present; cerebral eyespots in two elongated rows, not clearly separated in the middle. Seminal vesicle very muscularized and developed; male atrium shallow and uterine duct with muscular sphincter.
Description. External characters as described in Bahia & Padula (2009).
Epidermis and body wall: Ventral epidermis 66 µm tall and dorsal epidermis 44 µm tall. Body wall with external longitudinal muscular layer and internal diagonal muscular layer. Rhabdites are observed both dorsally and ventrally.
Gonopores: Male and female gonopore closely together at 22 mm from the anterior margin. Pores open independently ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B).
Male reproductive system: Testicles ventral. Penis papillae ( 0.5 mm) muscular and directed backwards as the rest of the male structures ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B). Seminal vesicle rounded and well developed (1.5 x 1.3 mm), male atrium shallow ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B). Ejaculatory duct filled with sperm and granules of eosinophylic secretion.
Female reproductive system: Ovaries dorsally disposed. Uterine duct epithelium tall ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D). Uterine ducts separated from vagina by a muscular sphincter ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D). Vagina directed backwards ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B and D), 410 µm long, with folds at the epithelium and cement pouch present ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D).
Taxonomic remarks. We found larger specimens (from 23 x 22 mm to 45 x 34 mm) than those observed in the original description (from 27 x 21 mm to 33 x 21 mm), but external morphological and anatomical differences were not found. Other species in this genus ( P. bayerleyana , P. orbicularis , P. hymanae ) do not present a sphincter in the uterine duct and seminal vesicle as large as P. c a t a ( Marcus & Marcus 1968), or present a deeper male atrium ( Meixner 1907; Hyman 1953; Poulter 1975), and cerebral eyespot clusters clearly separated ( Hyman 1953).
Ecology. One specimen of Pericelis cata was, during one collection, placed in the same container with a nudibranch specimen of Felimare lajensis (Troncoso, Garcia & Urgorri 1998) . When they were released, P. c a t a was “wounded” (a rip in the median part of the body) and there were only pieces of gonad and epithelial tissue from F. lajensis ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C). No contact was observed between these species in the field, but P. c a t a may have chemical compounds that match or exceed the ones present in F. lajensis , such as furodisine lactone, obtained from its dysideid sponge prey ( Pereira et al. 2012).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |