Antomicron chinensis, Zhai & Wang & Huang, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2020.1781948 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D12E87C2-9321-6818-FEC5-442EFB6E6953 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Antomicron chinensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Antomicron chinensis sp. nov. ( Figures 4–6 View Figure 4 View Figure 5 View Figure 6 and Table 1)
Type material
One male and one female were obtained . Holotype male is on slide number JZW(42–8) . Paratype female is on slide number JZW(51–26) . ( The holotype specimen is deposited in the Marine Biological Museum of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, and the paratype specimen is deposited in the biodiversity laboratory of Liaocheng University.)
Type locality and habitat
Specimens were collected from the surface 0–2 cm sublittoral silt sediment in Jiaozhou Bay (JZW-4: 36.176°N, 120.312°E) GoogleMaps . Water depth of 9.5 m.
Etymology
The species is named after China, the country of the type locality .
Measurements
All measurement data are given in Table 1.
Description
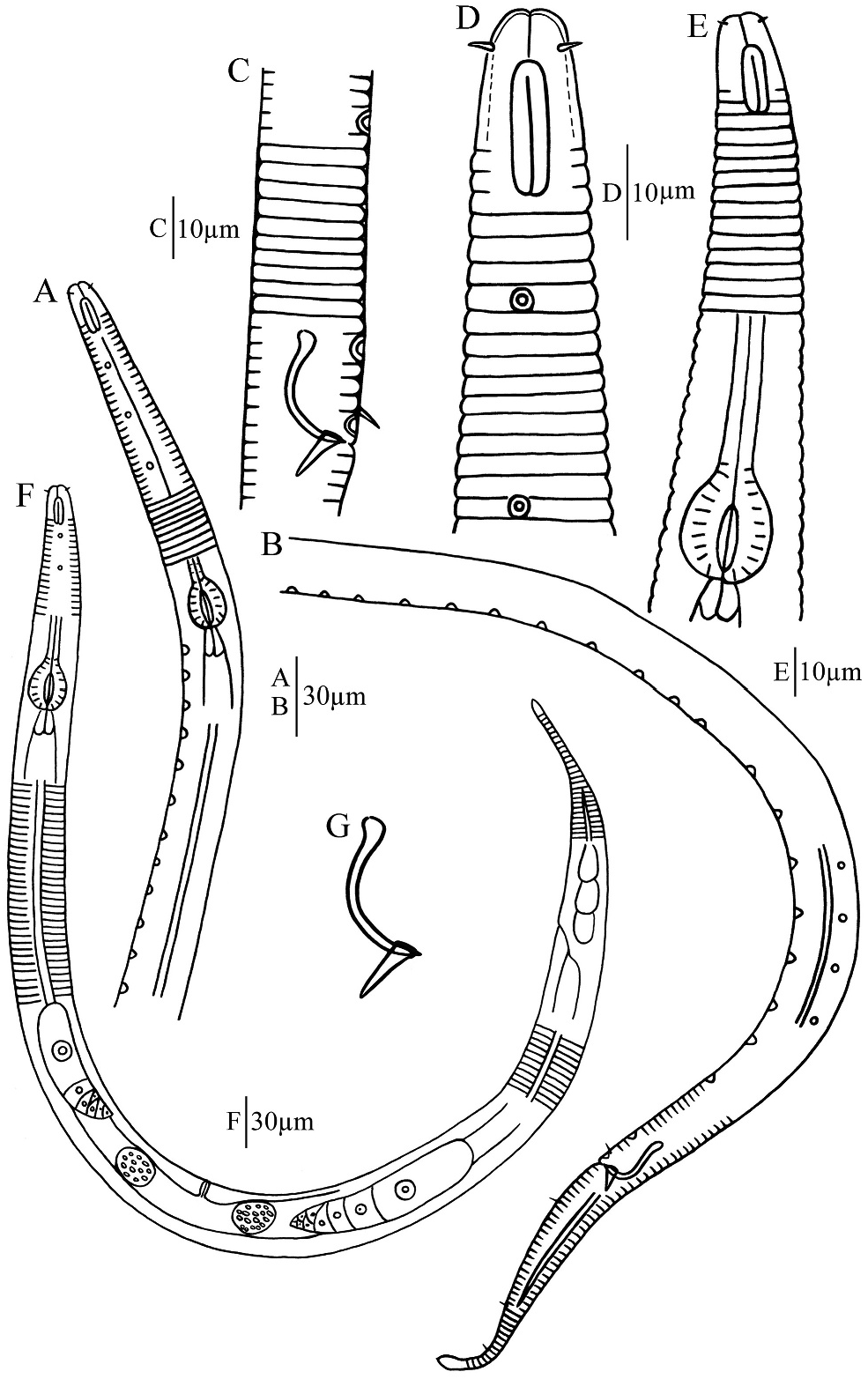
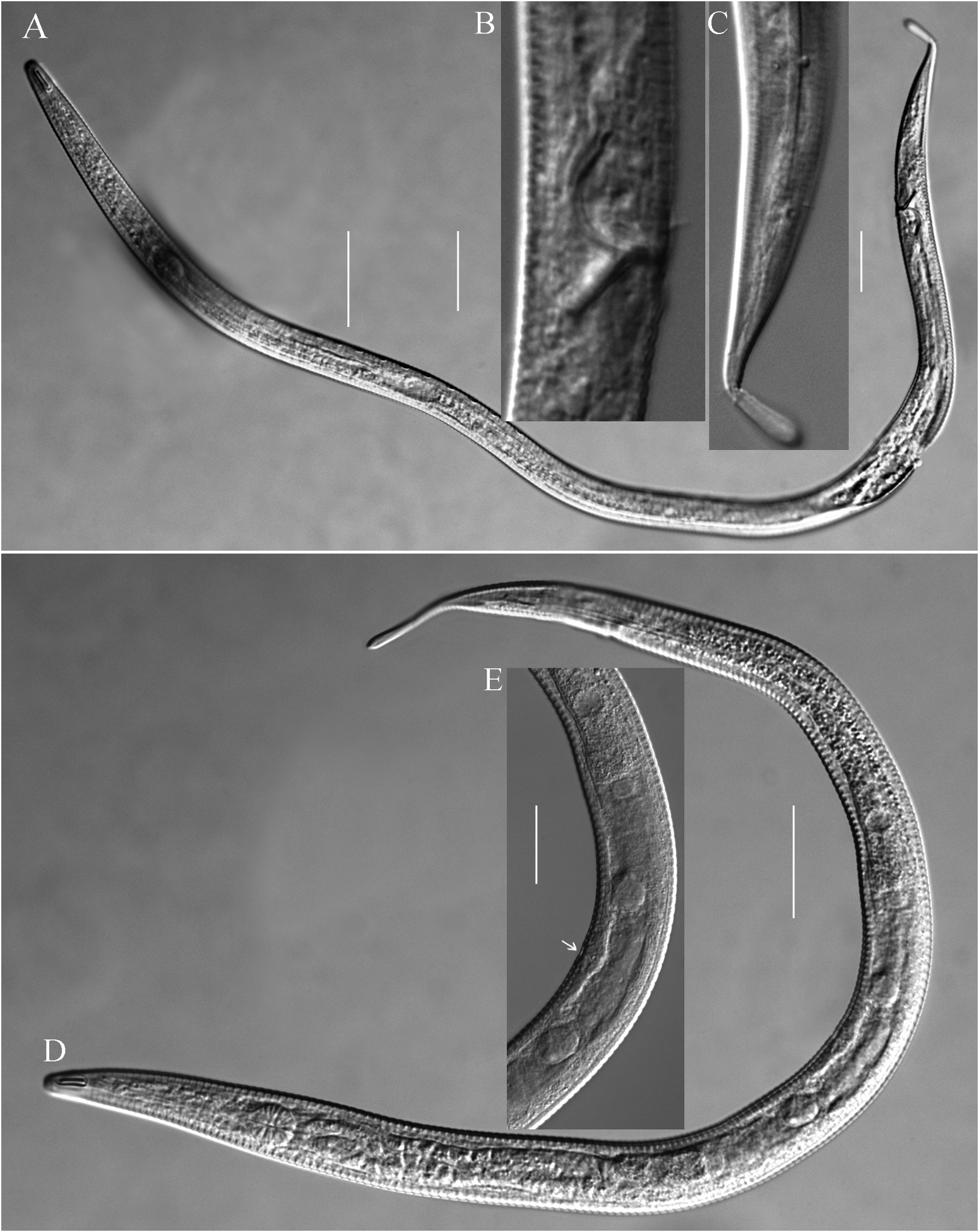
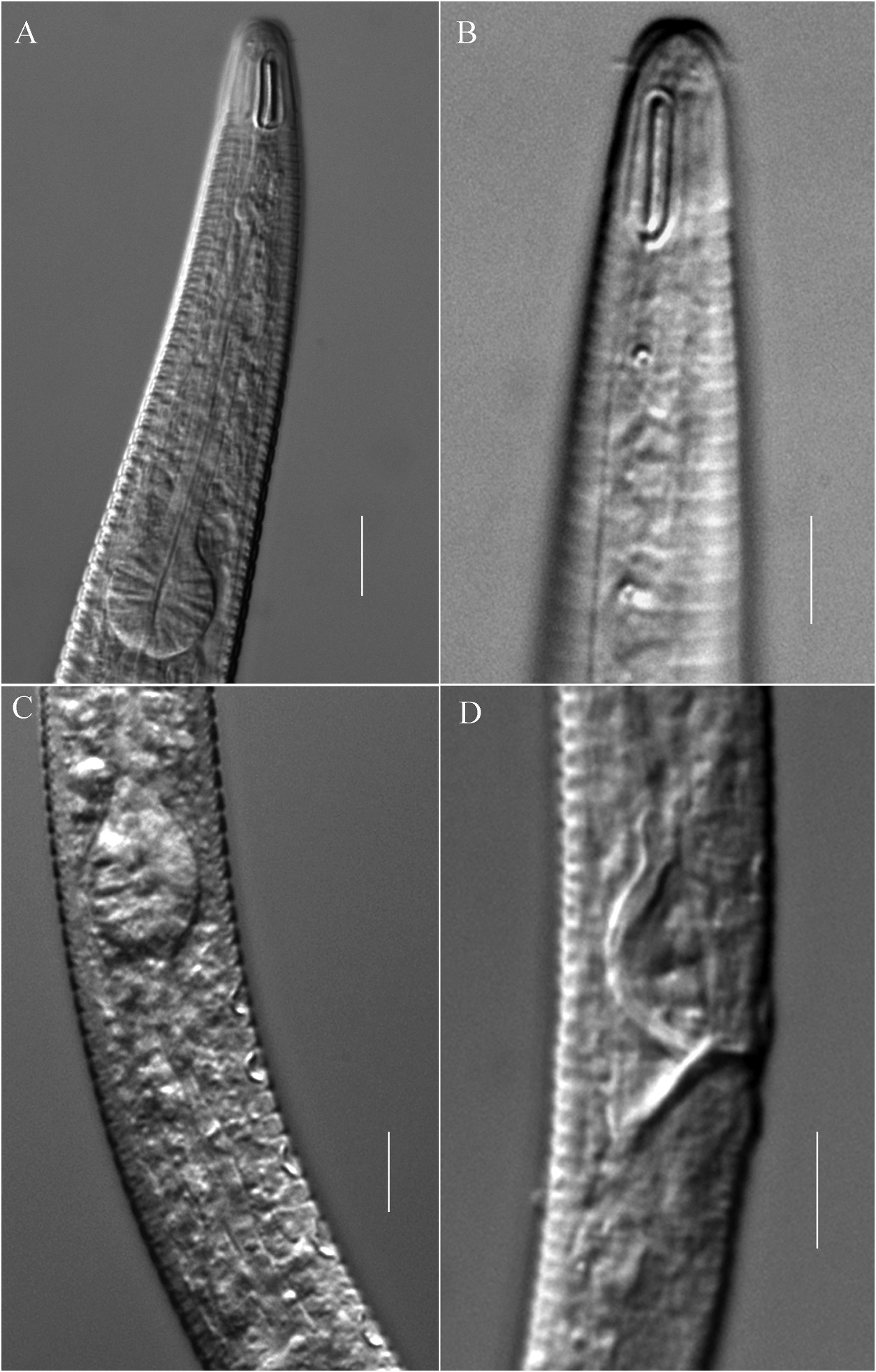
Male. Body slender. Cuticle annulated; annuli 3 µm wide on the whole body, without ornamentation. Lateral field present, consists of single ala, 3 µm wide at mid-body; originating at base of amphideal fovea and extending to position of two-thirds of tail length. Labial region bluntly rounded, continuous with body contour. Cephalic capsule distinct. Anteriormost body annule located at back edge of amphideal fovea. Inner and outer labial sensilla indistinct. Cephalic sensilla setiform, 2 µm long. Amphidial fovea elongate, loop shaped, 13 µm long and 3.5 µm wide (3.7 times as long as it is wide), 7 µm from the anterior end. Nerve ring and secretory-excretory system not observed. Buccal cavity minute. Pharynx cylindrical with oval basal bulb, with strong cuticular internal lining. Cardia conical, embedded in intestine. Tail conico-cylindrical, gradually narrowing to posterior third cylindrical portion, 6.2 cloacal body diameters long. Unstriated tail tip swollen. Caudal setae scattered, 3 µm long. Three caudal glands present. Spinneret distinct.
Reproductive system diorchic. Spicules slender, slightly inverted S-shaped, with cephalated proximal end and tapered distal end, 1.5 cloacal body diameter long. Gubernaculum rectangular, with a straight dorsal caudal apophysis, 9 µm long. Accessory apparatus composed of only 33 alveolar supplements, extending anteriorly to the level of pharyngeal base, without tubular supplements. Anteriormost alveolar supplement located at just posterior pharyngeal bulb base, 150 µm from anterior end, posteriormost alveolar supplement just in front of cloaca. A ventral precloacal seta located just anterior to posteriormost supplement, 3 µm long.
Female. Body slightly wider (a = 25.5 vs 37.9 in male). Reproductive system didelphic, with two opposed and reflexed ovaries. Oviduct a narrow tube. Two oval saclike spermathecae located on each side (anterior and posterior) of vulva. Spermathecae filled with oval spermatozoa. Uterus a wide tube. Vagina strongly cuticularised and straight, 0.25 times vulval body diameters long. Vulva located at mid-body.
Differential diagnosis and discussion
Antomicron chinensis sp. nov. is particularly characterised by loop-shaped amphideal fovea; male with 33 alveolar supplements, without tubular supplement; short cephalic setae; slightly curved slender spicules with cephalated proximal end and tapered distal end, rectangular gubernaculum with a slender dorsal caudal apophysis. The new species is the only species in Antomicron in which males have only alveolar supplements, no tubular supplements. It is easily identified by loop-shaped amphideal fovea, only alveolar and no tubular supplements. In body length and loop-shaped amphideal fovea, the new species is similar to Antomicron alveolatum Villares and Pastor de Ward, 2011 and Antomicron lorenzeni Holovachov, 2012 , but the males of both the latter species all have tubular supplements. Further differences between Antomicron chinensis sp. nov. and other congeners can be found in Table 2 and the key below.
Updated key to species of Updated key to species of Antomicron Cobb, 1920
(based on Holovachov 2012 and Villares and Pastor, 2011)
1. Males with both tubular and alveolar supplements .................................................................. 2
- Males with only tubular or only alveolar supplements......................................................... 7
2. Number of alveoli more than 25 (29–41) ...................................................................................... 3
- Number of alveoli less than 15 (8–14) ........................................................................................ 5
3. Males with 3 tubular supplements, alveolus in pharyngeal region .......................................... ................................................................................. A. alveolatum Villares and Pastor de Ward, 2011 - Males with 5–9 tubular supplements; alveolus posterior to pharyngeal region ....... 4
4. Amphid doughnut shaped, 29–36 alveoli ........................................................................................... ......................................................................... A. intermedius Gagarin and Nguyen Vu Thanh, 2005 - Amphid loop shaped, 41 alveoli.......................................................... A. holovachovi sp. nov.
5. Males with 5 tubular supplements ................................................ A. profundum Vitiello, 1971 - Males with 2–3 tubular supplements .......................................................................................... 6
6. Males with 3 tubular supplements, cephalic sensilla papilliform ............................................... ........................................................................................................................... A. pratense Lorenzen, 1966 - Males with 2 tubular supplements, cephalic sensilla setiform ................................................
............................................................................................................. A. lorenzeni Holovachov, 2012 7. Males with only alveolar supplements .................................................................. A. chinensis sp. nov. - Males with only tubular supplements.......................................................................................... 8
8. Males with 15 tubular supplements, body length exceeds 1.3 mm ......................................... ............................................................................................... A. quindecimpapillatus Holovachov, 2012 - Males with 10 or fewer tubular supplements, body length is less than 1.1 mm ........ 9
9. Males with 10 tubular supplements, amphid loop-shaped... A. profundum Vitiello, 1971 - Males with 4–8 tubular supplements, amphid doughnut-shaped ................................ 10
10. Males with 6–8 tubular supplements, amphid oval in shape A. pellucidum Cobb, 1920 - Males with 4 tubular supplements, amphid elongate in shape ..............................................
................................................................................ A. elegans ( de Man, 1922) De Coninck, 1965
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Antomicron chinensis
| Zhai, H. X., Wang, C. M. & Huang, Y. 2020 |
A. chinensis
| Zhai & Wang & Huang 2020 |
A. lorenzeni
| Holovachov 2012 |
A. quindecimpapillatus
| Holovachov 2012 |
A. elegans ( de Man, 1922 )
| De Coninck 1965 |