Tanzawana flavomaculata Watanabe & Kasparyan
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4040.2.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C7AE923E-E86A-46E7-9CCF-13CE2DDFFE59 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6103418 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/DA583C31-1A40-527F-8ABE-FB0FFBB1FC59 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tanzawana flavomaculata Watanabe & Kasparyan |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Tanzawana flavomaculata Watanabe & Kasparyan sp. nov.
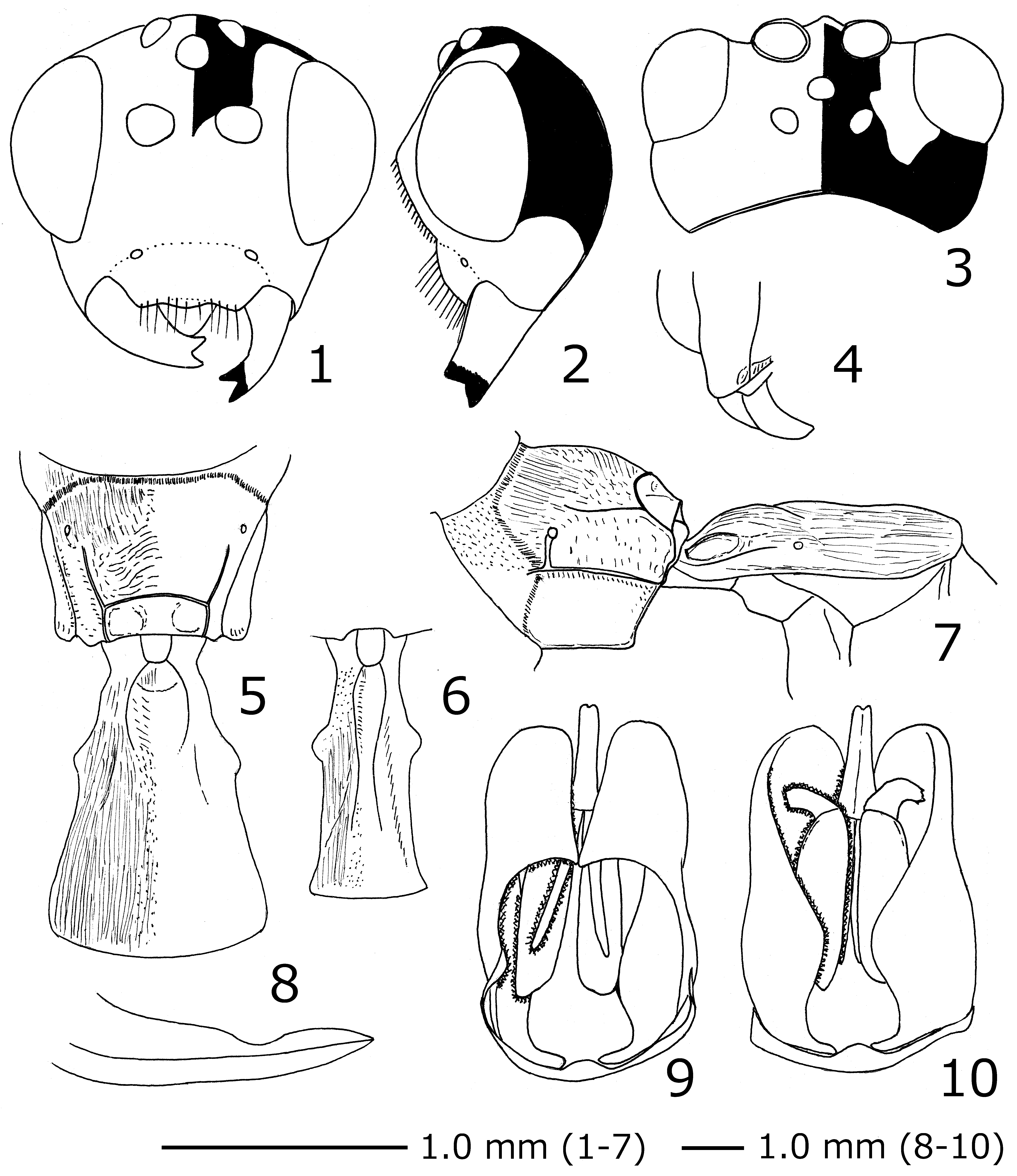
( Figs 1–14 View FIGURES 1 – 10 View FIGURES 11 – 12 View FIGURES 13 – 14 )
Type series. Holotype. Female, Kanagawa Pref., Mt. Tanzawa-san, Tennouji-one (1450 m alt.), 28. v. 2008, T. Taniwaki leg., yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH). Paratypes. 1 female, same locality (1350 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 11. v. 2008, em. from cocoon of Fagineura crenativora ( KPMNH); 1 male, same locality (1450 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 15. v. 2008 ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1350 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 21. v. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 2 females, same locality (1550 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 21. v. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1350 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 25. v. 2008 ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1250 m alt.) and data of holotype, 28. v. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female and 1 male, same locality (1480 m alt.) and data of holotype, 28. v. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 male, same locality (1560 m alt.) and data of holotype, 28. v. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1560 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 4. vi. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1350 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 10. vi. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( NSMT); 1 female, same locality (1480 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 10. vi. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1560 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 10. vi. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1450 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 17. vi. 2008, yellow flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality (1350 m alt.) and collector of holotype, 23. iv. 2009, em. from cocoon of F. crenativora ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality and collector of holotype, 6. vi. 2013, flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female and 1 male, Kanagawa Pref., Mt. Hinokiboramaru, 9. v. 2013, T. Taniwaki leg., flight interception trap ( KPMNH); 1 female and 1male, same locality, collector and method, 23. v. 2013 ( ZISP); 2 females, same locality, collector and method, 6. vi. 2013 ( KPMNH); 3 females and 2 males, same locality, collector and method, 14. vi. 2013 ( KPMNH); 1 female, same locality, collector and method, 23. vi. 2013 ( NIAES).
Description. Female (n=23). Body 5.0–6.5 (HT: 5.5) mm. Body polished, smooth and finely punctate, except for pronotum, propodeum and first metasomal tergite.
Head 0.6 × as long as wide. Clypeus 0.5 × as long as wide. Face 0.6 × as long as wide, flat in lateral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Malar space more or less elongate in anterior view ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ), 0.7 × as long as basal width of mandible. Gena slightly narrower than eye in lateral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Base of mandible flat. Minimum length between lateral ocellus and eye 0.9–1.0 (HT: 0.9) × as long as minimum length between each lateral ocellus. Antenna with 32–35 (HT: 35) flagellomeres, its first segment 1.7–1.9 (HT: 1.8) × as long as second segment.
Mesosoma. Pronotum covered with fine oblique striae. Ventral part of epicnemial carina absent. Propodeum covered with longitudinal striae on anterior part and with transverse striae before area postero ( Figs 5, 7 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Area postero of propodeum with a pair of weak concavities ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Fore wing 5.0–6.5 (HT: 6.5) mm. Hind femur 5.2– 5.5 (HT: 5.5) × as long as maximum width in lateral view. Ratio of tarsomeres of hind tarsus 1: 2: 3: 4: 5 = 2.0: 0.6: 0.5: 0.3: 0.5.
Metasoma. First metasomal tergite 1.2–1.4 (HT: 1.2) × as long as maximum width, covered with longitudinal striae ( Figs 5, 7 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Median dorsal carina of first metasomal tergite borders laterally basal concavity and absent beyond the concavity ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Ovipositor sheath 0.25–0.3 (HT: 0.25) × as long as hind tibia.
Colouration ( Figs 1–3 View FIGURES 1 – 10 , 11–14 View FIGURES 11 – 12 View FIGURES 13 – 14 ). Head whitish-yellow, except for: median part of frons, vertex, occupit, upper part of gena, dorsal surface of antenna black; apex of antenna more or less tinged with reddish-brown, scape, pedicel and flagellomeres 1–3(4) yellow ventrally. Mesosoma (excluding legs and wings) and metasoma black, except for: propleuron, posterodorsal and posteroventral spots of pronotum, anterolateral spots on mesoscutum and H-shaped marking at its dorsum, scutellum, tegula, subalar prominence, posterior part of postscutellum, ventral part of mesopleuron, mesosternum, posterior end of axillae, median part of second to seventh metasomal tergites, sternites, ovipositor and ovipositor sheath white to whitish-yellow. Legs whitish-yellow to brownish-yellow, except for base and apex of hind tibia brown. Outer surface of hind femur and hind tarsus sometimes tinged with brown. Wings hyaline, with brown veins except for stigma with whitish-yellow base and apex.
Male (n=7). Similar to female. Clypeus 0.4 × as long as wide. Face 0.5–0.6 × as long as wide. Flagellum with first segment 1.9–2.0 × as long as second segment. Ratio of hind tarsus 1: 2: 3: 4: 5 = 2.0: 0.7: 0.6: 0.3: 0.5. First metasomal tergite more slender than female, 1.8–1.9 × as long as maximum width, its median dorsal carina longer than in female ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Apex of paramere short, its margin round ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Inner margin of ventral side of paramere concave at base ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ). Tip of aedeagus somewhat swollen, decurved, its apex rounded. Whitishyellow areas relatively larger than female, those of pronotum united into a single large spot. Hind femur without brown area.
Distribution. Japan (Honshu).
Etymology. The specific name is from the Latin “ flavo ” (yellow, golden) plus “ maculata ” (with marking).
Bionomics. Koinobiont endoparasitoid of Fagineura crenativora ( Tenthredininae , Nematinae ). Like other species of Ctenopelmatinae , oviposition is into the larva, with emergence after the host cocoon is spun.
Remarks. This species can be easily distinguished from other parasitoids of F. cranativora by the mesoscutum with an H-shaped light yellow median marking, by body completely yellow ventrally and the posterior part of metasoma with large yellow pattern ( Figs 11, 12 View FIGURES 11 – 12 ) ( Taniwaki & Watanabe 2012).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.