Macvicaria flexuomeatus, Aken'Ova & Cribb & Bray, 2008
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3897/zookeys.1.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:66595057-9C2C-4AEF-AD29-9E2F52BF99FD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3793481 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A0798785-8523-5635-4F30-DF10FE7FFEC5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Macvicaria flexuomeatus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Macvicaria flexuomeatus View in CoL n. sp.
Type-host: Goniistius gibbosus (Richardson) (Cheilodactylidae) .
Other host: Cheilodactylus rubrolabiatus Allen & Heemstra (Cheilodactylidae) .
Type-locality: Off Woodman Point, W. A. 32º08'S 115º45'E
Site: Gut, intestine.
Material studied: Ex Goniistius gibbosus : 17 from off Woodman Point, December 1994; Ex Cheilodactylus rubrolabiatus : 3 from off Woodman Point, December, 1994.
Type-material: Holotype: QM G 230390, paratypes: QM G 230391 - 230403, BMNH 2008.7.5.6-13.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:CD873C9A-5940-4EB8-B981-2317670F48F9
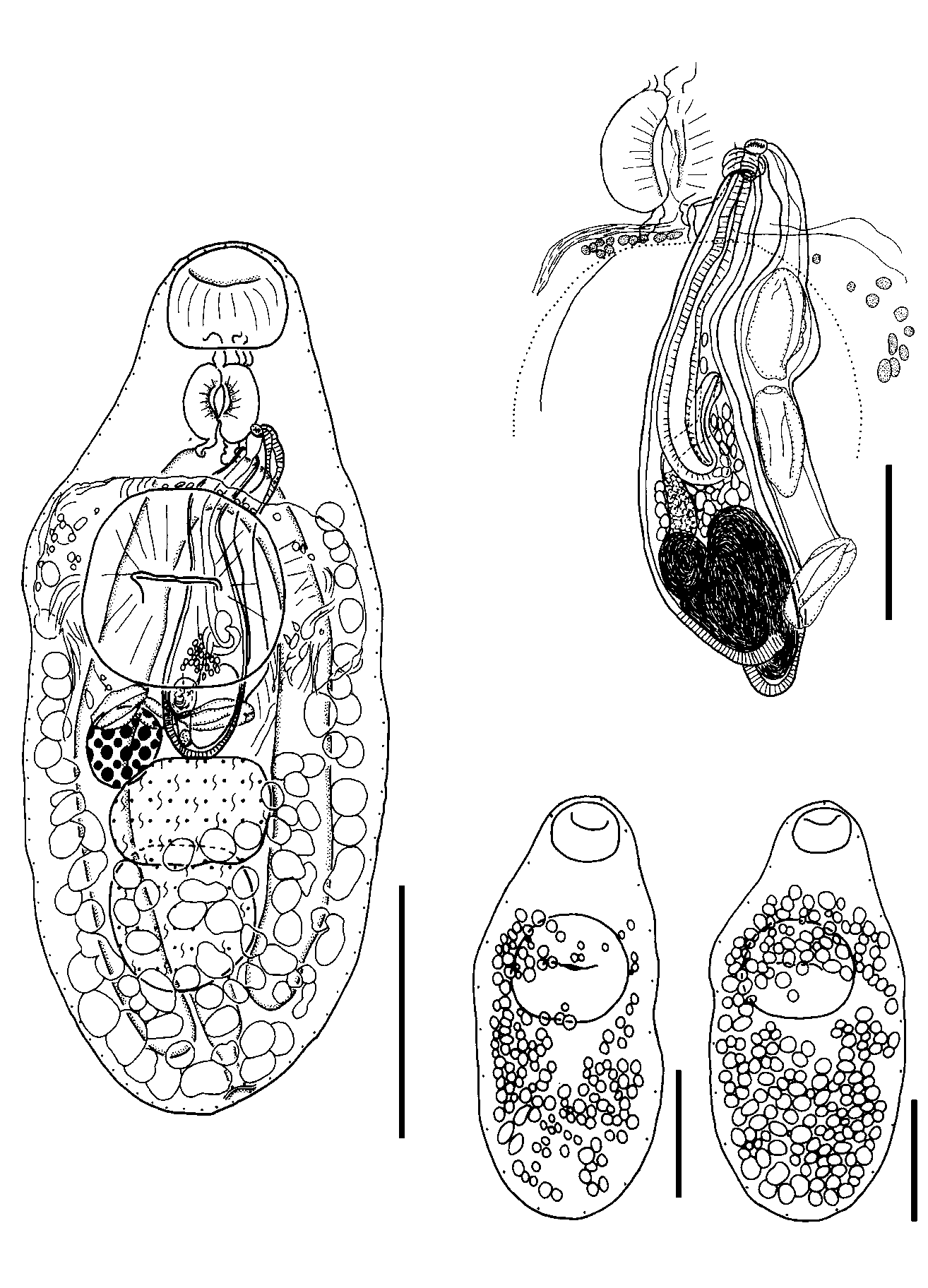
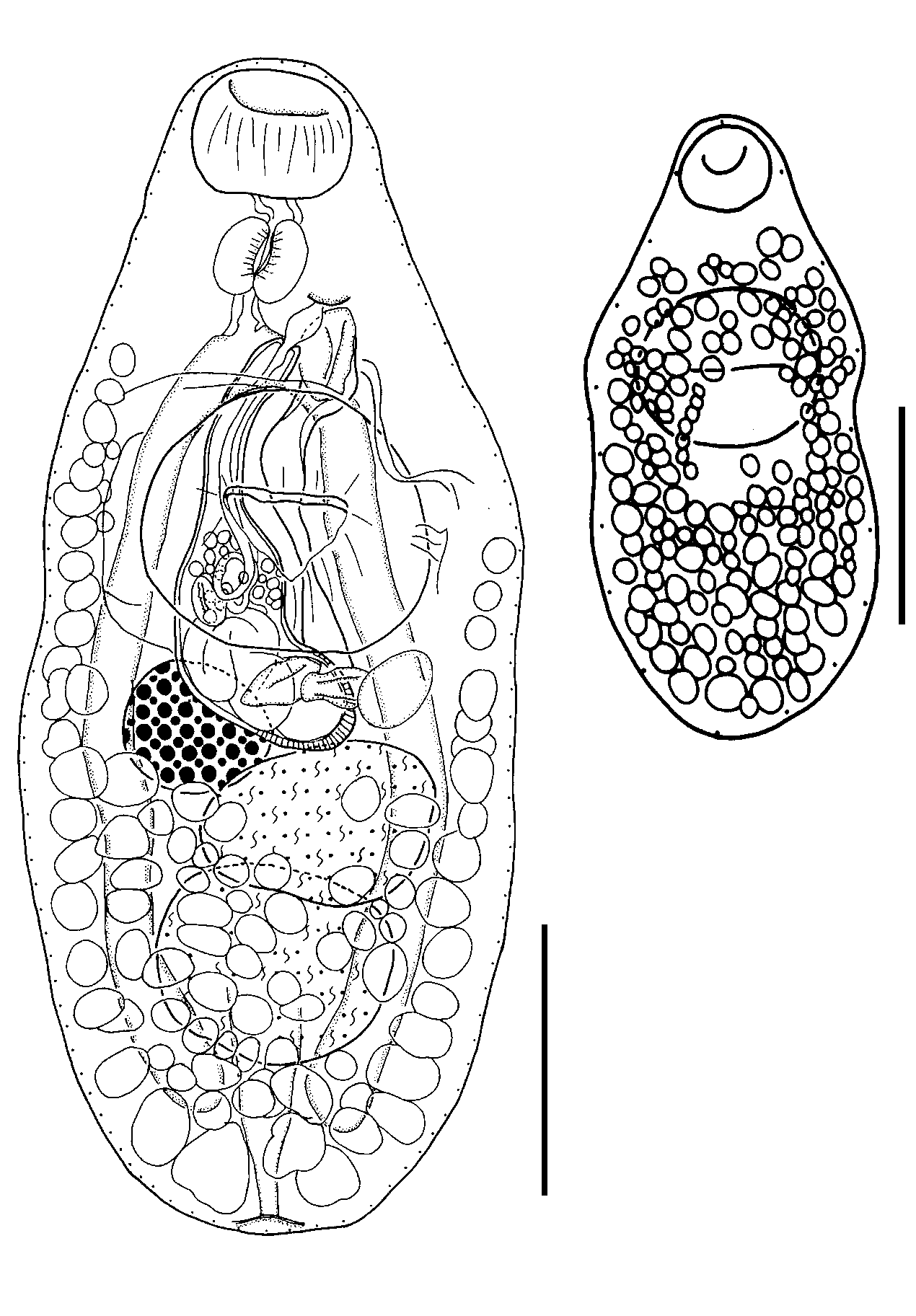
Description ( Figs 16-20 View Figs 16-18 View Figs 19-20 )
Based on 15 mature whole-mount specimens and 2 sets of serial sagittal sections from Goniistius gibbosus . Measurements of worms from Cheilodactylus rubrolabiatus are given in Table 2 View Table 2 .
Measurements are of 10 gravid, unflattened whole-mount worms from Goniistius gibbosus . Body robust, oval, sub-cylindrical, maximum width in region of gonads, 688- 1119 (904) × 316-481 (408); width to length ratio 1:2.1-2.4 (2.2). Oral sucker ventrally subterminal, subglobular, 90-118 (105) × 112-159 (133). Ventral sucker larger than oral sucker, transversely oval, margin of anterior portion bordered by tegumental fold, supplied with numerous prominent muscle fibres, in anterior half of body, 169- 234 (205) × 206-256 (232); sucker width ratio 1:1.6-1.9 (1.7). Forebody short, 205- 297 (251) long, 26-30 (28)% body-length. Prepharynx distinct, short, almost entirely dorso-posterior to oral sucker. Pharynx well developed, spherical to sub-spherical, 67- 86 (76) × 68-99 (83); pharynx to oral sucker width ratio 1:1.5-1.8 (1.6). Oesophagus short, thick walled, surrounded by few gland cells. Intestinal bifurcation usually posterior to anterior margin of ventral sucker, sometimes slightly anterior to (n=2) or level with anterior margin of ventral sucker (n=1). Caeca broad, terminate blindly close to posterior extremity.
Testes 2, rarely one (n=1), spherical to sub-spherical, contiguous, overlapping, usually tandem or oblique, sometimes neither distinctly tandem nor oblique (n=2), in posterior half of body, anterior 88-143 (118) × 125-200 (164), posterior 109-181 (145) × 112-221 (169), overlaps anterior testis dorsally. Post-testicular area small, 89-179 (137) long, 11-18 (15) % body-length. Cirrus-sac large, claviform, thick walled particularly at posterior end, extends from point antero-sinistral to pharynx, reaching past ventral sucker dorsally, usually medially, sometimes laterally, to anterior margin of anterior testis, usually deflecting to left side at level of ovary, sometimes deflecting to right (n=2), or not (n=1); posterior tip may overlap ovary or anterior testis dorsally, depressing anterior margin of anterior testis at point of contact or wedged between ovary and
20
anterior testis; 314-404 (351) × 76-101 (91). Internal seminal vesicle, tubular, occupies posterior portion of cirrus-sac. Pars prostatica well developed, thick walled, surrounded by numerous gland cells. Ejaculatory duct long, thick walled, convoluted at posterior end, surrounded by gland cells. Male terminal genitalia absent in one specimen. Genital atrium small, surrounded by few gland cells. Genital pore sinistral, extracaecal, at level of posterior half of pharynx, usually about half way between median and lateral margin, sometimes overlapping left margin of pharynx (n=3); 157-220 (195) from anterior end, 20-23 (22)% of body-length.
Ovary entire, spherical, normally smaller than testes, hypertrophied and about twice size of solitary testis in one worm, contiguous with, and dextral or antero-dextral to anterior testis, occasionally separated from (n=2) or anterior to anterior testis (n=1), 66-110 (88) × 67-114 (89). Mehlis’ gland distinct, dorsal to ovary. Canalicular seminal receptacle large, saccate, usually dorsal to anterior testis, overlapping anterior portion of posterior testis, occasionally overlapping ovary and posterior testis dorsally (n=1). Uterine coils mainly intercaecal, between anterior testis and posterior margin of ventral sucker, overlapping ovary, anterior testis and cirrus-sac ventrally and dorsally and, sometimes inner margins of caeca; coils may extend posteriorly to posterior margin of posterior testis (n=1) or anteriorly to posterior portion of ventral sucker (n=2). Metraterm distinct, thick walled, extensive, usually containing eggs, distal extremity surrounded by gland cells. Eggs large, oval, operculate, 50-75 (65) × 25-41 (32). Vitelline follicles extend from 163-247 (208) from anterior extremity, 21-27 (23)% of bodylength, to 9-23 (13) from posterior extremity; fields separate ventrally in forebody, confluent in post-testicular area, covering almost all surface of posterior testis and posterior portion of anterior testis ventrally; dorsal field almost confluent throughout length, but interrupted in area of posterior half of ventral sucker, particularly in area of male terminal genitalia, sometimes follicles feebly developed on left or right side of forebody (n=2). Fields lie lateral, dorsal and ventral to caeca with bilateral follicle-free patches in area of ventral sucker ventrally; anterior extent of follicles usually level with posterior end of oesophagus, intestinal bifurcation or sometimes varying between posterior margin of ventral sucker and intestinal bifurcation, rarely to posterior margin of pharynx ventrally (n=1) or dorsally (n=2).
Excretory pore usually dorsally subterminal, sometimes terminal (n=4), or occasionally ventrally subterminal (n=1). Excretory vesicle I-shaped, tubular, posterior end narrow, anterior portion broad, extends anteriorly to terminate just anterior to posterior margin of anterior testis as observed in sagittal section.
Etymology: The species name flexuomeatus (L. flexuosus, full of bends; L. meatus, passage) is derived from the species’ characteristic convoluted ejaculatory duct.
Comments: The specimens of Macvicaria flexuomeatus n. sp. from Cheilodactylus rubrolabiatus are very similar to those from G. gibbosus ; no significant visible or morpho-metrical differences were observed.
Macvicaria flexuomeatus n. sp. fits the concept of Group C.
M. synagris differs in its general body form (fusiform in M. synagris ), sucker-ratio (1:2.5), and a more anterior genital pore (13% of body-length from the anterior extremity).
Macvicaria mutovitellina is more elongate with a width to length ratio of 1:2.5-3.0 (2.8) and it has a longer post-testicular space (15-22 (19)% of the body-length). The caeca in M. flexuomeatus terminate just beyond the posterior margin of the posterior testis whereas they reach well into the post-testicular space in M. mutovitellina .
The other members of Group C differ from M. flexuomeatus in the same features as they do M. mutovillina .
Table 2. Measurements (in µm) of Macvicaria flexuomeatus n. sp. (n = 3) from Cheilodactylus rubrolabiatus.
| Total length | Min. | Max. | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| 675 | 824 | 755 | |
| Maximum width | 305 | 384 | 340 |
| Length/width | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
| Oral sucker length | 84 | 103 | 92 |
| Oral sucker width (OSW) | 107 | 113 | 109 |
| Pharynx length | 53 | 66 | 58 |
| Pharynx width | 60 | 68 | 63 |
| OSW/pharynx width | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Ovary width | 62 | 96 | 84 |
| Anterior testis length | 81 | 134 | 109 |
| Anterior testis width | 119 | 160 | 144 |
| Posterior testis length | 108 | 128 | 119 |
| Posterior testis width | 125 | 156 | 137 |
| Forebody-length (FBL) | 187 | 220 | 206 |
| FBL as % of body-length | 26.7 | 27.7 | 27.3 |
| Ventral sucker length | 165 | 183 | 176 |
| Ventral sucker width (VSW) | 189 | 212 | 203 |
| VSW/OSW | 1.8 | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| Anterior extremity to genital pore (AEGP) | 153 | 166 | 158 |
| AEGP as % body-length | 18.6 | 23.0 | 21.1 |
| Cirrus-sac length | 256 | 289 | 275 |
| Cirrus-sac width | 74 | 83 | 78 |
| Post-testicular region (PTR) | 106 | 137 | 121 |
| PTR as % of body-length | 15.7 | 16.6 | 16.0 |
| Anterior extremity to vitellarium (AEV) | 157 | 178 | 166 |
| AEV as % of body-length | 21.2 | 23.3 | 22.0 |
| Posterior extremity to vitellarium | 8 | 16 | 12 |
| Eggs | 57-74 (64) × 25-42 (34), n=12 | ||
| QM |
Queensland Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.