Aeolothrips fukushimensis, Masumoto & Okajima, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4564.2.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:37ACBBFC-D8EF-42D5-A0C0-AD4F6DE228C6 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5931421 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C628CF31-4110-FF80-FF36-911D08C4FA4D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Aeolothrips fukushimensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Aeolothrips fukushimensis View in CoL sp. n.
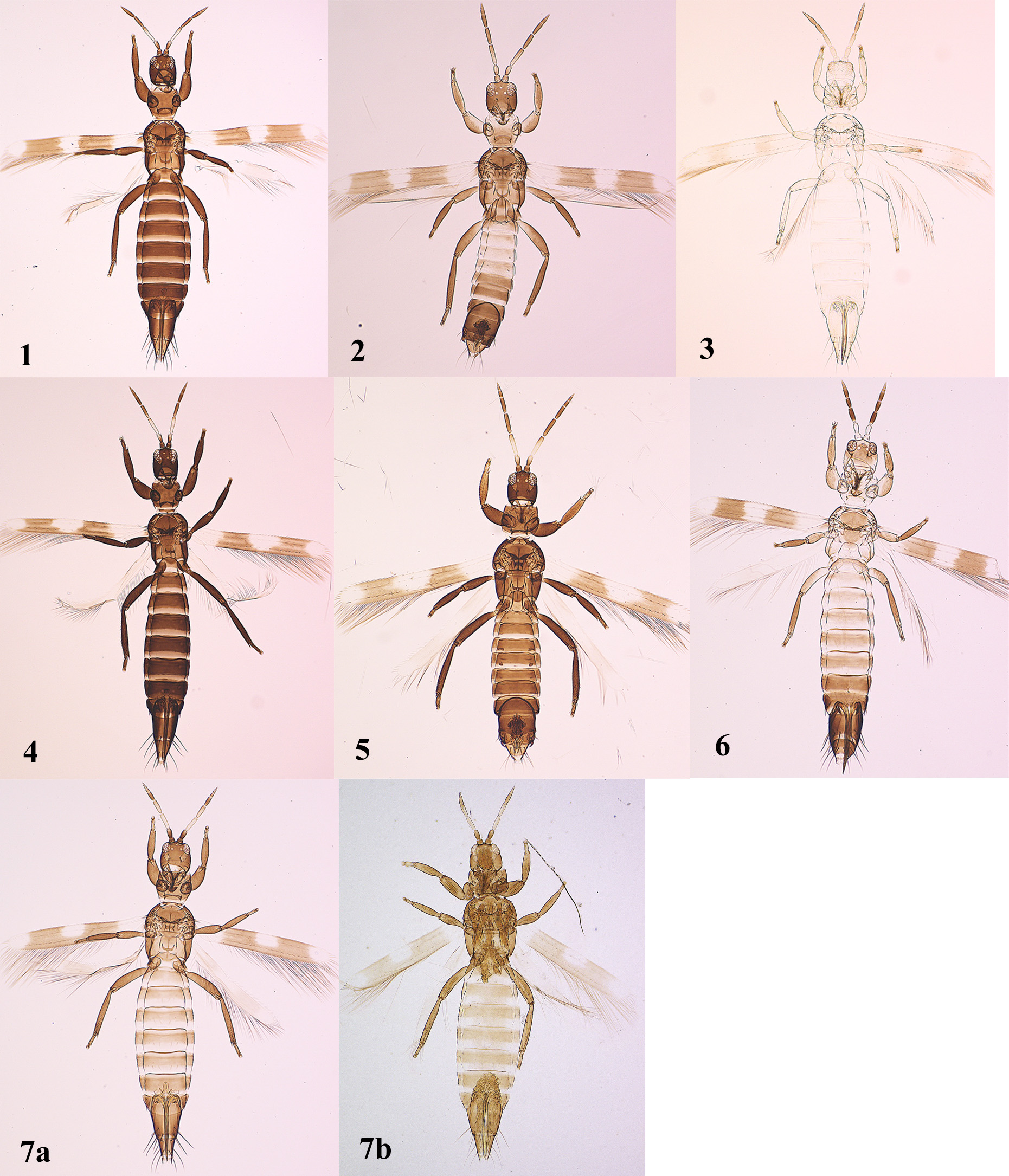
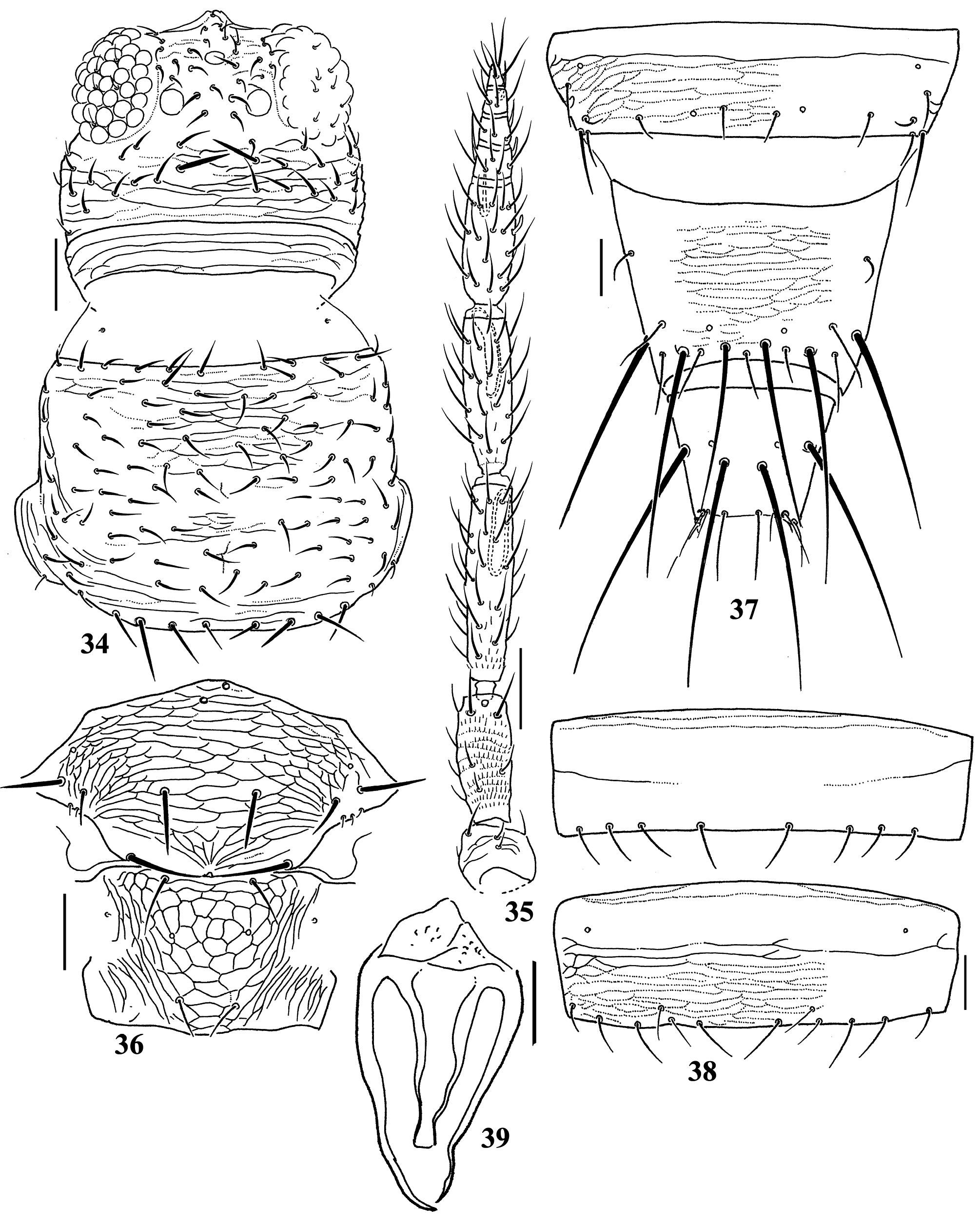
( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–7 , 16 View FIGURES 15–24 , 34–39 View FIGURES 34–39 )
Female macroptera. Body almost uniformly yellowish white, abdominal tergites II–VII slightly shaded anterolaterally, sternites IV–VII dark at middle of antecostal ridges ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–7 ); antennal segments I–III yellow but III shaded in distal third, IV–VIII brown; fore wings with two separate pale brown bands at submedian and subdistal areas, vein not shaded on pale area, clavus pale; all legs yellowish white; prominent body setae pale. Head 0.7–0.8 times as long as wide, arched at cheeks, sculptured with anastomosing striae on dorsal surface ( Fig. 34 View FIGURES 34–39 ), ventrally with 18 pairs of setae between compound eyes, a pair of mid-lateral setae beside compound eyes slightly longer than median setae; paired interocellar setae slightly stout, middle postocular setae much stouter than others. Antennal segment III and IV with sensoria 0.4 and 0.6 times as long as length of the segments, respectively, V subequal in length to combined length of VI–IX with ventral sensorium having oval base ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 34–39 ). Antennal segments I to IX ratio length/width as follows: 0.9–1.0, 2.4, 3.9–4.0, 2.9, 2.2, 0.8–0.9, 0.9–1.0, 1.0, 1.5–1.7. Pronotum 0.7–0.8 times as long as wide, weakly sculptured, with more than 60 discal setae and 2 pairs posteromarginal S2 and S3 setae distinctly longer and stouter than discal setae ( Fig. 34 View FIGURES 34–39 ). Mesonotum with lateral setae slightly shorter than median pair of setae; anteromedian CPS present. Metascutum with equiangular or transverse reticulations medially; CPS present ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 34–39 ). Abdominal tergites II–VIII weakly sculptured with anastomosing striae throughout ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 34–39 ); tergite I without posteromedian CPS, tergite IX with minor setae between S1 setae; sternites III–VI each with 6, 6 (rarely 7), 8 (rarely 7), 8 posteromarginal setae and all setae arising at posterior margin, VII with two pairs of accessory setae near posterior margin between S1 and S2 setae, interval between S1 setae subequal to interval between S1 and S2 setae ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 34–39 ). Spermatheca weak and with no internal teeth ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 34–39 ).
Measurements (holotype female in microns). Body length 1970; head length 131, width 178, compound eye length 55, width 48; pronotal median length 138, width 195; metascutal median length 80; fore wing length 900, width at middle 80; abdominal tergite IX length 130, tergite X length 90; ovipositor length 405. Antennal segments I–IX length (width) as follows: 37 (35), 65 (28), 93 (24), 73 (25), 56 (25), 15 (19), 15 (16), 13 (13), 13 (8).
Male. Unknown.
Specimens studied. Holotype female, JAPAN, Honshu, Fukushima Pref., Kitashiobara-mura, nr. Oguninuma, on flowers of Salix sp. [ Salicaceae ], 3.v.2007, M.Masumoto. Paratypes: 2 females collected together with holotype. 1 female, same place and plant, 4.v.2007, M.Masumoto. The holotype and paratypes are deposited in TUA.
Remarks. This species and A. setosus described below are very similar to each other in having the body and legs largely pale, and the head and pronotum with stout setae. However, they are distinguished in the key above. Moreover, S1 setae on abdominal tergite IX, and the major setae on X appear to be shorter than in the later species: in fukushimensis , S1 on IX 100–130µm (mean 118.6±8.7, n=8), S1 and S2 on X 156–173µm (mean 163.1±6.0, n=8) and 160–179µm (mean 169.6±6.5, n=8), respectively, where as in setosus S1 on IX 125–156µm (mean 141.6±8.7, n=30), S1 and S2 on X 163–188µm (mean 174.8±7.1, n=30) and 176–199µm (mean 188.3±7.1, n=30), respectively. A. fukushimensis is similar to A. novus from India ( Bhatti, 1970) and A. intactus from central Asia, U.S. S.R ( Pelikan, 1963) by having uniformly yellow body. These two species, however, have no long and stout setae on head and pronotum. Moreover, A. fukushimensis is slightly similar to A. bhatti from Iran ( Alavi et al., 2015). But the body is almost uniformly yellow and the head and pronotum bear stout setae, whereas bhattii has the head and abdominal segments IX and X dark, and all setae on the head and pronotum are small.
Etymology. In reference to type locality.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |