Marcusenius lucombesi, Maake, Pholoshi A., Gon, Ofer & Swartz, Ernst R., 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3780.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AFB77705-1519-413D-96CD-25EDE68A6C73 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4658258 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B4C498-A672-4B1D-A68B-169B6DA73399 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:03B4C498-A672-4B1D-A68B-169B6DA73399 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Marcusenius lucombesi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Marcusenius lucombesi View in CoL , sp. nov.
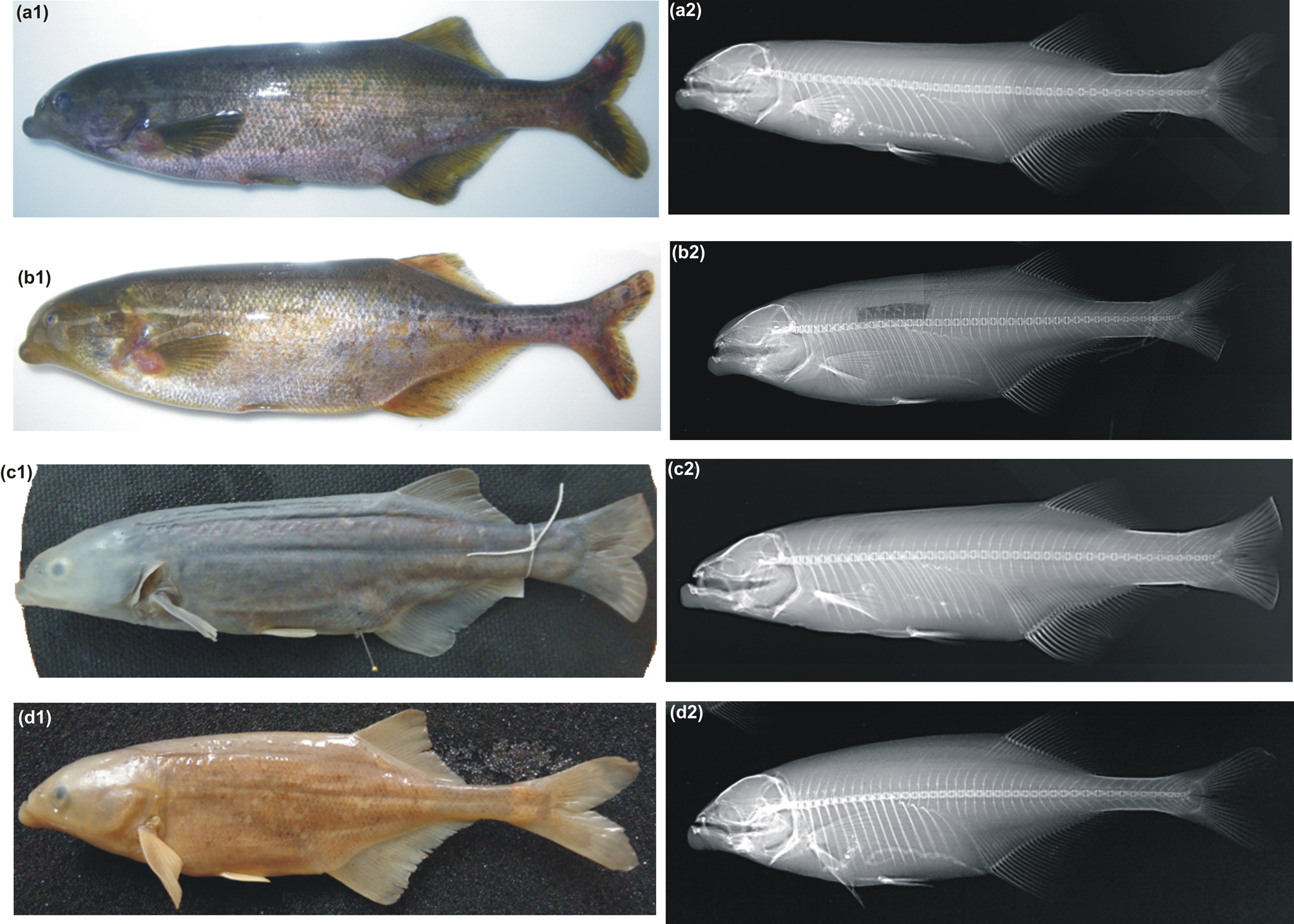
Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 d, Table 9 View TABLE 9
Marcusenius macrolepidotus: Kramer et al. 2007: 664 View in CoL View Cited Treatment , fig. 9 ( M. macrolepidotus Ruvuma View in CoL 25650 and 25651); p. 695, SAIAB 73790, SAIAB 73884.
Holotype. SAIAB 73884, 74.0 mm SL, male, Lucombe River, Lucombe stream pools, Nyati Road, Niassa Game Reserve, 12°5'15'' S, 37°33'38'' E, Ruvuma River system, R. Bills, 22 August 2003 Hologenetype COI (GenBank KJ174304 View Materials ), Hologenetype cyt b (GenBank KJ174293 View Materials ).
Paratypes. SAIAB 191226, 6: 52–72 mm SL, Paragenetype COI (GenBank KJ174303 View Materials ), paragenetypes cyt b (GenBank KJ174294 View Materials ), same collection as the holotype. MRAC, B3-16-P-4, 61.85 mm SL, same collection data as holotype. SAIAB 73885, 58.3 mm SL, same collection data as holotype. SAIAB 73886, 2: 48.8–55.5 mm SL, upper Lucombe River, isolated swamp pools in forest, Mbatamila-Nyati road, 12°5'2'' S, 37°33'43'' E, R. Bills, 26 August 2003. SAIAB 73816, 73 mm SL, Lucombe River, fourth stream, pools in bed, Mbatamila-Matondovela Road, 12°7'49'' S, 37°26'10'' E, R. Bills, 26 August 2003. SAIAB 73790, 4: 73.0– 121.5 mm SL, Nakanjambo River, Nakajambo stream, pools in bed, Mbatamila-Matondovela Road, 12°7'45'' S, 37°21'41'' E, R. Bills, 14 August 2003. BMNH 2013.9.4.75, 71mm SL, same collection data as previous lot.
Diagnosis. Distance dorsal fin origin to end of caudal peduncle 40.0–43.2% of SL; distance anal fin origin to end of caudal peduncle 43.6–45.9% of SL; shortest pre-anal length 56.6–59.2% of SL; pre-dorsal length 59.5– 63.3% of SL; low caudal peduncle depth 25.0–30.8% into its length; circumpeduncular scales 14–16; anal fin rays 28–29; dorsal fin rays 22–24; total vertebrae 44; lateral line scales 55–56; anterior GR (4–5) + (4–5) = (8–10); posterior GR (6) + (7) = 13; jaws with 5–5 conical teeth.
Description. Measurements and meristic counts are given in Table 9 View TABLE 9 . Head with terminal mouth well in front of eye, mental lobe on lower jaw protruding in front of upper jaw; head and body compressed; snout very pointy; pre-anal distance shorter than pre-dorsal distance; distance from origin of anal fin to origin of dorsal fin equal to the middle body depth; pre-pelvic distance twice as long as the distance between pelvic and anal fins; dorsal and anal fins set well back on the body, situated about two thirds of standard length from the snout and opposite each other; dorsal fin shorter, originating on vertical at 3rd anal fin ray and ending before anal fin base; distal margins of dorsal and anal fins obliquely orientated, with rays becoming gradually shorter posteriorly; dorsal fin rays 23 (22–24), its anterior rays highest, with distal margins rounded and slightly concave; anal fin rays 29 (28–29); males at sexual maturity have kink in the base of the anal fin distinctly curving in ward; anterior anal fin rays of sexually mature males longer, appear stronger, are crescentic and rounded, but are anteriorly sharp or pointy in females and juveniles; pectoral fins rays 10; pectoral fins distinctly very long, reaching origin of pelvic fin (when pressed against body); middle body depth 28.4% (25.0–28.4%) of SL; caudal peduncle thinner, sub-cylindrical across its entire length 20.3% (19.7–21.7%) in SL; 14 (14–16) scales along the caudal peduncle circumference; caudal peduncle depth 26.7% (25.0–30.8%) into its length; jaws with 5-5 conical teeth; lateral line scales 55 (55–56); lateral line scales cycloid with reticulate striae; 44 vertebrae (excluding urostyle). gill rakers on anterior side covered with many minute spines, anterior GRt = 8 (8–9) on the first gill arch ( Table 6); posterior GRt 13 on the posterior side of first gill arch; gill rakers on posterior side shorter, thicker and with covered by minute spines.
NB: MP = M. pongolensis , ML = M. krameri , MK = M. caudisquamatus
Electric organ discharge. No data.
Coloration. All specimens light brown when preserved. Homogeneous coloration without any blotches, increasingly lighter on the belly.
Distribution. This species is currently known only from the Lucombe River and its small tributary streams, as well as the Nakajambo River, both tributaries of the Ruvuma River system within the Niassa Game Reserve, Mozambique. It was collected with Petrocephalus catostoma ( Günther, 1866) in aquatic weed beds, marginal vegetation and root-stocks of bank vegetation in headwater streams through to floodplain margins ( Kramer et al. 2007; R. Bills, pers. comm.). Water conductivity was 104–268 ΜS/cm in August 2003, probably reflecting human impact on this aquatic system ( Kramer et al. 2012).
Remarks. Marcusenius lucombesi may be the smallest species of Marcusenius in southern Africa, reaching sexual maturity at only 56 mm SL, with none of the males at the SAIAB collection exceeding 75 mm SL. The largest female was 120.5 mm SL. In comparison to other species examined in this study, M. lucombesi has the lowest number of scales along the lateral line (55–56), and the anal fin has a more anterior origin than the dorsal fin by only three rays as compared to 4–5 rays in M. krameri and M. caudisquamatus . It should be emphasised that M. lucombesi also differs significantly from M. macrolepidotus of the Lower Zambezi in several characters, i.e. distance from dorsal fin origin to end of caudal peduncle, caudal peduncle depth, pre-anal and dorsal lengths, all of which were greater in M. macrolepidotus ( Kramer et al. 2007) . Marcusenius lucombesi is also genetically divergent, and morphologically distinct in having significantly smaller caudal peduncle depth, longer dorsal fin and head lengths, and one anal and dorsal fin ray more than in M. devosi (Krame et al. 2007) . Another bulldog species, Marcusenius livingstonii , occurs in the Ruvuma but it differs from M. lucombesi in having a dark uniform bar on the body below the origin of the dorsal fin and bicuspid teeth. These two characters also distinguish M. livingstonii from all other known species of Marcusenius in southern and eastern African rivers. Marcusenius lucombesi is therefore distinct from M. livingstonii and M. macrolepidotus .
Etymology. The specific name refers to the type locality of this species, Lucombe River, a tributary of the Ruvuma River system in the Niassa Game Reserve.
TABLE 9. Basic statistics for morphological characters of Marcusenius lucombesi. See Table 1 for characters definitions. Asterisks indicate non-overlapping characters with other Marcusenius species.
| Character | Holotype | N | Mean/Median | Min | Max | Std. Dev | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL, mm | 77.0 mm | 13 | 64.92 | 53.00 | 74.00 | 7.54 | |
| HL, mm | 15.0 mm | 13 | 14.23 | 12.00 | 16.00 | 1.30 | |
| Ratio of SL | |||||||
| HL | 0.2027 | 13 | 0.2199 | 0.2027 | 0.2333 | 0.0101 | |
| vBD | 0.2703 | 13 | 0.2576 | 0.2429 | 0.2703 | 0.0084 | |
| mDB | 0.2838 | 13 | 0.2648 | 0.2500 | 0.2838 | 0.0104 | * MP |
| dAD | 0.2838 | 13 | 0.2689 | 0.2545 | 0.2838 | 0.0103 | |
| CPL | 0.2027 | 13 | 0.2086 | 0.1972 | 0.2167 | 0.0067 | |
| PDL | 0.6216 | 13 | 0.6167 | 0.5946 | 0.6333 | 0.0110 | |
| PAL | 0.5811 | 13 | 0.5767 | 0.5660 | 0.5915 | 0.0092 | |
| pD | 0.4189 | 13 | 0.4155 | 0.4000 | 0.4324 | 0.0096 | * MP |
| pA | 0.4595 | 13 | 0.4479 | 0.4364 | 0.4595 | 0.0084 | * MP |
| pPL | 0.2203 | 13 | 0.2271 | 0.2143 | 0.2394 | 0.0075 | |
| pVL dVA | 0.3919 0.2027 | 13 13 | 0.3861 0.1926 | 0.3731 0.1786 | 0.3944 0.2083 | 0.0075 0.0093 | |
| dPA | 0.3649 | 13 | 0.3500 | 0.3378 | 0.3662 | 0.0100 | * MP |
| dPV | 0.1757 | 13 | 0.1709 | 0.1607 | 0.1833 | 0.0067 | |
| LD | 0.1946 | 13 | 0.1893 | 0.1803 | 0.2000 | 0.0067 | * MP |
| LA | 0.2487 | 13 | 0.2384 | 0.2264 | 0.2537 | 0.0091 | |
| CPD/CPL | 0.2667 | 13 | 0.2794 | 0.2500 | 0.3077 | 0.0198 | |
| Ratio of HL | |||||||
| HW | 0.6000 | 13 | 0.5611 | 0.5000 | 0.6000 | 0.0343 | |
| LSN | 0.5333 | 13 | 0.4601 | 0.4167 | 0.5333 | 0.0405 | |
| IOW | 0.4667 | 13 | 0.4421 | 0.4000 | 0.5000 | 0.0279 | |
| ED | 0.2667 | 13 | 0.2382 | 0.1875 | 0.2757 | 0.0302 | |
| Counts | Median | ||||||
| nD | 23 | 13 | 23 | 22 | 24 | 0.6304 | |
| nA | 29 | 13 | 29 | 28 | 29 | 0.4804 | |
| SPc | 14 | 13 | 15 | 14 | 16 | 0.4385 | *MP, MK |
| nTL | 5 | 13 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 0.5547 | |
| nTU | 5 | 13 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 | |
| Total vertebrae | 44 | 13 | 44 | 44 | 44 | 0 | * MP |
| LSS | 55 | 8 | 55 | 55 | 56 | 0.5470 | *MP, MK, MC |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Marcusenius lucombesi
| Maake, Pholoshi A., Gon, Ofer & Swartz, Ernst R. 2014 |