Biddulphia tridens (Ehrenberg) Ehrenberg, 1841
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.517.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8071943 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1304879D-DB3C-ED3D-EAF6-2AC30AC3F7A1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Biddulphia tridens (Ehrenberg) Ehrenberg |
| status |
|
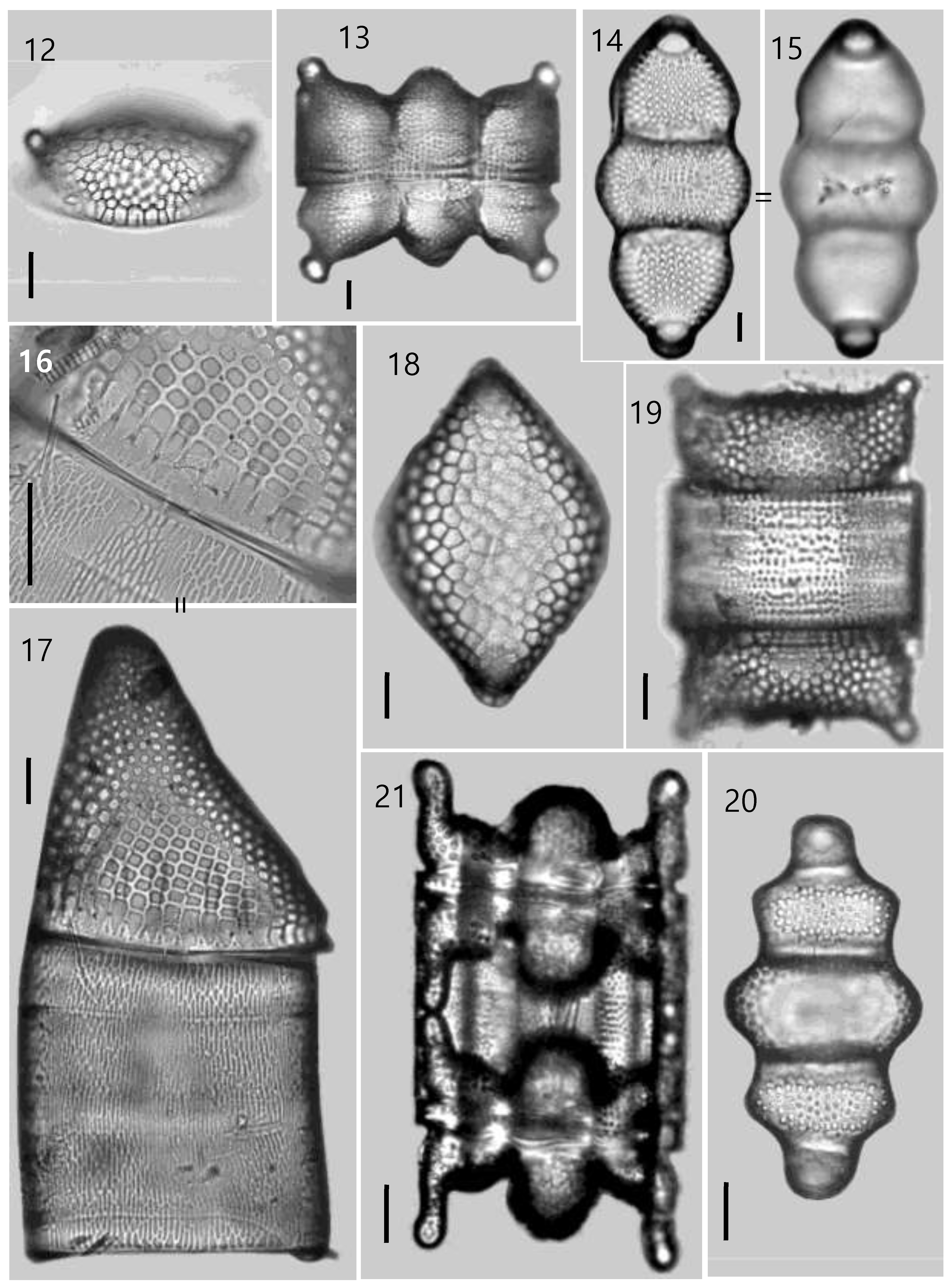
5. Biddulphia tridens (Ehrenberg) Ehrenberg ( Figs 20, 21 View FIGURES 12–21 )
Basionym: Denticella tridens Ehrenberg.
Synonym: Biddulphia tuomeyi (Bailey) Roper.
Type locality: Kreidemergel (fossil).
References: Boyer 1900, p. 695–697; Hustedt 1927 –1930, p. 834, fig. 490.
Morphometrics: Valves 40–67 (30–250) μm in apical length, 23–35 (20–60) μm wide, areolae 6–7 (4–7) in 10 μm.
Remarks: Biddulphia tridens is widely distributed in the littoral zone of coasts in the warmer oceans, and only in the southern coasts of Europe ( Hustedt 1927 –1930). This taxon is common along the South Atlantic coast of North America ( Boyer 1900), in estuarine coast of Indian Sea ( Gopinathan 1975), Tahiti Islands ( Ricard 1977), North Island harbor of New Zealand ( Stidolph 1980), temperate estuary of western Portugal ( Resende et al. 2005), northeast coast of Brazil ( Pereira et al. 2007), and along the coast of Baja California Peninsula in Mexico ( Gárate-Lizárraga et al. 2014, Siqueiros-Beltrones et al. 2017). It is listed on the diatom catalogue of Caribbean Sea ( Navarro & Hernández-Becerril 1997). This species is generally widespread along the coasts and estuaries of warmer oceans. It is detected frequently along the coast of Korean Peninsula ( Shim 1994), and more or less frequently encountered as an epiphyte on seaweeds in the Seogwipo coast in Jeju Island.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |