Chaunax flavomaculatus, Ho, Hsuan-Ching, Roberts, Clive D. & Stewart, Andrew L., 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3620.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E056EC4E-1DE6-4CC9-A53A-4CA1D03D2473 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5617632 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0D82711E-DAE0-4604-A8B5-38111057EC48 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:0D82711E-DAE0-4604-A8B5-38111057EC48 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chaunax flavomaculatus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chaunax flavomaculatus View in CoL sp. nov.
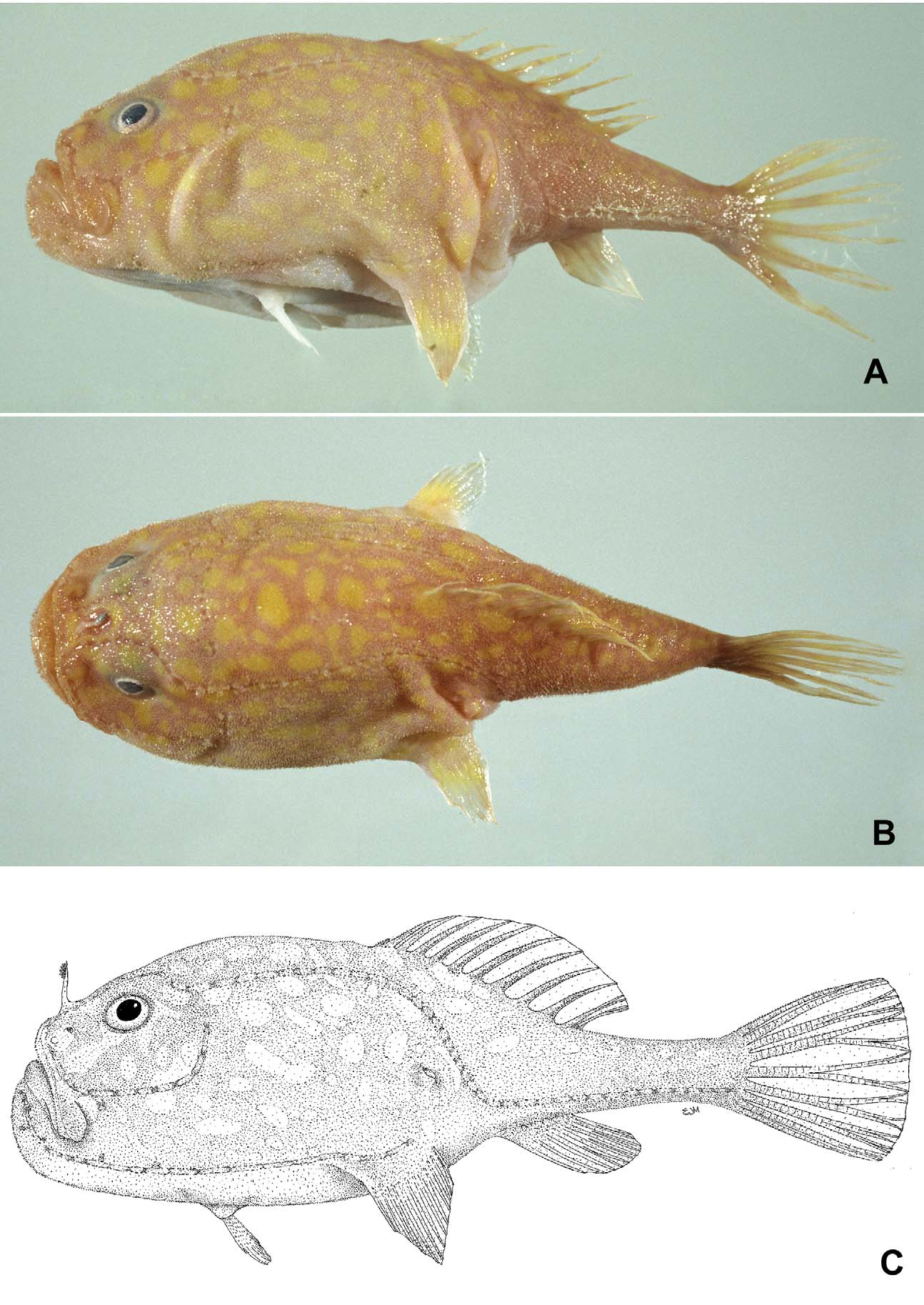
New English name: Yellowspot frogmouth ( Figures 3 View FIGURE 3 A–C, Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Chaunax sp. A: Roberts et al., 2009: 532 (listed).
Holotype: NMNZ P. 032620, 105 mm, NE of Great Barrier Island, New Zealand, 35º43.65'S, 175º52.8'E, 370–375 m, F/V Albatross II, stn. OBS 0864/031, bottom trawl, 16 Jul. 1995, coll. D. Wrightson.
Paratype: NMNZ P.034946, 122 mm, Moa Seamount, New Zealand, 35º45.15'S, 175º50.1'E, 353–355 m, F/V Drysdale, stn. OBS 1054/062, bottom trawl, 13 Dec 1997, coll. B. Liddle.
Diagnosis. A member of the Chaunax abei -species group distinguished from its congeners in having a mix of bifurcated and simple dermal spinules and large yellow spots on a pinkish background dorsally when fresh, uniformly creamy white in preservation. Gill rakers: GRi = 11 (2+9); GRii = 9; GRiii = 8–9; GRiv = 7. Lateral-line neuromasts: AB = 11; AC = 8; BB' = 4; BD = 2; CD = 5–6; DG=3–4; EF = 4; FG = 3; GH = 12–13; BI = 32–34.
Description. Morphometric and meristic data are given in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Head length 2.4 (2.6) in SL; head width 5.4 (5.7) in SL, 2.2 (2.2) in HL; pre-dorsal length 2.1 (2.0) in SL; pre-gill opening length 1.6 (1.5) in SL; prepreopercular length 3.6 (3.7) in SL, 1.5 (1.4) in HL; upper jaw 5.0 (5.2) in SL, 2.1 (2.0) in HL; illicial length 9.1 (8.7) in HL; illicial trough length 5.9 (6.3) in HL; eye diameter 5.0 (5.8) in HL; post-dorsal fin length 4.9 (4.9) in SL, 2.0 (1.9) in HL; post-anus length 2.9 (2.8) in SL, 1.2 (1.1) in HL; post-anal fin length 5.7 (5.5) in SL, 2.4 (2.1) in HL; caudal peduncle depth 4.9 (5.0) in HL; caudal fin length 3.4 (3.2) in SL, 1.4 (1.3) in HL
Head globular, skull elevated posteriorly; body deep; trunk cylindrical, slightly compressed, tapering posteriorly; ventral surface flattened; skin loose and flaccid; interorbital space broad; caudal peduncle short and stout, slightly depressed, tapering posterior. Eyes rounded, directed dorsolaterally, covered by a dermal membrane broadly connected to adjoining skin, forming a clear “window”.
Illicium long and slender; esca with a small central tongue bearing many thin brown cirri; second dorsal-fin spine close to illicium, embedded under skin; third dorsal-fin spine situated at about mid-point of pre-dorsal distance, embedded under skin. Illicial trough small and relatively concave, oval, longer than wide, its width less than diameter of eye pupil.
Two nostrils anterior to each eye, anterior nostril surrounded by a fleshy membrane, posterior part higher than anterior part, posterior nostril a simple round hole; mouth wide, terminal, its opening nearly vertical; lower jaw slightly protruding beyond upper jaw; maxilla tapering above, broad below; a blunt symphyseal spine on lower jaw symphysis.
Broad transparent membrane on first gill arch; first ceratobranchial broadly connected to opercular wall; gill filaments present on second to fourth gill arches, two rows of gill filaments on second and third gill arches, one row of gill filaments on fourth gill arch; gill filaments on inner row of third and fourth gill arches about half length of those on other arches; inner surface of fourth gill arch completely connected to body. Single row of 11 rakers on 1st gill arch, 2 on upper limb and 9 on lower limb, 9 paired rakers on 2nd arch, 8–9 paired rakers on 3rd arch and single row of 7 rakers on 4th arch.
Skin thin, tips of pectoral- and pelvic-fin rays free. Dermal spinules relatively short and stout, mixed with simple and bifurcated spinules covering entire body, except for the eye window, outer half of pectoral fins, entire anal fin and inter membranes of all fins. Wide band of 8–10 rows of dermal spinules in front of illicial trough. Lateral-line network system as described by Caruso (1989). Interspaces of lateral-line neuromast complex slightly wider than its width; 3 pairs of short spines bridging neuromasts.
Teeth villiform, short, fang-like; 5–6 irregular rows in upper jaw, similar in size, except for those in innermost row that are slightly longer than others; teeth in lower jaw with same arrangements. Teeth on vomer small, forming two wide bands, in about 3 rows, distinctly separated by small medial space; those on palatine small, forming elongate patch, close to outer end of vomerine tooth patch.
Dorsal fin rays III, 12, first ray shortest, about half length of the second; all except last 2 rays branched. Pectoral fin fan-shaped, with 13 rays, the 4th or 5th ray longest, those below 6th ray gradually shorter. Anal fin with 7 rays, first shortest, first and second simple, last 5 branched. Caudal fin truncate, with 9 rays, second to seventh rays branched, other 3 simple, lower most ray shortest, close to adjacent one.
Cirri present on outside of both jaws, laterally on body and caudal peduncle, but absent from dorsal surface of head.
Colouration. Fresh ( Fig.3 View FIGURE 3 A–B): large irregular-sized yellow blotches on dorsal surface; all fins yellowish; esca with grey cirri. Preserved: body creamy white; esca with brownish cirri.
Distribution. Known only from the type series collected from northern New Zealand at depths of 353–375 m (Fig. 4).
Etmology. From the Latin “flavo” – yellow and “maculatus” – spot, in reference to the fresh colouration of the dorsal body.
BI 32*(2), 33*(1), 34(1) 32*(2), 33*(6), 34(7), 35(5), 36(7), 39, 40
37(4), 38(6), 39(7), 40(4)
Remarks. Chaunax flavomaculatus sp. nov. is most similar to C. abei and C. endeavouri , with which it shares a mix of numerous bifurcated and simple dermal spinules. Chaunax flavomaculatus sp. nov. is unique in having many large yellow spots on the pinkish background of the dorsal surface when fresh, and a creamy white body when preserved. Chaunax abei has much smaller green spots each circled by a yellow ring, and C. endeavouri has relatively numerous, irregular green spots on the dorsal surface when fresh; and these spots of both species turn to gray or brown in preservation. Moreover, C. abei is restricted to the northwestern Pacific Ocean ranging from Japan to southern Taiwan and into the South China Sea (Ho, unpublished data); and C. endeavouri is endemic to eastern Australia, ranging from Queensland to Tasmania (Gomon & Ho, 2008), whereas C. flavomaculatus sp. nov. is apparently endemic to northern New Zealand.
TABLE 1. Morphometric and meristic data for three Chaunax species in present study. Meristic features are counted on both sides when paired. H = holotype. SD = standard deviation. * donates value of holotype.
| C. flavomaculatus sp. nov. | C. mulleus sp. nov. | C. nudiventer |
|---|---|---|
| H All types | H | |
| SL (mm) 105 105–122 (n=2) | 146 112–146 (n=24) | 71–94 (n=4) |
| Morphometrics values (% SL) | Mean (Range) SD | Mean (Range) SD |
| Head length 41.7 39.1–41.7 | 40.2 40.9 (38.7–43.0) 1.0 | 40.3 (38.6–41.7) 1.3 |
| Head width 18.7 17.4–18.7 | 20.1 19.3 (18.0–20.4) 0.8 | 17.1 (16.2–17.9) 0.8 |
| Pre-dorsal length 47.1 47.1–49.8 | 46.7 47.9 (45.9–50.6) 1.2 | 49.4 (48.2–51.3) 1.7 |
| Pre-gill opening length 62.3 62.3–65.5 | 62.9 61.9 (59.3–66.3) 1.7 | 61.9 (60.5–63.5) 1.5 |
| Pre-preopercular length 27.8 27.0–27.8 | 28.1 28.4 (26.7–31.6) 1.2 | 27.9 (27.2–28.8) 0.7 |
| Upper jaw length 20.1 19.1–20.1 | 20.8 21.2 (19.4–24.2) 1.1 | 19.9 (17.9–21.6) 1.7 |
| Illicial length 4.6 4.5–4.6 | 3.6 4.1 (3.4–4.7) 0.4 | 3.5 (2.8–3.9) 0.5 |
| Illicial trough length 7.0 6.2–7.0 | 5.8 6.5 (5.5–7.9) 0.4 | 6.0 (5.0–6.6) 0.7 |
| Eye diameter 8.3 6.7–8.3 | 8.5 8.5 (7.5–9.3) 0.5 | 8.5 (7.6–9.1) 0.7 |
| Post-dorsal fin length 20.6 20.3–20.6 | 19.4 20.1 (17.6–22.4) 1.2 | 20.8 (20.4–21.4) 0.4 |
| Post-anus length 34.0 34.0–35.8 | 34.5 33.5 (29.1–35.9) 1.5 | 33.3 (29.3–37.9) 3.8 |
| Post-anal fin length 17.6 17.6–18.3 | 17.9 17.5 (15.1–19.3) 0.9 | 18.4 (17.6–20.6) 1.5 |
| Caudal peduncle depth 8.6 7.9–8.6 | 8.9 8.2 (7.2–9.3) 0.6 | 7.3 (6.8–7.7) 0.4 |
| Caudal fin length 29.4 29.4–31.0 | 30.4 30.5 (27.0–34.2) 1.7 | 31.1 (29.8–32.4) 1.2 |
| Meristics values n=2 | n=24 | n=1 |
| Pectoral-fin rays 13*(4) Lateral-line neuromasts Value (frequency) | 12*(46), 13(2) Value (frequency) | 14(2) |
| AB 11*(4) | 11 (5), 12*(39), 13(4) | 11 |
| BB' 4*(4) | 4*(37), 5(11) | 4 |
| AC 8*(4) | 8*(47), 9(1) | 8 |
| BD 2*(4) | 2*(34), 3 (14) | 4 |
| CD 5*(2), 6*(2) | 6*(24), 7(23), 8*(1) | 6, 7 |
| DG 3*(4) | 3*(37), 4(11) | 3 |
| EF 4*(4) | 3*(2), 4*(40), 5(5), 6(1) | 4 |
| FG 3*(4) GH 12*(2), 13*(2) | 4*(42), 5(6) 11*(4), 12*(26), 13(6), 14(11), 15(1) | 3 14, 15 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |