Sarimissus maculifrons, Wang & Zhang & Bourgoin, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4706.2.10 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9B5D50B0-4A39-4351-9BE9-E816A1F4B5A2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5943244 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B45787A8-122C-FF95-FF16-43BBFC27FE64 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sarimissus maculifrons |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Sarimissus maculifrons View in CoL sp. nov.
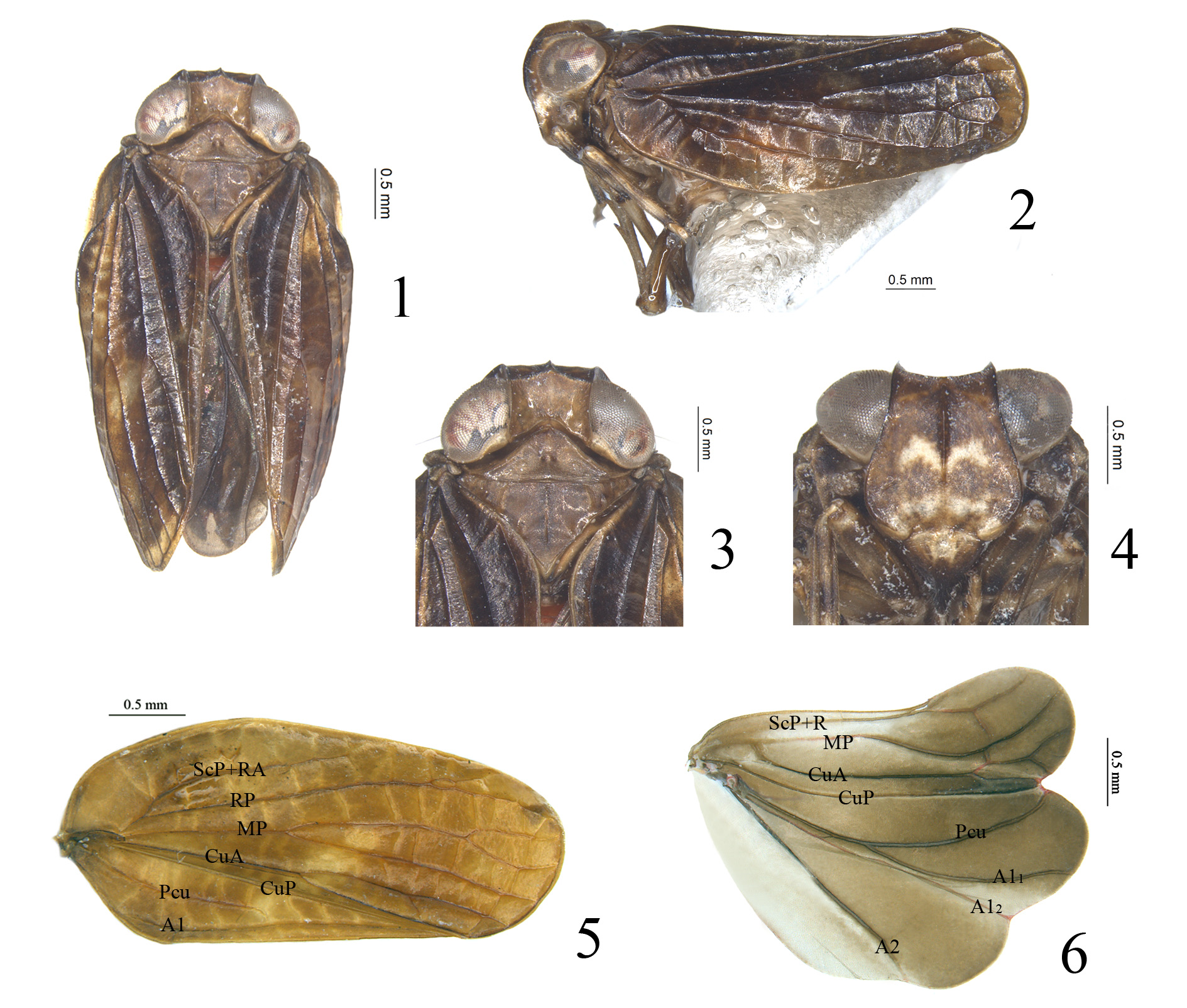
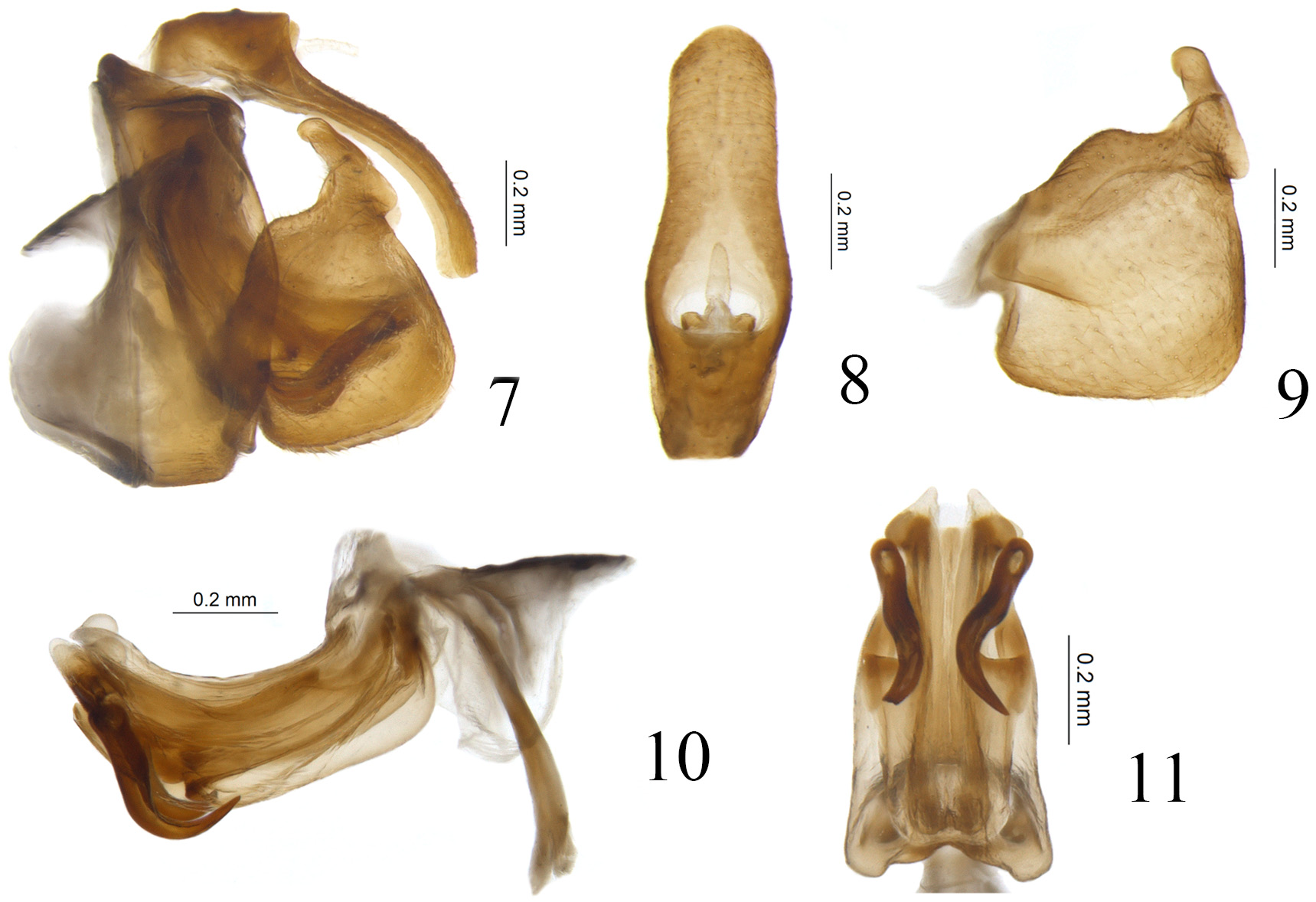
( Figs 1–11 View FIGURES 1–6 View FIGURES 7–11 )
Diagnosis. This new species appears similar to Eusarima contorta Yang, 1994 , but differs by: 1) Frons with a pair of curved eyelike markings on the disc ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ), but the latter species without these eyelike markings ( Chan & Yang,1994, fig. 45B); 2) Capitulum of gonostylus thick and short, with tip obtuse ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7–11 ), but long and slender, with tip acute in E. contorta ( Chan & Yang, 1994, fig. 45E); 3) Aedeagus with a pair of short hook-like processes ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7–11 ), but the latter species with a pair of extremely long processes ( Chan & Yang, 1994, fig. 45H).
Etymology. This species name is a combination of Latin words “ macula ” and “ frons ”, referring to the light yellowish M-shaped markings on the frons.
Description. Length: male (including forewings) (N=4): 5.1–5.2 mm.
Coloration. Vertex brown, anterior, lateral and posterior margins all brown ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Compound eyes grayish brown, supported by grayish callus ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Frons brown, with an obvious light yellowish M-shape eyelike marking on the middle and some irregular yellow patches near base ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); median carina brown from apex extending to near base, but not reaching to the frontoclypeal suture ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); apical margin and lateral margins brown ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Antennae brown ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Postclypeus mainly brown, with light yellow near the base ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Gena brown, with one light yellow transverse fascia below compound eyes in lateral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Pronotum brown, anterior and posterior margins brown, median carina brown, only visible at middle ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Mesonotum brown, median and sublateral carinae all brown ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Forewings tawny to brown, longitudinal veins brown ( Figs 1, 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Hind wings brown ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Legs tawny, distributed with irregular brownish markings ( Figs 2, 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ).
Head and thorax. Vertex 1.5 times wider in midline than long in midline, lateral margins nearly parallel, slightly concave at middle ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Frons 1.0 times wider at widest part than long in midline, 1.6 times wider at widest part than apical margin ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); lateral margins nearly parallel from the apex to the middle of compound eyes, then expand to below antennae and finally narrow to the base ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); sublateral carinae weakly present or invisible ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Pronotum 3.0 times wider at posterior margin than long in midline, 1.0 times longer in midline than vertex ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ); median carina weakly present or absent, with a small incision on each side of midline ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Mesonotum with anterior margin 1.8 times wider than long in midline, 1.7 times longer in midline than pronotum, median carina visible from anterior margin elevated to the basal 1/4, sublateral carinae elevated from anterior margin to the posterior margin ( Figs 1, 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Forewings 2.2 times longer at longest part than widest part, CuA forking slightly after MP ( Figs 2, 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ), MP1+2 vein bifurcate at apical 1/6 ( Figs 2, 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ), MP3+4 vein forked at apical 1/6 ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–6 ) or unforked ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ), CuA1 and CuA2 unforked ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Metatibiotarsal formula: (2)–7/(8-10)/2.
Male genitalia. Anal tube in lateral view curved downward near apex ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7–11 ), in dorsal view long cylindrical, widest at basal 1/3, 3.0 times longer in midline than widest part, apical margin rounded, lateral margins nearly parallel at apical half and convex at basal half ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 7–11 ); anal opening located at basal 1/3 of anal tube ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Pygofer in lateral view long and slender, 2.6 times higher in midline than broad in midline, dorsal margin strongly sloping posterior, posterior margin convex at middle ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7–11 ); tectiductus large and broad ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Gonostylus in lateral view gradually broadened to apex, widest at apical 1/4, dorsal margin elevated at middle, then parallel with ventral margin; ventral margin deeply expand downward at basal 1/9 then straight with caudo-ventral angle subrectangular ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Capitulum of gonostylus directed cephalad, with an arc-shaped antero-lateral process on the base and a finger-shaped postero-lateral process at base ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Periandrium dorsal lobes slightly shorter than lateral lobes, the apical part laminar ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Periandrium lateral lobes in lateral view rounded in the apex ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7–11 ), in ventral view the median part deeply biforked ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Periandrium ventral lobe in lateral view rounded at apex ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7–11 ), in ventral view with apical margin rounded, lateral margins nearly parallel ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Aedeagus with a pair of short broad hook-like processes derived from apical 1/6, this pair of processes in lateral view curved downward then extending to the apical 1/3 of periandrium, tip pointed slightly surpassing the ventral margin ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7–11 ), in ventral view this pair of processes curved outward ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 7–11 )
Type materials. Holotype: ♂, China, Hainan Province, Jianfengling, Chahekou , N 18º 44.727′, E 108º 59.632′, 235 m, 17 viii 2010, coll. Guo Zheng ( IZCAS). GoogleMaps
Paratypes: 1♂, same data as holotype ( IZCAS) GoogleMaps ; 1♂, China, Hainan Province, Dialuoshan , N 18º 40.440′, E 109º 52.600′, 494 m, 10 viii 2010, coll. Guo Zheng ( IZCAS) GoogleMaps ; 1♂, China, Hainan Province, Yinggeling, Yinggezui , 797 m, 22 viii 2010, coll. Guo Zheng ( IZCAS) .
| IZCAS |
Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |