Megastigmus pistaciae Walker, 1871
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.181647 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5661045 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CA3DF744-9003-FFC7-FF4A-F8951DAFFB53 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Megastigmus pistaciae Walker, 1871 |
| status |
|
Megastigmus pistaciae Walker, 1871 View in CoL
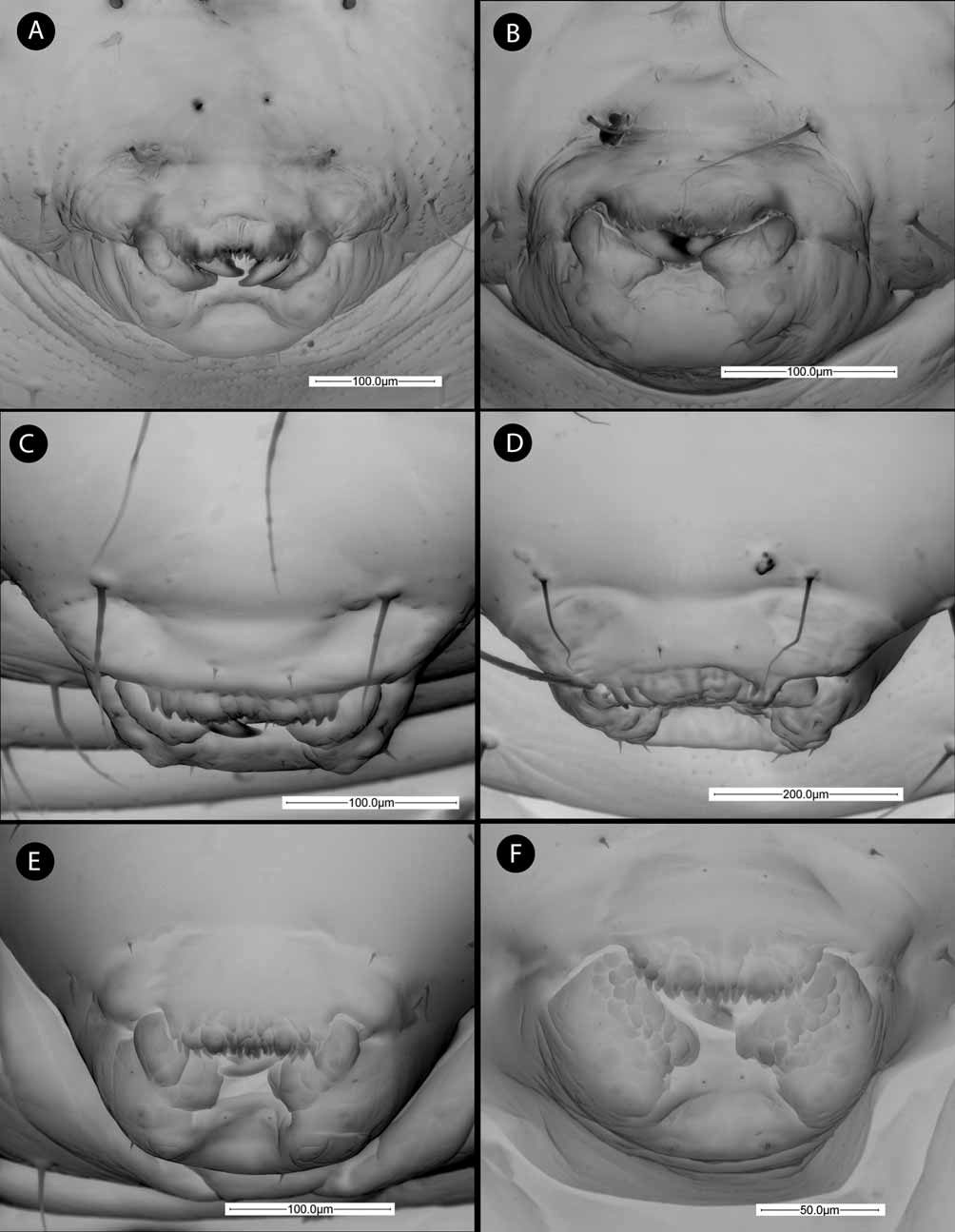
Description: Body length: 1.7 mm, body width, 0.9 mm. Body (ventral view) ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 E) composed of head and 13 body segments. T1–T3 have no more than 12 short setae, shorter than half length of thoracic segment; the abdominal segments appear almost bare, with only three or four setae visible on the last body segments. The integument is mostly smooth, with the first body segment slightly rugose in the anterior view. Head (anterior view) ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 E) more or less hemispherical or slightly trapezoidal, smooth and approximately as high as wide. Antennae small and button-like, situated at a middle distance between the vertex and the clypeus. Upper margin of vertex entire, lacking medial groove or medial frontal pit. Vertex setae, antero-medial setae of the antennal area, genal setae, latero-clypeal setae and hypostomal setae are present and short, measuring less than 1/5 of the separation of the antennae. Vertex setae situated at the margin of vertex, with a distance between vertex setae 1.5 times the distance between antennae; antero-medial setae of the antennal area situated clearly above antennae, with a distance between antennal setae of 0.4 times the distance between antennae. Clypeal setae very short, less than 0.1 as long as distance between antennae. Hypostomal setae 0.4 x as long as distance between antennae. Clypeus large, its anterior margin indistinct and unmarked. Labrum rectangular, with three irregular rows of flaps or lobes, which are more dense and acute on the anterior margin ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 E). Maxillae well differentiated from labium, divided into three more or less discernable parts or lobes; two pairs of maxillary palps more or less visible ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 E). Labium slightly depressed, with two pairs of labial setae visible. Mandibles hidden by the labrum, with only the tip of first tooth being visible. The right mandible ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 C) has four acute, triangular teeth.
Remarks: The larva of M. pistaciae is similar to the larvae of the parasitic species of Megastigmus in shape and general appearance. However, the larva of M. pistaciae can be readily distinguished by its narrower head, the entire vertex, and the absence of a medial frontal pit. Furthermore, the shape of the labrum and the maxillae is different and the relative length of setae on the head and thoracic segments is shorter than in the Megastigmus species associated with oak gall-wasps.
Biology: The larva of M. pistaciae feed only within seeds of Pistacia species ( Anacardiaceae ). Megastigmus pistaciae reproduces by thelythokous parthenogenesis, distributed from the western Mediterranean to Afghanistan and China, and has also been introduced in Mexico and USA ( Roques & Skrzypczynska 2003).
Materials examined. ex seeds of Pistacia lentiscus , Spain, Cádiz, Aguilillas, 15/x/2005. JLN-A leg. (n=1).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |