Trypoxylon, FROM
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.15298/rusentj.32.1.07 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C85FDE4D-EF19-FFF3-FCF3-A685FAD4D6C4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Trypoxylon |
| status |
|
KEY TO THE SPECIES OF TRYPOXYLON FROM View in CoL NORTHERN VIETNAM
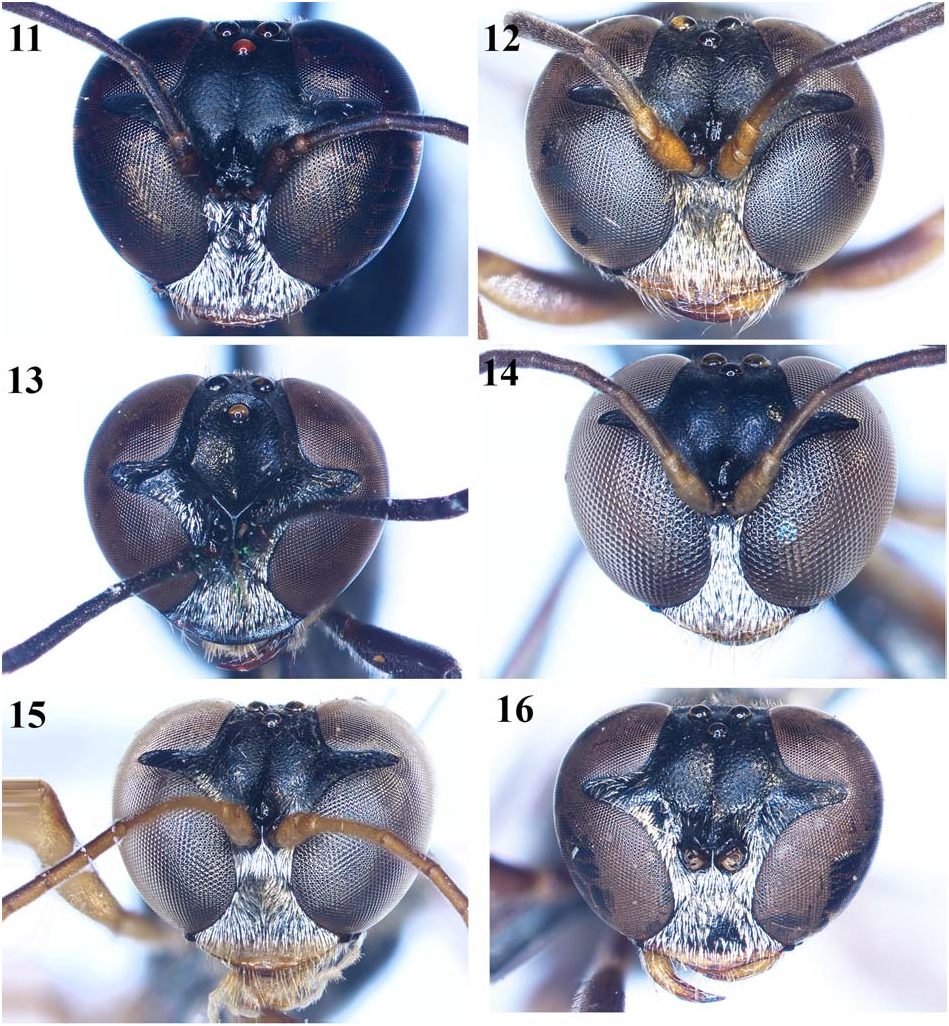
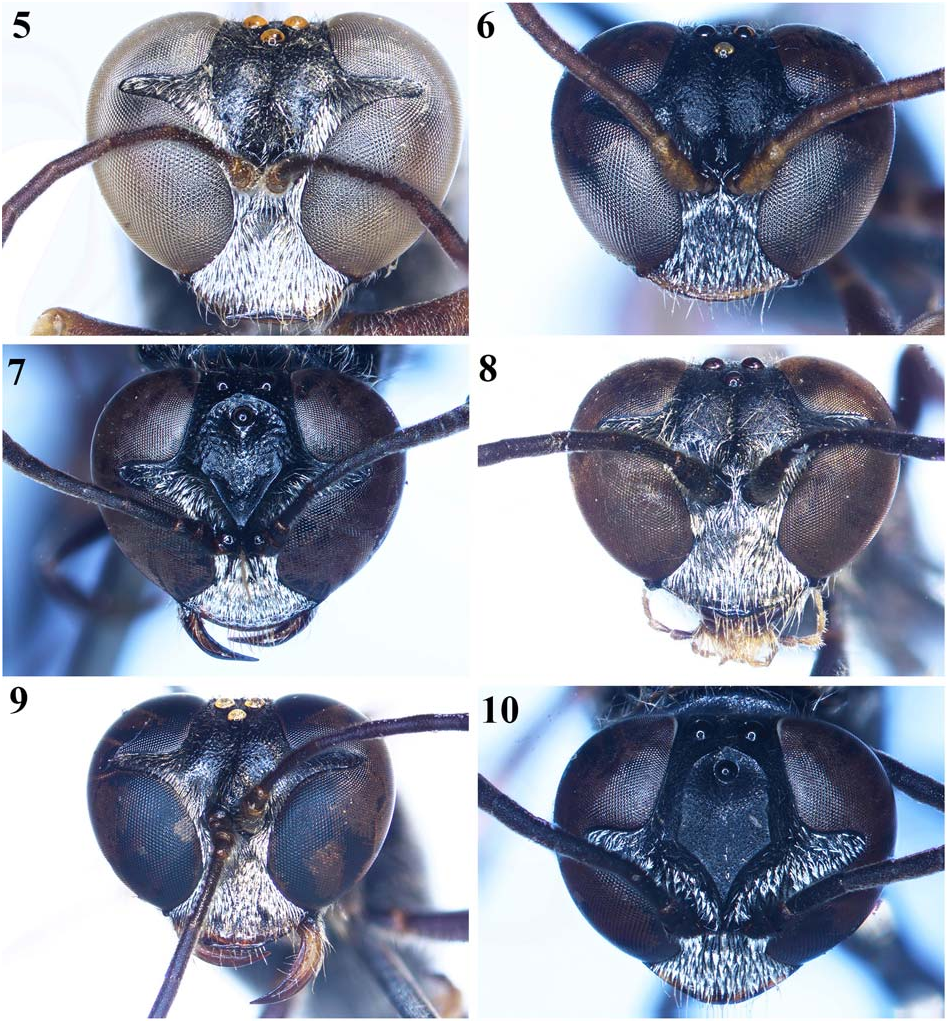
1. Frons with shield ( Figs 7, 10 View Figs 5–10 , 13 View Figs 11–16 ); gaster wholly black ( Figs 19 View Figs 17–20 , 26, 28 View Figs 25–30 ) .......................................................... 2
— Frons without shield ( Figs 1, 3 View Figs 1–4 , 5–6, 8–9 View Figs 5–10 , 11–12, 14–16 View Figs 11–16 ); gaster wholly or partly ferruginous ( Figs 17–18, 20–25, 27, 29–30 View Figs 17–20 View Figs 21–24 View Figs 25–30 ) .................................................................... 4
2. Frontal shield with upper lateral carinae broadly interrupt- ed, dorsal carina distinctly present, lower carina straight ( Fig. 7 View Figs 5–10 ); pronotum undiscoloured posteriorly; body length 12–13 mm (female) ......... T. interruptum Tsuneki, 1978 View in CoL
— Frontal shield with upper lateral carinae uninterrupted, lower carina curved or lightly zigzag ( Figs 10 View Figs 5–10 , 13 View Figs 11–16 ); pronotum discoloured or undiscoloured posteriorly; body length 8–12 mm ............................................................ 3
3. Frontal shield with lower area nearly flat, upper area deeply depressed around fore ocellus ( Fig. 10 View Figs 5–10 ); interantennal transverse carina without hole above ( Fig. 10 View Figs 5–10 ); mesoscutum weakly microcoriaceous; body length 8 mm (female) .............................. T. pileatum F. Smith, 1856 View in CoL
— Frontal shield with lower area conspicuously inclined ( Fig. 13 View Figs 11–16 ); interantennal transverse carina with deep hole above ( Fig. 13 View Figs 11–16 ); mesoscutum fairly and sparsely punctate; body length 11–12 mm (female) .................................... ............................................ T. thaianum Tsuneki, 1961 View in CoL
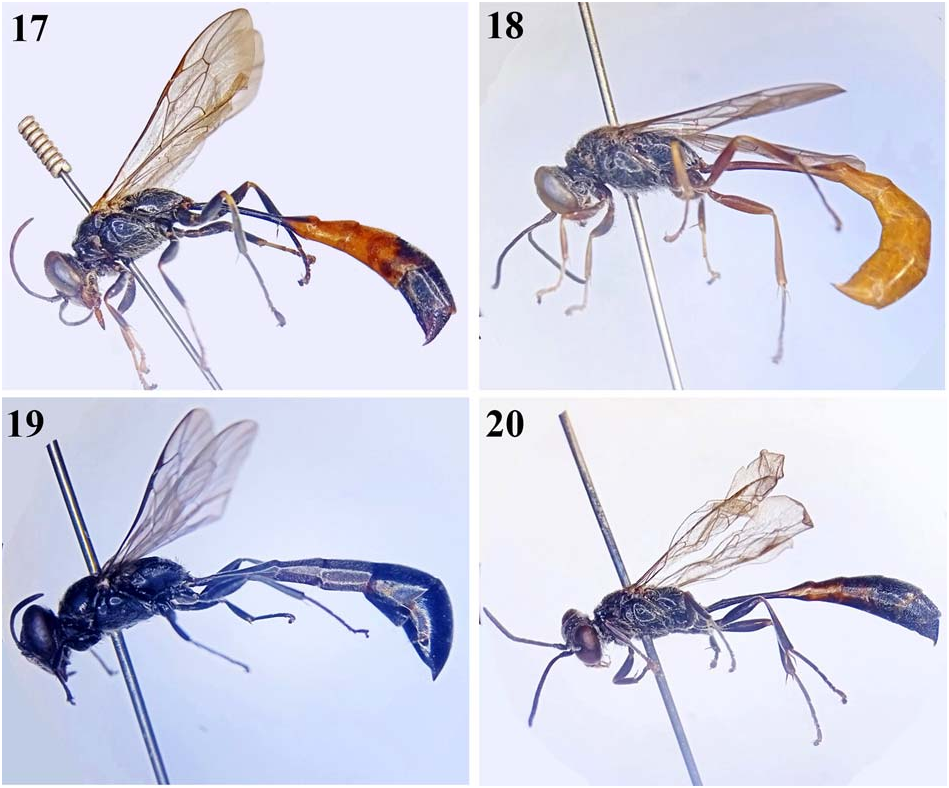
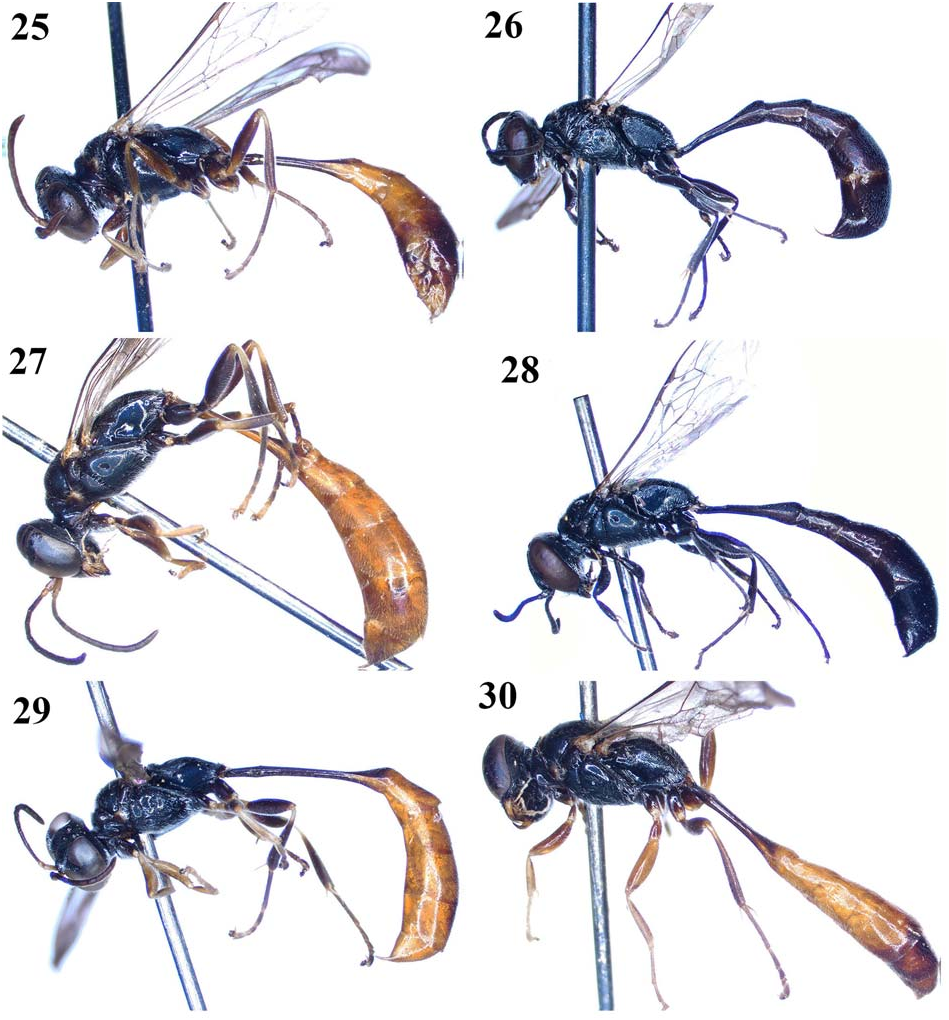
4. Gaster black with median area (from apex of petiole to gastral segment 3 or from apex of petiole to base of gastral segment 4) ferruginous ( Figs 17, 20 View Figs 17–20 , 22–23 View Figs 21–24 ) ............. 5
— Gaster wholly or from apex of petiole to last gastral segment ferruginous ( Figs 18 View Figs 17–20 , 21, 24 View Figs 21–24 , 25, 27, 29–30 View Figs 25–30 ). ............. 8
5. Clypeus conspicuously protruded mediapically ( Fig. 8 View Figs 5–10 ); gaster from apex of petiole to gastral segment 3 ferruginous lateraldorsally, darkly marked dorsally and ventrally ( Fig. 20 View Figs 17–20 ); legs black ( Fig. 20 View Figs 17–20 ); IODs = 1:1 ( Fig. 8 View Figs 5–10 ); body length 11–14 mm (both female and male) ..................... ........................................... T. orientale Cameron, 1904 View in CoL
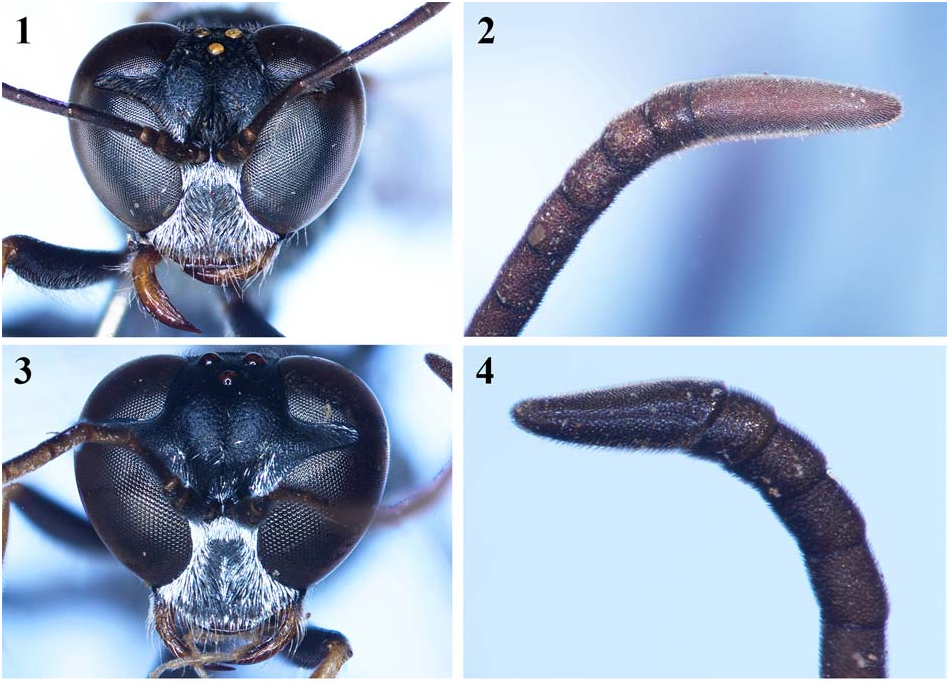
— Clypeus round mediapically ( Figs 1, 3 View Figs 1–4 , 11 View Figs 11–16 ); gaster from apex of petiole to base of gastral segment 4 ferruginous ( Figs 17 View Figs 17–20 , 22–23 View Figs 21–24 ); legs black, with ferruginous spots ( Figs 17 View Figs 17–20 , 22–23 View Figs 21–24 ); IODs varied ( Figs 1, 3 View Figs 1–4 , 11 View Figs 11–16 ) ..................... 6
6. SAT with apical margin roundly curved and acutely edged, produced over PAFs; head lightly convergent at lower part (nearly round); IODs = 3:2 ( Fig. 11 View Figs 11–16 ); flagellum black ( Figs 11 View Figs 11–16 , 23 View Figs 21–24 ); body length 12–13 mm (female) ... ........................................... T. prominens Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
— SAT without apical margin roundly curved and acutely edged; head conspicuously convergent at lower part; IODs = 5:4 or 4:3 ( Figs 1, 3 View Figs 1–4 ); flagellum brown beneath ( Figs 17 View Figs 17–20 , 22 View Figs 21–24 ); body length 10–19 mm ......................... 7
7. Vertex conspicuously depressed ( Fig. 1 View Figs 1–4 ); anterior margin of clypeus moderately curved ( Fig. 1 View Figs 1–4 ); IODs = 5:4 ( Fig. 1 View Figs 1–4 ); in males, flagellomere 11 in lateral view distinctly tapering ( Fig. 2 View Figs 1–4 ); body length 14–19 mm (both female and male) ...................................... T. bicolor F. Smith, 1856 View in CoL
— Vertex undepressed ( Fig. 3 View Figs 1–4 ); anterior margin of clypeus conspicuously curved ( Fig. 3 View Figs 1–4 ); IODs = 4:3 ( Fig. 1 View Figs 1–4 ); in males, flagellomere 11 in lateral view not tapering, lightly curved medially; body length 9–14 mm (both female and male) ................................ T. petiolatum F. Smith, 1858 View in CoL
8. Gaster wholly ferruginous ( Fig. 27 View Figs 25–30 ); scape, pedicel and base of flagellomere 1 yellowish brown ( Fig. 12 View Figs 11–16 ); body length 11–12 mm (female). T. rufigaster Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
— Gaster from apex of petiole to last gastral segment ferruginous ( Figs 18 View Figs 17–20 , 21, 24–25, 29–30 View Figs 21–24 View Figs 25–30 ); scape, pedicel and base of flagellomere 1 black or ferruginous ( Figs 5–6, 9 View Figs 5–10 , 14–16 View Figs 11–16 ) .......................................................................... 9
9. PAF shallow ( Fig. 9 View Figs 5–10 ); IODs = 10:9 ( Fig. 9 View Figs 5–10 ); legs mostly black ( Fig. 21 View Figs 21–24 ); body length 17 mm (female) ................ ................................... T. paeninsulicola Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
— PAF deep ( Figs 5–6 View Figs 5–10 , 14–16 View Figs 11–16 ); IODs varied; legs mostly ferruginous or pale brown ( Figs 18 View Figs 17–20 , 24–25, 29–30 View Figs 21–24 View Figs 25–30 ) .. 10
10. IODs = 3:1 ( Fig. 14 View Figs 11–16 ); clypeus distinctly pointed mediapically ( Fig. 14 View Figs 11–16 ); scape and pedicel pale brownish ( Fig. 14 View Figs 11–16 ); body length 9 mm (female) ........ T. tomi Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
— IODs varied; clypeus nearly round or largely truncated mediapically; scape and pedicel ferruginous or black ... .................................................................................... 11
11. Anterior oblique flattened area of SAT with distinct hole ( Fig. 16 View Figs 11–16 ); gastral segment 5 and 6 darkly red ( Fig. 30 View Figs 25–30 ); IODs = 5:4 ( Fig. 16 View Figs 11–16 ); body length 10 mm (male) ......... ................................................... T. yumi Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
— Anterior oblique flattened area of SAT without hole; gastral segment 5 and 6 ferruginous ( Figs 18 View Figs 17–20 , 24–25 View Figs 21–24 View Figs 25–30 ); IODs = 3:2 or 10:9 ( Figs 5–6 View Figs 5–10 , 15 View Figs 11–16 ) ............................ 12
12. Antennae wholly and legs mostly ferruginous ( Fig. 24 View Figs 21–24 ); ASR roundly inclined to PAF; hairs whitish brassy; body length 13 mm (female) .... T. varipilosum Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
— Antennae except scape and pedicel black ( Figs 5–6 View Figs 5–10 ); legs mostly pale brown or ferruginous ( Figs 18 View Figs 17–20 , 25 View Figs 25–30 ); ASR steeply inclined to PAF; hairs silvery ....................... 13
13. Clypeus largely truncated mediapically ( Fig. 5 View Figs 5–10 ); scape and pedicel brownish black; legs largely ferruginous ( Fig. 18 View Figs 17–20 ); IODs = 3:2 ( Fig. 5 View Figs 5–10 ); body length 16 mm (female). ............................................... T. cagrum Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
— Clypeus round mediapically ( Fig. 5 View Figs 5–10 ); scape and pedicel ferruginous; legs pale brown to black ( Fig. 25 View Figs 25–30 ); IODs = 5:4 ( Fig. 6 View Figs 5–10 ); body length 9 mm (male) ........................... .......................................... T. fulviventre Tsuneki, 1979 View in CoL
| SAT |
Angelo State University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |