Homalictus groomi, Dorey & Schwarz & Stevens, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4674.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A4017D06-FFC3-FFB0-FF61-6D3EBBE6F8E0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Homalictus groomi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Homalictus groomi sp. nov.
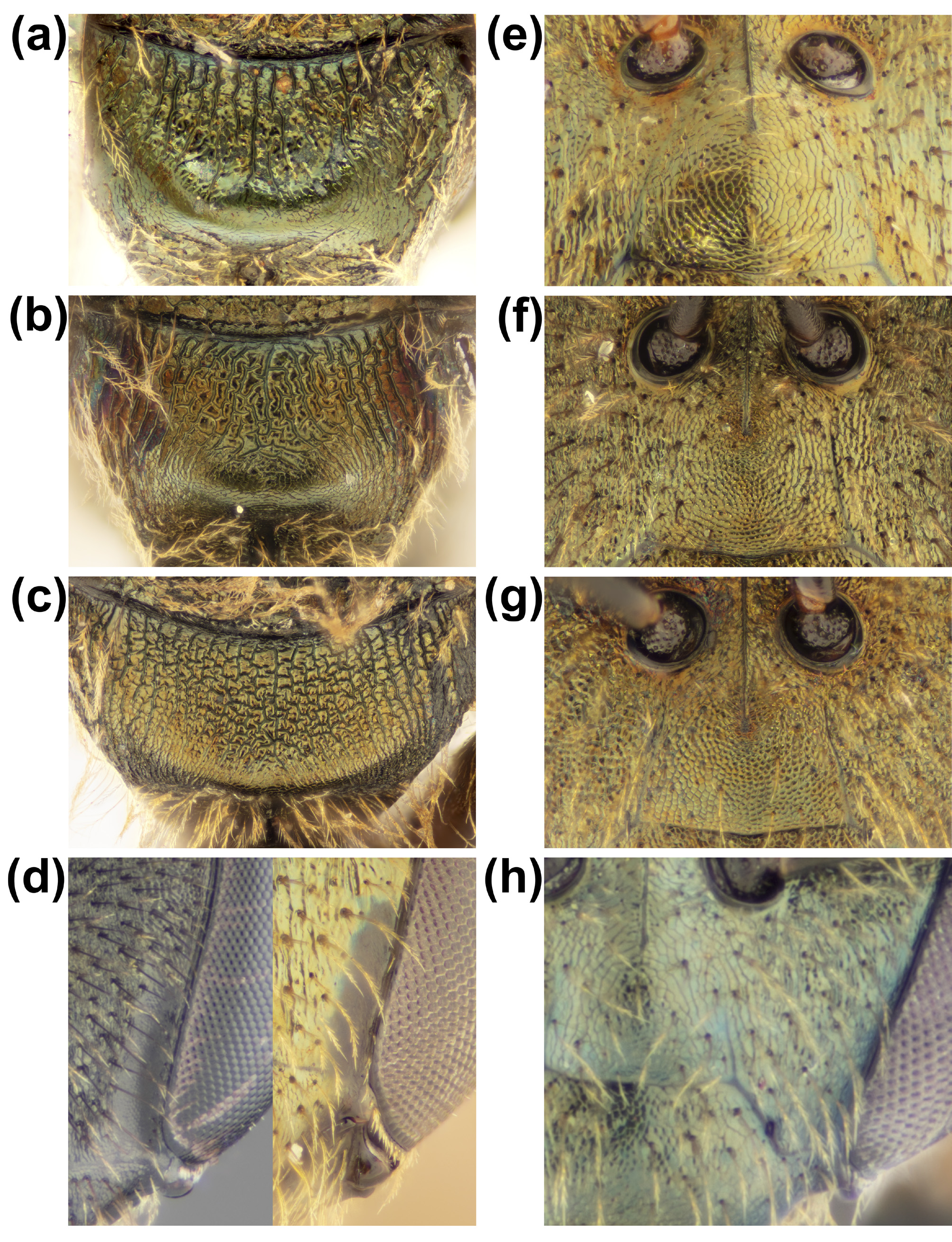
( Figs 15–16 View FIGURE 15 View FIGURE 16 )
Material examined. Holotype ♂: yCMR_136 (SAMA 32-036178), 4/5/ 15, 922 m asl, -17.58268, 177.93645, C Matthews, Viti Levu. GoogleMaps
Allotype ♀: ED31_F04 (SAMA 32-036179), 1/4/15, 1,004 m asl, -17.58508, 177.91965, E Deans, Viti Levu. GoogleMaps
Paratypes 3 ♂: yCMR52_E06 (SAMA 32-036180), 5/5/ 15, 889 m asl, -17.57001, 177.95586, C Matthews, yCMR44_E05 (SAMA 32-036181), 5/5/ 15, 889 m asl, -17.57001, 177.95586, C Matthews, and yCMR41_B05 (SAMA 32-036182), 6/5/ 15, 923 m asl, -17.58268, 177.93645, C Matthews; and 1 ♀: yCMR27_D03 (SAMA 32- 036183), 6/5/ 15, 923 m asl, -17.58268, 177.93645, C Matthews.
Diagnosis. Males: In combination: Antennal sockets and paraocular area strongly depressed ( Fig. 15d View FIGURE 15 ) and posterior surface of the propodeum has diagonal striae ventrally and proximally and joins dorsal striae ( Fig. 15c View FIGURE 15 ). Additionally, male genitalia have a large ridge proximal to the gonostylus ( Fig. 15e View FIGURE 15 ).
Females: In combination: Bee mostly green, supraclypeal area mostly moderately colliculate ( Fig. 1e View FIGURE 1 ) and posterior margin of scutum concave ( Fig. 15f View FIGURE 15 ).
Description. Males: Measurements: UID 0.65 mm. LID 0.55 mm. AOD 0.2 mm. IAD 0.13 mm. OAD 0.37 mm. IOD 0.17 mm. OOD 0.21 mm. GW 0.15 mm. EW 0.31 mm. BL 4.75 mm. ML 0.13 mm. SL 0.27 mm. FL 2.9 mm.
Colouration: Clypeus, supraclypeal area, frons, paraocular area, scutum and propodeum dorsally golden green and metallic. Scutellum golden green and metallic or some pink and blue. Metasoma dark green or green and dark green along posterior edges.
Sculpturing: Paraocular area colliculate, some horizontal striae along central margin of compound eyes, longitudinal striae posteriorly and proximally above antennal socket and striae course and messy. Frons mostly longitudinal striae, transverse striae under ocelli, striae messy and colliculate above antennal sockets. Supraclypeal area mostly moderately colliculate. Clypeus fine and moderate colliculate. Vertex punctures fine, close and open. Scutum anteriorly moderately colliculate and lineolate; medially finely colliculate; posteriorly finely and moderately fine colliculate. Scutellum punctation open. Propodeum; dorsally strong striae, posterior striae triangular, weak medial anterior groove and coarsely strigate-rugose; laterally moderately colliculate and some striae anteriorly and dorsally; posteriorly finely colliculate, striae originating ventrally and medially almost forms circles with dorsal striae and diagonal striae ventrally and proximally.
Morphology: Scape extends to or below anterior margin of medial ocellus. Interantennal distance greater than diameter of socket. Labrum simple. Area posterior of vertex striae strong and close. Region around antennal sockets extending to paraocular area depressed. Posterior margin of scutum shape concave. Gonostylus with strong posterior projection and weaker proximal projection, dorsoapical crest of gonocoxite well developed. Entire genital is smaller and the gonocoxite narrower than in H. fijiensis .
Females: Measurements: UID 0.7 mm. LID 0.66 mm. AOD 0.22 mm. IAD 0.1 mm. OAD 0.42 mm. IOD 0.18 mm. OOD 0.18 mm. GW 0.27 mm. EW 0.32 mm. BL 5.31 mm. ML 0.16 mm. SL 0.29 mm. FL 4.04 mm.
Colouration: Clypeus anteriorly black. Middle and upper clypeus golden and partly iridescent. Supraclypeal area golden, blue and purple. Frons golden and some purple iridescence. Paraocular area golden, golden green and metallic and some purple iridescence. Scutum and scutellum very dark green, strongly metallic purple and pink and partly metallic orange. Propodeum dorsally golden green and metallic. Metasoma black, dark green and some iridescent purple.
Sculpturing: Paraocular area colliculate, some messy striae below antennal sockets, longitudinal striae posteriorly and proximally above antennal socket and striae course. Frons mostly longitudinal striae. Supraclypeal area mostly moderately colliculate, medial area finely colliculate or finely colliculate anteriorly. Clypeus finely colliculate. Vertex punctures fine, close and open and small and open. Scutum anteriorly moderately colliculate and lineolate; medially and posteriorly finely colliculate. Scutellum punctation open. Propodeum; dorsally linear pattern, weak medial anterior groove and finely strigate-rugose; laterally finely colliculate, some striae anteriorly, dorsally and ventrally; posteriorly finely colliculate, striae originating ventrally meet those from dorsal side and diagonal striae ventrally and proximally. Pygidial plate with close and fine punctures.
Morphology: Scape extends to posterior margin of medial ocellus. Interantennal distance about equal to diameter of socket. Labrum with two medial projections parallel from one another. Clypeus not depressed medially. Area posterior of vertex with strong striae and broken. Posterior margin of scutum concave.
Comments. Like H. hadrander , H. groomi is found mostly at higher elevations but has also been sampled at a lower elevation site in the southern part of Viti Levu. It is possible that the climate (or some other factor) in this region is similar to climates at higher elevations.
Distribution. Homalictus groomi has mostly been sampled from the central highlands of Viti Levu, near Nadarivatu ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 ). A single specimen has been collected from a remote forested region in the south of Viti Levu at 250 m asl; otherwise, H. groomi has been collected between 730 m asl and 1,000 m asl.
Etymology. Homalictus groomi is named after Dr. Scott V. C. Groom who initiated recent studies of Fijian bees and provided the first understandings of their origins and phylogenetics.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Halictinae |
|
Tribe |
Halictini |
|
Genus |