Ptygomastax nihilsulcus Ge, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5068.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:38C16DF3-C0C4-4713-B045-87BD693CA11B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5707047 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/991C87FF-4605-4D4D-FF12-7DDC7D044962 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ptygomastax nihilsulcus Ge |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Ptygomastax nihilsulcus Ge View in CoL , sp. nov.
Material examined. Holotype: 1 ♂, paratypes: 1 ♂, 2 ♀. China, Luhuo (Sichuan), 4229 m, (31°73’89’’N 100°75’33’’E), August, 2020. Coll. Jun-Jie Ge, Ke-Yao Zhang & Kuo Sun; deposited in the Zoological and Botanical Museum, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China. ( ZBM).
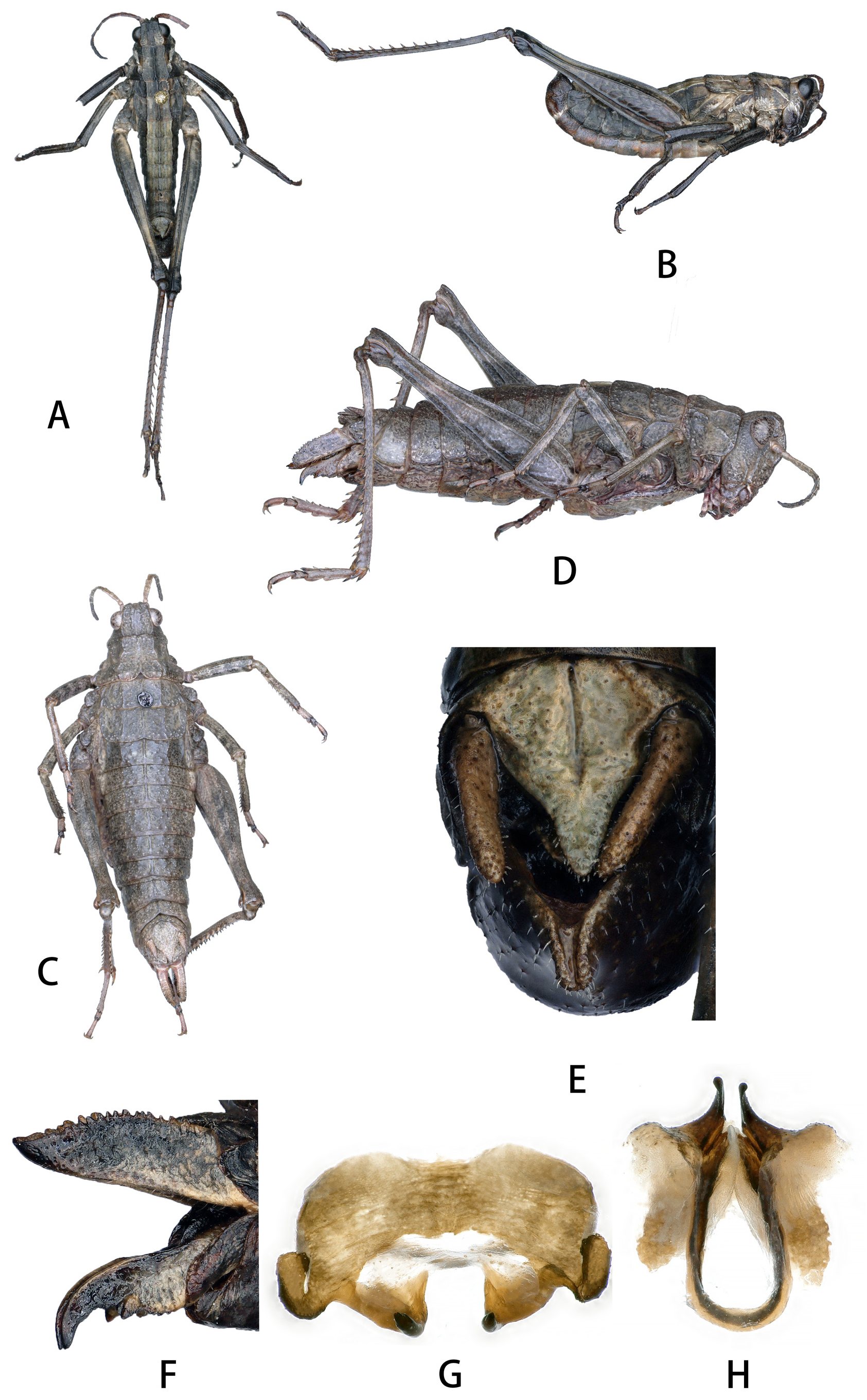
Description. Male ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Body size small, head shorter than the length of pronotum; vertex wide, distinctly prominent between the eyes, median keel distinct; face slightly oblique in profile, forming a rectangular fastigium; frontal ridge sulcate and widened margins between antennae, constricted above the lateral ocellus and below the median ocellus, slightly rounded prominent; antennae clavate, shorter and thicker, with 14 segments and slightly wider in apical part, antennal organ on the tenth segment; eyes oval, longitudinal diameter is 1.4 times than the horizontal diameter and almost of equal diameter with subocular furrow; pronotum flattened, without transverse sulci, median keel sharp and distinct, lateral keels irregularly curved, posterior margin incised mesally forming a triangular structure, its apex being in continuity with the median keel, lateral lobes of pronotum with an oblique keel; wings, sound producing organ and tympanum absent; hind femur 5.2 times longer than its width, median keel of upper side smooth without spine, the lower lobe of knee blunt; hind tibia with 15~17spines on outer side and 11~13 spines on inner side; first segment of hind tarsus with 3 inner and 4 outer spines; with equal claw, arolium of tarsus tiny; tergum with distinct median keel, lateral keels clearly visible before fifth segment; tympanal organ absent; epiproct triangle; cerci long conical, apex blunt, extending to the tip of epiproct; subgenital plate short conical ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ); epiphallus bridged, lophi thick and hook-like, lateral plate wide and short, with big flaky structure on lateral side ( Fig. 1G View FIGURE 1 ); phallic structure simple, forming a U-shaped, dorsal with two big flaky structures, apical valves of penis hook-like ( Fig. 1H View FIGURE 1 ).
Female. Similar to male but larger and more robust; fastigium of vertex bifid on the anterior margin; outer side of dorsal valves with serrate teeth and acute apex; outer side of ventral valves with big teeth, apex hooklike; cerci short conical; the middle of posterior margin of subgenital plate with conical prominent, apex acute ( Fig. 1F View FIGURE 1 ).
Coloration. Body dark-brownish; antennae brown, apical segments of antennae black-brownish; oblique keel on lateral lobe of pronotum yellowish-brown; sternum gray-brown; between median keel and lateral keel of tergum yellow; epiproct and cerci yellowish.
Habitat. Alpine brushwood.
Measurements. (In mm) Body length: ♂ 14.1-15.4 mm, ♀ 19.1-21.4 mm; pronotum length: ♂ 2.3 mm, ♀ 2.3 mm; hind femur: ♂ 11.1-11.3 mm, ♀ 11.2-11.4 mm.
Diagnosis. Antennae 14 segments. Pronotum without transverse sulci. Hind femur without spine. Epiphallus bridged, lophi thick and hook-like, lateral plate wide and short, with big flaky structure on lateral side; phallic structure simple, forming a U-shaped, dorsal with two big flaky structures, apical valves of penis hook-like. The new species Ptygomastax nihilsulcus sp. nov. is similar to Ptygomastax longifemora Yin, 1984 China, Qinghai, Guinan. Some of the characteristic differences are shown in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Eumastacoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Gomphomastacinae |
|
Genus |