Asbestopluma rickettsi, Lundsten & Reiswig & Austin, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3786.2.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9C3B70D0-4092-4ACC-A134-1CEC31E232C7 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4913434 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C6548780-9D39-FFCA-E3EF-FDBBF577FC03 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Asbestopluma rickettsi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Asbestopluma rickettsi View in CoL sp. nov.
Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 & 6 View FIGURE 6
Type material. Holotype: CASIZ 192771 ; MBARI specimen D472-A13b; collected by ROV Doc Ricketts May 19, 2013, northwest of La Jolla, California, USA; latitude: 32.90433, longitude: -117.78224, depth 1020 m . Paratype: CASIZ 192772 ; MBARI specimen D472-A13a; collected by ROV Doc Ricketts May 19, 2013, northwest of La Jolla, California, USA; latitude: 32.90433, longitude: -117.78224, depth 1020 m .
Type locality. Northwest of La Jolla , California, USA .
Etymology. Named in honor of Edward F. Ricketts, marine biologist and ecologist made popular as ‘Doc Ricketts’ in John Steinbeck’s Cannery Row. He is best known as co-author of Between Pacific Tides, a pioneering book on intertidal ecology. Coincidentally, the type specimens were collected by MBARI’s ROV Doc Ricketts.
Diagnosis. Branching Cladorhizidae with three size classes of megascleres and three microscleres including an acanthose tylostyle, and sigma of one size class, and palmate anisochelae of two size classes.
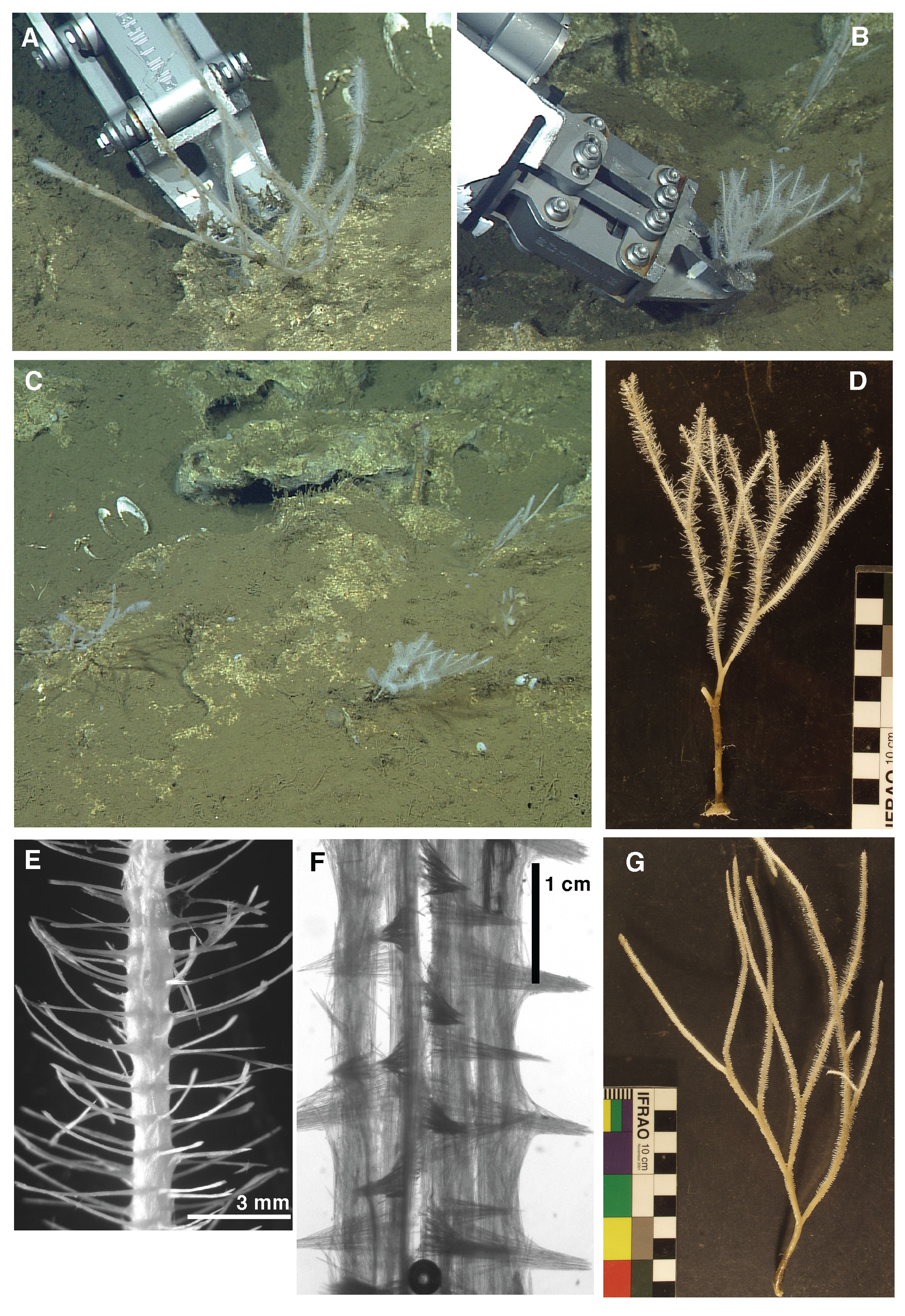
Description. An arborescent, dichotomously-branching sponge with bottle-brush arrangement of filaments ( Fig. 5A–C View FIGURE 5 ). Holotype: Sponge is 21.78 cm tall and 12.38 cm wide ( Fig. 5D View FIGURE 5 ). At the base, the stalk is 4.5 mm wide and branches all taper to approximately 1 mm in width distally. Filaments are 0.9–1.2 mm in length ( Fig. 5E–F View FIGURE 5 ). Attached to hard substrate via conic holdfast disk, 1.26 cm in width. Paratype: Filaments are 1.5 – 5 mm in length. Sponge is 21.78 cm tall and 12.38 cm wide ( Fig. 5G View FIGURE 5 ). At the base, the stalk is 3.4 mm wide and branches all taper to approximately 1 mm width distally. Sponge is white in situ and in preserved state.
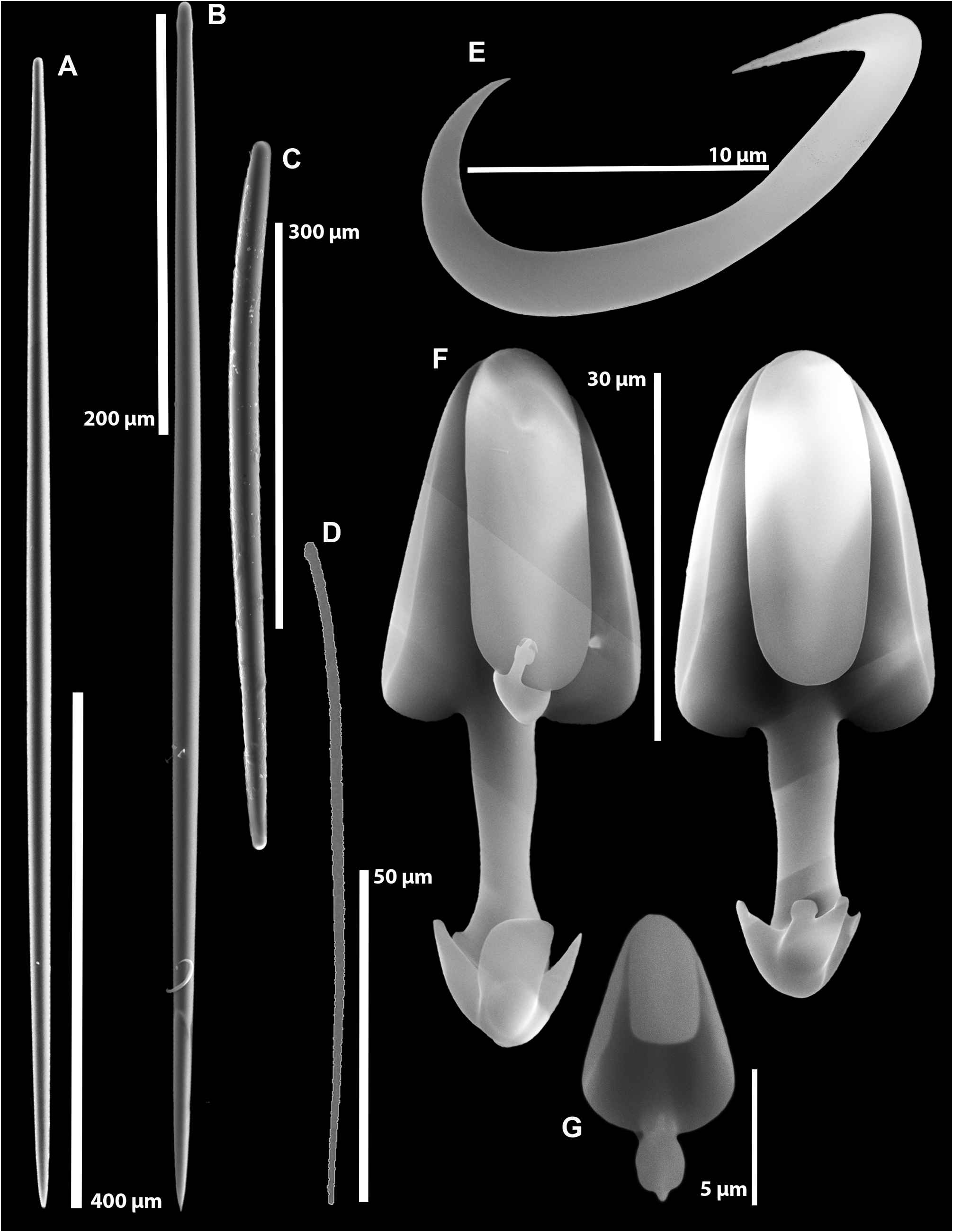
Spicules. Large styles 1 ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6 , Table 1 View TABLE 1 ) fusiform, straight, often with pointed end rounded, in axes of branches and stem: L 956 ± 50 µm (n=50), W 19.8 ± 1.8 µm (n=50). Large styles 2 ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ), fusiform, straight or slightly curved, in filaments and their inserts in branch axes: L 642.6 ± 62.6 µm (n=50), W 14.0 ± 2.5 µm (n=66). Large styles to anisostrongyles 3 ( Fig. 6C View FIGURE 6 ), fusiform, thick, strongly bent, mainly in basal cone: L 555 ± 53 µm (n=50), W 26.6 ± 6.4 µm (n=50). Microacanthotylostrongyle ( Fig. 6D View FIGURE 6 ) thin, rough, mostly curved, occurs in basal cone and sparsely throughout branch axes: L 102.6 ± 9.8 µm (n=50), W 1.5 ± 0.4 µm (n=50). Sigma ( Fig. 6E View FIGURE 6 ) without profile discontinuity near ends (not clearly sigmancistroid), rare throughout specimen: L 17.06 ± 1.3 µm (n=50). Anisochelae 1 ( Fig 6F View FIGURE 6 ) robust, palmate with wide lateral wings and narrow tooth slightly wider than shaft: L 53.5 ± 5.3 µm (n=50), occurs rarely throughout. Anisochelae 2 ( Fig. 6G View FIGURE 6 ) palmate head, foot with frontal tooth bearing two broad lateral flukes, lateral wings short and never meet the frontal tooth; narrow lower foot shaft looks like a short blunt spur but true spur is lacking; occurs abundantly throughout the specimen: L 9.3 ± 0.7 µm (n=50).
Habitat and associated fauna. Asbestopluma rickettsi was observed and collected while surveying a chemosynthetic community in a low-oxygen basin off southern California, northwest of La Jolla. Twenty-one individuals were observed in an area of active fluid flow. The substrate was composed of outcrops of authigenic carbonate with a thin sediment veneer. Other organisms observed include vesicomyid clams, siboglinid tube worms, and mats of flocculent bacteria. Average depth of observation was 1031 m (±48.5; n=21), oxygen concentration was low at 0.33 ml/L (±0.001; n=21), and temperature averaged 3.93 °C (±0.02; n=21). No evidence of crustacean prey capture was observed in A. rickettsi . This specimen was collected in an area with an active chemosynthetic community and was found to be utilizing methane-oxidizing bacteria as a food source (V. Orphan, California Institute of Technology, pers. comm.). It remains to be seen whether these bacteria are true symbionts, as has been demonstrated in one other species of Cladorhizidae .
Remarks. Asbestopluma rickettsi differs from A. formosa ( Vacelet, 2006) , in that it lacks the characteristic embryo-containing branching enlargements, it does not have fan shaped branches divided dichotomously three or four times in a single plane with terminal branches being long, thin, and parallel, and it does not have microstrongyles. It differs from A. desmophora ( Kelly and Vacelet, 2011) as it lacks both desmas and sigmancistras. This new species differs from A. bitrichela ( Lopes et al., 2011) in a lack of desmas and anchorate/ unguiferate anisochelae. Asbestopluma rickettsi differs from A. delicata ( Lopes et al., 2011) in absence of microstrongyles and palmate isochelae. It differs from A. magnifica ( Lopes et al., 2011) considerably in size ( A. magnifica is ~50% longer), in size classes of megascleres ( A. rickettsi has larger styles), a larger anisochelae 1 size (~ 34 µm vs. 52 µm) and presence of large alae of large anisochelae. Asbestopluma rickettsi differs from A. furcata ( Lundbeck, 1905) in having larger megasclere style sizes. A comparison of spicule data for all known Asbestopluma species through 2011 is published in Lopes et al., (2011). A. rickettsi differs from A. monticola in that it has two size classes of anisochelae.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.