Podonomus amarali, Pinho & Shimabukuro, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4402.3.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5DD153C9-13F9-4B51-BFBE-0022624CBFC1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5986717 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D25B6A5B-CB4B-FF8C-BAC9-3F7FD3C26BF6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Podonomus amarali |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Podonomus amarali View in CoL sp. n.
( Figures 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
Type material. Holotype: male adult, Brazil, Santa Catarina State, São Joaquim National Park, Grão-Pará, Serra do Corvo Branco , 28°03’21” S 49°22’00” W, 1241m a.s.l., 10.ix.2016, seepage, LC Pinho & AP Amaral ( MZSP) GoogleMaps . Paratypes: One female with pupal exuvia and 3 males, same data as holotype GoogleMaps . 1 male, same data as holotype except for 23.iv.2016. One pupa with larval exuvia, one female with pupal exuvia, one male pharate pupa and 7 larvae GoogleMaps , same data as holotype except for 15.viii.2017, LC Pinho. Two pupae GoogleMaps , same data as holotype except for 29.ix.2016, LC Pinho ( MZSP, UFSC, UFSCar) GoogleMaps
Derivatio nominis. The specific epithet honours our friend André Pereira do Amaral, who helped us in fieldwork.
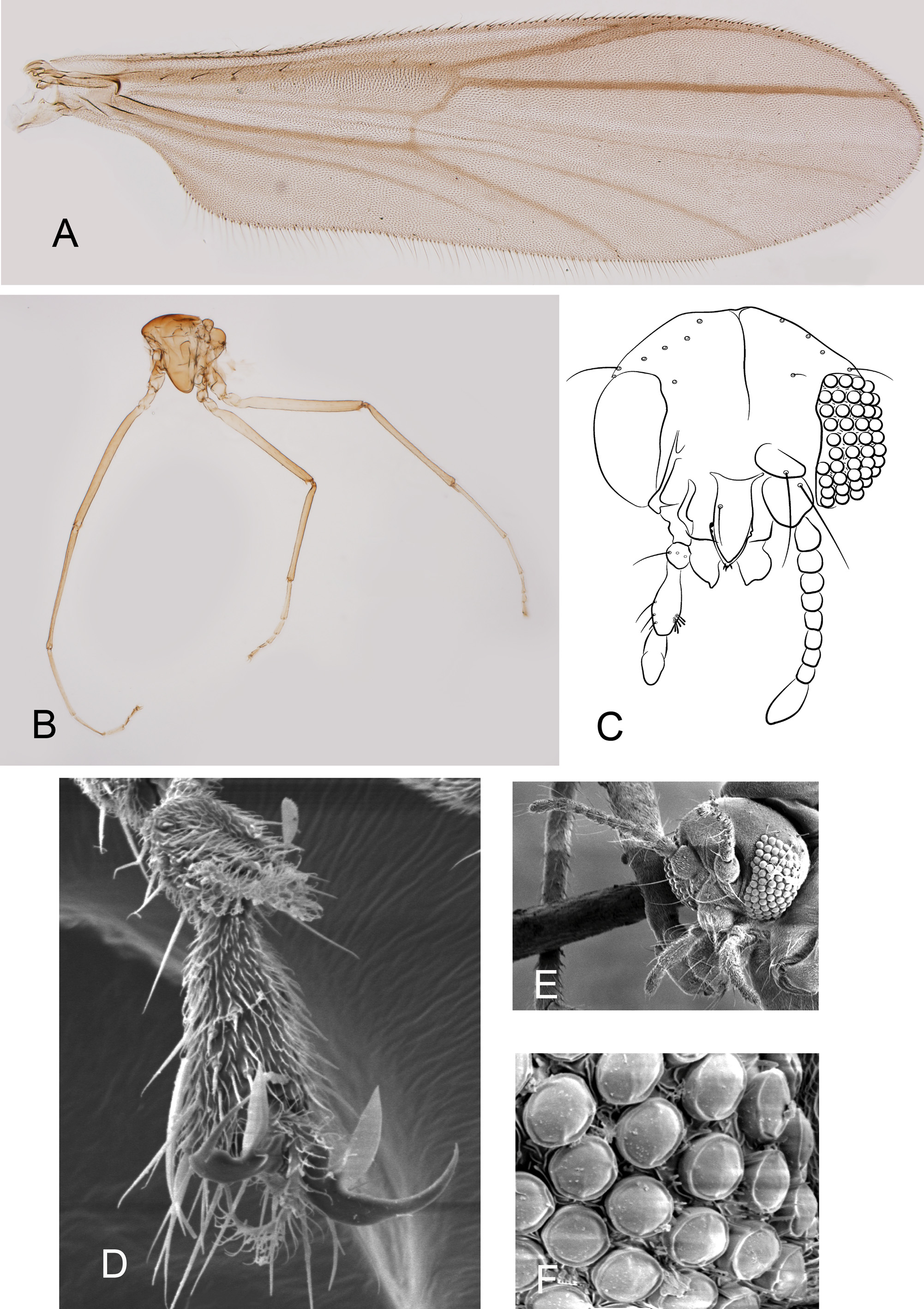
Diagnostic characters. The new species can be separated from other Podonomus species by combination of the following characters: Male. Antenna with reduced number of flagellomeres (9–10) and few setae; enlarged distal portion in R1 vein, similar to that in female wings; gonostylus with a long and slender apical lobe, tapering in the tip; t-setae in apical lobe often absent, when present, long and lanceolate; and absence of a subapical lobe; 1–3 p-setae present, long, grouped and parallel to the apical lobe. Female. Cercus simple, oval; and setae on gonapophysis VIII mostly trifid. Pupa. Very large lamella on sternite II; a strongly curved and frontally directed lateral process on abdominal segment VII; and anal lobe with only 5–6 wavy and 2 distal slender setae.
Description. Male (n = 5). Total length 1.59–1.88, 1.76 mm. Wing length 1.20–1.41, 1.33 mm. Total length/ wing length 1.28–1.39, 1,32. Wing length/length of profemur 0.62–0.67, 0.64.
Colouration. Blackish brown; wings light brown; legs uniformly dark brown, except for trochanter, and the very base of femora pale.
Head ( Figure 1c,e,f View FIGURE 1 ). Antenna with 9–10 flagellomeres, AR 0.18–0.31, 0.21. Ultimate flagellomere 40–50, 42 µm. Temporal setae 8–11, 9. Clypeus with 0–2, 1 setae. Palp segment lengths in µm (II–V): 12–37, 26; 25–72, 61; 25–70, 56; 30–52 (2). Third palpomere with 3–9, 7 sensilla clavata in apical third; 10–17, 14 µm long. Eyes pubescent, oval, without dorsal extension.
Thorax ( Figure 1b View FIGURE 1 ). 10–14, 12 acrostichals in mid scutum, 7–8, 8 dorsocentrals, 4–5, 5 prealars, 1–2, 2 supraalars; scutellum with 1–4, 2 dispersed setae, humerals 2–4, 3.
Wing ( Figure 1a View FIGURE 1 ). Membrane with a patch of perpendicular setae on r cell . VR 1.0–1.05, 1.04. Costal extension 50–75, 63 µm long. R with 6–9, R4+5 with 1–2, 1 apical setae. Remaining veins, brachiolum and squama bare. R1 vein distally swollen.
Legs. Spur of fore tibia 20–27, 23 µm long, spurs of mid tibia 17–27, 22 µm and 25–30, 27 µm long, spurs of hind tibia 70–77, 75 µm and 42–65, 49 µm long. Width at the apex of fore tibia 37–42, 40 µm, of mid tibia 37 (1) µm, of hind tibia 37–55 (4) µm. Distal membranous sole on fourth tarsal segment with ornamented edge ( Figure 1d View FIGURE 1 ). Comb with 12–14, 13 setae. Tarsal claws as in figure 1d. Lengths and proportions of legs as in Table 1.
Hypopygium ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Gonocoxite 162–172, 167 µm long, strongly curved with apical inner hook; Phallapodeme 67–110, 90 µm long; transverse sternapodeme 30–47, 36 µm long. Gonostylus 50–67, 57 µm long; subapical lobe absent; 1–3 aligned strong p-setae; long, slender and bare apical lobe, tapering toward the tip; lanceolate t-setae 20 µm long, if present (present in only one apical lobe of a single specimen); x- and y-seta indistinct. HR 2.50–3.35, 2.93; HV 2.62–3.61, 3.08.
Female (n = 1). Total length 2.32 mm. Wing length 1.38 mm. Total length/wing length 1.68. Wing length/ length of profemur 2.19.
Colouration: Blackish brown; wings light brown; legs uniformly dark brown except for trochanter and the very base of femora pale.
Head. Antenna with 9 flagellomeres, AR 0.30. Ultimate flagellomere 47 µm. Temporal setae 6. Clypeus with 2 setae. Palp segment lengths in µm (II–V): 22, 25, 80, 50. Third palpomere with 4 sensilla clavata in apical third; 15 µm long. Eyes pubescent.
Thorax. 12 acrostichals in mid scutum, 9 dorsocentrals, 3 prealars, 1 supraalar; scutellum with 4 setae, humerals 2.
Wing. Membrane without patch of perpendicular setae on r cell . VR 0.97. Costal extension 30 µm long. R with 6 setae, R4+5 with 1 apical seta. Remaining veins, brachiolum and squama bare. R1 distally swollen. Legs. Spur of fore tibia 17 µm long, spurs of mid tibia 12 and 10 µm long, spurs of hind tibia 67 µm and 37 µm long. Width at the apex of fore tibia 74–78 µm, of mid tibia 74 µm, of hind tibia 53 µm. Distal membranous sole on fourth tarsal segment with ornamented edge. Comb with 13 setae. Tarsal claws both with subapical tooth. Lengths and proportions of legs as in Table 2.
Genitalia ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 ). Gonocoxite IX fused with Tergite IX, forming a gonotergite IX, with 29 setae. Setae on gonapophysis VIII mostly trifid. Cercus 37 µm long. Seminal capsules 30 µm long. Notum 117 µm long.
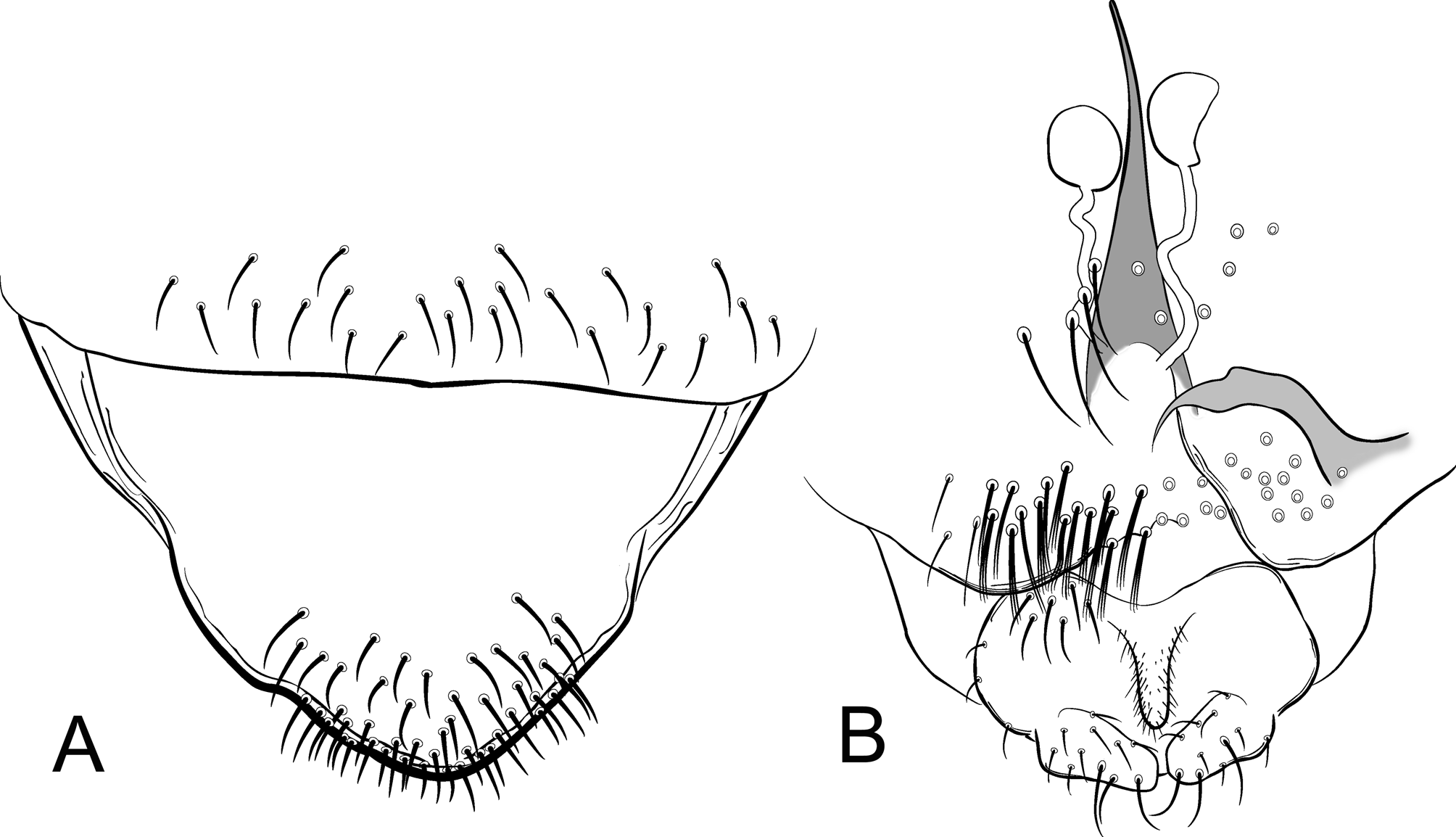
Pupa (n = 6). Total length 2.13–2.92 (5) mm, cephalothorax 542–690 (3) µm long. Exuviae light brown. Cephalothorax ( Figure 4a–d View FIGURE 4 ). Frontal setae as in Fig. 4a View FIGURE 4 . Antepronotals 2. Precorneals 2. Thoracic horn ( Fig. 4c, d View FIGURE 4 ) 194–256, 232 µm long, with spiculose stalk; ratio between plastron plate and stalk lengths 1.20–1.89, 1.80. Abdomen ( Figure 4e View FIGURE 4 ). Sternite II with large lamella, occupying more than half width of segment. Posterior angles of segments II–VIII protracted into sharp-pointed processes basally covered with spinules, process of segment VII strongly curved in frontal direction. Tergite I bare, T II–VIII with fine and small spinules sparsely distributed, T IX with anterior shagreen. Sternites I–II bare; S II–IX with fine and small spinules. Segment VIII with 8–10, 9 wavy L setae. Anal lobe 169–237, 205 µm long, with 5–6, 5, wavy setae and 2 distal slender setae, longest 55–62 (5) µm long, shortest 22–27 (5) µm long.
Larva (n= 7–8). Total length 2.40–3.05, 2.79 mm. Head capsule 224–286, 237 µm long, triangular.
Head. Antenna as in Fig. 4g View FIGURE 4 . Length of antennal segments (in µm): 22–35 (4), 12–15 (4), 6–7 (4), 1–2 (4). Blade 18–20 (4) µm long, accessory blade 9–10 (3) µm long, apical style of second segment 15–16 (3) µm long. Mandible ( Fig. 4h View FIGURE 4 ) 60–80, 67 µm long, with one apical and six inner teeth. Mentum with 11 teeth ( Fig. 4f View FIGURE 4 ). Abdomen. Procercus ( Figure 4i View FIGURE 4 ) blackish, 74–98, 82 µm long, bearing 6–7, 6 anal setae, longest 176–255, 201 µm. Supraanal seta with 3–6, 4 branches, 30–50, 38 µm long. Posterior parapods 284–368, 309 µm long with a middle segmentation; claws dark brown, distributed in two rows, one with very short claws and another with well developed claws. Anal tubules 98–221 (4) µm long.
| MZSP |
Sao Paulo, Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Podonominae |
|
Genus |