Parasopubia hofmannii Pradeep & Pramod, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.15553/c2013v681a16 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5706259 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D55587CD-FFD6-2221-E812-FA1F45C9FDC4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Parasopubia hofmannii Pradeep & Pramod |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Parasopubia hofmannii Pradeep & Pramod View in CoL , spec. nova
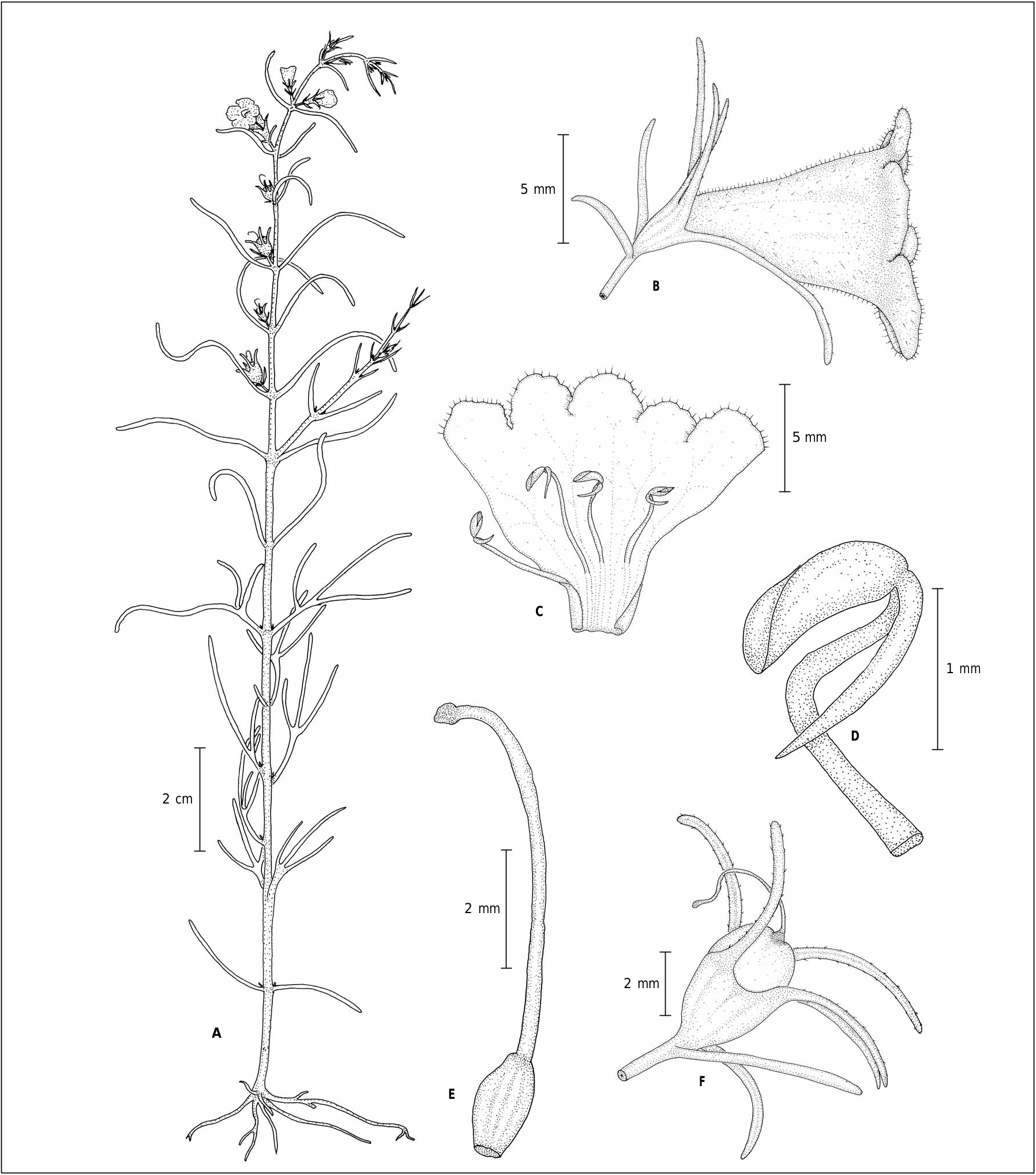
( Fig. 1 View Fig ).
Typus: INDIA: Kerala, Kannur, Madayippara , 36 m, 12º 01.792’N 75º15.246’E, 27.IX.2011, Pramod CU 126793A (holo-: G; iso-: MH). GoogleMaps
Closelyallied to P. delphinifolia , but can easilybe distinguished by itsless or non-segmented leaves, calyx with 2 mm long tube and up to 4 mm long divergent lobes, shorter (<1.2 cm) campanulate corolla tube and the capsules being obovoid and much exceeding the calyx tube.
Erect annual herb, to 50 cm high. Stem stiff, terete at base, sulcate and tetragonous above, seldom branched, glabrous, slightly purplish; internodes 5-10 mm long. Leaves opposite, 1-4 cm long; lower leaves usually with 3 linear segments or rarely 5-segmented or entire; upper leaves entire, slightly purplish, margins entire, midrib depressed, strigose on margins, glabrous on both the surfaces; segments 1 mm broad, filiform, terminal segment longer than laterals; leaves reduced towards apex. Flowers axillary, solitary, 1 0.7-1 cm; pedicels up to 1-2 mm long. Bracteoles 2, linear, 2-2.5 × 0.25 mm, slightly purplish, glabrous, tip acute. Calyx 6 mm long; lobes 5, unequal, tube 2-2.5 mm long, green, 10-ribbed; lobes linear, to 4 mm long, acute to acuminate at apex, slightly purplish, margins minutely strigose or glabrous, glabrous on both surfaces, persistent in fruits. Corolla campanulate, pale pink or mauve, often with deep pink blotches, 1 × 0.7-1 cm, tube to 7 mm long, narrow (1-1.5 mm) up to 2-3 mm of tube, then expanding; lobes 5, subequal, subrotund, ca. 3 × 4 mm, minutely puberulous with gland tipped hairs, glabrous within. Stamens 4, unequal, filaments attached below the middle of corolla tube, deep pink, glabrous, 2 longer (5 mm), 2 shorter (3 mm), arched, attached above longer stamens. Anthers 2, pendent from the apex of the filament, one perfect, oblong, shortly apiculate, 1.5-2 mm long, dehiscence from base, the other empty and spur-like, 1.5-2 mm long, cuspidate. Ovary ellipsoid, 1 × 0.5 mm, green, glabrous; cells 2, placentation axile, ovules many. Style simple, 6 mm long, pale pink, glabrous; stigma globose, glabrous. Capsules obovoid, 2.5 × 4 mm, purplish green, much exceeding the calyx tube, emarginate at apex, apiculate with withered style, glabrous; fruiting calyx to 7 mm long, lobes 4-5 mm, tubes 2-3 mm long, purplish. Seeds many, oblong, 0.5 mm long, brownish, glabrous, testa cells narrow, walls almost parallel, secondary testa cells absent or ill-developed, cell walls almost smooth.
Phenology. – Flowering and fruiting in June to October.
Specimina visa. – INDIA. Kerala: Kannur, Madayippara , 36 m, 12º01.792’N 75º15.246’E, 11.IX.2009, Pramod CU 123592 ( CALI); GoogleMaps Kannur, Madayippara , 36 m, 12º01.792’N 75º15.246’E, 20.VIII.2010, Pramod CU 126555 ( CALI); GoogleMaps Kannur, Madayippara , 36 m, 12º01.792’N 75º15.246’E, 1.VIII.2010, Pramod CU 126510 ( CALI); GoogleMaps Kannur, Parassinikkadavu , 200 m, 29.IX.1982, R. Ansari 73940 ( MH); Kannur , 25.VII.1988, E. Jayakumar CU 2152 ( CALI); Kannur, Cheemeni , 8.X.1990, C. T. Indu CU 4098 ( CALI); Kannur, Thalipparamba , 30.XII.1988, P. P. Sudhirkumar CU 2886 ( CALI).
Etymology. – The species is named in honor of Hans-Peter Hofmann ( Germany), who together with Eberhard Fischer ( Germany) have made great contribution to the taxonomy of Sopubia and erected Parasopubia .
Habitat. – Parasopubia hofmannii grows in the crevices of hard laterite and also on the surrounding shallow soiled areas ( Fig. 2A View Fig ), along with species such as Lepidagathis keralensis Madhu. & Singh , Cyanotis burmanniana Wight , Indigofera trifoliata L., Geissaspistenella Benth., Desmodium triflorum (L.) DC., Polycarpaea corymbosa (L.) Lam. and Heteropogon contortus (L.) Roem. & Schult.
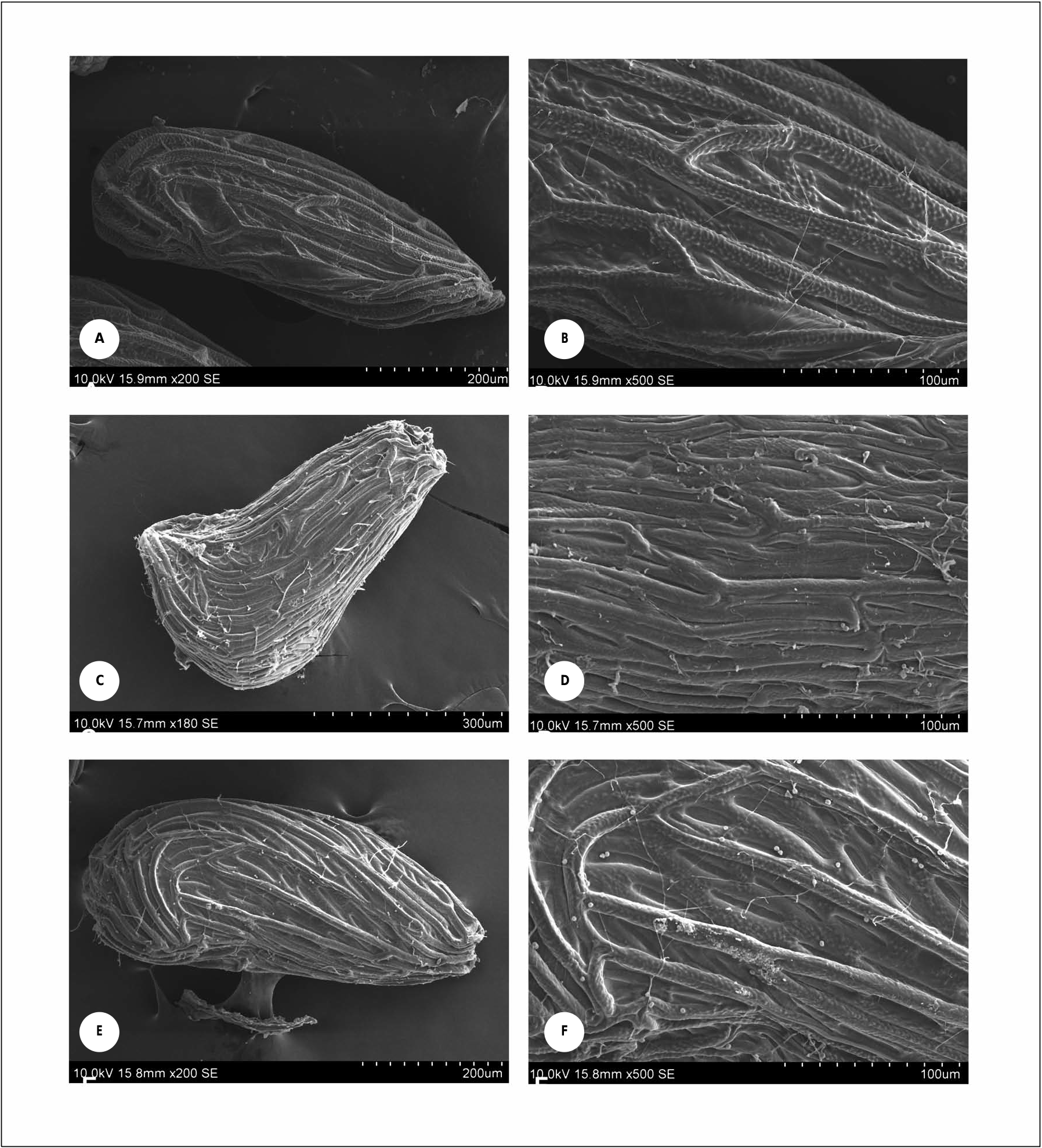
Taxonomical notes. – Parasopubia hofmannii ( Fig. 1A View Fig ) differs from the one Indian species P. delphinifolia in its stouter habit with less branching, leaves with fewer segments ( Fig. 2 View Fig B-C), shorter campanulate flowers ( Fig. 2 View Fig D-E), obovate capsules with fruiting calyx tube reaching only up to the middle, and also by seeds with narrow testa cells and almost parallel and smooth walls, where secondary testa cells are absent or ill-developed ( Fig. 2 View Fig F-G; Fig. 3 View Fig A-D). Being stouter, it is similar to the other Asian P. bonatii , but differs in having long-linear calyx lobes against the short and triangular calyx lobes in P. bonatii .
| G |
Conservatoire et Jardin botaniques de la Ville de Genève |
| MH |
Naturhistorisches Museum, Basel |
| CALI |
University of Calicut |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |