Chthonius elymus, Gardini, Giulio, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3655.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FC302AA5-49CC-41B0-9A66-23C11AB4EBAE |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6155937 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DE87C1-FFC9-F947-6B99-FDCB1C12A1B7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chthonius elymus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chthonius View in CoL (E.) elymus n. sp.
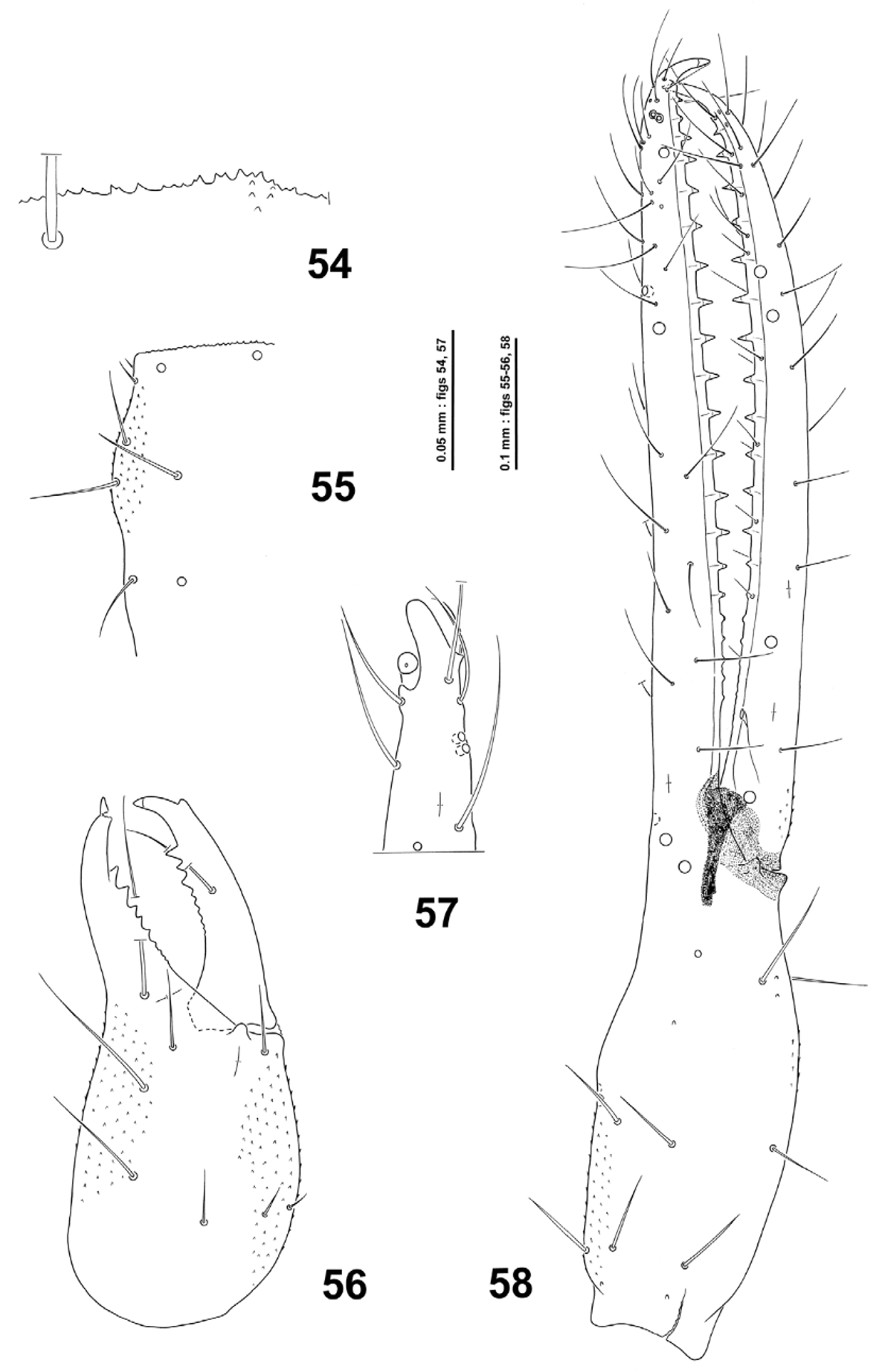
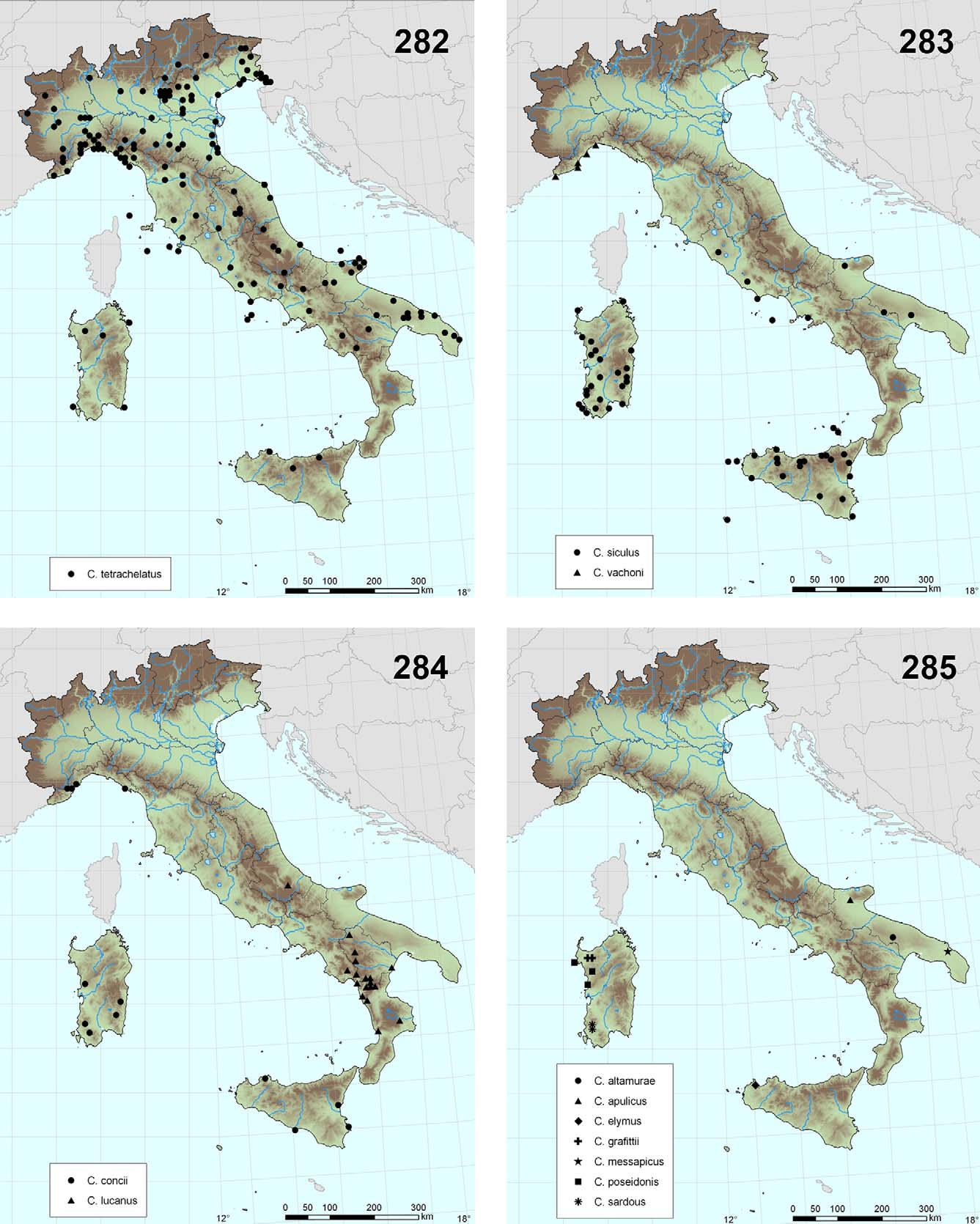
( Figs 54–58 View FIGURES 54 – 58 , 285 View FIGURES 282 – 285 )
Type locality: Italy, Sicily, Trapani Prov., Custonaci, Abisso del Purgatorio 8064 Si/TP (38°04ʹ44.2ʺN 12°43ʹ35.6ʺE).
Distribution. Italy: Sicily.
Diagnosis (3). An anophthalmic hypogean Chthonius (Ephippiochthonius) from Sicily that differs from other species of the C. tetrachelatus group in the following combination of characters: movable cheliceral finger without isolated subapical tooth (di); males with spinneret; carapace with 2 preocular microsetae on each side; fixed and movable chelal finger respectively with 16 and 13 triangular teeth; pedipalpal fixed finger at level of est-it with 4 teeth occupying 0.1 mm (distance between apices 0.027 mm); length of chela 1.02 mm, length of movable chelal finger 0.63; chela 6.8 times as long as deep; ratio of pedipalpal femur/carapace 1.55.
Type material. ITALY — Sicily: Trapani Prov.— 1 3 (holotype), Custonaci, Monte Palatimone, Abisso del Purgatorio 8064 Si/TP (38°04ʹ44.2ʺN 12°43ʹ35.6ʺE), XI.1993, I. Galletti leg. (deposited in MHNG).
Derivatio nominis. The Elymians were the ancient inhabitants of the western part of Sicily, descendants, according to Thucydides (Historiae, VI, 2), of Trojan refugees.
Description of adult (3; Ƥ unknown). Troglomorphic facies. Integument with weak pigmentation, pale yellow-brown; marked hispid granulation on lateral surface of carapace, on cheliceral palm, on dorsal surface of pedipalpal hand and on the base of movable chelal finger. Carapace (broken during dissection of right chelicera) 1.1 times longer than broad, posteriorly slightly constricted; anterior margin (fig. 54) between median macrosetae dentate, with weakly prominent epistome; ocular area as in fig. 55, no eyes or eye-spots; chaetotaxy mm 4mm:6:4:2:2 (18), macrosetae moderately thick; length of anteromedian macrosetae 0.095 mm. Chaetotaxy of tergites I–X 4:4:4:4:6:6:6:6:6:4. Chaetotaxy of sternites II–X 10:(3)8(3):(2)7(2):8:6:6:6:6:7. Chelicerae (fig. 56) 2.5 times as long as broad, palm with 6 setae and 2 microsetae laterally; fixed finger with 7 teeth proximally reduced in size and 4 proximal microtubercles; movable finger with 7 teeth proximally reduced in size, isolated subapical tooth (di) absent; gl ratio 0.58; spinneret weakly prominent at a right angle, apically rounded; rallum with 11 blades; serrulae interior and exterior respectively with 12 and 14 blades. Coxal setae: pedipalp 5 (including 2 on manducatory process), I 4 + 3 marginal microsetae, II 4, III 5, IV 6; coxae II with 10 and 11 coxal spines, coxa III with 6 coxal spines; intercoxal tubercle bisetose. Pedipalp (figs 57–58): femur 7.3 times as long as broad, with hispid granulation basally; chela 6.8 times as long as deep; hand of chela 2.5 times as long as deep, with a weak and deep hump distad of ib-isb; dentition of chelal fingers similar to that of C. siculus ; fixed chelal finger with 21 teeth: 16 upright, triangular and sharp teeth with dental canals gradually reduced and less sharp towards the base of the finger and 5 proximal small, rounded teeth without dental canals; tip of fixed finger with a modified accessory tooth (td) on antiaxial face; fixed chelal finger at level of est - it with 4 teeth occupying 0.1 mm (distance between successive apices 0.027 mm); movable chelal finger with 17 teeth: one distal smaller tooth, 12 upright, triangular and sharp teeth with dental canals and 4 small rounded teeth—without dental canals—gradually reduced back to proximad of sb; coupled sensilla pc halfway between b and sb; trichobothria as in fig. 58, eb-esb-ist placed in a straight line; basal apodeme of movable finger strongly sclerotized, rectangular and apically truncate; ratio of movable finger/hand of chela 1.65; ratio of pedipalpal femur/movable finger 1.15; ratio of pedipalpal femur/ carapace 1.55.
Measurements (in mm). Body length 1.6. Carapace 0.47 × 0.43 (0.39 anteriorly). Chelicerae 0.425 × 0.17, movable finger length 0.21. Pedipalp: femur 0.73 × 0.10; chela 1.02 × 0.15; hand length 0.38; movable finger length 0.63.
Remarks. Among the species of the Chthonius tetrachelatus group, C. elymus n. sp. is presumably related to the epigean C. siculus because of less spaced dentition of fixed chelal finger, but it differs from the latter in most troglomorphic characters. C. elymus n. sp. is similar to the hypogean species C. altamurae from Apulia, from which it differs chiefly in dentition of chelal fingers: fixed chelal finger at level of est-it with 4 teeth occupying 0.1 mm (distance between successive apices 0.027 mm) in C. elymus , fixed chelal finger at level of est-it with 3 teeth occupying 0.1 mm (distance between successive apices 0.037 mm) in C. altamurae .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Ephippiochthonius |