Afrithelphusa Bott, 1969
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2023.2216908 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8221719 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D5791142-FFEE-D172-FE29-5EBAFD2FFE98 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Afrithelphusa Bott, 1969 |
| status |
|
Afrithelphusa Bott, 1969 View in CoL View at ENA
( Figures 1–8 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 View Figure 3 View Figure 4 View Figure 5 View Figure 6 View Figure 7 View Figure 8 ; Tables 1–3 View Table 1 View Table 2 View Table 3 )
Globonautes Bott, 1959: 997–999 View in CoL ; 1969: 360; Monod 1977: 1209; 1980: 380; Cumberlidge 1987: 2210–2214.
Afrithelphusa Bott, 1969: 359 View in CoL ; 1970: 25–27; Monod 1977: 1208–1210; 1980: 380; Cumberlidge 1996a: 684–688, table 1; 1996b: 814, 1999: 218–219; Ng et al. 2008: 169; Cumberlidge et al. 2008: 402, 405, 407–411, tables 1,2, fig. 2; Cumberlidge and Daniels 2022: 1276, 1279, 1299–1300, 1303, table 2.
Type species
Afrithelphusa gerhildae Bott, 1969 View in CoL , by original designation, gender feminine.
Diagnosis
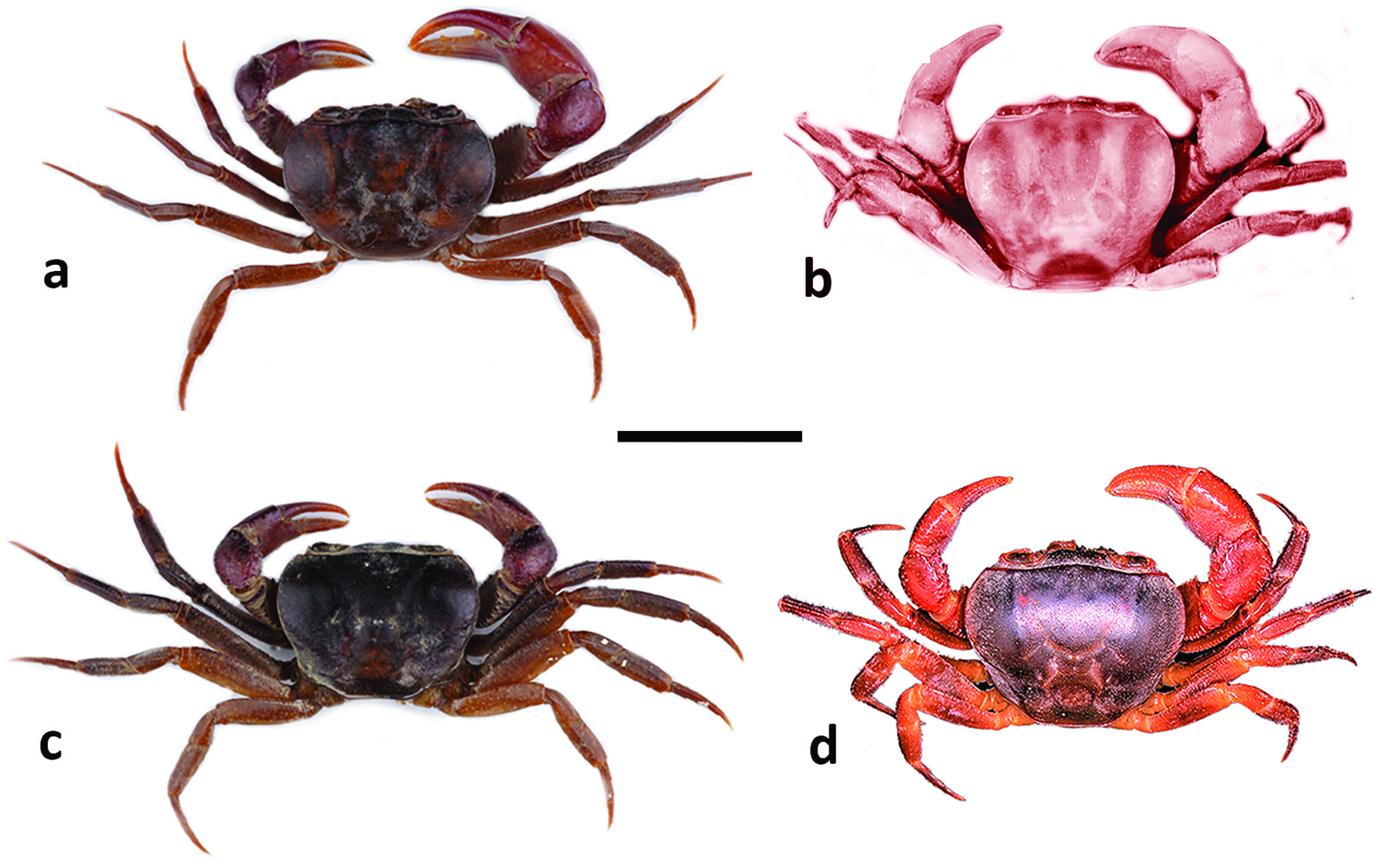
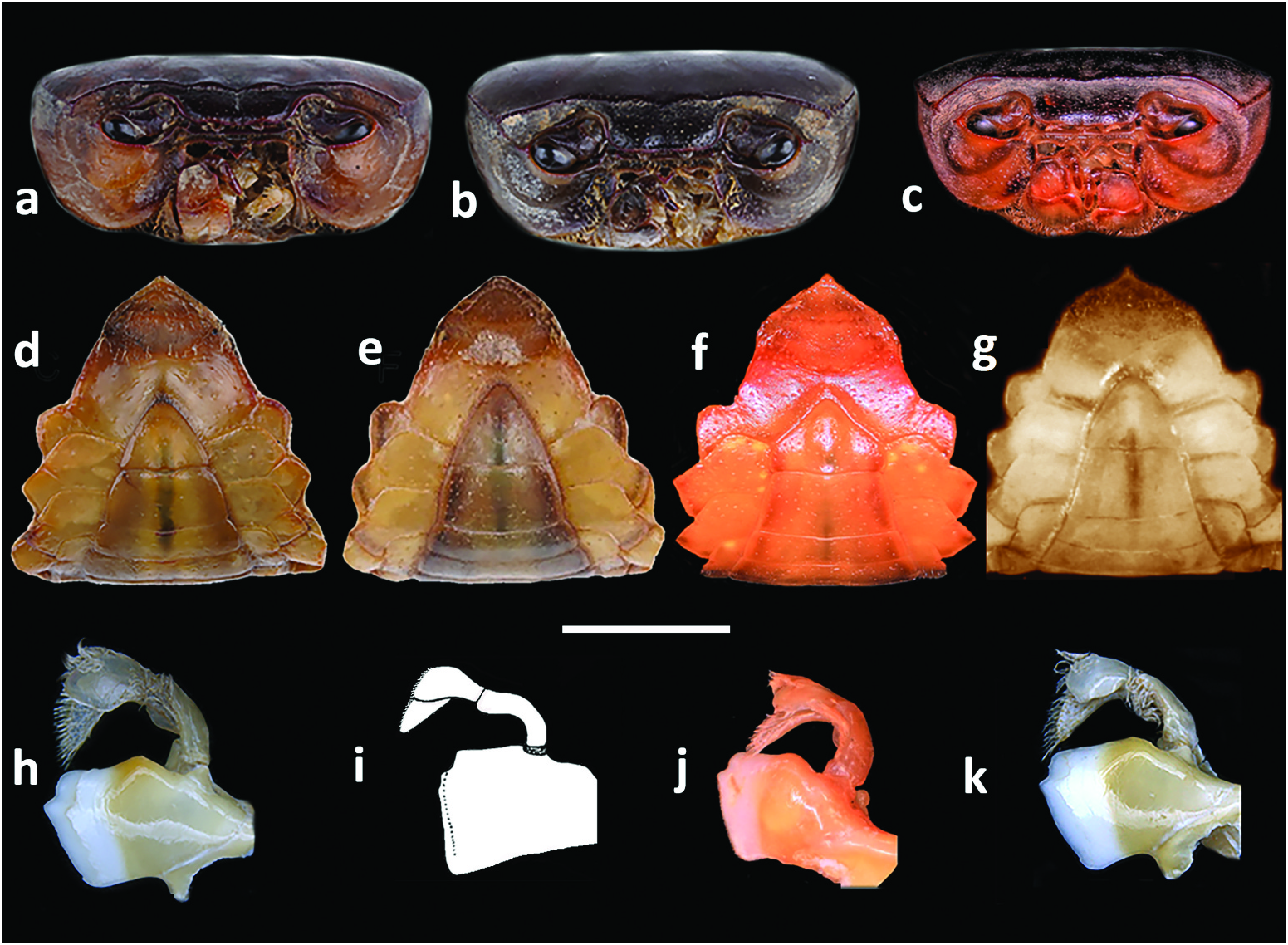
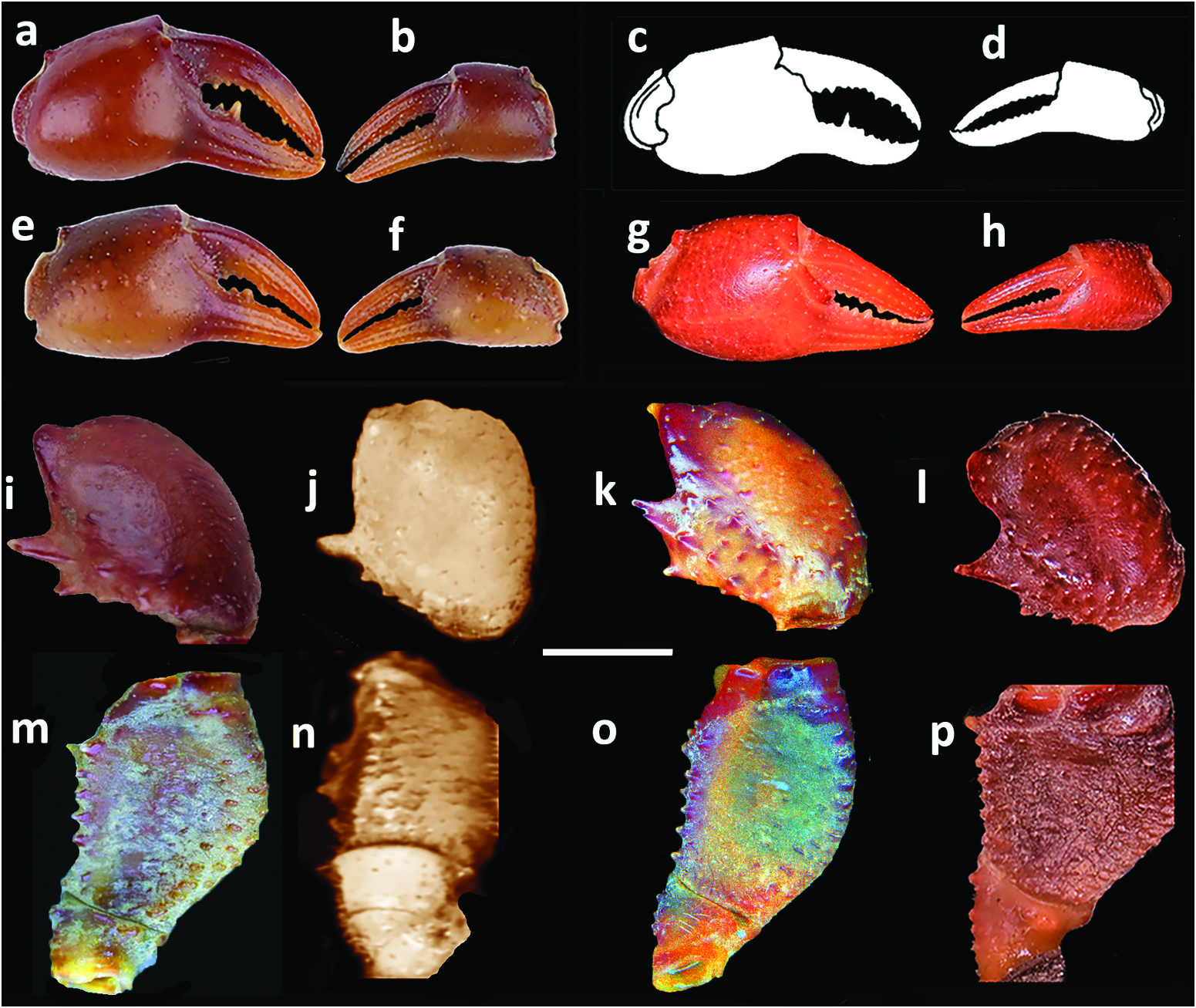
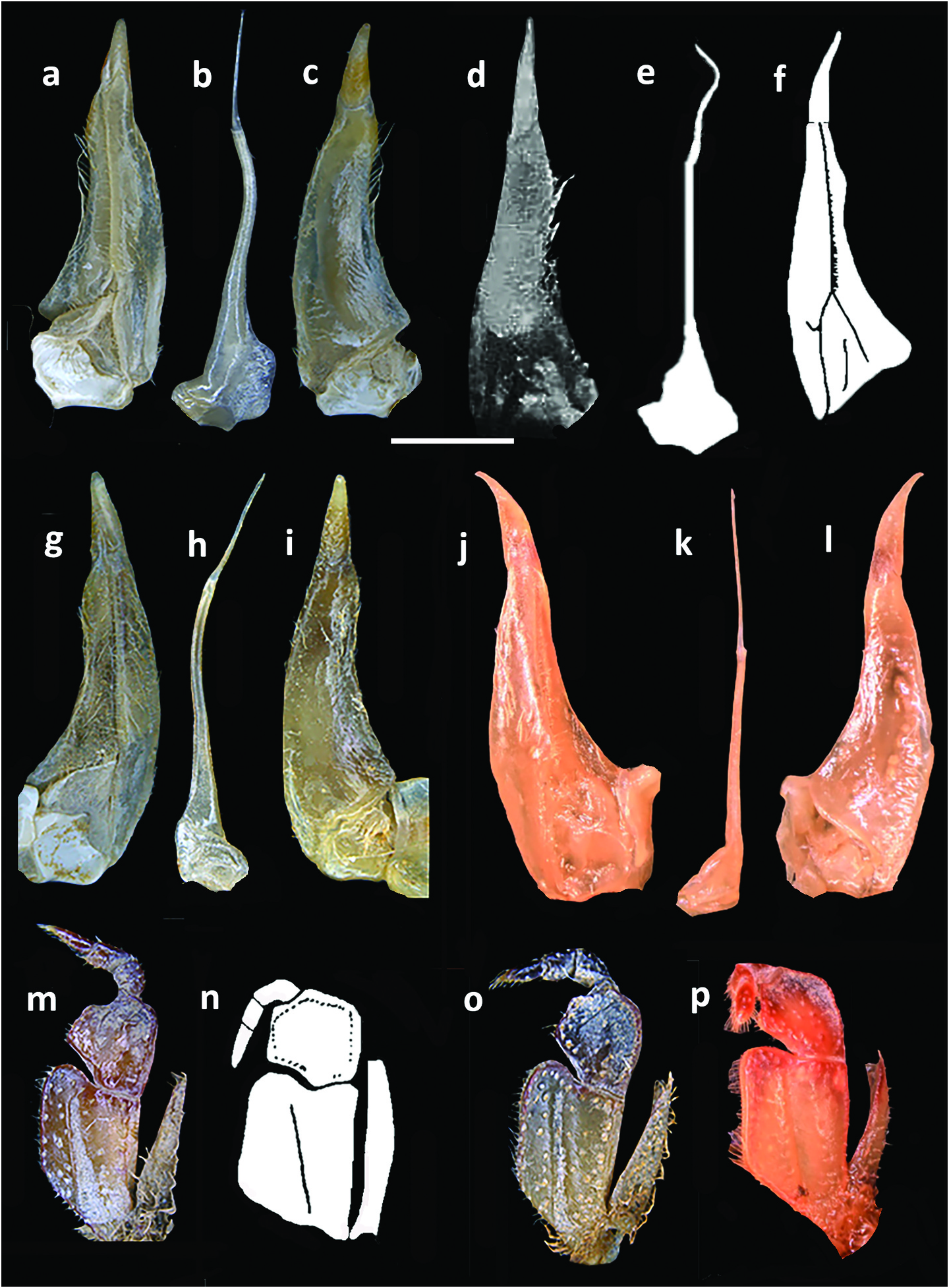
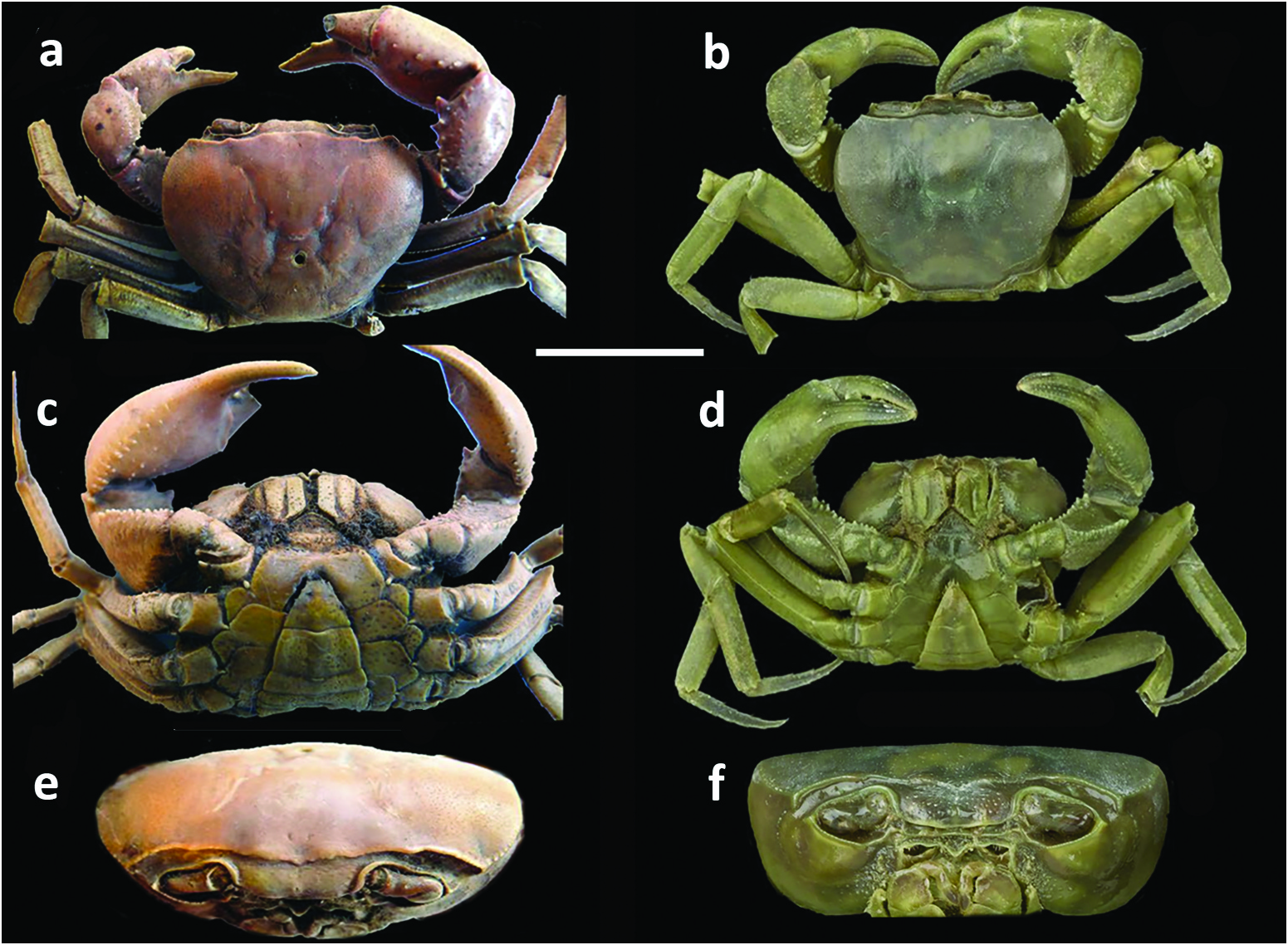
Carapace smooth, lacking visible granules, lateral carinae; carapace highly arched ( CH / FW = 1.4–1.8; Table 2 View Table 2 ); front medium width (CW/FW = 3.5–3.7) ( Figures 2 View Figure 2 (a–d), 3(a–d), 4(a–c), 7(a,b,e,f); Table 2 View Table 2 ), postfrontal crest sharp-edged completely traversing carapace, meeting carapace lateral margins at epibranchial teeth,anterolateral margin lacking intermediate tooth between exorbital, epibranchial teeth ( Figures 2 View Figure 2 (a–d), 3(a–d)). Vertical sulcus on carapace branchiostegite meeting anterolateral margin at epibranchial tooth ( Figure 4a–c View Figure 4 ). Mandibular palp consisting of basis followed by two articles; terminal article (MPTA) distinctly bilobed (MPAL/MPTA = 0.5–0.7) ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 (h–k); Table 3 View Table 3 ). Third maxilliped exopod lacking flagellum ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (m–p)); Cumberlidge 1999, fig. 49A). Cheliped carpus inner margin with large pointed distal tooth, small proximal tooth, followed by series of small teeth; cheliped merus inferior margins lined with small granules ( Figures 2 View Figure 2 (a–d), 5(i–p), 7(a–d)).Sternal sulci Sl/ 2, S2/3, S3/4 deep, all completely crossing thoracic sternum; anterior margin of sterno-pleonal cavity terminating half-way along S4 ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 (d–g)). G1TA medium length (G1TA/G1SA = 0.4), slim, broadest proximally, tapering to broad tip; medial, lateral folds on G1TA equal sized, low; G1TA-G1SA junction with clearly visible sulcus on ventral, dorsal sides ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (a,c,d,f,g,i,j,l). G2TA medium length,flagellum-like (G2TA/G2SA = 0.4–0.5) ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (b, e, h, k)).Maximum size up to 29.5 mm.
Distribution
Afrithelphusa is found only in the Upper Guinea forests of West Africa from Guinea to Sierra Leone ( Cumberlidge 1999); most species have a restricted distribution and are known only from a small type series or from a single locality ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 ).
Species included
Afrithelphusa afzelii Colosi, 1924 , A. gerhildae Bott, 1969 , A. leonensis ( Cumberlidge, 1987) , and A. monodosa (Bott, 1959) .
Remarks
Afrithelphusa leonensis and A. monodosa were formerly assigned to Globonautes but were transferred to Afrithelphusa by Cumberlidge (1996a) in recognition of significant differences between these taxa and the type species, G. macropus , with respect to the gonopods and carapace ( Cumberlidge 1996a, 1996b, 1999; Cumberlidge and Daniels 2022). For example, the postfrontal crest of the four species of Afrithelphusa is sharp-edged and runs uninterrupted across the carapace ( Figures 1 View Figure 1 (a–d), 2(a–d)); Cumberlidge 1999, fig. 46A–D), (vs postfrontal crest poorly defined and periodically interrupted in G. macropus ( Cumberlidge 1999, fig. 46E)), the G2TA of all four species of Afrithelphusa is a medium-length flagellum (G2TA/G2SA = 0.4– 0.5) ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (b,e,h,k)), (vs a G2TA that is extremely short and stub-like (G2TA/G2SA = 0.1) in G.macropus )( Table 3 View Table 3 ; Cumberlidge 1999,fig.53Z),and each of the four species of Afrithelphusa has a G1TA with a visible sulcus on the ventral and dorsal sides of the G1TA-G1SA junction ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (c,d,i,l)); Cumberlidge 1999, fig. 52AA, BB, CC, DD) (vs an obscured sulcus on the ventral side of the G1TA-G1SA junction in Globonautes ; Cumberlidge 1999, fig. 52EE).
Balss (1936, p. 200) and Bott (1955) questioned the validity of Sierra Leone as the collection locality of A. afzelii , and incorrectly speculated that this taxon was actually not even from Africa. This question was later resolved by Bott (1970) who included A. afzelii in Afrithelphusa , a genus he had earlier established (Bott 1969) for A. gerhildae from Guinea, West Africa. Cumberlidge (1996a, 1996b) subsequently added A. monodosa from Guinea and A. leonensis from Sierra Leone to this genus.
Cumberlidge and Daniels (2022) revised the higher classification of the Afrotropical freshwater crabs, recognising the family Deckeniidae with Globonautinae (for Afrithelphusa , Globonautes Bott, 1959 , Deckenia Hilgendorf, 1869 and Seychellum Ng, Stevcic and Pretzmann, 1995 ) and Hydrothelphusinae Bott 1955 (for all genera of Malagasy freshwater crabs). The Deckeniidae are reported from West Africa including Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone ( Afrithelphusa and Globonautes ), and East Africa including Tanzania, Kenya, Somalia ( Deckenia ), the granitic Seychelles ( Seychellum ) and Madagascar (12 endemic genera) ( Ng et al. 1995; Cumberlidge 1999; Reed and Cumberlidge 2006; Cumberlidge and Daniels 2022).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
InfraOrder |
Brachyura |
|
SuperFamily |
Potamoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Deckeniinae |
Afrithelphusa Bott, 1969
| Cumberlidge, Neil, Mvogo Ndongo, Pierre A., Clark, Paul F., Salieu, Sankoh & von Rintelen, Thomas 2023 |
Globonautes
| Cumberlidge N 1987: 2210 |
| Monod T 1980: 380 |
| Monod T 1977: 1209 |
Afrithelphusa
| Cumberlidge N & Daniels SR 2022: 1276 |
| Ng PKL & Guinot D & Davie PJF 2008: 169 |
| Cumberlidge N & Sternberg R & Daniels SR 2008: 402 |
| Cumberlidge N 1996: 684 |
| Monod T 1980: 380 |
| Monod T 1977: 1208 |