Telogmometopius Jacobi, 1922
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222930601059082 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AE26A23B-BF3F-FFBA-FE75-FD0FFD95FB19 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Telogmometopius Jacobi |
| status |
|
Telogmometopius Jacobi View in CoL
Telogmometopius Jacobi 1921, p 43 View in CoL ; Wu 1935, p 48; Schulze, Kükenthal and Heider 1938,
p 3406; Neave 1940, p 417; Lallemand 1949, p 56, 57; Metcalf 1961, p 327. Type species: Telogmometopius obsoletus Jacobi, 1921 View in CoL , by original designation and monotypy.
Description
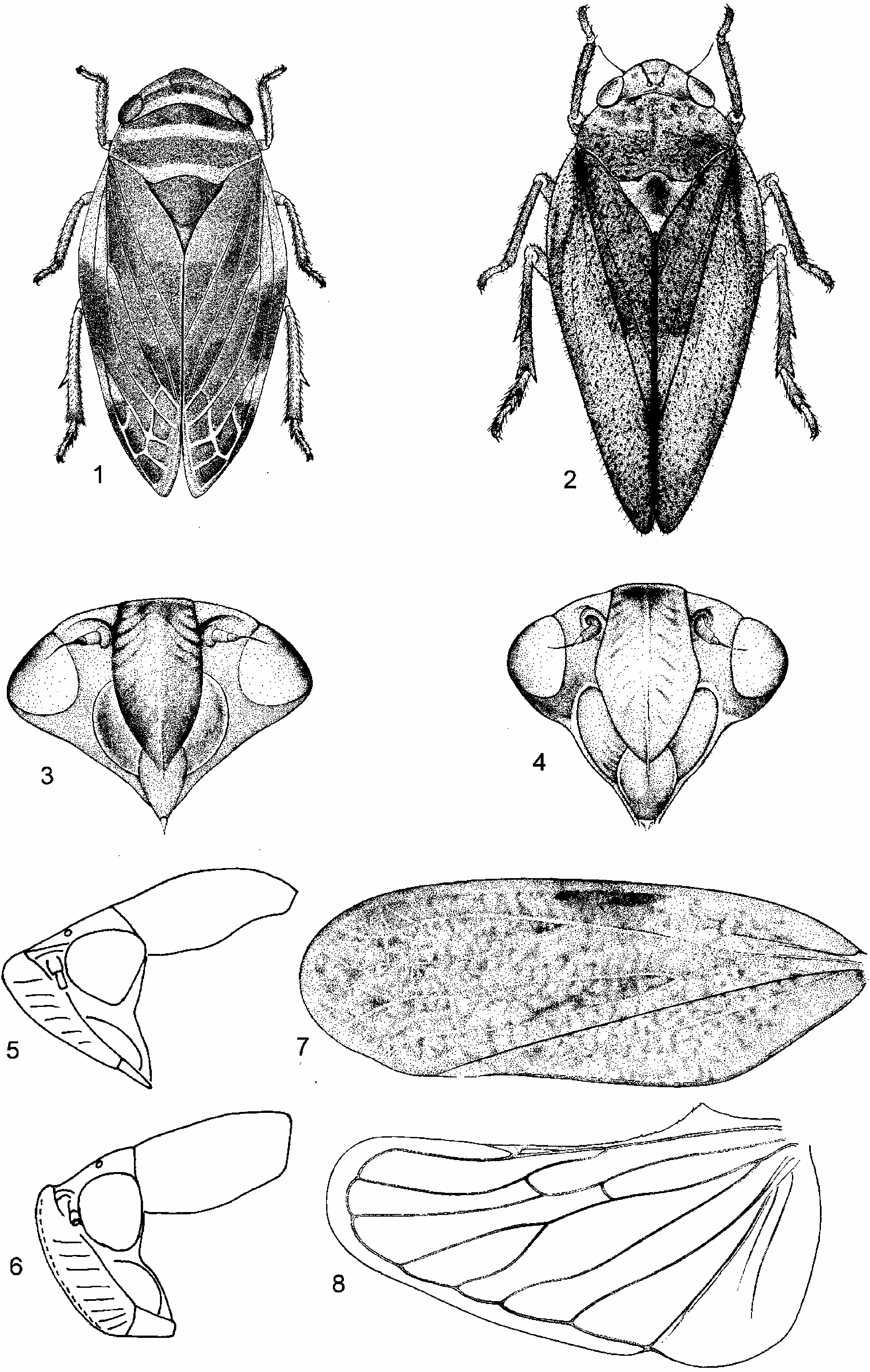
Small to medium-sized, slender, finely pubescent spittlebugs, length (from apex of vertex to tip of fore wings): „ 5.0–8.4 mm, ♀ 5.3–8.5 mm.
General colour grey brown or brown; vertex and pronotum usually ochraceous, probably olivaceous yellow in life.
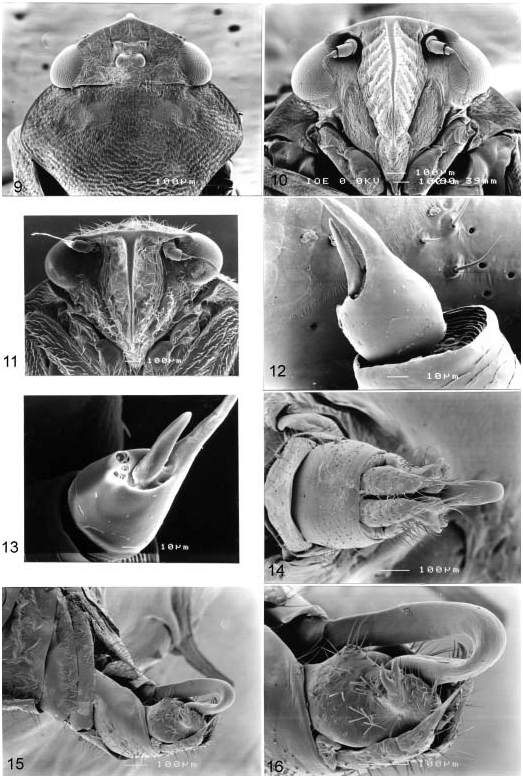
External features as in Baibarana with the following differences. Head ( Figures 2 View Figures 1–8 , 9 View Figures 9–16 ) relatively narrow, broad in profile; posterior margin of vertex more or less straight; ocelli situated slightly basad of mid-distance from anterior to posterior margin of vertex; postclypeus ( Figures 4 View Figures 1–8 , 10, 11 View Figures 9–16 ) strongly compressed laterally and medially longitudinally keel-like. Ultrastructure of antennal pedicel: very sparsely setose and sculptured with scalelike pattern, apex hollowed with inner surface strongly spiralled ( Figure 12 View Figures 9–16 ); flagellum base nearly smooth, sensory organs in subglobose base including one long blunt, peg-like, basiconic sensillum located in a broad, shallow pit adjacent to a group of about five, small, coeloconic sensilla on rim ( Figures 12, 13 View Figures 9–16 ). Rostrum tip ( Figures 17, 18 View Figures 17–24 ) consisting of two lateral lobes separated by a dorsal stylet groove, each lateral lobe with about 12 peg sensilla, numerous short cuticular teeth and some divided acanthae near inner edge. Fore wings with relatively distinct venation. Male pregenital segment very short, much shorter than pygofer in ventral view.
Male genitalia as in Baibarana with the following differences. Lateral plates very small. Styles strongly expanded over distal half in lateral aspect with apex excavate with two lobes, outer lobe with two small, dorsally directed teeth on outer dorsal edge. Aedeagal shaft with basal part horizontal, thereafter strongly and narrowly curved anteriorly, with an apical or dorsal subapical, anteriorly directed, sinuate or coiled, filamentous process.
Biology
In common with most spittlebug genera, no biological data are currently available for species of Telogmometopius . Species of the genus may be associated with bamboos (see collecting data under T. sabahensis ). Collecting data show that adults can be collected in all seasons and certain species, e.g. T. obsoletus and T. himalayensis , can be attracted and collected at light (see collecting data below).
Distribution
Oriental Region, including southern China (Tibet, Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan, Hubei, Gansu, and? Jiangxi), Burma, Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and northern Borneo. The identity of one female specimen from Vietnam ( Tam Dao , 950 m, 15–30 September 1989, V. Novotny, IZCAS), cannot be verified due to the absence of associated males .
Remarks
The monobasic genus Telogmometopius Jacobi was placed by Lallemand (1949) and Metcalf (1961) in the Afrotropical tribe Bandusiini Lallemand , together with the Afrotropical genus Bandusia Stål. We here transfer Telogmometopius to the tribe Rhinaulacini based on the following characters: postclypeus weakly bulbous; hind tibiae with one lateral spur; subgenital plates with an expanded basal region and a spine-like apical process; lateral plates present; aedeagal shaft elongate, cylindrical, and strongly curved; distribution and type of antennal sensilla (see Liang 2001; Liang and Jiang 2001; Liang and Fletcher 2002; Liang and Webb 2002; A.-P. Liang, unpublished data).
Telogmometopius can be distinguished from other Oriental cercopid genera by its strongly laterally compressed postclypeus, with a median carina, keel-like in ventral view ( Figures 10, 11 View Figures 9–16 ) and in the male genitalia by the small lateral plates and very elongate aedeagus with the basal part horizontal and strongly and narrowly curved anteriorly with an apical or subapical filamentous process.
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
| IZCAS |
Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Telogmometopius Jacobi
| Liang, Ai-Ping, Jiang, Guo-Mei & Webb, M. D. 2006 |
Telogmometopius
| Wu CF 1935: 48 |
| Jacobi A 1921: 43 |