Protzia persica Bader & Sepasgozarian, 1980
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.1019.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E12EEDB4-54F6-4B39-806F-A35B11EDDA55 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D606560F-6612-FF95-D074-4FE0AC58FE59 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Protzia persica Bader & Sepasgozarian, 1980 |
| status |
|
Protzia persica Bader & Sepasgozarian, 1980
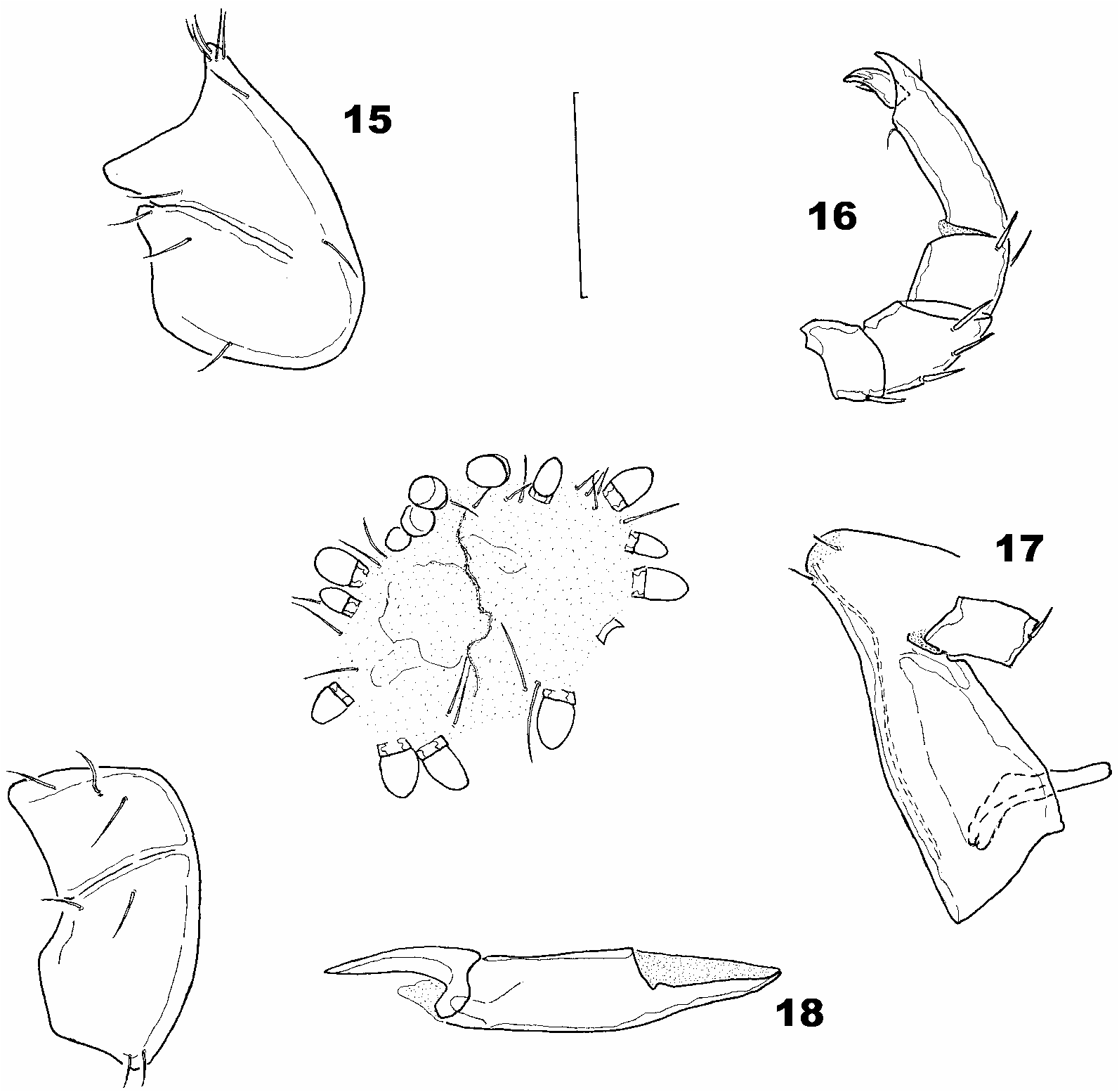
( Figs. 15–18 View FIGURES 15–18 )
Type series: Lectotype, male, here designated: dissected and slide mounted in Hoyer's fluid. Iran: 19770605 _3[23]; Gebiet Schiraz, Esfahan; Quelle u. Quellbach Behreghan. Von Dobiz einige km in Richtung Esfahan (> 110 km NW von Shiraz), leg. Bader. Paralectotypes: 46 males, 17 females, same data as lectotype , 6 males and 1 female of them dissected and slide mounted on Hoyer's fluid.
Diagnosis: Characters of the eximia species group; genital field with 14–16 Ac, caudal Ac on short stalks (L 5–10 µm, ratio caudal stalk length/Ac length 0.2–0.4); genital skeleton L 97–110 µm.
Description: Variability given as mean (minimum–maximum); Males (n=7): leg claws with 4 Lcl and 5–6 Mcl; genital field ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 15–18 ) with 15 (14–15) Ac; CAc L 24.6 (21–28), CAc W 20 (16–24), ratio L/ W 1.24 (1.0–1.6); CAc stalk L 7 (5–10), stalk L/L of CAc 0.29 (0.23–0.37); genital skeleton (n=2) L 97–110; gnathosoma ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 15–18 ) L 192 (182–205), L/ W ratio 2.26 (2.1–2.39); chelicera ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 15–18 ) L 229 (215–238), ratio basal segment/claw 1.8 (1.74–1.9), ratio L/H 5.5 (5.0–5.9); palp ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 15–18 ) total L 280 (268–238), dorsal length: P 1 26 (25–28), P2 69 (66–72), P3 43 (40–44), P4 109 (100–116), P5 34 (32–37), L/H ratio: P1 0.61 (0.58–0.65), P2 1.83 (1.65–1.92), P3 0.98 (0.9–1.03), P4 3.3 (3.1–3.5), P5 2.4 (2.3–2.5), relative length (given as % of total length): P1 9.2 (8.7–9.5), P2 24.5 (24.0–25.2), P3 15.4 (14.6–16.4), P4 39 (37.3–40.0), P5 12 (11.7–12.4); L ratio P2/P 40.63 (0.6–0.66).
Female: Ac number 16; CAc L 23–27, CAc W 15–18, ratio L/ W 1.5; CAc stalk L 7, stalk L/L of CAc 0.29; gnathosoma L 188; chelicera L 247; palp total L 294, dorsal length and L/H ratio (in parentheses): P1 29 (0.64), P2 73.5 (1.85), P3 45 (1.02), P4 113 (3.35), P5 34 (2.4), relative length (given as % of total length): P1 99, P2 25.0, P3 15.3, P4 38.4, P5 11.5; L ratio P2/P4 0.65.
Remarks: Generally, e.g. with regard to the variability of CAc, low number of Ac, caudal Ac on relatively short stalks (L <20 µm), P. persica is similar to the other species of the eximia group in Iran, P. zagrosiensis and P. caucasica . From the aforementioned spe cies (in parentheses), P. persica can be distinguished by the shorter stalks of CAc (L stalk> 10 µm, stalk L/L of CAc> 0.5), and the longer Gsk (L> 130 µm). The short stalked (L stalk 6–10 µm), Central Mediterranean P. felix Gerecke, 1996 (in parentheses, from Gerecke 1996b) can be easily distingushed from P. persica in the increased number of Ac (17–22 in male; 20–25 in female), and in the L of the Gsk (L> 125 µm).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |