Squalius namak, Khaefi, Roozbehan, Esmaeili, Hamid Reza, Sayyadzadeh, Golnaz, Geiger, Matthias F. & Freyhof, Jörg, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4169.1.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5C73C13D-5A89-4B01-9F30-3AF702A35A71 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5658197 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E85887B3-A30F-091D-C589-A4B5FB7D21DF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Squalius namak |
| status |
sp. nov. |
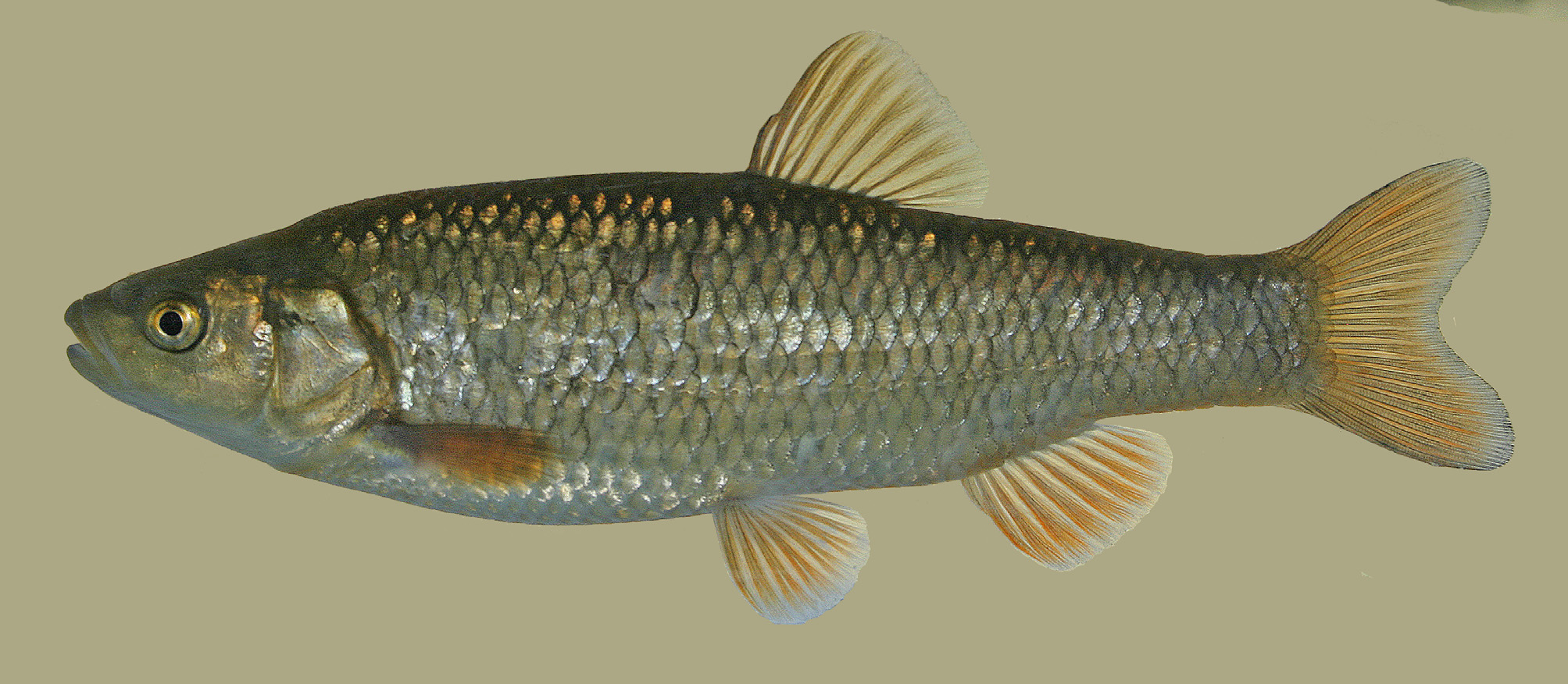
Squalius namak , new species
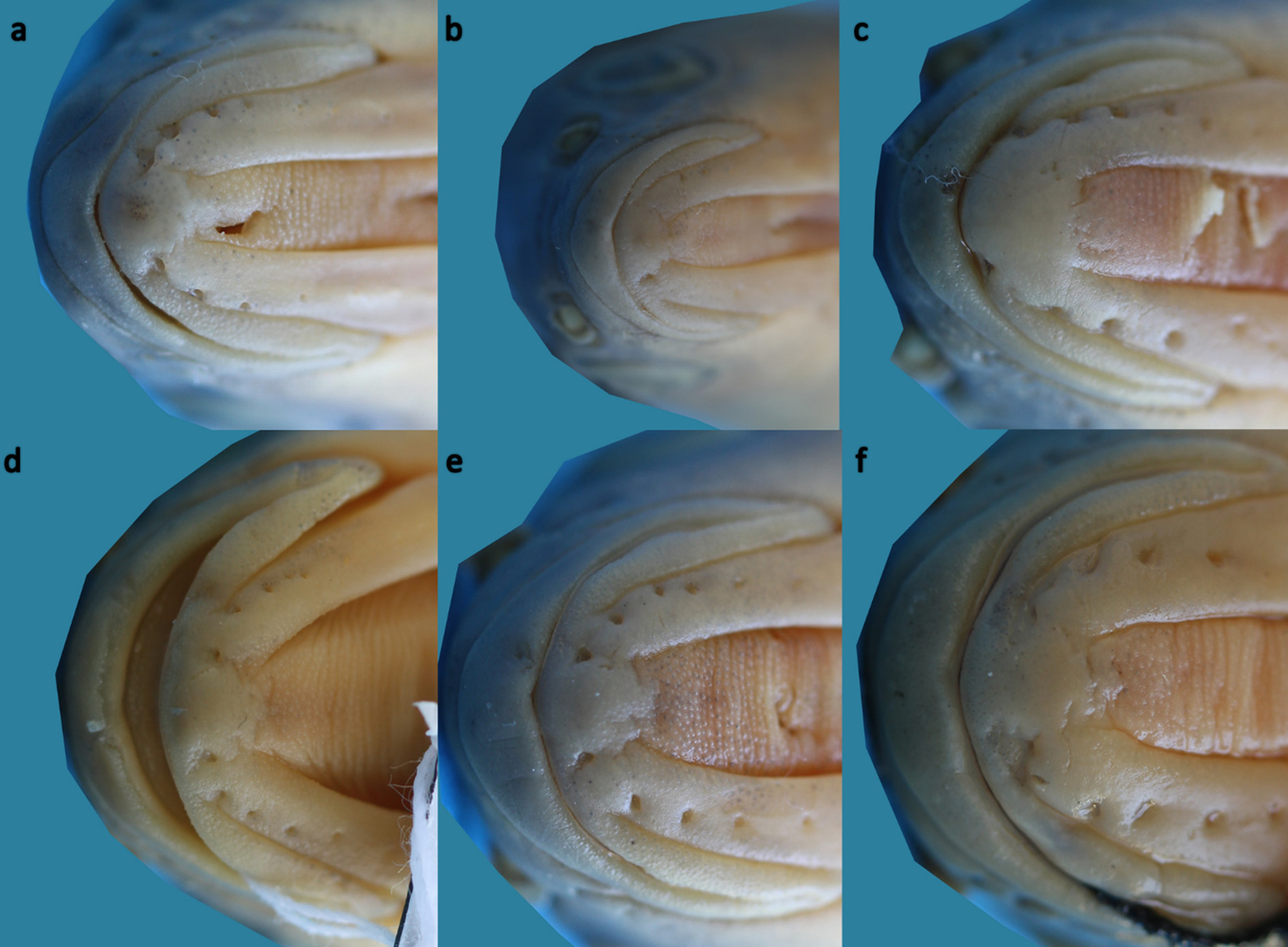
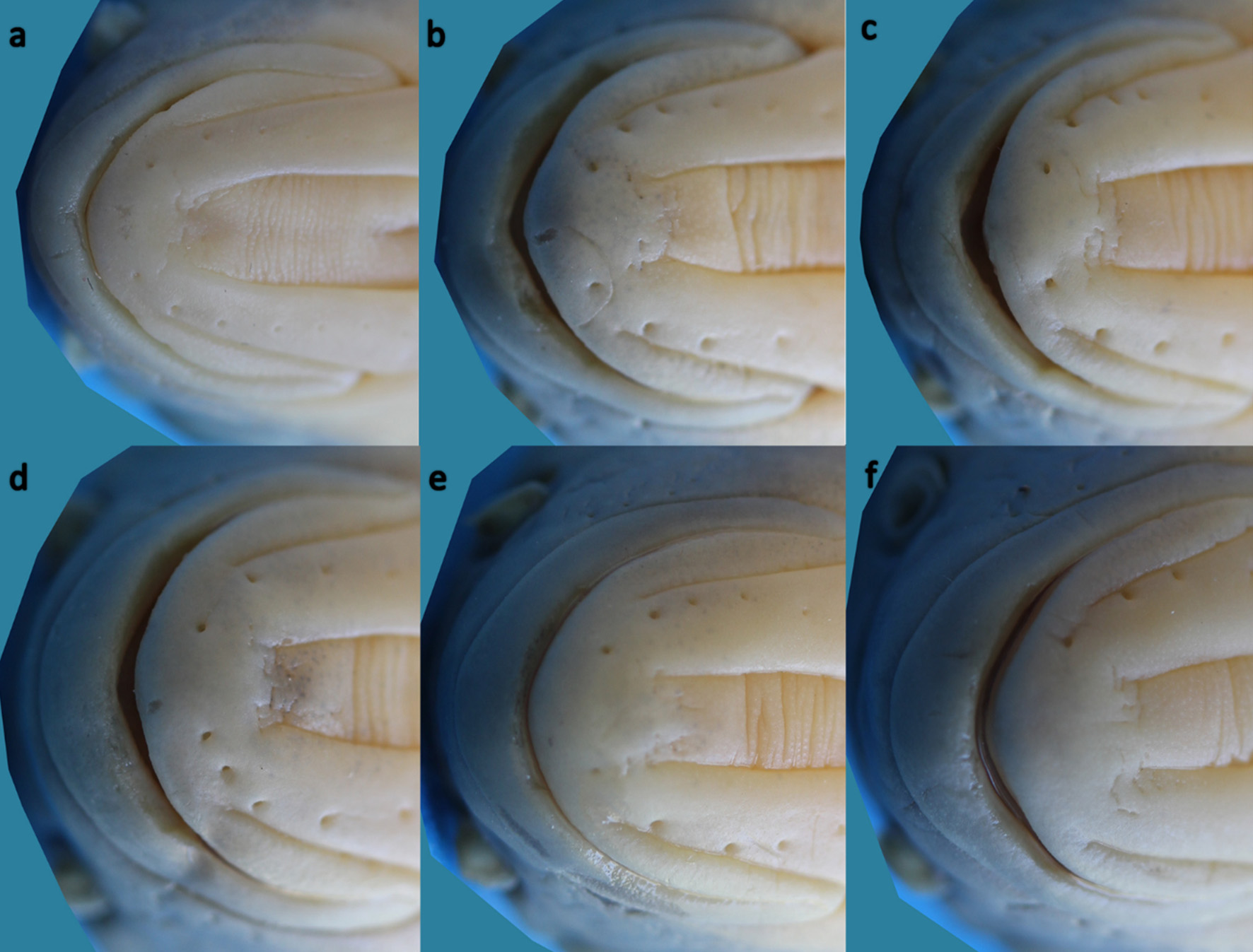
( Figs. 2–4 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
Holotype. ZM-CBSU G 121, 136 mm SL; Iran: Markazi prov.: spring Bolagh (Cheshmeh Bolagh) at Shazand, east of Anjirak , 34°00'38"N 49°50'51"E; H.R. Esmaeili, A. Gholamifard & A. Teimori, 22 June 2009. GoogleMaps
Paratypes. All from Iran: Markazi prov.: ZM-CBSU G111, 10, 170– 202 mm SL; ZM-CBSU E769, 28, 57– 188 mm SL; ZM-CBSU G433, 5, 144- 168 mm SL; FSJF 3521, 5, 105– 146 mm SL; same data as holotype.—ZM- CBSU G1001, 2, 155– 189 mm SL; spring Bolagh (Cheshmeh Bolagh) at Shazand, east of Anjirak, 34 ° 0 0 ' 38 " N 49 ° 50 ' 51 " E.—ZM-CBSU D871, 22, 37–110 mm SL; FSJF 3522, 5, 57–122 mm SL; Poledoab River at Shazand, 34 ° 0 2 ' 36 " N 49 ° 21 ' 0 9 " E.
Material for molecular genetic analysis. All from Iran: ZM-CBSU M271; M272; M273, Markazi prov.: spring Bolagh (Cheshmeh Bolagh) at Shazand , east of Anjirak , 34°00'38"N 49°50'51"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516770 View Materials , KX516771 View Materials , KX516772 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M361; M362, Markazi prov.: Poledoab River at Shazand , 34°02'36"N 49°21'09"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516773 View Materials , KX516774 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M132; M134, Hamedan prov.: Saleh Abad River between Hamedan and Sanandaj , 34°35'23.3"N 48°19'48.1"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516768 View Materials , KX516769 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. Squalius namak is distinguished from the Squalius species found in the adjacent Caspian Sea and Persian Gulf basins by having an unique pigmentation pattern of the flank scales (a bold, grey or brown, roundish or crescent shaped blotch at the tip of each flank scale vs. no bold blotch at the tip of each flank scale: Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 , 5 View FIGURE 5 ). Squalius namak is further distinguished from the species of Squalius in the Caspian Sea and Persian Gulf basins by a combination of characters. It differs from S. berak and S. turcicus by having a wide and thick symphysial knob on the lower jaw ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 ) (vs. no knob or knob thin and small, Figs. 10–11 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 11 ). It is distinguished from S. lepidus from the Euphrates and Tigris drainages by having fewer scales along the lateral line (39–43+1–3 vs. 45–50+1–3), a convex (vs. straight) posterior anal-fin margin, and orange caudal-, anal- and pelvic-fin rays ( v. hyaline or with a yellow hue). Further, the head of S. namak is blunt (vs. pointed) and deeper (head depth 50–63% HL vs. 44–53) and the caudal peduncle shorter than in S. lepidus (15–20% SL vs. 19–23). Squalius namak is distinguished from S. berak from the Qweik, Euphrates and Tigris drainages by having poorly-pigmented scale pockets of the flank scales above the lateral line (vs. scale pockets with a dark-grey, crescent-shaped mark at least on midlateral flank) and orange caudal-, anal- and pelvic-fin rays (vs. hyaline or with a yellow hue). Squalius namak is distinguished from S. turcicus from the Caspian Sea basin by the upper lip clearly projecting beyond the lower lip ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ) (vs. tip of upper lip level with that of lower lip, Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 ). Squalius namak is also characterized by four fixed, diagnostic nucleotide substitutions in the mtDNA COI barcode region.
Description. See Figures 2–4 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 for general appearance and Table 1 View TABLE 1 for morphometric and Table 2 for meristic data. Body elongated, compressed; dorsal and ventral body profile slightly convex; upper head profile concave or straight. Interorbital area concave. Belly between anus and posterior pelvic-fin base compressed. Snout pointed, conical. A shallow hump at nape. Mouth subterminal, upper lip projecting beyond lower lip. Mouth cleft straight, oblique. Snout obtuse, markedly rounded. Head length greater than body depth at dorsal-fin origin. Uppermost point of mouth cleft between level of lower margin of pupil and lower margin of eye. Lower jaw-quadrate junction about at vertical through anterior margin of eye. A very wide, thick symphysial knob on lower jaw ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 ). Upper lip thick, anterior depth 1.6–2.0 times in its lateral length. Eye diameter 1.3–2.5 times in interorbital distance, 15– 32% HL. Caudal-peduncle depth 1.2–1.9 times in its length. Largest recorded individual 189 mm SL.
Holotype Range Mean SD
Standard length (mm) 135.9 32.1–189 91.7
In percent of standard length
Dorsal fin with 3–4 (mode 3) simple and 7½–10½ (mode 8½ or 9½) branched rays, distal margin straight or slightly convex. Dorsal-fin origin behind vertical through pelvic-fin origin. Tip of dorsal fin reaching vertical through anal-fin origin when adpressed. Anal fin with 3–4 (mode 3) simple and 7½–10½ (mode 8½) branched rays; distal margin convex. Posteriormost point of anal fin at tip of 3rd or 4th branched ray. Pectoral fin with 15–18 (usually 16–17), pelvic fin with 9–11 (mode 9) rays. A large axillary pelvic lobe present. Caudal fin forked, with 9+8 branched rays. Lateral line complete, with 39–43 scales on body, 1–3 on caudal-fin base. Scale rows between dorsal-fin origin and lateral line 6½–8½ (mode 7½), scale rows between pelvic-fin origin and lateral line 3½–4½ (mode 3½); 14–18 (mode 16) circumpeduncular scales, 19–24 predorsal scales. Gill rakers on first gill arch 9–12 (mode 10). No external sexual dimorphism observed.
Total lateral-line scales
N 3 9 4 0 4 1 4 2 4 3 4 4 4 5 4 6 4 7 4 8 4 9 5 0 5 1
S. berak * 1 6 6 7 3
S. lepidus 1 5 1 3 5 4 1 1 S . namak 56 6 14 17 14 3 2
S. turcicus 4 4 3 1 1 1 4 1 2 4
S. turcicus * 24 1 6 11 5 1
Scales above lateral line Scales below lateral line
N 6 7 8 9 1 0 N 3 4 5
S. berak * 1 6 1 6 S. berak * 16 4 12
S. lepidus 15 14 1 S. lepidus 15 15
S. namak 56 2 53 1 S. namak 56 52 4 S . turcicus 44 1 28 14 1 S . turcicus 44 42 2 S . turcicus * 2 4 1 2 3 S . turcicus * 2 4 2 2 2 Predorsal scale
N 1 6 1 7 1 8 1 9 2 0 2 1 2 2 2 3
S. berak 3 2 1
S. lepidus 1 5 1 2 3 4 3 S. namak 5 6 1 5 1 5 1 7 1 2 6 S . turcicus 44 1 1 10 17 6 5 4 Branched anal-fin rays Branched dorsal-fin rays
N 6½ 7½ 8½ 9½ N 6½ 7½ 8½ 9½
S. berak * 1 6 1 4 2 S . berak * 1 6 1 6 S. lepidus 15 6 9 S . lepidus 15 2 13 S . namak 56 1 15 36 4 S . namak 56 11 43 2 S. turcicus 44 10 32 2 S. turcicus 44 1 4 39 S. turcicus * 24 19 5 S . turcicus * 24 3 21 Coloration. In life: head and body silvery brown, darker on back. Belly white. A faint black bar from uppermost gill opening to pectoral-fin base. Peritoneum black. Each flank-scale margin with dark brown or black pigments forming a reticulate pattern. Scale pocket poorly pigmented above lateral line, with a bold, brown or black, crescent-shaped, vertically elongated or roundish anterior scale mark on scales below lateral line. Free margins of scales above lateral line pale brown or grey, each with a bold, brown or black, crescent-shaped, vertically elongated or roundish blotch on posterior tip ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 , 5 View FIGURE 5 ). Caudal-, anal- pelvic- and pectoral-fin rays orange, caudal-fin rays with black pigments. Dorsal-fin membranes hyaline with dark-grey rays.
In preservation: Head and body pale brown, darker on back. Dorsal and caudal fins with blackish rays and hyaline membranes; rays whitish and membranes yellowish in pectoral, pelvic and anal fins.
Distribution. Squalius namak is known from the springs Bolagh ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 ) and Eskan in the Poledoab River drainage and the spring Emamzadeh Abdolah in the Qom River drainage, all in the Namak Lake basin. It also occurs in the Hableh River in the Kavir basin.
Etymology. The species is named for the Namak Lake basin. A noun in apposition.
Remarks. In the Euphrates and Tigris drainage, S. lepidus is very widespread and usually inhabits larger rivers and streams in lowland habitats (own observations). In headwater streams and rivers in mountainous habitats, a second Squalius species is found in the Euphrates and Tigris drainage (own observations) usually identified as S. cephalus ( Abdoli 2000) . A syntopic occurrence of both species was detected by JF in the Little Zab River drainage (Tabon River) in Iraqi Kurdistan. Here we identify this chub as S. berak , a species described from the Qweik River in Syria, a small endorheic drainage west to the Euphrates. Squalius berak from the Sünnep, a headwater stream of the Qweik in Turkey, shares the COI barcode sequence with superficially similar, round-headed Squalius found in the Euphrates and Tigris drainage. However, the lineage sorting between S. lepidus and S. berak is not complete and both species seem occasionally to hybridize. This might lead to the false classifications of a few individuals and populations of both species based on their COI barcode sequence as seen in Figure 1.
Naseka & Bogutskaya (2009) identified the Squalius populations of the southern Caspian Sea basin as S. orientalis . Squalius orientalis was described from Abkhazia ( Berg 1949), which is situated between Georgia and Russia, in the easternmost Black Sea basin. Squalius orientalis is treated as a valid species by Stoumboudi et al. (2006), Doadrio & Carmona (2004) and Turan et al. (2009, 2013), without discussing in detail how it is distinguished from S. cephalus . Özuluğ & Freyhof (2011) discussed the case and kept S. orientalis as a synonym of S. cephalus based on the lack of studies of the morphological characters distinguishing S. orientalis from S. cephalus . The present analysis, however, includes COI sequences of S. orientalis from Georgia and Turkey. These fishes are very close to S. turcicus , a species described from the upper Arax River in Turkey by De Filippi (1865). Özuluğ & Freyhof (2011) suggested that S. turcicus might be a valid species occurring in the southern Caspian Sea basin and Turan et al. (2013) supported this view and provided some morphological data distinguishing this species from S. orientalis . Our molecular data suggest that S. orientalis and S. turcicus are very closely related and might represent just one species ( S. orientalis ). Squalius turcicus might be more widespread and Squalius populations from the Lake Urmia basin, as well as those from the Iranian Sefid River and from the Iranian Talar River (flowing to the Caspian Sea at Bahnamir), might belong to this species. More and geographically focused studies are needed to better understand the distribution of S. turcicus in the rivers of the southern Caspian Sea basin.
Comparative materials. Squalius berak : NMW 48915, 6 , syntypes, 64–304 mm SL ; Syria: Aleppo.— ZM- CBSU J1725, J1740, J1741, 3, 133– 137 mm SL ; Iran: West Azerbaijan prov.: Little Zab River at road between Piranshahr and Sardasht, 36°28'36"N 45°19'54"E.—ZM-CBSU G1723, 2, 43-52 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Iran: Kordistan prov.: Boeen River at road between Baneh and Boeen, 35°56'35.5"N 45°56'36.5"E.— IUSHM 2010-984, 4 , 112– 143 mm SL; FSJF 2912, 4 , 113– 146 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Turkey: Kilis prov.: stream Sünnep 10 km east of Kilis, 36°45'50"N 37°15'14"E.— FSJF 3262, 8 , 83–135 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Iraq: Nalparez River , 35°34.24'N 45°51.78'E.— FSJF 3349, 9 , 45– 158 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Iraq: Kuna Massi stream in Sevanja , 35°47.35'N 45°24.18'E. GoogleMaps
Squalius lepidus : FSJF 2893, 15, 43–190 mm SL; Turkey: Gaziantep prov.: tributary to Merziman stream south of Yavuzeli , 37°16'36"N 37°31'56"E.— FSJF 2996, 6 , 109– 133 mm SL GoogleMaps , Turkey: Gaziantep prov.: Merziman stream south of Yavuzeli , 37°17'32"N 37°43'23"E.— IUSHM 2010-991, 2 , 174– 188 mm SL; FSJF 2862, 2 , 183– 213 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Turkey: Batman prov.: Tigris River 5 km west of Hasankeyf , 37°43'25''N 41°21'37''E.—ZM-CBSU G794, 3, 145– 125 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Iran: Kermanshah prov.: Seymareh River west of Charu Dareh , 33°39'40"N 47°03'29"E.—ZM-CBSU G797A, 1, 127 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Iran: Kermanshah prov.: Seymareh River south of Mahizan , 33°40'54"N 47°03'22"E. GoogleMaps
Squalius turcicus : IUSHM 2013-1057, 6 , 87–178 mm SL; Turkey: Kars prov.: stream between Sarikamis and Handere, about 4 km southwest of Sarikamis , 40°19'10"N 42°32'41"E.—ZM-CBSU D864, 4, 137– 65 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Iran: Ardabil prov.: spring Chay Almas east of Sarein , 38°09'31"N 48°11'37"E.—ZM-CBSU D504, 22, 38–145 mm SL GoogleMaps ; Iran: East Azarbaeijan prov.: stream Chay near Vardin , 38°26'49"N 46°59'14"E. GoogleMaps
Materials used for molecular analysis. Squalius berak : FSJF DNA- 1383 , Turkey: Kilis prov.: stream Sünnep 10 km east of Kilis, 36°45'50"N 37°15'14"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516744 View Materials , KX516745 View Materials , KX516746 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .—FSJF DNA-1416; FSJF DNA- 2355 , Turkey: Sivas prov.: Kangal stream under railway bridge at Çetinkaya , 39°15'4.644"N 37°37'7.464"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516734 View Materials , KX516735 View Materials , KX516736 View Materials , KX516737 View Materials , KX516741 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— FSJF DNA- 1585 , Turkey: Erzurum prov.: Karasu stream at Kandilli , 39°91'24''N 40°85'40''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516738 View Materials , KX516739 View Materials , KX516740 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .—FSJF DNA-2257; FSJF DNA- 2275; FSJF DNA- 2290 ; Iraq: Tabin River west of Zarbi , 35°48'06''N 44°58'47''E (GenBank accession number: KX516752 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— FSJF DNA- 2259 , Iraq: stream Zalm at Khurmal , 35°18.38'N 45°58.26'E (GenBank accession number: KX516750 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— FSJF DNA- 2389 , Turkey: Erzurum prov.: stream Arkaçayırlar at Paşayurdu close to the road from Ilıca to Aşkal , 39°58'59.952"N 40°59'31.308"E (GenBank accession number: KX516743 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M464; M465, Iran: West Azerbaeijan prov.: Badin Abad River at Piranshahr , 36°28'36''N 45°19'54''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516747 View Materials , KX516748 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .
Squalius lepidus : FSJF DNA- 1445 , Turkey: Gaziantep prov.: tributary to Merziman stream south of Yavuzeli , 37°16'36"N 37°31'56"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516753 View Materials , KX516754 View Materials , KX516755 View Materials ). GoogleMaps —FSJF DNA-1441; FSJF DNA-1442; FSJF DNA-1447; FSJF DNA- 1462 ; Turkey: Batman prov.: Tigris River 5 km west of Hasankeyf , 37°43'25''N 41°21'37''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516764 View Materials , KX516765 View Materials , KX516766 View Materials , KX516767 View Materials ). GoogleMaps —FSJF DNA-2248; FSJF DNA-2271; FSJF DNA- 2287 ; Iraq: Tabin River west of Zarbi , 35°48'06''N 44°58'47''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516761 View Materials , KX516762 View Materials , KX516763 View Materials ).—ZM-CBSU M751; M752; M755; M756 GoogleMaps , Iran: Ilam prov.: Seymareh River at Seymareh bridge, at Darehshar , 33°39'19''N 47°02'15''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516756 View Materials , KX516757 View Materials , KX516758 View Materials , KX516759 View Materials ).—ZM-CBSU M1116 GoogleMaps , Iran: Kohkiluye and Boyerahmad prov.: Bashar River at Talegah , 30°38'55''N 51°37'06''E (GenBank accession number: KX516760 View Materials ). GoogleMaps
Squalius orientalis : FSJF DNA- 260 , Georgia: River Galidzga about 5 km upstream from coast, 42°42'28'' N 41°29'06''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516776 View Materials , KX516777 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— FSJF DNA- 1589 , Turkey: Çoruh River at Borçka , 41°36'54''N 41°67'77''E (GenBank accession number: KX516775 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— FSJF DNA- 1780 , Georgia: Chakhota River at Natanebi , 42º55'59''N 41º50'10''E (GenBank accession number: KX516778 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— ZFMK:ICH:TIS:NB203; Georgia: Chakhvata stream ca. 30 km west of Guria, 41°55'59''N 41°50'10''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516779 View Materials , KX516780 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .
Squalius turcicus : FSJF DNA- 2344 ; Turkey: Kars prov.: Güllü stream at Bölükbaşı village 3 km west of Selim , 40°28'15.924"N 42°44'11.76"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516786 View Materials , KX516787 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .—FSJF DNA-2357; FSJF DNA 2372 About DNA ; Turkey: Ardahan prov.: Lake Çıldır at Akçakale village , 41°4'53.292"N 43°17'42.432"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516788 View Materials , KX516789 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— FSJF DNA- 2393 , Turkey: Kars prov.: stream crossing the road between Sarıkamış and Handere, 4 km southwest of Sarıkamış , 40°19'9.588"N 42°32'41.46"E (GenBank accession number: KX516790 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M461, Iran: Ardabil prov.: Aras River at Pasrabad Moghan , 38°35'05"N 47°48'09"E (GenBank accession number: KX516783 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M152; M153, Iran: Zanjan prov.: Qezel Owzan River south west of Balobin village , 36°19'26"N 48°09'13"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516798 View Materials , KX516799 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M359; M360, Iran: Ardabil prov.: Gharehsu River at Kangavar , 38°35'05"N 47°48'07"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516781 View Materials , KX516782 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M462, M463, Iran: Ardabil prov.: Balakhluchay River at Nir , 38°02'02"N 47°58'30"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516784 View Materials , KX516785 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— ZM- CBSU S928F, Iran: Kurdistan prov.: Serudan River at road between Marivan and Saghez, 35°44'34''N 46°26'40''E (GenBank accession number: KX516803 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M154, Iran: Kurdistan prov.: Divan Darreh at Nesar Olya , 35°52'22''N 47°04'17''E (GenBank accession number: KX516800 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . —ZM-CBSU M285, Iran: Mazandaran prov.: Azar River at Shirgah , 36°18'15''N 52°53'07''E (GenBank accession number: KX516802 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— ZFMK:ICH:TIS:NB80; Russia: stream Shuraozen about 2 km west of Korkmaskala , 42°59'55''N 47°12'06''E (GenBank accession number: KX516801 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .—ZFMK:ICH:TIS:66542; ZFMK:ICH:TIS:66543; Turkey: Digor stream at Digor , 40°22'32.48"N 43°24'57.57"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516791 View Materials , KX516792 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— ZFMK:ICH:TIS:66572; ZFMK:ICH:TIS:66573; Turkey: stream Selim in Selim , 40°28'9.68"N 42°46'57.64"E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516793 View Materials , KX516794 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .—ZFMK:ICH:TIS:66601; ZFMK:ICH:TIS:66602; IUSHM 2012-1052 ; Turkey: Çıldır Lake , 41°3'3.44"N 43°13'46.64"E (GenBank accession numbers: KU729274 View Materials , KX516795 View Materials , KX516796 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .
Petroleuciscus borysthenicus : ZFMK:ICH:TIS:NB187; Georgia: Gubistskali stream about 8 km east of Samtredia, 42°10'10''N 42°25'53''E (GenBank accession numbers: KX516732 View Materials , KX516733 View Materials ). GoogleMaps
TABLE 1. Morphometric data of Squalius namak (holotype ZM-CBSU G 121, paratypes ZM-CBSU E 100, n = 10; ZM- CBSU E 769, n = 28; ZM-CBSU G 1001, n = 2; ZM-CBSU D 871, n = 22).
| Head length 28.4 | 24.6–32.5 | 28.4 | 1.5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snout length 9.3 | 6.8–9.7 | 8.2 | 0.5 |
| Postorbital distance 15.3 | 12.4–17.7 | 15.3 | 0.9 |
| Interorbital distance 10.3 | 8.8–12.3 | 10.3 | 0.7 |
| Predorsal length 56.4 | 50.6–59.3 | 56.0 | 1.5 |
| Postdorsal length 52.9 | 45.4–61.9 | 54.2 | 2.8 |
| Dorsal-fin base length 18.7 | 15.7–24.7 | 20.0 | 2.0 |
| Dorsal-fin depth 11.7 | 9.1–15.5 | 11.1 | 0.8 |
| Anal-fin base length 13.8 | 13.1–21.2 | 16.8 | 1.7 |
| Anal-fin depth 10.3 | 7.6–13.5 | 10.3 | 0.8 |
| Preanal length 74.5 | 65.7–75.8 | 72.9 | 1.5 |
| Pectoral-fin length 16.9 | 13.3–20.0 | 17.5 | 1.2 |
| Pelvic-fin length 14.8 | 12.9–17.8 | 15.4 | 0.9 |
| Depth of caudal peduncle 12.2 | 9.2–12.8 | 11.7 | 0.6 |
| Body depth at dorsal-fin origin 24.8 | 22.5–28.4 | 25.4 | 1.3 |
| Distance between pectoral and anal-fin origins 46.3 | 39.4–48.5 | 44.7 | 2.2 |
| Distance between pectoral and pelvic-fin origins 25.3 | 20.4–27.0 | 23.6 | 1.5 |
| Distance between pelvic and anal-fin origins 21.6 | 17.4–24.2 | 21.3 | 1.4 |
| Length of caudal fin 20.6 | 16.8–29.4 | 22.4 | 2.7 |
| Length of caudal peduncle 15.1 | 14.0–20.5 | 17.3 | 1.3 |
| In percent of head length | |||
| Head depth 56 | 50–63 | 56 | 3.0 |
| Snout length 33 | 25–33 | 29 | 1.9 |
| Postorbital distance 54 | 44–61 | 54 | 2.4 |
| Interorbital width 36 | 32–44 | 36 | 2.1 |
| Eye diameter 20 | 15–32 | 22 | 3.2 |
| Length of caudal fin 73 | 48–73 | 61 | 5.6 |
| Mouth width 31 | 18–35 | 25 | 3.5 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |