Coeliccia duytan, Phan, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4324.1.12 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:Fbe20203-F19F-42E6-Bdb5-22A1D04Fa427 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6015841 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DA879D-0379-FFC2-A6F9-F935B2EEFE35 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Coeliccia duytan |
| status |
|
Coeliccia duytan View in CoL s p. nov. ( Figs 1a View FIGURE 1 , 2a–c View FIGURE 2 , 3–5 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 )
Holotype. ♂, Chu Mom Ray National Park , Kon Tum Province, the Central Highlands of Vietnam, 19.V. 2017, Quoc Toan Phan leg.
Paratypes. 8♂♂, 3♀♀, same date, location and collector as holotype; 2♂♂, 1♀, same location, 10.V.2016, Nguyen Dang Van leg.
Etymology. This specific epithet is derived from my office Duy Tan University; duytan , a noun in apposition.
Description of holotype. Head ( Figs 1a View FIGURE 1 , 3a View FIGURE 3 ). Anteclypeus pale blue except for two isolated black spots adjacent to labrum; labrum and mandibles matte black. Genae pale blue, extending to the level of scape ( Fig. 3a View FIGURE 3 ). Antennae black, pedicel yellow. Top of head matt black with two spots posteriolateral of median ocellus and two streaks at the anterior corners of the lateral ocelli and a transverse wedged shaped pale yellow spot on just posterior to postoccipital lobes ( Fig. 1a View FIGURE 1 ).
Thorax ( Fig. 1a View FIGURE 1 ). Anterior and posterior lobes of prothorax black, middle lobes pruinose blue. Most of propleuron matt black, lower part yellow. Synthorax largely black. Mesepisternum black with a pruinose spot occupying ventral fourth. Mesepimeron, metepisternum and mesinfraepisternum black except for a small pale yellow on mesinfraepisternum adjacent to mesocoxa and ventral fourth of metepisternum above coxa and encompassing metastigma. Metinfraepisternum yellow excluding a black spot adjacent to metepisternum. Large rectangular pruinose area extending from posterior half of mesepimeron to anterior third of metepisternum including metapleural suture. Metepimeron entirely yellow.
Legs ( Fig. 1a View FIGURE 1 ). Coxae pale yellow. Femora and tibiae pale yellow with flexor surface of femora and extensor surfaces of tibiae black. Tarsi and armature black.
Wings hyaline, 17–18 and 17 postnodal crossveins in forewings and hindwings, respectively. Pterostigma brown with narrow pale margin, surmounting 1.5–2 underlying cells.
Abdomen. Black above with pale yellow markings as follows: S1 yellow, black dorsally; S2–8 black above, shading into pale yellow ventrally, black at apices of each segment; S9 black with posterior 1/6 yellow; S10 entirely yellow ( Fig. 2a–b View FIGURE 2 ).
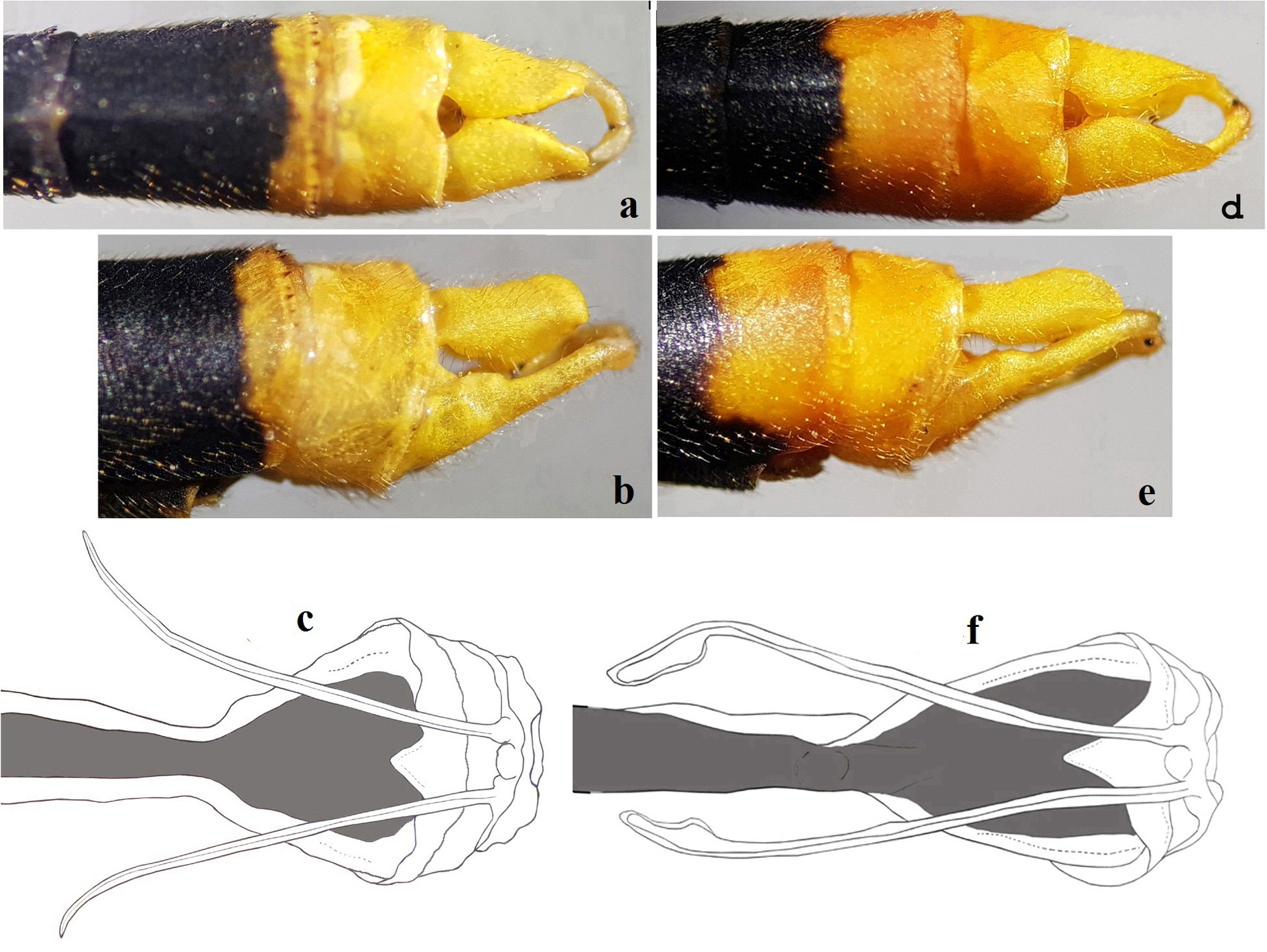
Genital ligula shown in Fig. 2c View FIGURE 2 with terminal segment armed medially with a pair of long flagella.
Anal appendages ( Fig. 2a–b View FIGURE 2 ) yellow, cerci short and robust, ca. length of S10, in lateral view bearing a small ventral tooth along swollen medial portion; in dorsal view, cercus narrowing distally and rounded at apex. Linear paraproct ca. 1/ 3 longer than cercus, its medially directed tip ending in a black tooth.
Measurements (in mm). Hindwing 26; abdomen (incl. appendages) 41.
Description of female. Head ( Fig. 3b View FIGURE 3 ). Head color pattern similar to that of male except yellow bands from lateral ocelli extending to the eyes.
Thorax ( Figs 3c–d View FIGURE 3 , 4b View FIGURE 4 ). Prothorax black except except for two large, mediolateral separated yellow spots on middle lobe; propleuron yellow. Posterior lobe armed medially with a sconcave subrectangular lobe, its base constricted, dorsolaterally to medial lobe strongly concave in a semicircular fashion before terminating as a medially pointed lateral lobe ( Fig. 3c View FIGURE 3 ); a recessed obtuse tooth present below semicircular concavity as shown in Fig. 3d View FIGURE 3 . Synthorax black with yellow areas as follows: thin antehumeral stripe; mesepimeron with small isolated yellow spot above antehumeral stripe ( Fig. 4b View FIGURE 4 ); ventral margin of mesinfraepisternum; metepisternum except for distinct black metapleural stripe; metepimeron entirely yellow.
Legs. Coxae and femora pale yellow, flexor and extensor surfaces black. Tibiae pale yellow, flexor surface black. Tarsi and armature black.
Wings. Hyaline, 18 postnodal crossveins in forewings and 17–18 postnodal crossveins in hindwings. Pterostigma brown with narrow pale margin, surmounting 1.5–2 cells.
Abdomen. S1 largely black dorsally; S2–7 black dorsally and laterally becoming pale ventrally; S8 almost entirely yellow but basal 0.70 black dorsolaterally; S9 dark yellow, black ventrally; S10 black with anterior margin dark yellow. Cerci black, ovipositor black with small yellow spot anteriorly and dorsally at apex ( Fig. 3e View FIGURE 3 ).
Measurements (in mm). Hind wing 25; abdomen (incl. appendages) 35.
Variation in paratype males. Some paratype males have a yellow spot near the posterior margin of the metepisternum below the rectangular pruinosity on the thorax.
Variation in other paratype females. Paratype females shown little variation with the paratype used for the description of the female in this paper.
Differential diagnosis. Adult males of C. duytan sp. nov. and C. hayashii can be easily separated from all described Coeliccia by the presence of a large rectangular pruinose spot on the synthorax spreading out, but not fully covering, on both mesepimeron and metepisternum ( Fig. 1a–b View FIGURE 1 ). C. duytan differs from C. hayashii by the following diagnostic characters:
(1) Mesepisternum of C. duytan with a large quadrate pruinose spot ( Fig. 1a View FIGURE 1 ) while C. hayashii has a long blue narrow antehumeral stripe ( Fig. 1b View FIGURE 1 ).
(2) Apex of cercus in C. duytan slightly inflated ( Fig. 2a–b View FIGURE 2 ), but tapering into a point apically in C. hayashii ( Fig. 2c–d View FIGURE 2 ).
(3) S 9 in C. duytan is almost entirely black except for a narrow yellow apical ring posteriorly ( Fig. 2a–b View FIGURE 2 ). In C. hayashii the posterior half of S9 is largely yellow ( Fig. 2d–e View FIGURE 2 ).
(4) Flagella of genital ligula gradually tapering with acute apices in C. duytan ( Fig. 2c View FIGURE 2 ), but apical 1/5 spatulate in C. hayashii ( Fig. 2f View FIGURE 2 ).
(5) The examined specimens of C. duytan are smaller than C. hayashii (hindwing 26 and 29, abdomen incl. appendages 41 and 45 in C. duytan and C. hayashii , respectively).
The female of C. duytan can be separated from most other congeners by the complex morphology of the prothoracic lobes ( Fig. 3c–d View FIGURE 3 ).
Habitat and Ecology. This is a shy species, usually perching ca. 20–30 cm high in dark forest underlain with decomposing leaf litter. It was found at streams (4–6m width) with large stones in pristine forest. At the type locality, this species occurs with two other congeners C. mientrung Kompier & Phan, 2017 and C. dydima (Selys, 1863) (new record for Vietnam, unpublished).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.