Paramorariopsis irenae, Brancelj, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222930600646608 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03973324-FFFC-FF83-618E-FDF2DCAFFE3C |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Paramorariopsis irenae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Paramorariopsis irenae n.sp.
( Figures 1–14 View Figures 1–6 View Figures 7–14 )
Material examined
Two females from a pool filled with percolating water in the Letuška Jama cave (type locality), near the town of Mozirje, northeast Slovenia, collected 24 March 2004 .
Holotype: adult female (total length of 402 mm), preserved in alcohol; deposited in the Natural History Museum (London), registration no. 2005.218. Paratype: adult female completely dissected; legs and mouth parts mounted on a slide in glycerol and sealed with nail polish; deposited in the Natural History Museum (London), registration no. 2005.219. Slide was partly broken during transport. Abdomen of the dissected female is in the author’s collection.
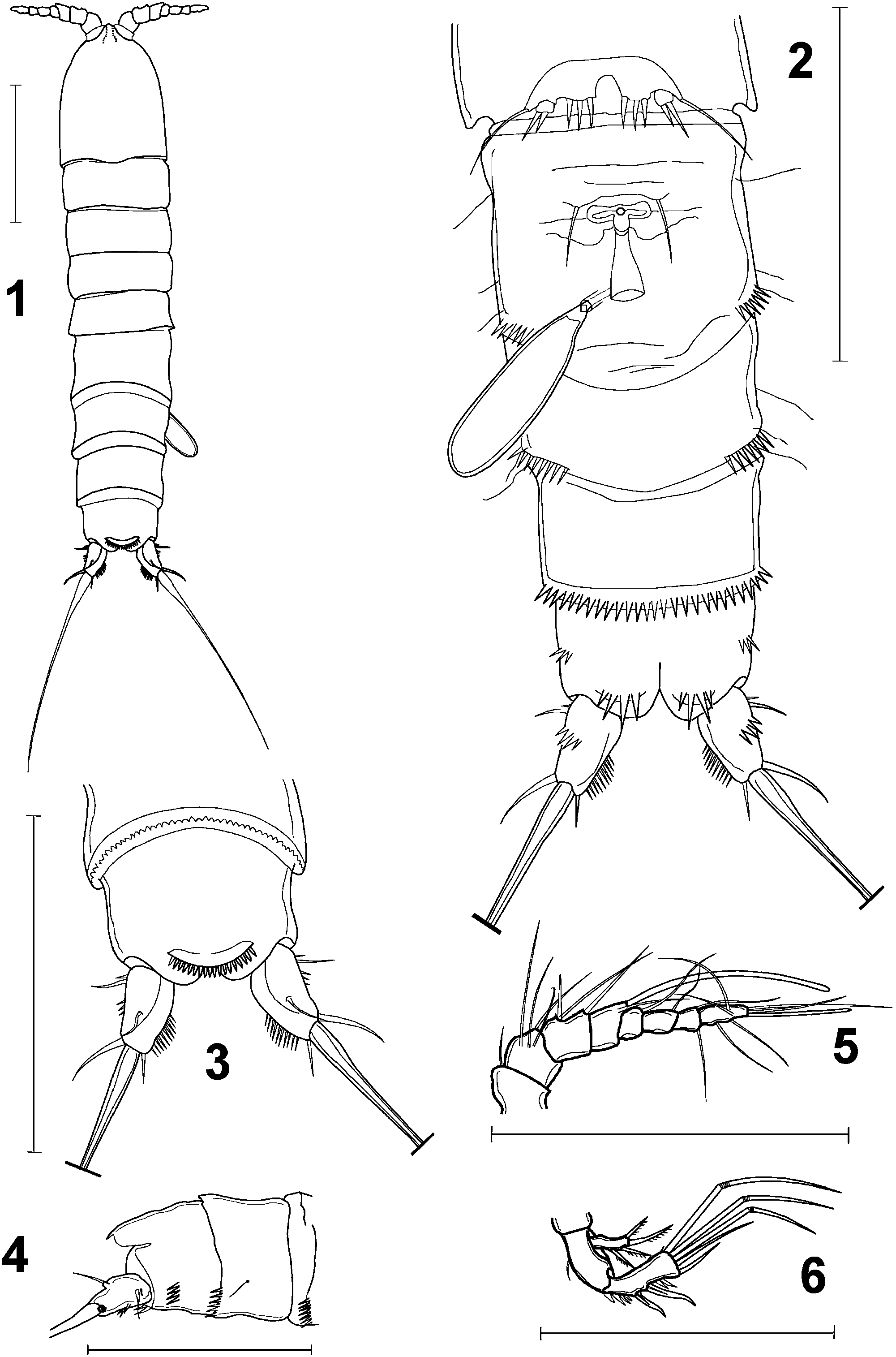
Description Female. Body length 402–410 mm (n 52); elongated, cylindrical, colourless ( Figure 1 View Figures 1–6 ).
Naupliar eye absent. Hind margins of all abdominal somites dorsally serrated. Genital double-somite and second abdominal somite distally on both ventro-lateral parts with five to six spinules. Ventral margin of both somites smooth and without spinules. Third abdominal somite ventrally with a row of strong and robust spinules. Three pairs of sensillae (5hair-like structure; two long and one short) on the lateral side of genital doublesomite and second abdominal somite ( Figure 2 View Figures 1–6 ). Anal somite with three to four spinules on ventro-lateral side, positioned at about two-thirds of the length of the segment. Four strong and robust spinules, unequal in length, at base of each caudal ramus ( Figure 2 View Figures 1–6 ). Anal
Nitrate (mg NO 3 2 l 21) 5.14
Total nitrogen (mg N l 21) 2.46
pH 8.17
Alkalinity (meq l 21) 3115.00 Conductivity (mS cm 21; T525 ° C) 412.00
Calcium (mg Ca l 21) 56.94 Magnesium (mg Mg l 21) 14.92
operculum large, rounded, with about 20 strong spinules around free margin, reaching to distal end of anal somite ( Figure 3 View Figures 1–6 ).
Receptaculum seminis ( Figure 2 View Figures 1–6 ) identical to that of Paramorariopsis anae and resembling condition in genus Moraria . Genital apertures closed off by operculum derived from fused P6, with one seta on each side. Attached spermatophore characteristic for Canthocamptidae .
Caudal rami divergent, each about 1.5 times as long as wide, tapering posteriorly ( Figures 2–4 View Figures 1–6 ). Inner margin with about 10 strong and robust spinules in distal half of ramus. Outer margin with two setae positioned close to base of caudal ramus; one of them short and spine-like, the other about four times longer, not exceeding basal width of ramus. Dorsal surface of ramus with weakly expressed hyaline ridge along its entire length. Dorsal seta inserting at about half distance from the base of ramus, as long as lateral one. Ventrolateral surface with oblique row of four small spinules positioned halfway along ramus. Outer terminal seta spiniform, slightly curved, as long as ramus. Inner terminal seta short, spiniform. Middle terminal seta as long as abdomen, with few spinules at tip.
Rostrum small.
Antennule ( Figure 5 View Figures 1–6 ) short and moderately stout, eight-segmented. Aesthetasc on segment four cylindrical, slightly curved, with rounded tip and longer than antennule. Second aesthetasc on terminal segment slightly overreaching tip of first aesthetasc.
Antenna ( Figure 6 View Figures 1–6 ) comprising coxa, allobasis, and one-segmented exo- and endopod; short and robust. Two strong spines on the outer margin of endopod accompanied by several strong and short spinules; terminal armature consisting of one spine, one simple and three geniculate setae. Exopod with four spiniform setae, armed with coarse spinules.
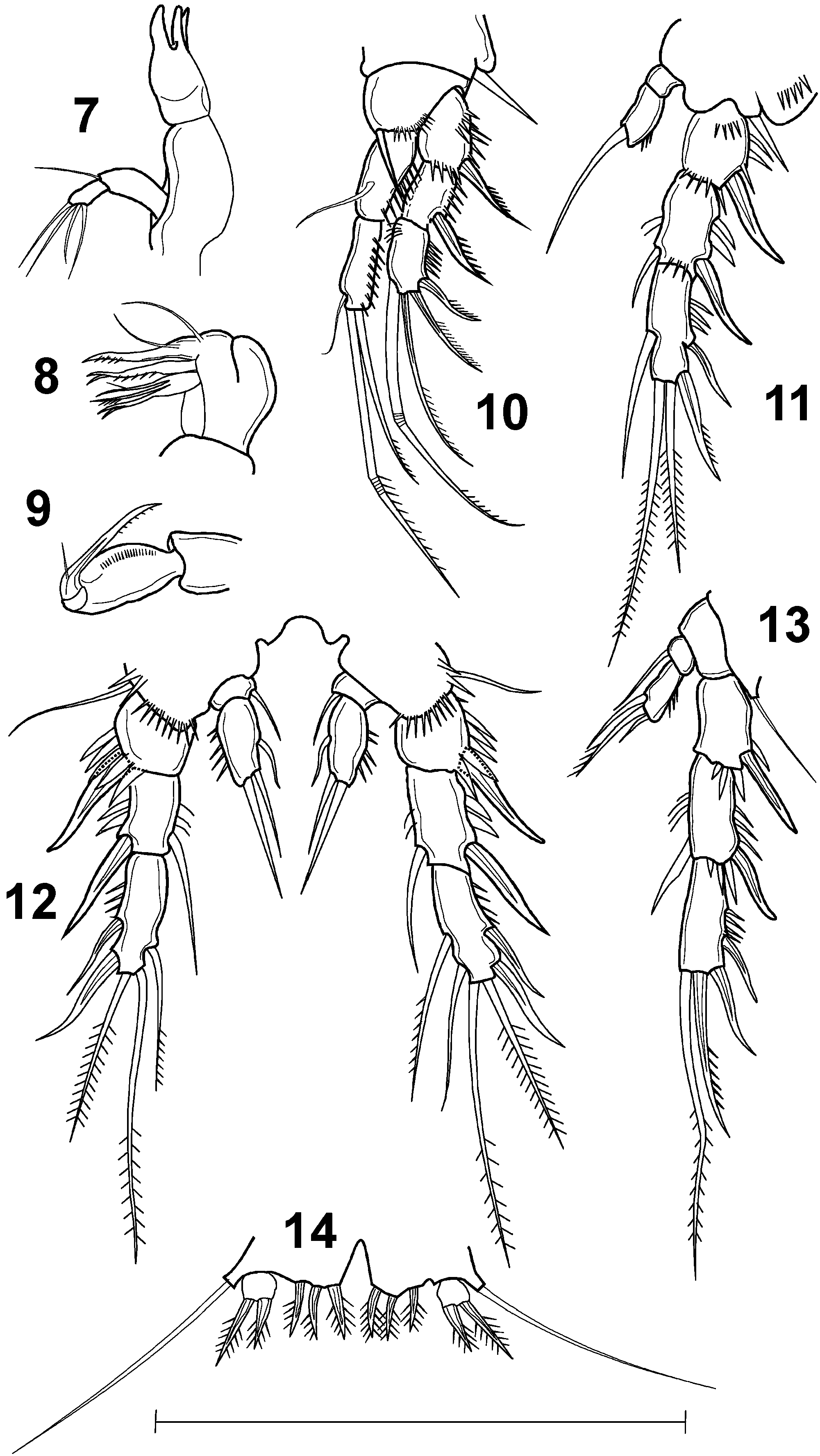
Mandible ( Figure 7 View Figures 7–14 ) short and robust, with three strongly chitinised teeth on gnathobase. Mandibular palp relatively long, two-segmented, with one seta on proximal segment (basis) and four setae, sub-equal in length, on distal segment (endopod).
Maxillule with five strong and robust spines on praecoxal arthrite and additional strong seta, originating from the dorsal side of the segment. Basis with two strong, beak-like outgrowths, with several short bristles on distal part and four setae at the base.
Maxilla two-segmented ( Figure 8 View Figures 7–14 ); proximal one wide and robust. Distal segment with three lobes. Outer one with beak-like outgrowth with two setae, middle one with two strong spines, the inner one with four strong spines.
Maxilliped comprising syncoxa, basis, and one-segmented endopod ( Figure 9 View Figures 7–14 ). Syncoxa slightly longer than wide, with no spinules or setae. Basis with about 20 spinules positioned near palmar margin. Endopod drawn out into strong, acutely curved claw; slightly longer than basis and armed with spinules in distal half; accessory armature represented by short seta.
P1 ( Figure 10 View Figures 7–14 ) with three-segmented exopod and two-segmented endopod. Endopod as long as exopod. Basis with a strong inner and outer basal spine. Exopod with one strong outer spine and several small spinules on proximal and median segments. Distal segment with one strong spine laterally, two long setae terminally and one long, geniculate, inner seta subdistally. Outer terminal seta as long as exopod and spine-like, with several small spinules unilaterally in distal half. Proximal segment of endopod with a row of about eight strong spinules along outer margin; long seta at two-thirds length of inner margin. Distal segment with three setae; innermost small, median seta very long and geniculate, outer one spiniform with strong spinules unilaterally at tip. Outer margin with a row of about 10 spinules.
P2 ( Figure 11 View Figures 7–14 ) outer basal seta spiniform; with three-segmented exopod and twosegmented endopod. Endopod slightly longer than proximal segment of exopod. Proximal segment of exopod as long as wide; with one strong outer spine, with slightly rounded tip; with three short spinules on outer margin and one group with four to five spines on proximal anterior surface and one group around distal margin. Middle segment with one strong outer spine and one short, inner, spiniform seta; with two short spinules along outer margin. Distal segment with two outer spines, two terminal setae (outer seta shorter than inner one; inner one as long as exopod) and spiniform inner seta. Proximal segment of endopod as long as wide, unarmed. Distal segment twice longer than wide, with one basal seta, positioned sub-terminally and about 1.5 times longer than endopod. Inner margin of endopod with three to four small spinules around distal outer margin.
P3 ( Figure 12 View Figures 7–14 ) outer basal seta setiform; exopod similar to P2 but additional seta on inner margin of terminal segment can be present. Endopod two-segmented; proximal segment very short, with short inner seta. Terminal segment with two terminal setae of unequal length (inner seta shorter; as long as terminal segment); inner margin with one short spine-like seta at half length of the segment.
P4 ( Figure 13 View Figures 7–14 ) outer basal seta setiform; with three-segmented exopod and twosegmented endopod. Proximal and middle segments of exopod similar to those in P2 and P3. Terminal segment with two outer and two distal setae (inner one about twice as long as outer one; outer one distally with row of small but strong spinules along outer margin); no seta or spine on inner margin. Proximal segment of endopod with one inner seta, reaching tip of the distal segment. Distal endopod segment with three setae positioned laterally on inner margin of endopod; proximal two approximately as long as endopod; third one shorter than terminal segment of endopod.
P5 ( Figure 14 View Figures 7–14 ) with separate exopod and baseoendopod; endopodal lobe small, with three short, strong spines of equal length, bearing five to six strong spinules on each side. Exopod small, as long as wide, with two strong and robust setae, slightly longer but similar in shape to those on endopodal lobe. Outer lateral seta on baseoendopod very long.
Male. Not known.
Etymology
The new species is dedicated to my wife Irena.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.