Anaptomecus suni, Guala, Mariel E., Labarque, Facundo M. & Rheims, Cristina A., 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.280012 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6173968 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038DE965-AB71-FFE3-FF73-FD3CFC9AFAD2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Anaptomecus suni |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Anaptomecus suni View in CoL sp. nov.
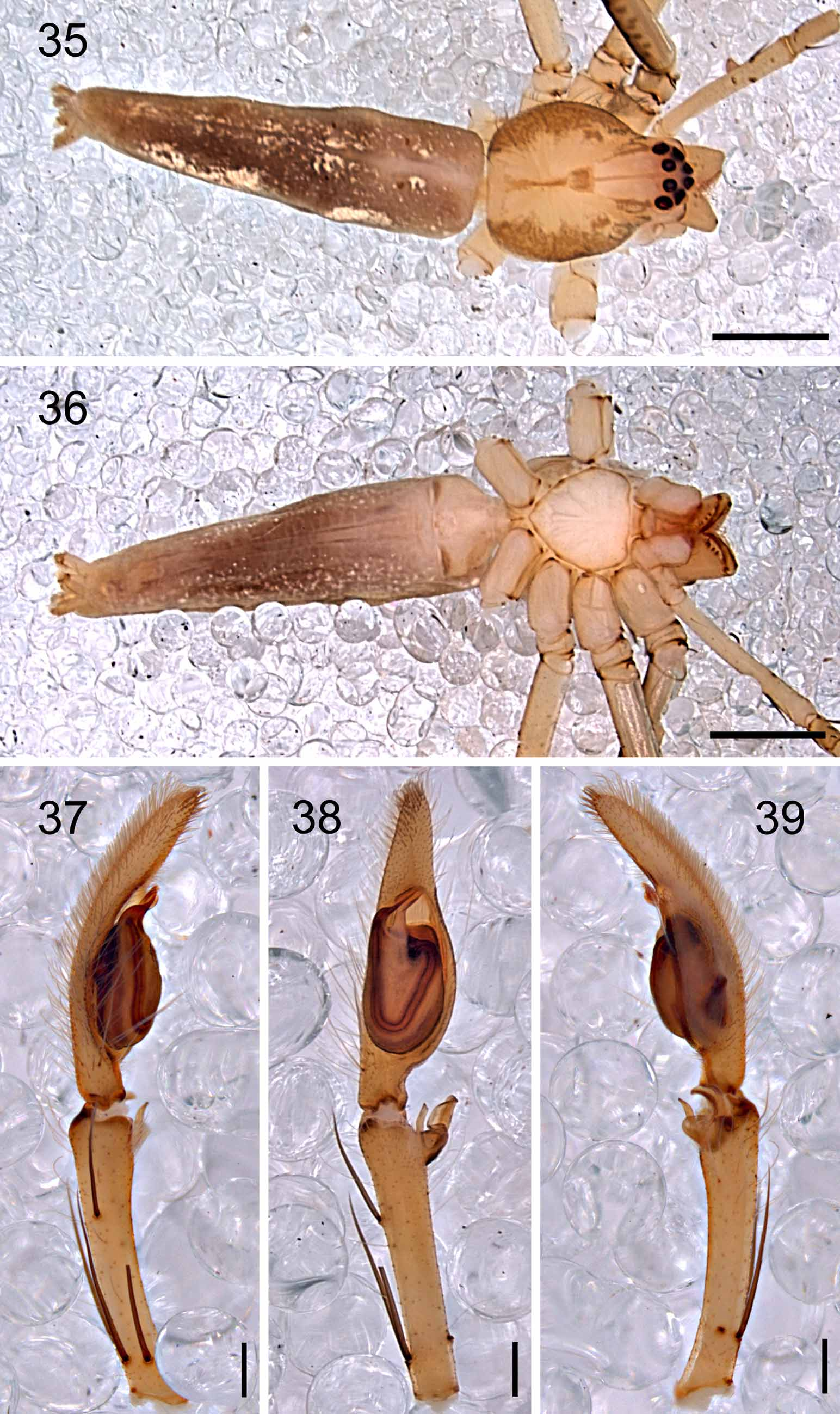
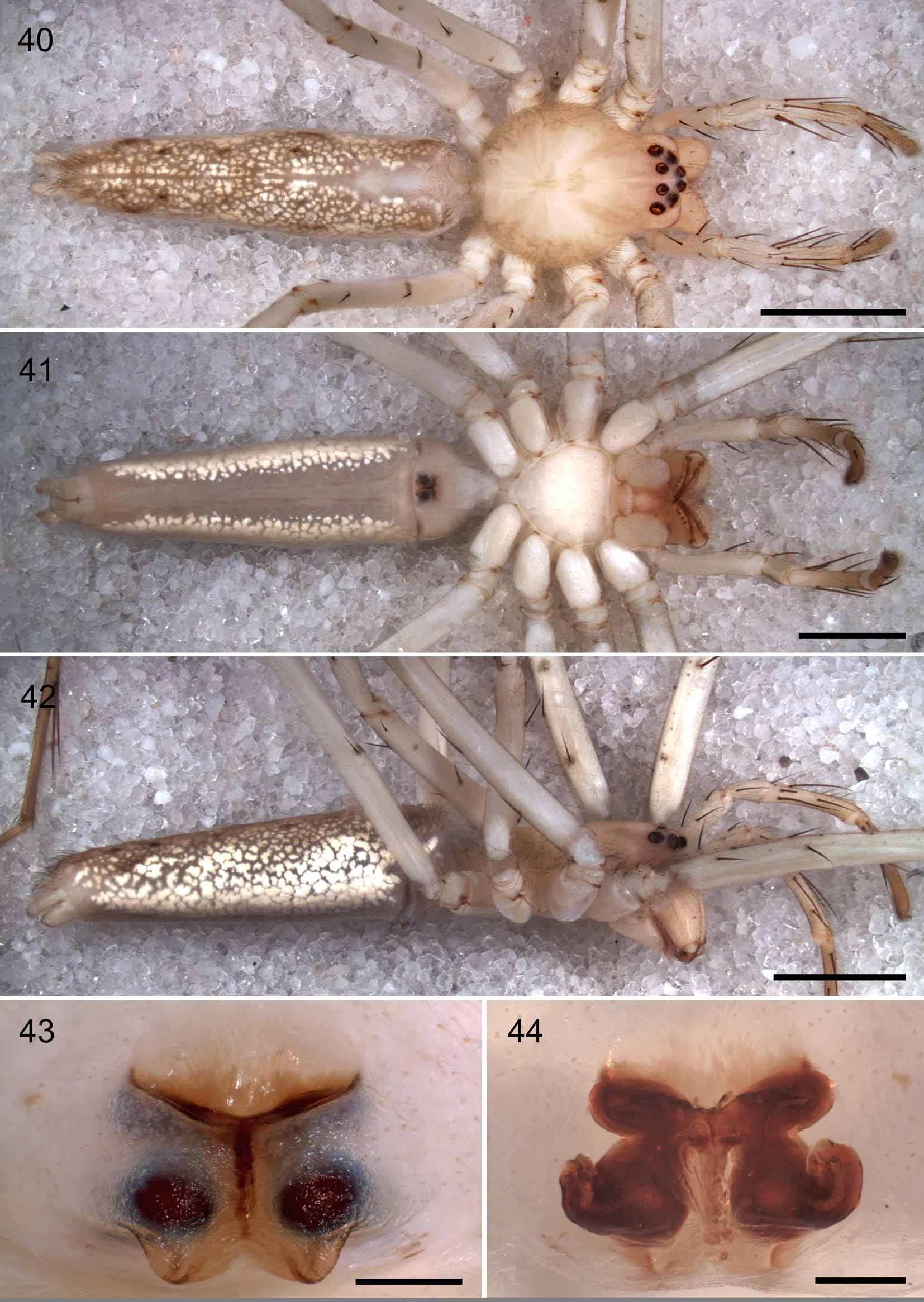
Figs 31–44 View FIGURES 31 – 34 View FIGURES 35 – 39 View FIGURES 40 – 44 Type material. Holotype: 3 from ECUADOR, Napo Province, Cantón Tena, Parroquia Puerto Napo, Jatun Sacha Biological Station, S 1,065972º, W 77,616722º, 410 m, 1–5 December 2009, C.A. Rheims leg. in PBI Oonopidae Expedition (QCAZ). Paratypes: 2Ƥ, same date as for holotype, C. Grismado & F. Labarque leg. in PBI Oonopidae Expedition , (MACN-Ar 26894, 26895; preparation codes MEG-00011, MEG-00012-14).
Etymology. The specific name means long or elongated in Quechua, the language of the native people of Ecuador, and refers to the long opisthosoma typical for Anaptomecus species; term in apposition.
Diagnosis. Males are distinguished from those of congeners by a folded RTA with a ventral elongated and fine projection and an untwisted embolus ( Figs 31–32 View FIGURES 31 – 34 , 37–39 View FIGURES 35 – 39 ). Females are diagnosed by two copulatory openings distinctly separated situated in an atrium directed anteriorly and a longitudinal median septum in ventral view ( Figs 33 View FIGURES 31 – 34 , 43–44 View FIGURES 40 – 44 ).
Description. Male (holotype): Total length 11.2. Prosoma: 3.5 long. 3.0 wide. Opisthosoma: 7.5 long, 2.2 wide. Eye diameters: 0.26, 0.28, 0.18, 0.26; interdistances: 0.12, 0.02, E 0.20, 0.20, 0.22, 0.18. Legs (leg formula: 1243): I: 43.6 (11.0, 2.1, 12.5, 14.5, 3.5); II: 43.5 (11.2, 2.1, 12.4, 14.2, 3.6); III: 26.4 (7.3, 1.6, 7.9, 7.7, 1.9); IV: 31.6 (9.1, 1.5, 7.8, 10.5, 2.7). Spination: femur I–III p1-1-1, d0-1-1, r1-1-1; femur IV p1-1-1, d0-1-1, r0-0-1; tibiae I–II p1-0-1; d0-1-1; r1-0-1; v2-2 -0; tibiae III–IV p1-0-1; d1-0-1; r1-0-1; v2-2 -0; metatarsi I–II p1-0-0; r1-0-0; v2- 2 -0; metatarsus III p1-1-0; r1-1-0; v2-2 -1; metatarsus IV p1-1-1; r1-1-1; v2-2 -0. Palp as in diagnosis. Short embolus arising ventrally on tegulum at the prolateral side, without teeth at its base, with thin, drawn-out tip; hyaline conductor well developed. Dorsal cymbium with dense scopula gradually diminishing from half to basal ( Figs 31–32 View FIGURES 31 – 34 , 37, 39 View FIGURES 35 – 39 ). Coloration: Dorsal shield of the prosoma pale yellow, slightly darker at eye area, pale brown laterally and along margins of cephalic region, a median longitudinal line extending between PME and pedicel-like wider at middle point. Legs pale yellow, slightly darker at metatarsi and tarsi. Legs I–II mottled with pale brown spots. Pedipalps pale yellow. Labium and endites cream colored. Sternum cream colored with pale orange margins. Opisthosoma dorsally brownish gray with conspicuous cream colored heart mark and scattered marks of bright guanine crystals medially and laterally ( Fig 35 View FIGURES 35 – 39 ). Venter cream colored anterior to epigastric furrow and brownish posteriorly ( Fig 36 View FIGURES 35 – 39 ).
Female (MACN-Ar 26895, paratype): Total length 11.8. Prosoma: 3.9 long, 3.2 wide. Opisthosoma: 7.7 long, 2.0 wide. Eye diameters: 0.18, 0.22, 0.16, 0.20; interdistances: 0.18, 0.10, 0.26, 0.28, 0.26, 0.24. Legs (leg formula: 1243): I: 28.3 (7.7, 1.9, 8.5, 8.0, 2.2); II: 27.7 (7.7, 2.0, 8.2, 7.7, 2.1); III: 17.9 (5.2, 1.5, 5.0, 4.8, 1.4); IV: 21.4 (6.5, 1.5, 5.7, 6.0, 1.8). Spination as in male, except femur I–II: d1-0-1; femur III: d0-0-1; femur IV: p0-1-1; d0-0-0; tibia I–III: p1-1-0; d0-0-0; r1-1-0; tibia IV: p1-1-0; d0-0-0; r1-1-0; metatarsus III: r1-0-0; v2-2 -0; metatarsus IV: p1-1-0; r1-1-0. Epigyne as in diagnosis. Anterior margins of the atrium procurved, a longitudinal internal septum in the middle line (seen in transparency) and posterior epigynal margin with conspicuous lobes, projecting posteriorly; copulatory ducts emerging laterally; fertilization ducts short twisted and terminating medially; spherical spermathecae with lateral glandular projections, pointing in an anterior direction ( Figs 33 View FIGURES 31 – 34 , 43–44 View FIGURES 40 – 44 ); schematic course of internal duct system shown in Fig. 34 View FIGURES 31 – 34 . Coloration as in male but lighter. Leg femora with brown spots encircling spine bases. Opisthosoma gray with a dorsal cream colored longitudinal band wider at the anterior third of the opisthosoma, bright guanine crystals dots and four pairs of dark hair patches, ventrally with a gray longitudinal central band due to lack of guanine crystals ( Figs 40–42 View FIGURES 40 – 44 ).
Variation. Females (n=2): total length 11.8–15.2; prosoma length 3.9–4.3; femur I 7.7–7.8.
Natural history. One gravid female (paratype) was collected under a tree leaf.
Distribution. Ecuador (known only from the type locality).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.