Aulacophilinus amblygnathus Menke, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.11066844 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11092928 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A95287C7-FFDE-B54E-FFBF-D536FD63B581 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Aulacophilinus amblygnathus Menke |
| status |
|
Aulacophilinus amblygnathus Menke View in CoL
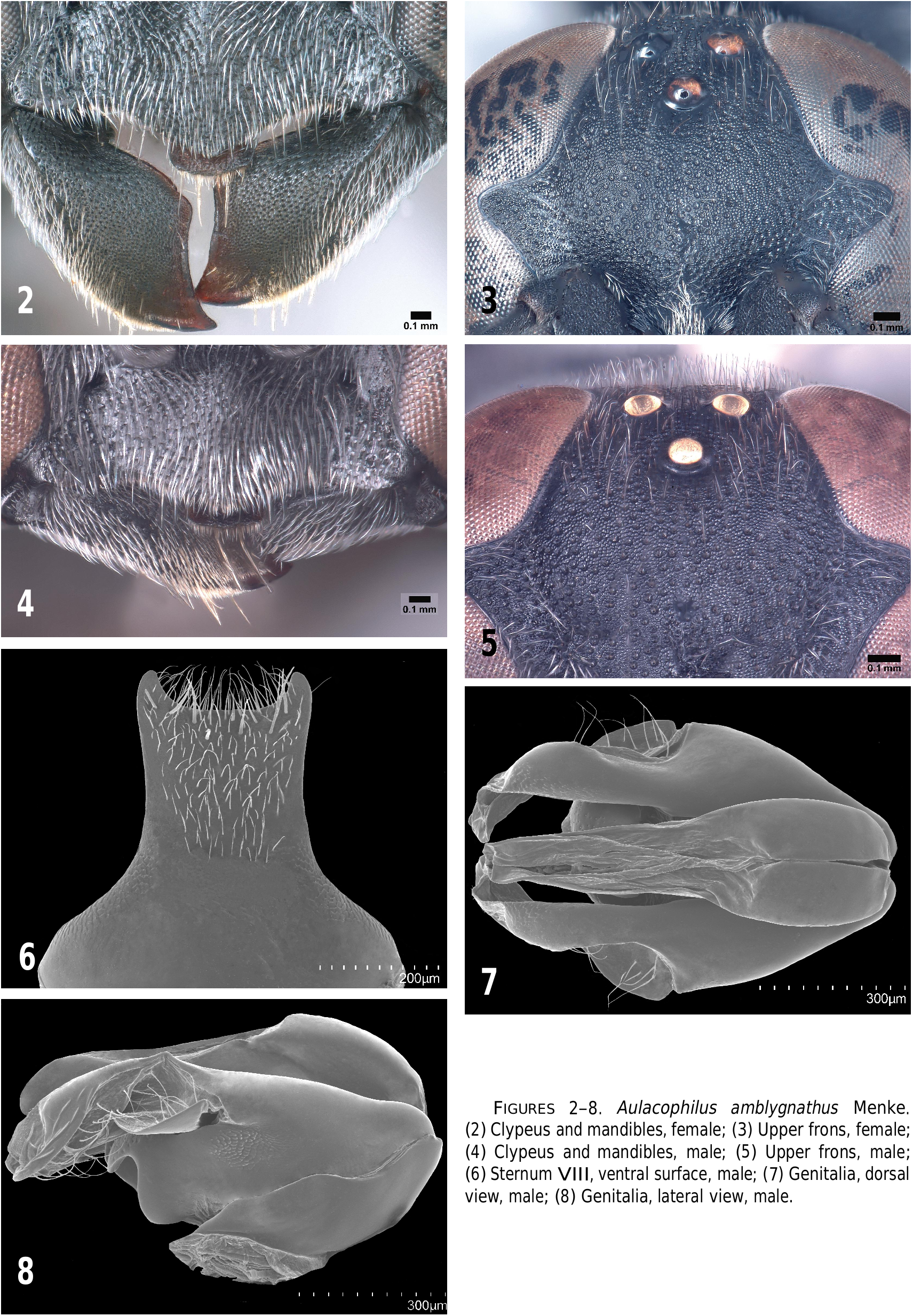
Figures 2–9 View FIGURES View FIGURE .
Aulacophilinus amblygnathus Menke, 2016:335 View in CoL , ♀, ♂. Holotype: ♂, New Guinea: Morobe Province: Wau ( AEI), examined.
RECOGNITION.— Aulacophilinus amblygnathus View in CoL is an all black endemic of New Guinea with three submarginal cells. It differs from all its congener in having the frontal punctures 2–3 diameters apart (rather than less than one to slightly more than one diameter apart), and also in having the frontal setae about as long as 1.5–2.0 midocellar diameters (while no longer than one midocellar diameter in the other species). The absence of silvery, setal fasciae on terga is a subsidiary recognition feature.
DESCRIPTION.— Frons dull, shallowly punctate, punctures averaging 2–3 diameter apart ( Figs. 3, 5 View FIGURES ). Free margin of clypeal lobe obtusely angulate to rounded ( Figs. 2, 4 View FIGURES ). Occipital carina slightly expanded ventrally. Width of labrum equal to 1.1 × midocellar diameter. Anteromedian pronotal pit transversely elongate, about as long as midocellar diameter. Scutum not foveate along flange, with short longitudinal ridges adjacent to posterior margin; scutal punctures well defined, varying from about one diameter apart on average on disk to less than one diameter apart; interspaces aciculate. Tegula impunctate in posterior half. Mesopleural punctures well defined, less than one diameter apart except about one diameter apart near center. Propodeum in most specimens without longitudinal carina separating side from dorsum and posterior surface, but evanescent carina present in some specimens or replaced by vague linear series of short, transverse rugae; dorsum, side and posterior surface with well-defined punctures; dorsum with punctures slightly more than one diameter apart near midline, less than one diameter apart laterally, with well defined, oblique ridges basally; side with punctures less than one diameter apart except about one diameter apart posterodorsally, with fine ridges visible from certain angles; posterior surface with punctures less than one diameter apart near midline, about one diameter apart laterally, with transverse ridges in ventral half ridges near base Forewing with three submarginal cells. Posteroventral forefemoral surface with fine punctures several diameters apart. Hindcoxal dorsum with outer margin obtusely carinate. Outer surface of hindtibia with several fine spines. Punctures of tergum I averaging about two diameters apart anterior of apical depression.
Setae silvery, on upper frons erect, sinuous, varying from about 1.5 × to 2.0 × midocellar diameters; on postocellar area erect, straight, shorter than midocellar diameter; on scutum erect, straight, about 0.5 × to 0.8 × midocellar width; on tergum I suberect, slightly shorter than midocellar width; on lower gena suberect, curved apically, slightly longer than midocellar diameter; not concealing integument on clypeus. Apical depressions of terga without silvery, setal fasciae.
Body all black.
♀.– Upper interocular distance equal to 0.58–0.62 × lower interocular distance; ocellocular distance equal to 0.6–0.7 × hindocellar diameter, distance between hindocelli equal to 1.0–1.3 × hindocellar diameter; eye height equal to 0.94–1.00 × distance between eye notches. Dorsal length of flagellomere I 1.9–2.1 × apical width. Length 7.2–7. 3 mm; head width 2.1 mm.
♂.– Upper interocular distance equal to 0.7 × lower interocular distance; ocellocular distance equal to 0.7 × hindocellar diameter, distance between hindocelli equal to 1.4 × hindocellar diameter; eye height equal to 1.06 × distance between eye notches. Dorsal length of flagellomere I 1.8 × apical width. Apical margin of sternum VIII emarginate ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES ). Genitalia ( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES ): Length 7.0 mm; head width 2.0–2. 1 mm.
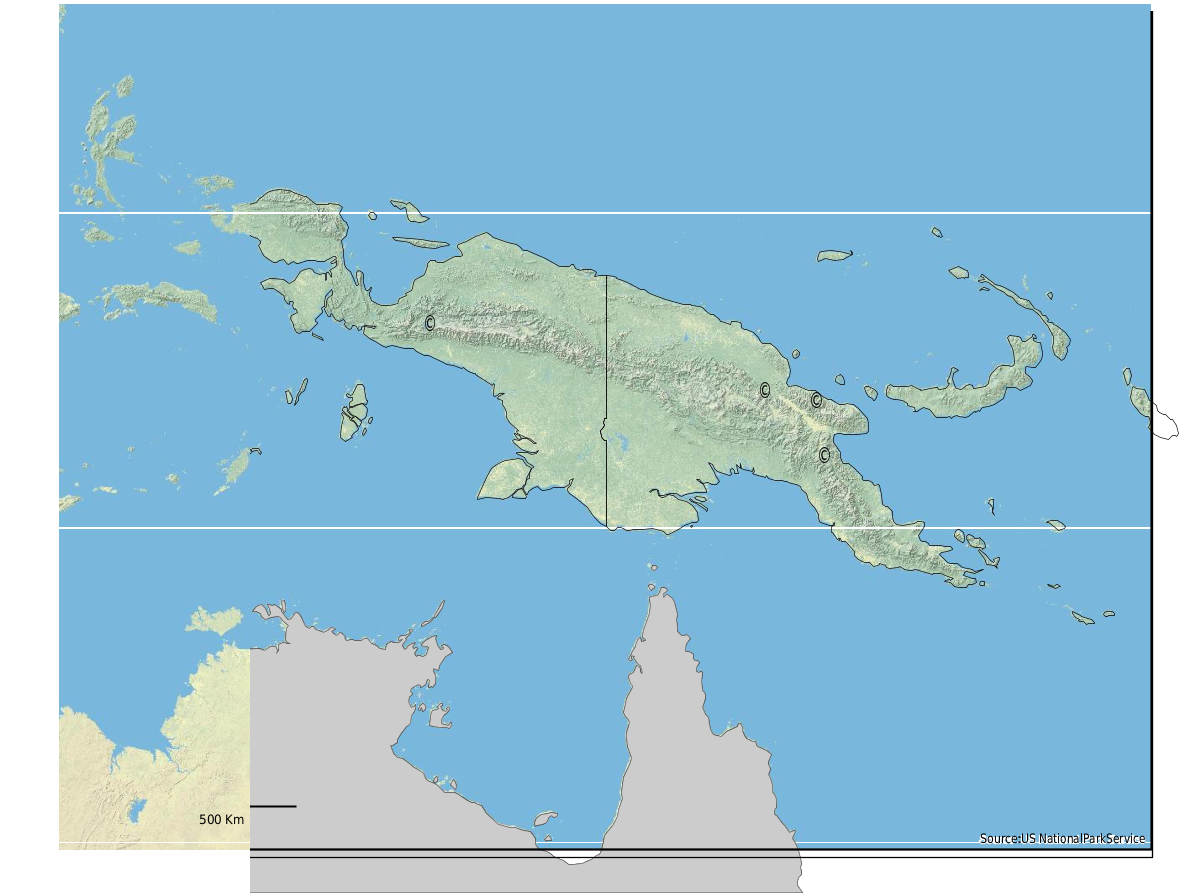
GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE ).— Higher elevations of New Guinea.
RECORDS.— INDONESIA: Western Papua: Paniai Lakes (as Wisselmeren): Enarotadi, elevation 1,850 m (1 ♀, BISH) , Top Camp [of 1939 Dutch-American New Guinea Expedition = approximately 122 km SW Jaiapura ] (1 ♂, RMNH) . PAPUA NEW GUINEA: Madang Province: Pandambai 6 air km W Bundi at 5º38′S 145º11′E, elevation 2,330 m (2 ♀, CAS) GoogleMaps , Teptep at 5°55′S 146°30′E, elevation 1,900 m (1 ♂, CAS) GoogleMaps . Morobe Province: Wau [elevation 1,134 m] (1 ♀, 1 ♂, AEI, holotype and paratype of A. amblygnathus ; 1 ♀, BISH) .
| AEI |
American Entomological Institute |
| BISH |
Bishop Museum, Botany Division |
| RMNH |
National Museum of Natural History, Naturalis |
| CAS |
California Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |