Cnemaspis koynaensis, Khandekar & Thackeray & Agarwal, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4656.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:23E2B306-B51A-4323-8628-B7DF5C64575F |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6D6FE89B-D099-48AE-9266-0CF06A33C8DD |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:6D6FE89B-D099-48AE-9266-0CF06A33C8DD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cnemaspis koynaensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cnemaspis koynaensis sp. nov.
Figs. 2–5 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 , 6 A&B View FIGURE 6 ; Table 3 View TABLE 3 & 4 View TABLE 4 .
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:6D6FE89B-D099-48AE-9266-0CF06A33C8DD
Holotype. NCBS-BH685 (AK 470), SVL 32.4 mm, adult male, collected near Dhanagarwada , Humbarli village , near Koyna (17.413° N 73.731° E; ca. 970 m asl.), Satara District , Maharashtra, India, by Akshay Khandekar , Swapnil Pawar and Tejas Thackeray, on 12 September 2018. GoogleMaps
Paratypes. NCBS-BH687 (AK 297) , SVL 31.1 mm, NCBS-BH688 (AK 298) , SVL 31.3 mm, BNHS 2538 View Materials (AK 301) , SVL 30.5 mm, BNHS 2541 View Materials (AK 580) , SVL 27.3 mm, adult males; NCBS-BH689 (AK 299) , SVL 23.9 mm, sub-adult male; BNHS 2539 View Materials (AK 578) , SVL 28.7 mm, BNHS 2540 View Materials (AK 579) , SVL 30.4 mm, adult females; NCBS-BH686 (AK 296) , SVL 22.1 mm, sub-adult female; same collection data as holotype GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The specific epithet is a toponym for Koyna in Satara District of Maharashtra, the type and only known locality for this species.
Suggested Common Name. Koyna dwarf gecko.
Diagnosis and comparison with Indian congeners. A small-sized Cnemaspis , SVL less than 33.0 mm (n =9). Dorsal pholidosis heterogeneous, weakly keeled, granular scales intermixed with large, strongly keeled, conical tubercles; 10–14 longitudinal rows of dorsal tubercles, 18–25 tubercles in paravertebral rows; spine-like scales present on flanks; ventral scales on belly smooth, subimbricate; 20–26 scales across mid-body, 128–139 longitudinal scales between mental to anterior border of cloaca; subdigital scansors smooth, entire, unnotched; subdigital lamellae under fourth digit of pes 17–21; males with three or four femoral pores on each thigh, separated by 22–25 poreless scales; dorsal side of tail with enlarged, strongly keeled, conical tubercles forming whorls; median row of subcaudals smooth, not enlarged.
Cnemaspis koynaensis sp. nov. can be distinguished from all other peninsular Indian congeners on the basis of the following differing or non-overlapping characters: spine-like scales present on flanks (versus absent in C. adii Srinivasulu, Kumar & Srinivasulu , C. agarwali Khandekar , C. ajijae , C. anamudiensis Cyriac, Johny, Umesh & Palot , C. australis Manamendra-Arachchi, Batuwita & Pethiyagoda , C. beddomei (Theobald) , C. boiei (Gray) , C. girii , C. gracilis (Beddome) , C. heteropholis , C. indica Gray , C. kolhapurensis , C. kottiyoorensis Cyriac & Umesh , C. limayei , C. maculicollis Cyriac, Johny, Umesh & Palot , C. mahabali , C. nairi Inger, Marx & Koshy , C. ornata (Beddome) , C. otai Das & Bauer , C. shevaroyensis Khandekar, Gaitonde & Agarwal , C. sisparensis (Theobald) , C. thackerayi Khandekar, Gaitonde & Agarwal , C. wynadensis (Beddome) , C. yercaudensis Das & Bauer ); scales on dorsal aspect of trunk heterogeneous (versus homogeneous in C. adii , C. assamensis , C. australis , C. boiei , C. indica , C. jerdonii , C. kolhapurensis , C. littoralis Jerdon , C. mysoriensis (Jerdon) , C. nilagirica and C. sisparensis ); original tail with smooth imbricate median row of unenlarged subcaudals (versus smooth enlarged median row of subcaudals in C. adii , C. agarwali , C. boiei , C. gracilis , C. heteropholis Bauer , C. indica , C. jerdonii , C. kolhapurensis , C. nairi , C. nilagirica Manamendra-Arachchi, Batuwita & Pethiyagoda , C. ornata , C. shevaroyensis , C. sisparensis , C. thackerayi , and C. wynadensis ; C. amboliensis , C. australis and C. goaensis with keeled subcaudals); absence of keeled scales on the venter or gular regions (versus keeled scales on the venter or gular region in C. australis , C. monticola Manamendra-Arachchi, Batuwita & Pethiyagoda and C. nilagirica ); males lacking precloacal pores and having three or four femoral pores on each side, separated by 22–25 poreless scales (versus males with only precloacal pores present in C. anamudiensis , C. beddomei , C. maculicollis , C. nairi , C. ornata ; males with both femoral and precloacal pores present in C. adii , C. agarwali , C. amboliensis , C. australis , C. goaensis ; C. gracilis , C. mysoriensis , C. otai , C. shevaroyensis , C. thackerayi , C. yercaudensis ; males with a continuous series of 26–28 precloacal-femoral pores in C. kolhapurensis ; males without femoral and precloacal pores in C. assamensis Das & Sengupta ; males with eight femoral pores in C. jerdonii (Theobald) , six in C. heteropholis , 14–18 in C. littoralis , seven or eight in C. sisparensis , 4–6 in C. wynadensis ).
C. koynaensis sp. nov. morphologically similar to C. flaviventralis , from which it can be distinguished by having 22–26 ventral scales across the mid-body (versus 28 or 29 in C. flaviventralis ), having 22–25 poreless scales between femoral pores (versus 27–29). Additionally, C. koynaensis sp. nov. is 18.4 % divergent from C. flaviventralis in ND2 sequences ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ). C. koynaensis sp. nov. is just 7.9% divergent from C. girii and differs only in the presence of spine-like scales on the flanks (versus absence in C. girii ), and slightly less ventral scale rows (20–26) across the mid-body (versus 26–28 in C. girii n = 9 each).
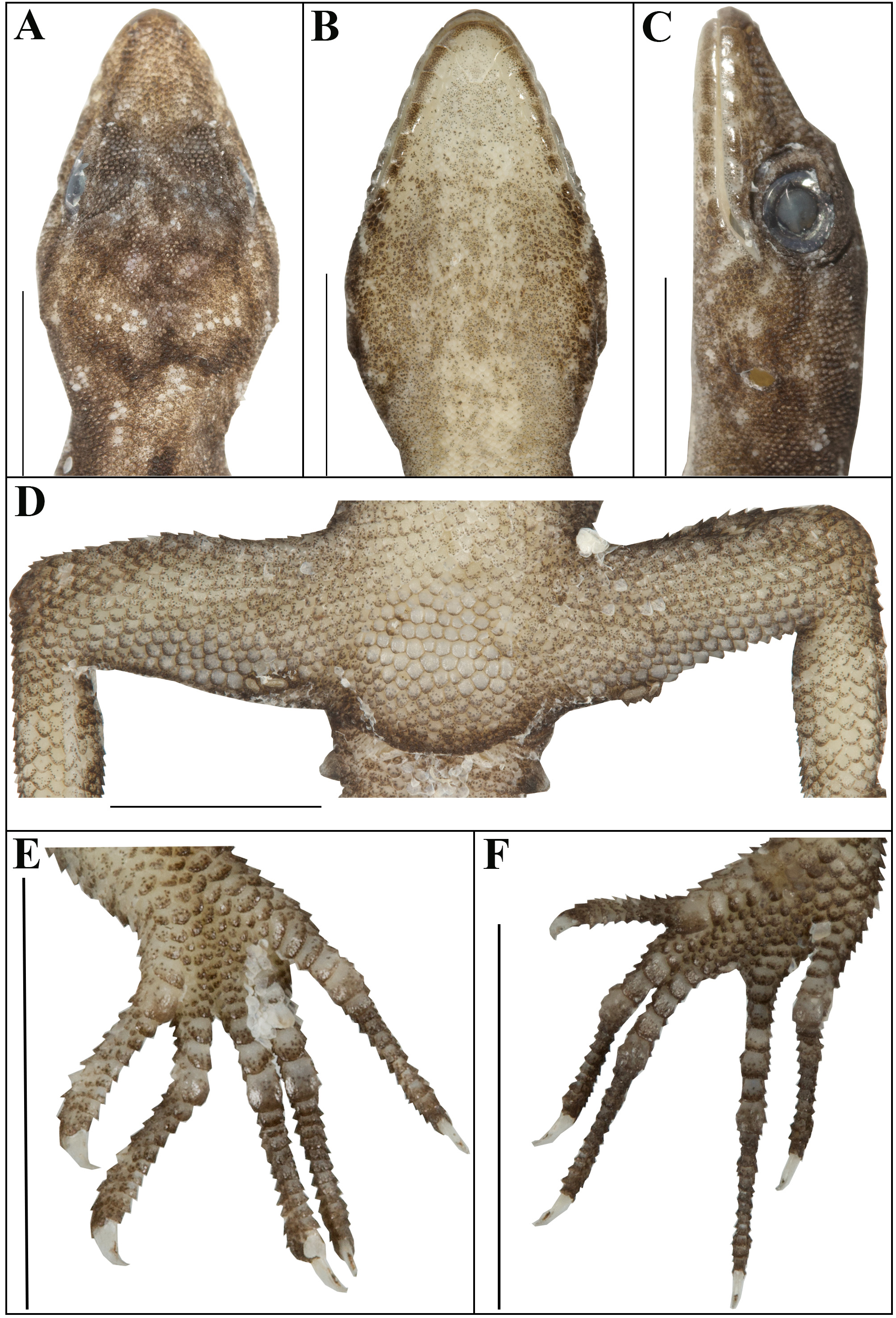
Description of the holotype. Adult male in good state of preservation except that the tail is slightly bent towards the left and about 2.8 mm long incision in the ventral side of mid-body for liver tissue sample ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ). SVL 30.4 mm, head short (HL/ SVL 0.26), wide ( HW /HL 0.66), not strongly depressed ( HD /HL 0.42), distinct from neck. Loreal region slightly inflated, canthus rostralis not prominent. Snout less than half of head length ( ES /HL 0.36), longer than eye diameter ( ED / ES 0.59); scales on snout and canthus rostralis large, weakly keeled, juxtaposed; larger than those on forehead and interorbital region; occipital and temporal region with much smaller granules, intermixed with larger, roughly rounded, tubercles ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Eye small ( ED /HL 0.21); with round pupil; orbit with extra-brillar fringe scales that are largest anteriorly; supraciliaries not elongate. Ear-opening deep, roughly circular, small ( EL /HL 0.05); eye to ear distance greater than diameter of eye ( EE / ED 1.42) ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ). Rostral much wider (1.5 mm) than long (0.8 mm), incompletely divided dorsally by a strongly developed rostral groove for more than half of its length; single enlarged supranasal on each side, roughly similar in size to postnasals, separated from each other by a smaller single internasal and two smaller scales on the snout; rostral in contact with first supralabial, nasal, supranasal and internasal; nostrils oval, each surrounded by postnasals, supranasal, rostral and first supralabial; two row of scales separate the orbit from the supralabials ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ). Mental enlarged, subtriangular, slightly wider (1.6 mm) than long (1.4 mm); two pairs of postmentals, first pair large, roughly rectangular, a single enlarged gular scale separated left and right first postmentals, bordered by mental, infralabial I, second postmentals and two enlarged chin scales; second postmentals slightly smaller than first postmentals, bordered by first and second infralabials, first postmentals and three enlarged chin scales; three enlarged gular scale prevents contact of left and right outer postmentals; chin scales bordering postmentals roughly conical, weakly keeled, smaller than outermost postmentals, rest granular, much smaller, smooth; infralabials bordered below by a row of slightly enlarged scales, decreasing in size posteriorly ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ). Supralabials to angle of jaw nine on each side and seven at midorbit on each side; supralabial I largest, decreasing in size posteriorly; nine infralabials to angle of jaw on each side, and seven at mid-orbit position on each side; first infralabial largest, decreasing in size posteriorly ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ). Extra-brillar fringe scales 15 or 16 on each side, interorbital scale rows across narrowest point of frontal seven or eight; 29 or 30 scale rows between left and right supraciliaries at mid-orbit ( Fig 3A View FIGURE 3 ).
Body relatively slender ( BW / SVL 0.18), trunk less than half of SVL ( AGL / SVL 0.36) with spine-like scales on lower flank and without ventrolateral folds. Dorsal scales on trunk heterogeneous, weakly keeled, granular scales intermixed with much larger, strongly keeled, conical tubercles. tubercles in approximately 13 longitudinal rows at mid-body; 19 tubercles in paravertebral row from above forelimb insertion to the hind limb insertion; scales on nape slightly smaller than those on paravertebral rows, smaller still on occiput. Ventral scales slightly larger than granular scales on dorsum, those on belly smooth, subimbricate, slightly rounded, subequal from chest to cloacal opening; ventral scale rows across mid-body 24; 128 scales from mental to anterior border of cloaca; scales on pectoral region slightly smaller than those on belly, flat and imbricate, smaller still on throat; gular region with much smaller, flattened granules with those on chin bordering postmentals, enlarged, juxtaposed and flattened ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 & 6B View FIGURE 6 ). Precloacal pores absent, three femoral pores on each side separated by 25 poreless scales ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ).
Scales on palm and sole, smooth, flat and roughly circular; scales on dorsal aspect of manus and pes heterogenous, upper arm slightly larger than those on mid-body dorsum, strongly keeled, and subimbricate; those near forelimb insertion, much smaller, granular, weakly keeled; scales on dorsal aspect of forearm smaller than those on upper arm, weakly keeled, flat, and roughly rounded; scales on elbow weakly keeled, subimbricate, and similar in size to those on upper arm; dorsal aspect of hand predominantly bearing small, flattened, weakly keeled, imbricate scales. Ventral aspect of upper arm with smooth, subimbricate scales; forearm and wrist with larger, weakly keeled, subimbricate scales. Scales on dorsal aspect of thigh larger than those on dorsum, strongly keeled, imbricate except those near hind-limb insertion which are much smaller, weakly keeled, and subimbricate. Scales on dorsal side of knee and shank slightly smaller than those on dorsum of thigh, weakly keeled, subimbricate; dorsal side of foot predominantly bearing flattened, strongly keeled, imbricate scales; scales on ventral aspect of thigh and shank similar in size of mid-body ventral scales, weakly keeled, and imbricate ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Forelimbs and hind-limbs moderately slender, long ( LAL / SVL 0.14); (CL/ SVL 0.18); digits long, with a strong, slightly recurved claws, distinctly inflected, distal portions laterally compressed. Series of unpaired subdigital lamellae on basal portion of digits separated from narrower distal subdigital lamellae at first interphalangeal joint; proximal lamellae series: 2–4–5–5–5 (right manus; Fig. 3E View FIGURE 3 ), 2–4–5–7–5 (right pes; Fig. 3F View FIGURE 3 ), 2–4–5–5–5 (left manus), 2–4–5–8–4 (left pes); distal lamellae series: 8– 9–11–12–10 (right manus; Fig. 3F View FIGURE 3 ), 8– 9–12–12–12 (right pes; Fig. 3E View FIGURE 3 ), 9– 9–12–11–10 (left manus), 8– 9–12–12–11 (left pes). Relative length of digits (measurements in mm in parentheses): III (3.3)> IV (3.2)> V (2.9)> II (2.8)> I (2.0) (left manus); IV (4.4)> V (3.5)> III (3.3)> II (2.5)> I (1.6) (left pes).
Tail partially regenerated at tip, cylindrical, relatively slender, flattened beneath, base distinctly swollen when viewed ventrally, tail slightly longer than snout-vent length (TL/ SVL 1.01) ( Fig. 2 C&D View FIGURE 2 ). Dorsal scales at tail base granular, weakly keeled, similar in size and shape to those on mid-body dorsum, gradually becoming larger, flattened, pointed, subimbricate posteriorly, intermixed with slightly enlarged, strongly keeled, conical tubercles forming whorls; 6–8 tubercles on first 2–5 whorls; scales on dorsal and ventral aspect of regenerated portion of the tail slightly smaller than the granular scales on original tail, smooth, subimbricate. Scales on ventral aspect of original tail roughly twice the size to those on dorsal, imbricate, smooth, without a series of enlarged sub-caudal scales; those on tail base slightly smaller, imbricate and smooth, a single enlarged tricarinate postcloacal spur on each side ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ).
Colouration in life. ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A–C) Dorsal ground colour of head, body, limbs, and tail light brown ( Fig. 5C View FIGURE 5 ) to greyish-brown ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 ); head with numerous dark brown blotches, brille yellowish. Pupil black, iris golden coloured; Radiating line from orbit forming an indistinct preorbital streak on snout; yellow and dark grey alternating bands on labials; single brown postorbital streak, merging with its counterpart from the other orbit to form an indistinct W-shaped band on occiput, behind it small whitish spots, which bordered by another W-shaped marking on occiput. A single large central black ocellus bordered by rusty coloured tubercles on the forelimb insertion. Dorsum with seven light yellow or white diffuse vertebral blotches, fourth and sixth blotch with dark anterior marking; from forelimb insertion to hind-limb insertion with six diffuse dark blotches parallel to vertebral blotches on lateral sides of the body; spine-like scales yellow coloured. Dorsum of limbs with alternating light brown and dark brown bands; digits with alternating dark and white markings; dorsum of original portion of tail with alternating dark brown and whitish bands, regenerated portion dark brown. Gular, pectoral, abdominal region, under limbs, and tail base offwhite, mottled in brown; no dark markings on underside of tail; postcloacal spur and spines on the lateral sides of tail close to the cloacal opening light yellow. Juvenile colour different from adults: dorsum colour lighter adults ( Fig. 5B View FIGURE 5 ), dorsal white vertebral markings extend to lateral sides; tail tip light yellow coloured.
Variation and additional information from type series. Mensural data for the type series is given in Table 3 View TABLE 3 . There are five male and three female specimens ranging in size from 22.1 mm to 31.3 mm. All paratypes resemble the holotype except as follows: the number of lamellae on digit I of the manus ranges from 10–12 and on digit IV from 15–17; on digit I of the pes ranges from 10 or 11, on digit IV from 17–21 and on digit V from 15–18. NCBS- BH687, NCBS-BH 689 and BNHS 2541 with nine supralabials up to angle of jaw on each side, and NCBS-BH 686, NCBS-BH 688, BNHS 2538 and BNHS 2539 with eight supralabials, and BNHS 2540 with ten supralabials up to angle of jaw on each side. NCBS-BH 688, NCBS-BH 689 and BNHS 2539 with seven supralabials up to midorbit on each side, NCBS-BH 686 and BNHS 2538 with six, and BNHS 25340 and BNHS 2541 with eight supralabials on each side up to midorbit. Tubercles in paravertebral rows varies from 18 in NCBS-BH 688 to 25 in BNHS 2539; NCBS-BH 687 and NCBS-BH 688 have 11 rows of dorsal tubercles, NCBS-BH 686, NCBS-BH 689, and BNHS 2538 have ten and BNHS 2539, BNHS 2540, and BNHS 2541 have 14 rows of dorsal tubercles. Ventral scale counts in longitudinal and transverse series vary from 128 in BNHS 2538 to 139 in BNHS 2539, and 20 in BNHS 2538 and to 26 in BNHS 2541 respectively. Four male paratypes, NCBS-BH 687, NCBS-BH 689, BNHS 2538, BNHS 2541 have three femoral pores and another male paratype NCBS-BH 688 has four femoral pores on each side. Three paratypes—NCBS-BH687, NCBS-BH 688 and BNHS 2538 with incomplete tail; five paratypes, NCBS-BH 686, BNHS 2539, BNHS 2540, NCBS-BH 689, and BNHS 2541 with complete tail, slightly longer than body (TL/ SVL 1.16, 1.19 and 1.10 respectively) and NCBS-BH 689 and BNHS 2541 with tails slightly shorter than body (TL/ SVL 0.98 and 0.77).
Distribution and natural history. Cnemaspis koynaensis sp. nov. is so far known only from the vicinity of Koyna Wildlife Sanctuary, Satara, Maharashtra at elevations between ca. 800–1100 m asl. (Fig. 1). The species was encountered during two days of fieldwork in the semi-evergreen forest patches and on exposed lateritic plateau ( Fig. 11A View FIGURE 11 ). Male holotype ( NCBS-BH 685) and two male paratypes ( NCBS-BH 687 & NCBS-BH 688) were collected from tree holes below ~ 3 m height along a seasonal stream during the daytime (1500h). Two female paratypes ( BNHS 2539 & BNHS 2540) and a subadult male ( NCBS-BH 689) were collected from under pile of rocks on an exposed lateritic plateau. Sympatric lizards at the type locality include Hemidactylus frenatus Duméril & Bibron , Hemidactylus sp., Eutropis carinata (Schneider) , Eutropis macularia (Blyth) , and Lygosoma punctata (Gmelin) , Ophisops beddomei (Jerdon) , Monilesaurus rouxii (Duméril & Bibron) and Calotes versicolor (Daudin) .
| BNHS |
Bombay Natural History Society |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.