Chimaera supapae, Ebert & Krajangdara & Fahmi & Kemper, 2024
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.26107/RBZ-2024-0006 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A78E445D-B869-4301-ADBF-C66F6D9CDB7C |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C87E87EB-3D2C-FF84-FC3A-FB5EFDEBBEB9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Chimaera supapae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chimaera supapae , new species
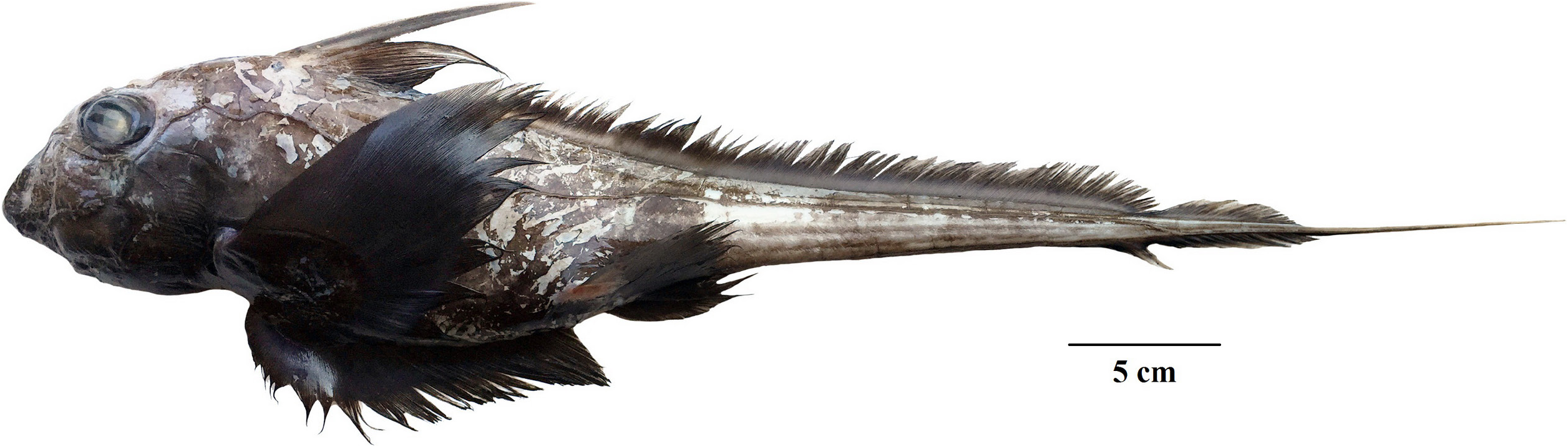
Andaman shortnose chimaera ( Figs. 1–3 View Fig View Fig View Fig ; Table 1)
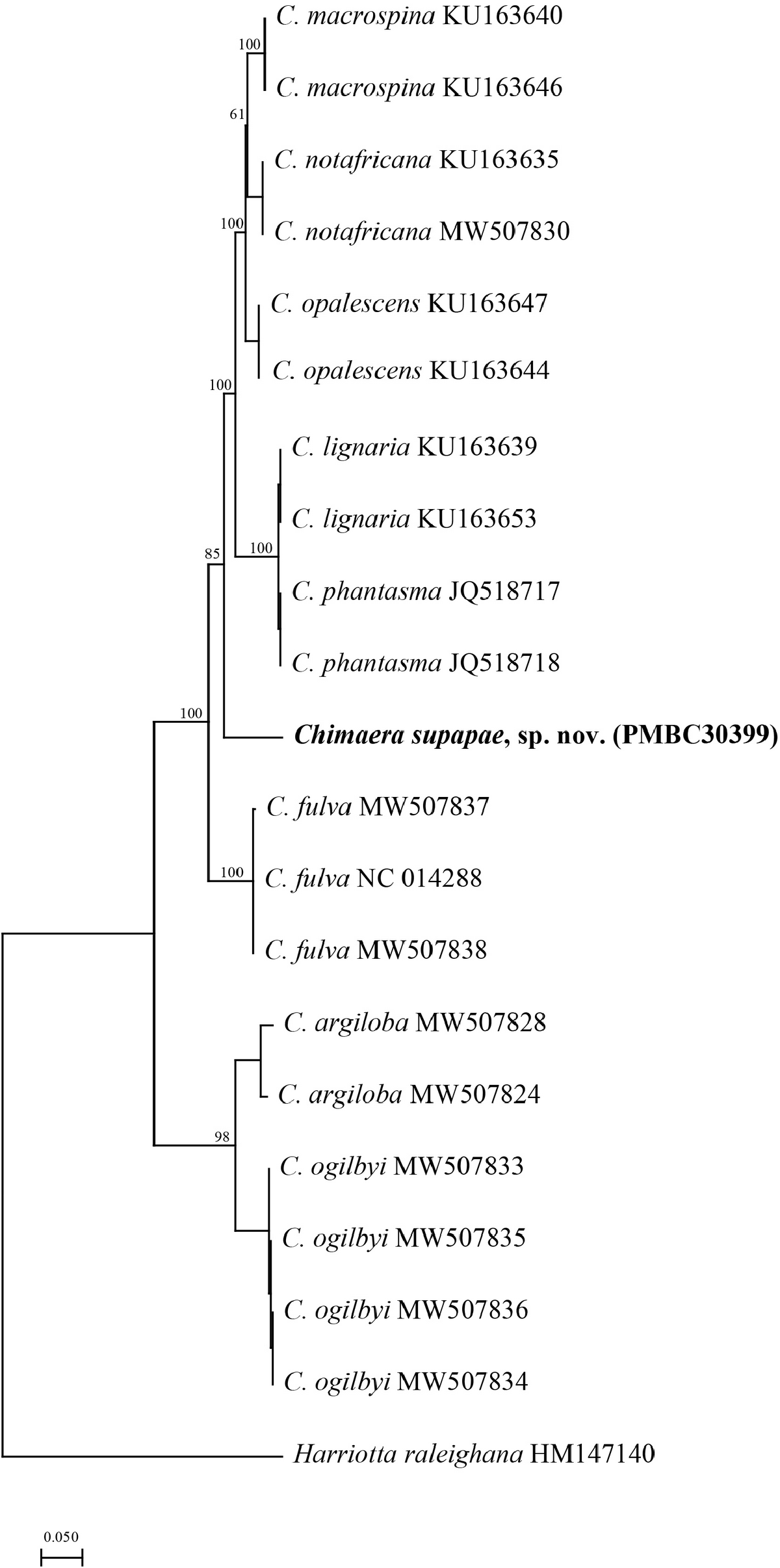
Chimaera aff. macrospina View in CoL : Krajangdara et al. 2021: 219, fig. 4.
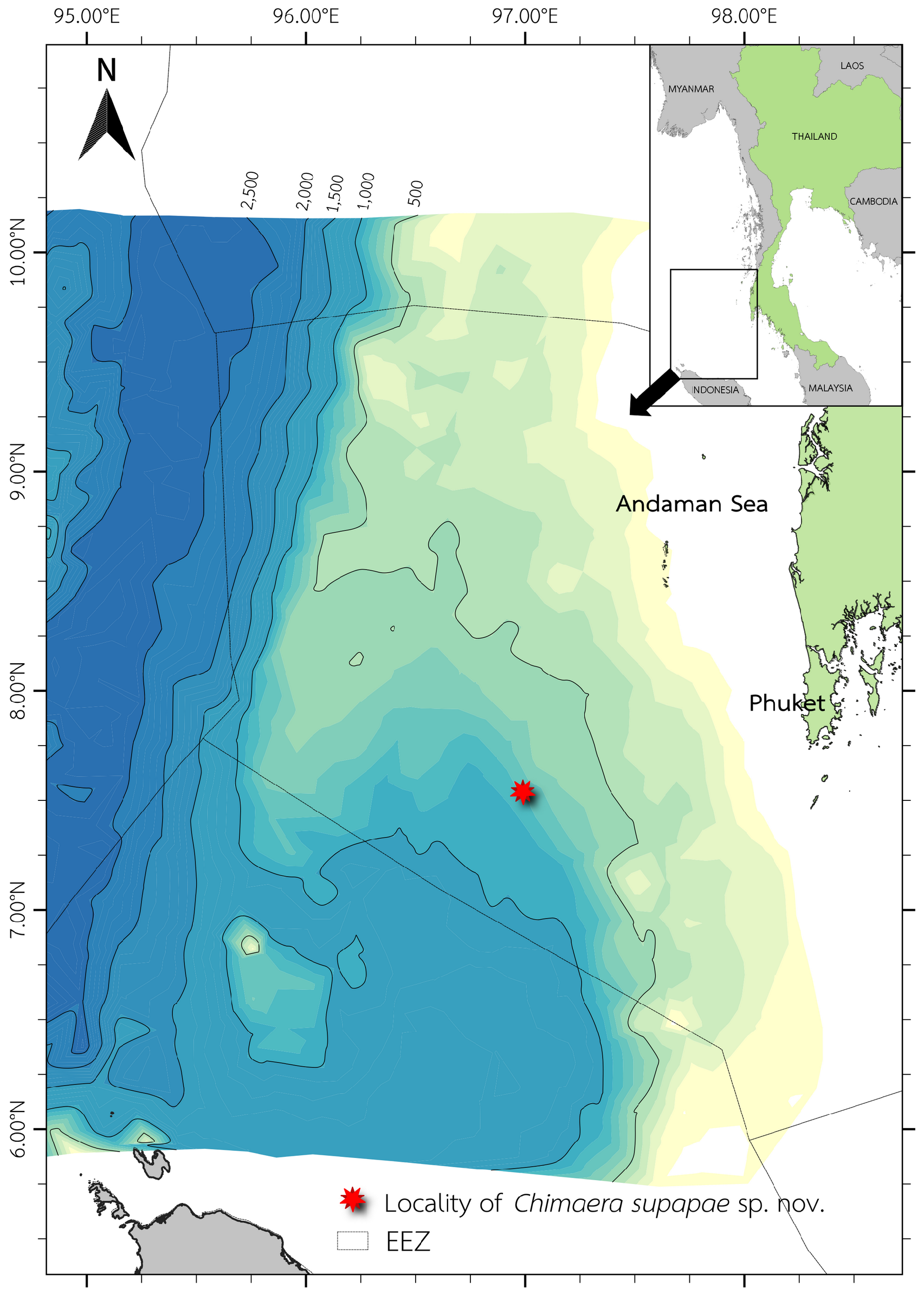
Holotype. PMBC 30399, 508 mm TL, 276 mm BDL, immature male, Andaman Sea of Thailand, 07.54° N, 96.99° E, bottom trawl between 772 m – 775 m, collected by I. Jithlang, 11 October 2018. GoogleMaps
Diagnosis. Chimaera supapae can be distinguished from all other chimaeroids by the following combination of characters: massive head with a short snout; eyes relatively large, horizontally oval, eye length 32.2% head length; thin and relatively long trunk 40% BDL, deciduous skin; uniformly dark brown, without any spots or stripes; preopercular and oral lateral line canals sharing a common branch; posterior margin of pectoral fins slightly convex; long dorsal spine 27 % BDL, longer than first dorsal fin.
Description. The holotype, 276 mm BDL, is an immature male ( Fig. 2 View Fig ). Morphometric proportions of the holotype are provided in Table 1. Body elongated, tapering to a caudal fin with a filamentous tail. Head moderate sized, length 30.4% BDL, 0.2 times precaudal length, height relatively tall 24.3% BDL, postorbital head compressed. Snout short, bluntly pointed; preorbital snout 0.1 times body length, preoral length 2.7 times in head length. Trunk slightly compressed, tapering slightly to pectoral fin origins before tapering somewhat rapidly to tail, and continuing into caudal filament. Tail moderately long making up 54.0% precaudal length, short trunk, 40.2% precaudal length. Eyes large, length 9.8% BDL making up about one-third (32.2%) head length, height 0.6 times its length, and horizontally oval, located in posterior half of head, preorbital length 33.2% head length.
Lateral lines on head open, preopercular and oral lateral line canals share a common branch connecting to the infraorbital canal on both sides of the head. Mouth narrow and short, upper labial folds and furrows prominent, upper and lower furrows deep. Body slightly compressed, lateral line canal originating at the level of upper eye, forming a notch anteriorly below the dorsal spine origin; lateral line on trunk relatively straight, not undulating and running along to caudal filament. Skin smooth without denticles, strongly deciduous.
Pectoral fins are relatively broad and long, semi-falcate, with slightly convex on both anterior and posterior margins; its anterior length is 36.2% of body length and reaches slightly posterior to the origin of pelvic fin. Pelvic fins are moderately broad and large, paddle-shape with angular apex; its maximum length is about 2.1 times in pectoral maximum length. First dorsal fin is relatively long with a narrow base; its base 15.6% body length, and its height 4.6 times in body length. Dorsal spine is straight and long, taller than the soft first dorsal fin; its length more than 1.3 times first dorsal fin height and 1.1 times in head length. The origin of the dorsal spine is just over the pectoral fin origin; anterior margin of spine forms a narrow keel, not serrated; posterior distal margin of the spine is finely serrated. First dorsal is shortbased and longer than preorbital length, posterior margin of fin slightly concave. Second dorsal fin is moderately low and prolonged, the upper margin relatively straight with similar height; its height 3.5 times in first dorsal fin height; its base 79.7% body length, and 5.1 times the first dorsal fin base. First dorsal and second dorsal fins are well separated, connected with a low membrane; the interdorsal space 5.8% body length. Anal fin present, the position of anal fin insertion is slightly behind the second dorsal fin insertion. Anal fin is separated from the lower caudal fin lobe by a deep notch; its base 14.5% lower caudal fin lobe. The lower caudal fin is slightly longer than the upper lobe, its length about 1.1 times but the height is similar to the upper lobe, origin slightly posterior to the upper caudal fin origin. Tail filament longer than caudal fin lobes, 1.7 times the length of upper caudal lobe, and 34.1% body length. The immature male specimen has a pair of undeveloped and short claspers, equipped with poorly developed pre-pelvic tenaculae. Denticles on the medial edge are not prominent and a frontal tenaculum is not fully developed.
Measurements Holotype
Pectoral fin anterior margin (P1A) 35.1
Pectoral fin base (P1B) 8.7
Pelvic fin max. length (P2L) 17.0
Pelvic fin anterior margin (P2A) 15.9
Pelvic fin base (P2B) 5.8
First dorsal fin anterior margin (D1A) 23.9
First dorsal fin base (D1B) 15.6
First dorsal fin height (D1H) 21.7
Dorsal spine height (DSA) 27.2
Second dorsal fin base (D2B) 79.7
Maximum height of anterior of second dorsal 6.2
fin (D2AH)
Maximum height of posterior of second dorsal 6.2
fin (D2 PH)
Second dorsal fin length (D2L) 81.2
Second dorsal fin inner margin (D2I) 2.9
Anal fin length (ANL) 6.5
Anal fin base (ANB) 3.3
Anal fin height (ANH) 4.7
Dorsal caudal margin length (CDM) 19.9
Ventral caudal margin length (CVM) 22.8
Caudal filament length (CFI) 34.1
Total caudal length (CTL) 54.0
Maximum height of upper lobe of caudal fin 2.9 (CDH)
Maximum height of lower lobe of caudal fin 2.9 (CVH)
Origin of D1 to origin of P1 (D1P1) 17.0
Origin of D1 to origin of P2 (D1P2) 39.5
Origin of D2 to origin of P1 (D2P1) 23.2
Origin of D2 to origin of P2 (D2P2) 22.5
Colouration. Prior to preservation body and head uniformly dark brown (whitish where skin deciduous), without any noticeable spots, stripes, or longitudinal striation along tail. Head darker brown on cheek area between lower posterior of eyes and pectoral fin origin, and extending ventrally across mouth. All fins are a slightly darker brown than body trunk. Eye an iridescent green. After preservation deciduous skin, body, and tail filament a uniform pale brown, head has somewhat darker colour than body trunk, and all fins uniformly dark brown.
Distribution. Known only from the type location at 07.54° N, 96.99° E in the Andaman Sea off Thailand, eastern Indian Ocean at 772–775 m depth ( Fig. 1 View Fig ).
Etymology. The epithet supapae is named to honor the late Professor Supap Monkolprasit (1934–2013), for her extensive work on the cartilaginous fishes of Thailand. She was the Dean of Faculty of Fisheries, Kasetsart University, Thailand during the years 1991–1995, but devoted her entire life to the study of cartilaginous fishes in Thailand.
| PMBC |
Phuket Marine Biological Centre |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Chimaera supapae
| Ebert, David A., Krajangdara, Tassapon, Fahmi & Kemper, Jenny M. 2024 |
Chimaera aff. macrospina
| Krajangdara T & Fahmi & Ebert DA & Chaorattana C & Khudamrongsawat J 2021: 219 |