Deanophlebia radsjoshi, Finlay, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4668.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:85A23DE6-F543-4D77-A303-F6BEEE85A628 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B63BA600-FF8F-FFF4-A8B1-3DEC7E87E4E4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Deanophlebia radsjoshi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Deanophlebia radsjoshi sp. nov.
Nousia sp. AV11 ( Dean 1999)
Types. Here designated. Deanophlebia radsjoshi sp. nov. Holotype. Frying Pan Raceline tributary, Telmark St, Falls Creek , 5 Jan 1999, 147 o 16′50′′ 36 o 52′00′′, 1560m, 1 ♂ NSI ( KJF), ( Fig. 23 View FIGURE 23 ). Paratypes. Frying Pan Raceline tributary, same collection data, 2 ♀ NSI, 4 ♀ N ( KJF) . McKay Creek tributary - waterfall, Mt McKay , Alpine Na- tional Park, 5 Feb 1999, 147 o 15′20′′ 36 o 52′19′′, 1700m, 1 ♂ NSI ( KJF) . Tanjil River east branch headwaters, Mt Baw Baw Alpine Village, 16 Feb 1999, 146 o 15′45′′ 36 o 50′25′′, 1440m, 1 ♀ NSI ( KJF) .
Distribution. Southern New South Wales, Eastern Victoria.
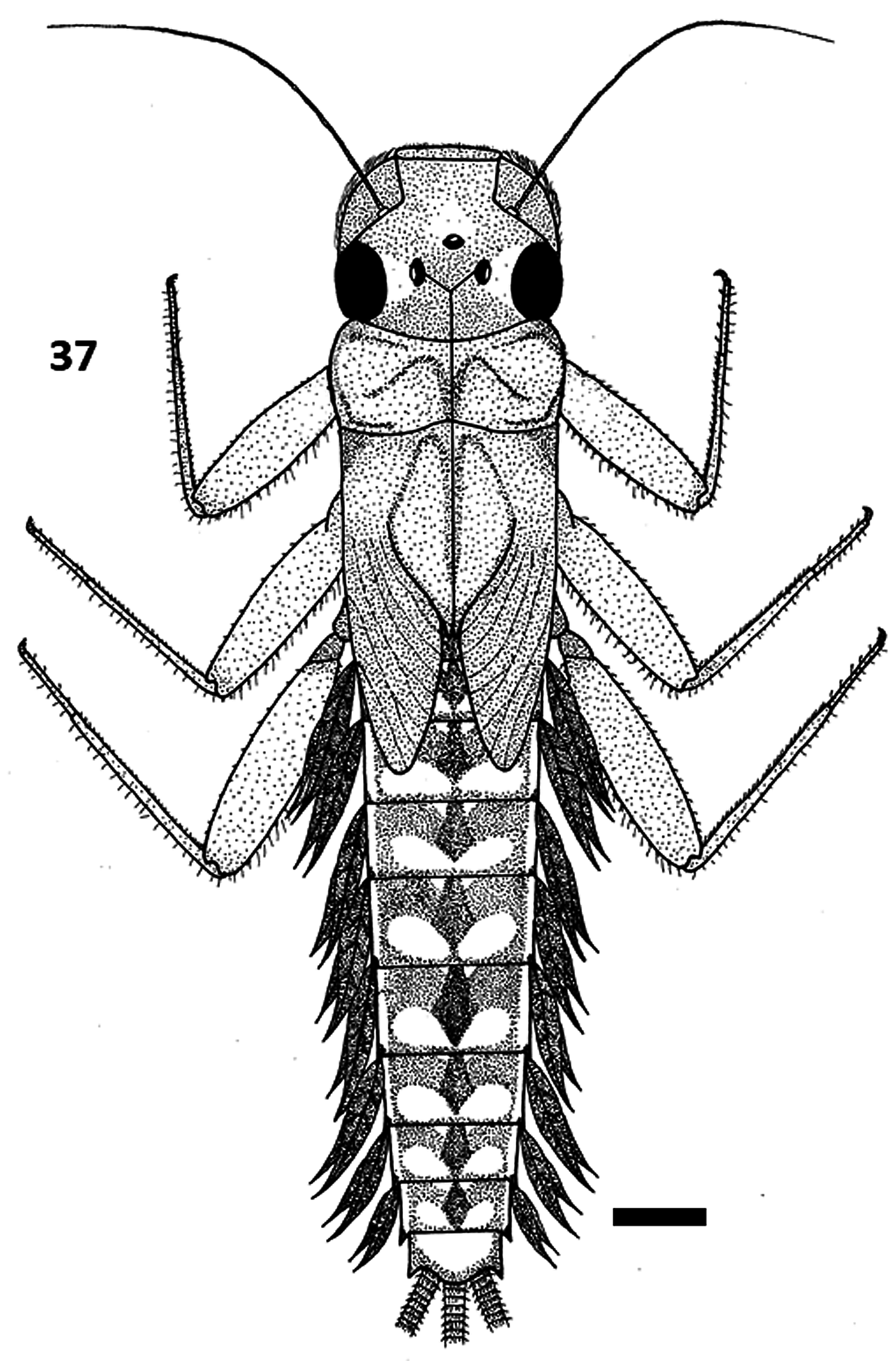
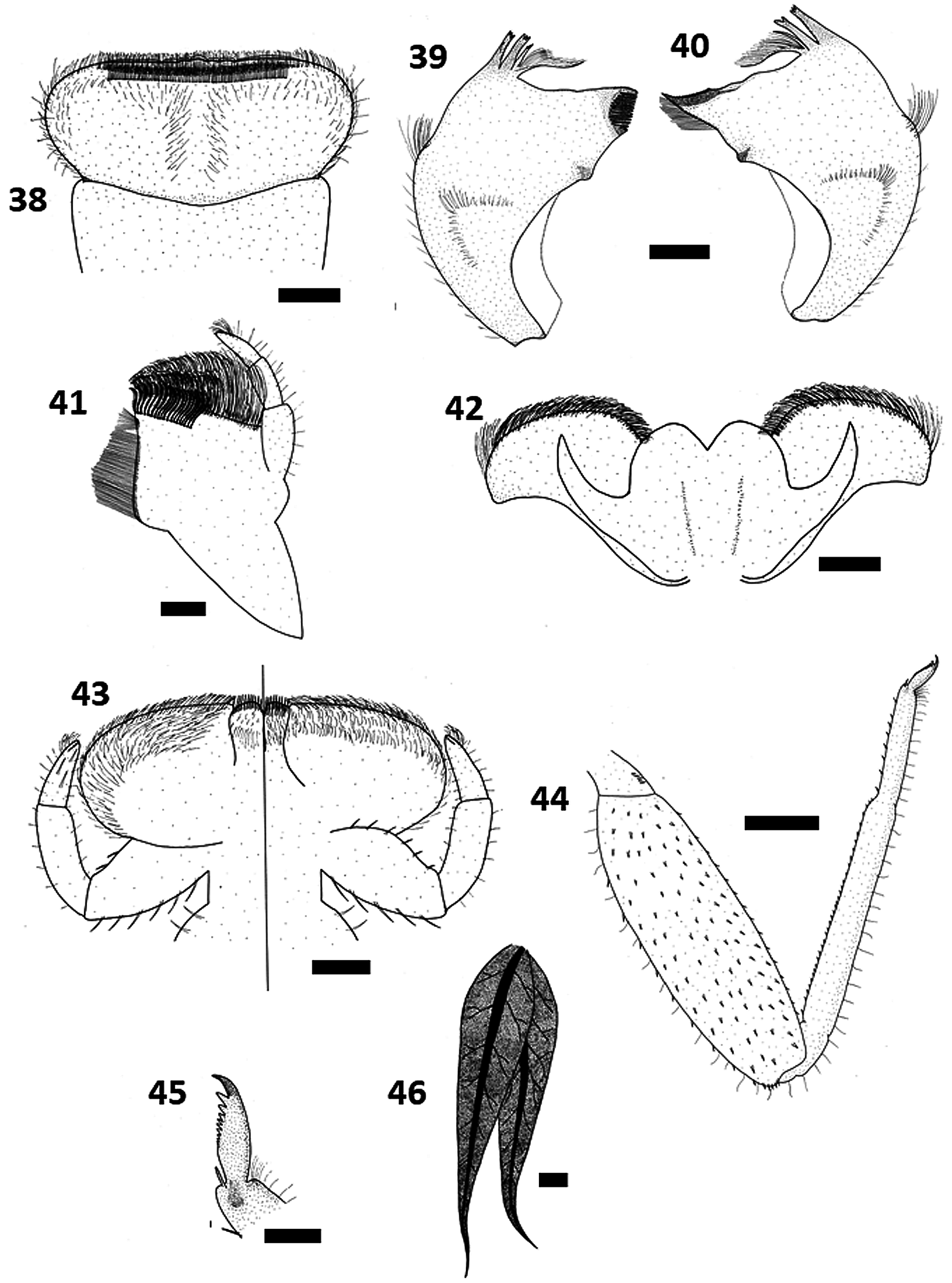
Diagnosis. Male imago. Dimensions: body length 8.6-13.5 (10.8±1.96, 10); forewing length 8.8–13.2 (10.5±1.66, 10); hindwing length 2.05–3.30 (2.50±0.46, 10); forewing hindwing ratio 3.81– 4.78 (4.24±0.31, 10). General body colour tan to brown with dark brown markings. Head dark brown. Antennae: pedicel, scape and flagellum dark brown. Ocelli: three, black with white-grey inserts, laterals larger than medial. Eyes: upper eye size large, sometimes contiguous, ES=0.00–0.09 (0.03±0.03, 10); upper lobes orange-brown, lower lobes grey-black. Thorax: pronotum and mesonotum shiny tan brown with darker markings. Legs: forelegs with femora tan brown, apices darker, tibiae and tarsi golden; total foreleg length 7.4–11.4 (9.0±1.32, 10); forelegs with seven segments; leg length ratios 1.00: 1.39: 0.06: 0.37: 0.35: 0.28: 0.16 (2.50±0.35, 9); tarsal claws of a pair similar, each apically hooked with an opposing hook ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 24–27 ). Wings. Forewing ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 24–27 ): membrane hyaline, pterostigmal slightly opaque, longitudinal and crossveins brown, anal veins yellow; costal and subcostal crossveins present in proximal and distal halves of wing; costal space with 7–11 ( 10) crossveins proximally, 14–17 ( 10) distally (some anastomosed), subcostal space with 7–10 ( 10) crossveins proximally, 11–14 ( 10) distally. Three bullae present on veins Sc, R 2 and R 4+5, MA forked at half to just over half the distance from wing base to margin, MP 2 connected to MP 1 and CuA, CuA and CuP linked by crossvein, ICu 1 recurved to join CuA and not linked to CuA-CuP crossvein, ICu 2 recurved to join ICu 1, ICu 1 and ICu 2 parallel as wing margin approached, CuP strongly recurved and linked by cross- vein to A 1. Hindwing ( Fig. 26 View FIGURES 24–27 ): mostly hyaline, costal space washed with yellow and very slightly opaque; costal margin slightly convex at midlength immediately preceding shallow concavity; costa joins subcosta at approximately four-fifths wing length; no crossveins in proximal half of costal space, 5–8 ( 10) in distal space, 5–9 ( 10) crossveins throughout subcostal space. Abdomen ( Fig. 27 View FIGURES 24–27 ): light to tan brown with darker brown markings, dark brown diamond shaped maculae forming central stripe on segments two to nine, flanked by golden markings anteriorly and posteriorly on each segment, segments one and ten predominantly brown. Genitalia ( Figs 28–31 View FIGURES 28–31 ): forceps three segmented ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 28–31 ); tan brown, progressively lighter apically, terminal segment angular, about the same length as middle segment; penes golden brown, fused along entire length dorsally ( Figs 28 & 29 View FIGURES 28–31 ) and ventrally ( Figs 30 & 31 View FIGURES 28–31 ), lobes often contiguous, two lobes distinct, outer lateral margins relatively straight; each lobe pointing outwards: two pairs of internal spines, two small triangular processes present apically, two pairs of internal spines seen from dorsal side, not always apparent. Caudal filaments: three, tan brown; terminal filament longer than cerci. Female imago. Dimensions: body length 8.0–13.6 (11.5±1.86, 13); forewing length 8.4–13.8 (11.8±1.91, 12); hindwing length 1.4–3.5 (2.5±0.59, 12); forewing hindwing ratio 3.94–6.00 (4.69±0.54, 12). General patterning and colouring similar to male. Eyes: grey black, separated on meson of head by a distance about four times maximum width of eye. Legs: total leg length shorter than male, total leg length 5.8–9.5 (7.5±1.29, 10); forelegs with six segments, leg length ratios 1.00: 1.36: 0.21: 0.19: 0.16: 0.14 (2.44±0.42, 11). Wings. Forewing ( Fig 32 View FIGURES 32–36 ): colour and venation similar to male except wings generally with more crossveins; costal space with 6–11 ( 12) crossveins proximally, 13–18 ( 12) distally, subcostal space with 5–10 ( 12) crossveins proximally, 12–17 ( 12) distally. Hindwing ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 32–36 ): no crossveins in proximal half of costal space, 5–8 ( 12) in distal half, 5–9 ( 12) crossveins throughout subcostal space. Abdomen: sternum seven with genital extension, segment nine moderately cleft ( Fig. 34 View FIGURES 32–36 ). Egg. Ovoid; polar cap absent, chorion with large and small circular shaped protuberances over surface, pattern variable ( Figs 35 & 36 View FIGURES 32–36 ). Male and female subimago. General colour and markings similar to imago. Wings uniformly greybrown, opaque. Forelegs of male not elongated. Genitalia not fully developed. Mature nymph. ( Fig. 37 View FIGURE 37 ). Body lengths: ♂ 10.0–13.3 (11.7±1.25, 10), ♀ 8.0–13.7 (11.8± 1.75, 14). General colour tan brown with darker markings. Head: prognathous; tan brown, slightly darker posteriorly; head width 1.98–2.48 (2.20±0.16, 11); head width pronotum width ratio 0.86-0.97 (0.91±0.04, 11). Ocelli: three; black with white inserts; laterals larger than medial. Antennae: pedicel and scape tan brown, flagellum golden; more than twice length of head. Eyes: upper lobes of male reddish brown, lower lobes black; eyes of female black. Mouthparts. Labrum and clypeus ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 38–46 ): lateral margins of clypeus very slightly diverging towards anterior; lateral margins of labrum slightly wider than clypeus, rounded; anterior margin of labrum straight with no apparent antero-median emargination; labrum length 0.45–0.60 (0.50±0.04, 14), labrum width 1.00–1.25 (1.08±0.08, 14), width length ratio 2.00–2.33 (2.16±0.09, 14); five denticles present on anterior margin; denticle width as proportion of labrum width 0.21–0.31 (0.26±0.03, 14); frontal setae arranged as a broad band; secondary hair fringe clearly separated from broad band. Mandibles ( Figs 39 & 40 View FIGURES 38–46 ): outer margins slightly curved; small indentation and sparse long spine-like setae at midpoint on outer lateral margins, shorter setae along margin between midpoint and base; dark coloured nodule at midpoint on inner lateral margins; row of setae in an inverted L-shape on lower mandible body. Left mandible ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 38–46 ): two incisors, each with three apical teeth, outer incisor inconspicuously serrated on inner lateral margins, often with subapical process; prostheca stout, prosthecal tuft slender with hairs on lateral margins only. Right mandible ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 38–46 ): spine-like setae on inner lateral margins; two incisors, outer incisor with three apical teeth, inconspicuously serrated on inner lateral margins, short spines on inner mesal surface; inner incisor with two apical teeth; prostheca slender; prostheca tuft slender with hairs on lateral margins only. Maxillae ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 38–46 ): galea-lacinae slightly wider than long, width length ratio 1.00–1.22 (1.10±0.06, 10); subapical row of 16–19 ( 10) pectinate setae; palpi three segmented, terminal palp with single spine apically; palp length ratios 1.00: 0.71: 0.67 (0.37±0.03, 11). Hypopharynx ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 38–46 ): well developed lateral processes; anterior margin of lingua deeply cleft, lined with short setae; superlingua with thick tufts of setae on anterior margins, lateral margins slightly angular. Labium ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 38–46 ): glossae not turned under ventrally and lying in same plane as paraglossae, series of blunted spines apically; palpi three segmented, first segment with sharp spines, terminal segment with row of triangular spines almost circling apex and stout spines on dorsal surface; palp length ratios 1.00: 0.81: 0.51 (0.51±0.05, 10); submentum with spines on lateral margins. Thorax: tan brown with darker brown markings; Legs. Foreleg ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 38–46 ): golden to tan brown, femora usually darker at apices; fore femora occasionally with white patch proximally but this is not always apparent; total foreleg length 3.80–6.03 (4.84±0.62, 12); fore femora length 1.75–2.38 (2.14±0.23, 12), fore femora width 0.63–0.90 (0.74±0.07, 12), fore femora length width ratio 2.69–3.14 (2.91±0.15, 12); fore tibiae with numerous short ventral spines, fore tarsi with 7–11 ( 10) ventral spines; tarsal claws ( Fig. 45 View FIGURES 38–46 ) with 11–14 ( 10) ventral teeth, progressively larger apically, apical tooth inconspicuously serrated; leg length ratios, foreleg 1.00: 0.89: 0.37 (2.14±0.23, 12), mid leg 1.00: 0.87: 0.35 (2.23±0.27, 10), hind leg 1.00: 0.88: 0.29 (2.58±0.36, 10). Abdomen: golden brown with darker brown markings, dark brown diamond shaped maculae forming central stripe on segments two to nine flanked by tan and golden markings anteriorly and posteriorly on each segment, segment ten predominantly golden; posterolateral spines present on segments two to nine, progressively larger apically. Gills ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 38–46 ): membrane opaque, grey-black, present on segments one to seven, progressively smaller posteriorly; double, upper and lower lamellae equally developed; each gill tapered to a thin point apically; main tracheal branch apparent, lateral tracheae poorly developed and visible under transmitted light only. Caudal filaments: three; golden, terminal filament longer than cerci.
Etymology. The species epithet is derived from the names of the author’s children: Radley and Josh, who were instrumental in delaying the publication of this paper.
Remarks. Deanophlebia radsjoshi can be distinguished from other species in the genus by the following combinations of characters. In the imago: (i) average male forewing length less than 11mm; (ii) male forewing hindwing ratio smaller, forewing 4.2 times larger on average than hindwing; (iii) average male foreleg lengths shorter than 9.0mm; (iv) abdomen with dark brown diamond shaped maculae forming central stripe; (v) penis lateral margins less bulbous medially.
In the mature nymph: (i) denticles on labrum extend approximately one-third the total width of the labrum; (ii) average total foreleg length less than 5mm; (iii) average total foreleg femora length less than 2.5mm; (iv) abdomen with dark brown diamond shaped maculae forming central stripe; (v) gills with membrane opaque, grey-black.
Other specimens examined. NEW SOUTH WALES. Ramshead Creek, “the Cascades”, Merritts Track , 27 Jan 1984, 1 ♂ N, 1 ♀ N ( JD) . Ramshead Creek, upstream Kosciusko Walking Track , 27 Jan 1984, 148 o 16′ 36 o 29′, 1940m, 2 ♂ N, 1 ♀ N ( JD) GoogleMaps . Unnamed tributary, south slope of North Ramshead , 27 Jan 1984, 1 ♀ I ( JD) . Unnamed trickle, small trickle on Cascade Trail , 1km upstream Deadhorse Gap, 21 Jan 1984, 1 ♂ N, 7 ♀ N ( JD) . VICTORIA. Baldy Creek, Mt Stirling Rd , 17 Apr 1975, 146 o 27′ 37 o 06′, 1220m, 1 ♂ N ( RM) GoogleMaps . Bluff Creek, 2 Nov 1981, 11.7km up Mt Stirling Rd , 146 o 28′38′′ 37 o 07′49′′, 1310m, 4 ♂ N, 10 ♀ N ( JD) . Bogong Jack Creek, West Kiewa Logging Rd , 6 Nov 1997, 147 o 10′12′′ 36 o 49′59′′, 1070m, 1 ♂ N ( KJF) . Brandy Creek, Great Alpine Rd, Alpine National Park : 5 Jan 1987, 147 o 11′22′′ 37 o 00′55′′, 1560m, 1 ♂ N, 2 ♀ N ( JD) ; 18 Nov 1996, 1 ♂ N ( KJF) ; 19 Nov 1996, 1 ♀ N ( KJF) ; 19 Jan 1997, 1 ♂ N ( KJF) . Breakfast Creek, Tamboritha Rd, Alpine National Park , 7 Jan 1997, 146 o 36′58′′ 37 o 31′09′′, 320m, 1 ♂ I ( KJF) . Caledonia River, Howitts Hut , 14 May 1996, 147 o 41′ 37 o 14′, 1480m, 4 ♀ N (coll. unknown) . Cement Creek, Mount Donna Buang Rd , 23 Nov 1978, 145 o 42′20′′ 37 o 42′48′′, 670m, 2 ♀ N, 1♂ N ( JD) . Charity Creek tributary, Mt Baw Baw Tourist Rd , 16 Feb 1999, 146 o 15′15′′ 37 o 50′47′′, 1180m, 1 ♀ NSI, 1 ♀ N ( KJF) . Falls Creek, Telephone Box Junction, Mt Stirling Rd , 2 Nov 1981, 146 o 27′43′′ 37 o 06′52′′, 1220m, 4 ♀ N, 9 ♂ N ( JD) . First Creek, Warburton-Jamieson Rd , 7 Dec 1985, 145 o 58′10′′ 37 o 25′25′′, 750m, 3 ♀ N, 2 ♂ N ( JD) . Frosty Creek, Frosty Creek Rd, 8 Nov 1996, 147 o 08′05′′ 37 o 05′55′′, 1380m, 1 ♂ NS, 1 ♀ S, 6 ♂ N, 3 ♀ N ( KJF) . Frying Pan Raceline tributary, Telmark St, Falls Creek , 5 Jan 1999, 147 o 16′50′′ 36 o 52′00′′, 1560m, 4 ♂ NSI, 3 ♀ NSI, 2 ♂ NS, 1 ♀ NS, 1 ♂ N, 6 ♀ N ( KJF) . Kiewa River west branch tributary, track between Blairs Hut and Westons Hut , Mt Hotham , 3 Nov 1991, 147 o 10′ 37 o 55′, 1320m, 1 ♂ N, 1 ♀ N ( JD) GoogleMaps . McKay Creek, Mt McKay-Howmans Gap Rd , 11 Jan 1980, 147 o 14′ 36 o 52′, 1580m, 3 ♂ N, 3 ♀ N ( JD) GoogleMaps . McKay Creek tributary - waterfall, Mt McKay, Alpine National Park , 9 Nov 1996, 147 o 15′20′′ 36 o 52′19′′, 1700m, 3 ♂ N, 10 ♀ N ( KJF) . Merritts Creek, Charlottes Pass, Mt Kosciusko National Park , 8 Dec 1996, 148 o 19′ 36 o 25′, 1920m, 1 ♀ SI, 1 ♀ N ( KJF) . Middle Creek tributary, Alpine National Park , 10 Nov 1996, 147 o 18′05′′ 36 o 54′55′′, 1620m, 1 ♀ N ( KJF) . Mt Baw Baw , 14 Jan 1975, 146 o 16′ 37 o 50′, 1460m, 32 ♂ I, 2 ♀ I, 1 ♂ S ( IC) GoogleMaps . Mt Buller , 17 Jan 1958, 146 o 25′ 37 o 08′, 1680m, 1 ♂ N, 1 ♀ N ( AN) GoogleMaps . Myrtle Creek, Mt Donna-Buang Rd : 6 Apr 1997, 145 o 36′42′′ 37 o 42′35′′, 780m, 1 ♂ N, 3 ♀ N ( KJF) ; 26 Feb 2000, 1 ♀ NSI, 3 ♂ NS, 1 ♀ S, 4 ♀ N ( KJF) ; 19 Mar 2000, 1 ♀ NSI, 3 ♀ NS, 1 ♂ N, 2 ♀ N ( KJF) . Sawpit Creek, Donnelly Weir Rd , 6 Apr 1997, 145 o 32′03′′ 37 o 38′15′′, 100m, 1 ♂ N ( KJF) . South Buller Creek headwaters, Mt Buller Summit , 15 Feb 1997, 146 o 25′ 36 o 08′, 1680m, 1 ♀ NS ( KJF) . Tanjil River headwaters, Mt Baw Baw Alpine Village : 12 Oct 1996, 146 o 15′45′′ 37 o 50′25′′, 1440m, 2 ♂ N ( KJF) ; 16 Feb 1999, 1 ♂ NS, 1 ♀ NSI ( KJF) . Target Creek tributary, Heyfield-Jamieson Rd , 5 Feb 1997, 146 o 33′57′′ 37 o 35′04′′, 20m, 1 ♂ S, 1 ♂ N, 4 ♀ N ( KJF) . Tarra River Tarra-Bulga National Park , 21 Nov 1998, 146 o 32′13′′ 38 o 26′57′′, 340m, 1 ♀ N ( KJF) . Tarra River, Tarra-Bulga National Park , 21 Nov 1998, 146 o 32′15′′ 38 o 27′00′′, 340m, 1 ♀ NS, 1 ♂ N ( KJF) . Unnamed Creek, NE slope of Mt Buller , 3 Nov 1981, 1 ♀ N ( JD) . Unnamed Ice melt, Mt Buffalo Rd , 7 Nov 1996, 146 o 48′06′′ 36 o 42′39′′, 1060m, 1 ♂ N ( KJF) . Upper Perkins Creek , 21 Nov 1994, (exact location unknown) 4 ♀ N (JBa) .
| RM |
McGill University, Redpath Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |