Paramonovius, Li & Yeates, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1111/aen.12361 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:936DFF93-AAA3-460F-AD5D-8EC342CB3132 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5658657 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E06587DF-5C61-FFED-FF1D-61E5FA5436C5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Paramonovius |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Genus Paramonovius View in CoL gen. nov.
http://zoobank.org/ urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
Type Species. Paramonovius nightking View in CoL sp.nov. (here designated).
Diagnosis
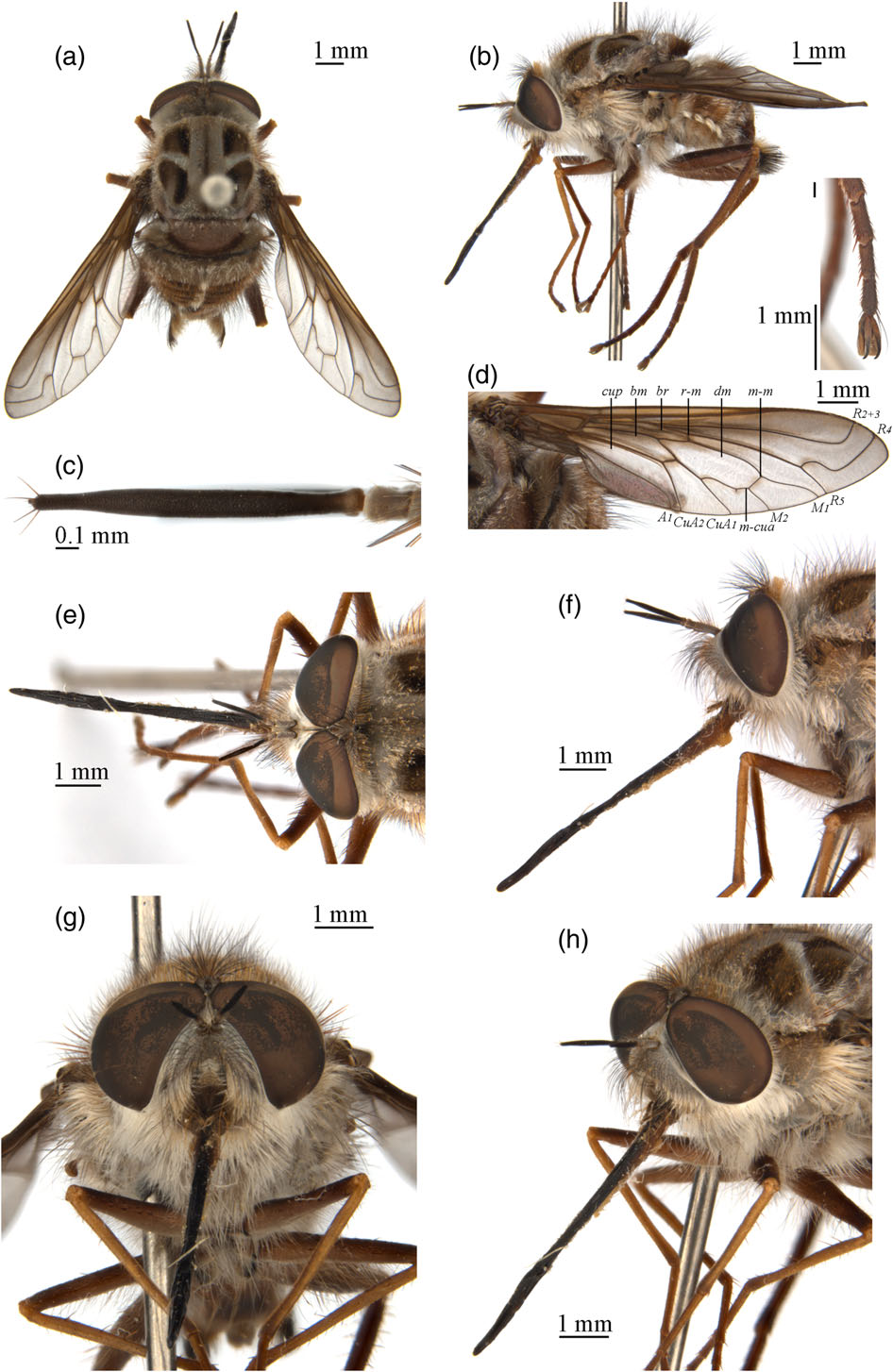
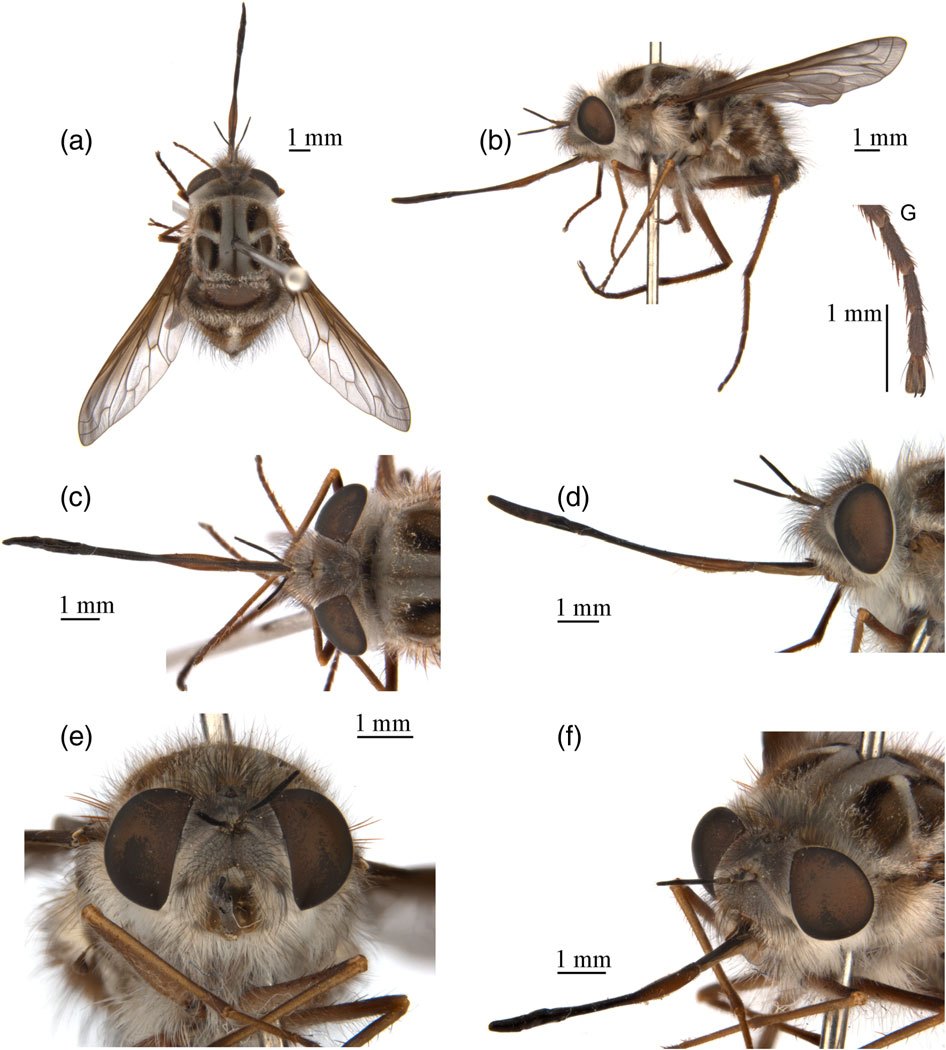
Medium-sized bombyliine (body length around 8–11 mm). Male eyes narrowly separated ( Fig. 2e View Fig ); female frons wide ( Fig. 3c View Fig ). Antennal flagellum one-segmented with apical stylus, subapex with 3–5 long hairs ( Fig. 2c View Fig ). Palpus short, one-segmented. Mouthparts long and slender, labellum thin and filiform ( Fig. 2f View Fig ). Scutum, scutellum, pleura and coxae densely clothed in hairs, except anepimeron, mero, laterotergite and mediotergite bare. Femora strong, with anterior blackish brown bristles. Claw and pulvillus enlarged, as long as distitarsus ( Figs 2i View Fig and 3g View Fig ). Wing with cell r 5 widely open; cell br nearly as long as cell bm, crossvein r-m arising at base of cell dm; cell cup open; alula well developed ( Fig. 2d View Fig ). Abdomen broad and short. Tergites with median stripe consisting of dense, decumbent short white scales. Male genitalia enlarged, epandrium posterolateral corner with thick long hairs ( Fig. 4d View Fig ); hypandrium fused with gonocoxite; gonocoxite basal half wide and apical half abrupt narrowed ( Fig. 4c View Fig ); anterior arm of aedeagal sheath long and wide, extending beyond gonocoxal margin. Female sand chamber present, tergite 8 fused and sclerotized. Acanthophorite spines present. Genital fork strong and broad, enlarged basally. Sperm pump strong and of normal length; common and basal spermathecal duct normal; apical spermathecal duct short; spermatheca elongate, cylindrical with apex spherical ( Fig. 4f View Fig ).
Description
Head. Head wide and relatively short, covered in admixed hairs and scales. Eyes narrowly separated in male, widely separated in female. Male eyes separated by 0.5× width of ocellus, frons short ( Fig. 2e View Fig ). Female eyes widely separated, frons wide, around 3.0× as wide as ocellar tubercle ( Fig. 3c View Fig ). Posterior eye margin slightly sinuous. Antennal scape elongate, about 3.5× as long as wide; pedicel elongate, about 1.5× as long as wide; flagellum one-segmented with apical stylus, subapex with 3–5 long hairs ( Fig. 2c View Fig ). Palpus short, not extending beyond oral cavity, onesegmented, without palpal pit. Mouthparts long and slender, labellum thin and filiform ( Fig. 2f View Fig ).
Thorax. Scutum and scutellum with pale pruinescence and covered with hairs and scales. Five notopleural setae present. Postalar callus setae absent. Pleura with thick pale pruinescence, anepisternum, katepisternum, katepimeron and coxae densely covered with long scales, but anepimeron, mero, laterotergite and mediotergite bare ( Figs 2b View Fig and 3b View Fig ). Femora strong, with anterior blackish brown bristles. Claw and pulvillus enlarged, as long as distitarsus ( Figs 2i View Fig and 3g View Fig ). Wing with cell r 5 widely open; cell br nearly as long as cell bm, crossvein r-m arising base of cell dm; crossvein m-m much longer than crossvein r-m; cell cup open; alula well developed ( Fig. 2d View Fig ).
Abdomen. Abdomen broad and short, tergites 3–7 compact, tergites 7–9 rotated, with epandrium and gonocoxite rotated 180°; tergites 2–6 with median stripe consisting of dense, decumbent short white scales. Male epandrium enlarged, nearly rectangular, anterior margin deeply concave, posterolateral corner with thick long hairs ( Fig. 4d View Fig ). Hypandrium fused with gonocoxite. Gonocoxite enlarged, basal half wide and apical half abruptly narrowed. Ejaculatory apodeme large ( Fig. 4a,b View Fig ); gonocoxal apodeme strong and pointed anteriorly; anterior arm of aedeagal sheath long and wide, extending beyond gonocoxal margin; lateral ejaculatory process strong; inner and outer apexes of gonocoxite sharp; gonostylus small and strongly incurved ( Fig. 4c View Fig ). Female sand chamber present. Tergite 8 fused and sclerotized. Around 30 acanthophorite spines present on each side. Genital fork strong and broad, enlarge basally. Sperm pump strong and about as long as basal spermathecal duct; common and basal spermathecal duct not elongate; apical spermathecal duct shorter than spermatheca; spermatheca elongate, cylindrical with apex spherical ( Fig. 4f View Fig ).
Etymology
This generic name is in honour of Dr. Sergei Jacques Paramonov for his significant contribution to Australian dipterology.
Included species
This genus is monotypic for Paramonovius nightking sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |