Coniella eucalyptorum (Crous & M.J. Wingf.) L.V. Alvarez & Crous, Stud. Mycol.
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.630.1.3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10377142 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6B13D369-1006-D170-9FDA-FC23221FFE63 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Coniella eucalyptorum (Crous & M.J. Wingf.) L.V. Alvarez & Crous, Stud. Mycol. |
| status |
|
Coniella eucalyptorum (Crous & M.J. Wingf.) L.V. Alvarez & Crous, Stud. Mycol. View in CoL 85: 15 (2016)
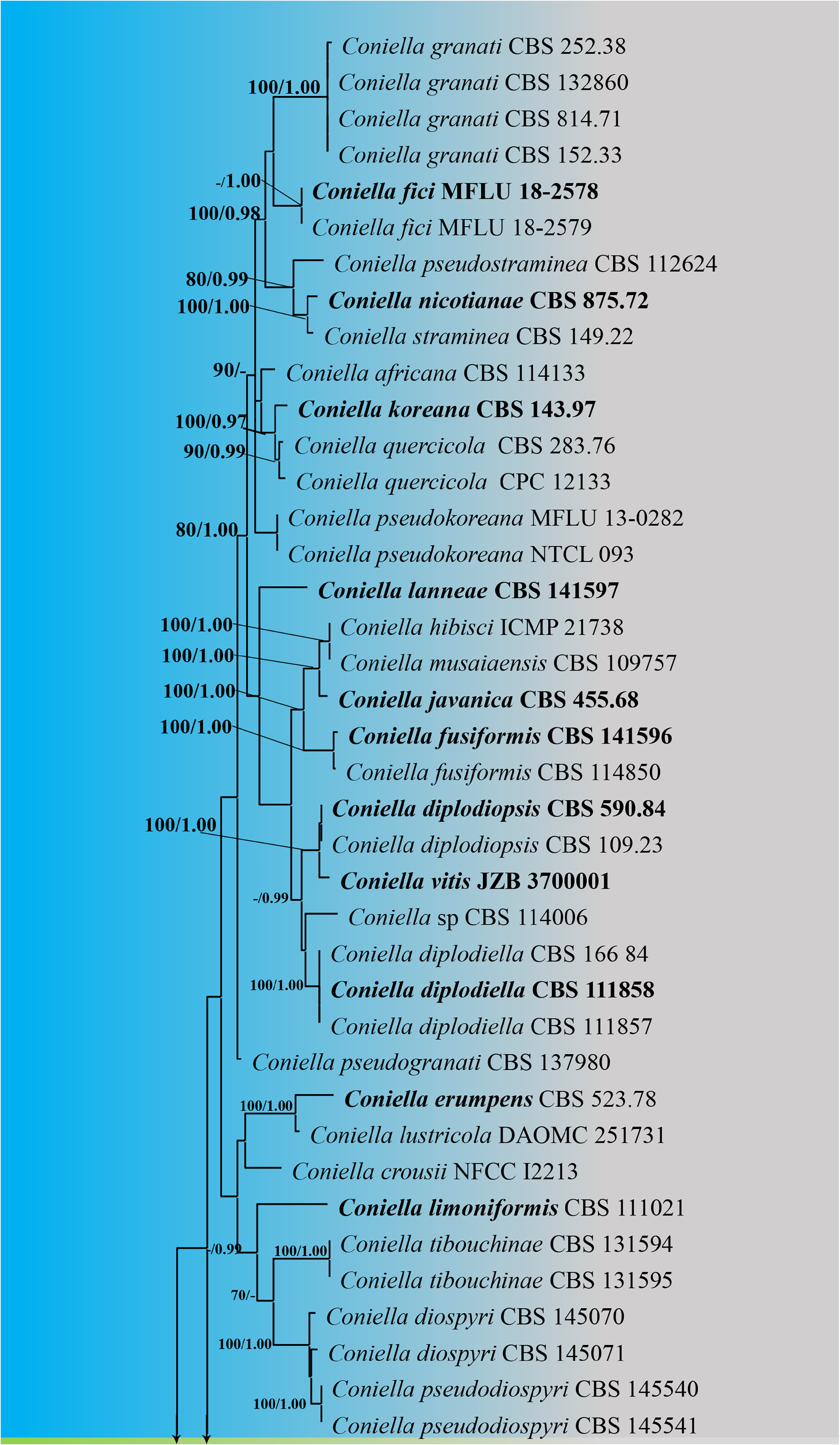
Index Fungorum Registration Identifier 817817, Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2
Basionym: Pilidiella eucalyptorum Crous & M.J. Wingf. View in CoL , in Van Niekerk, Groenewald, Verkley, Fourie, Wingfield & Crous, (2004).
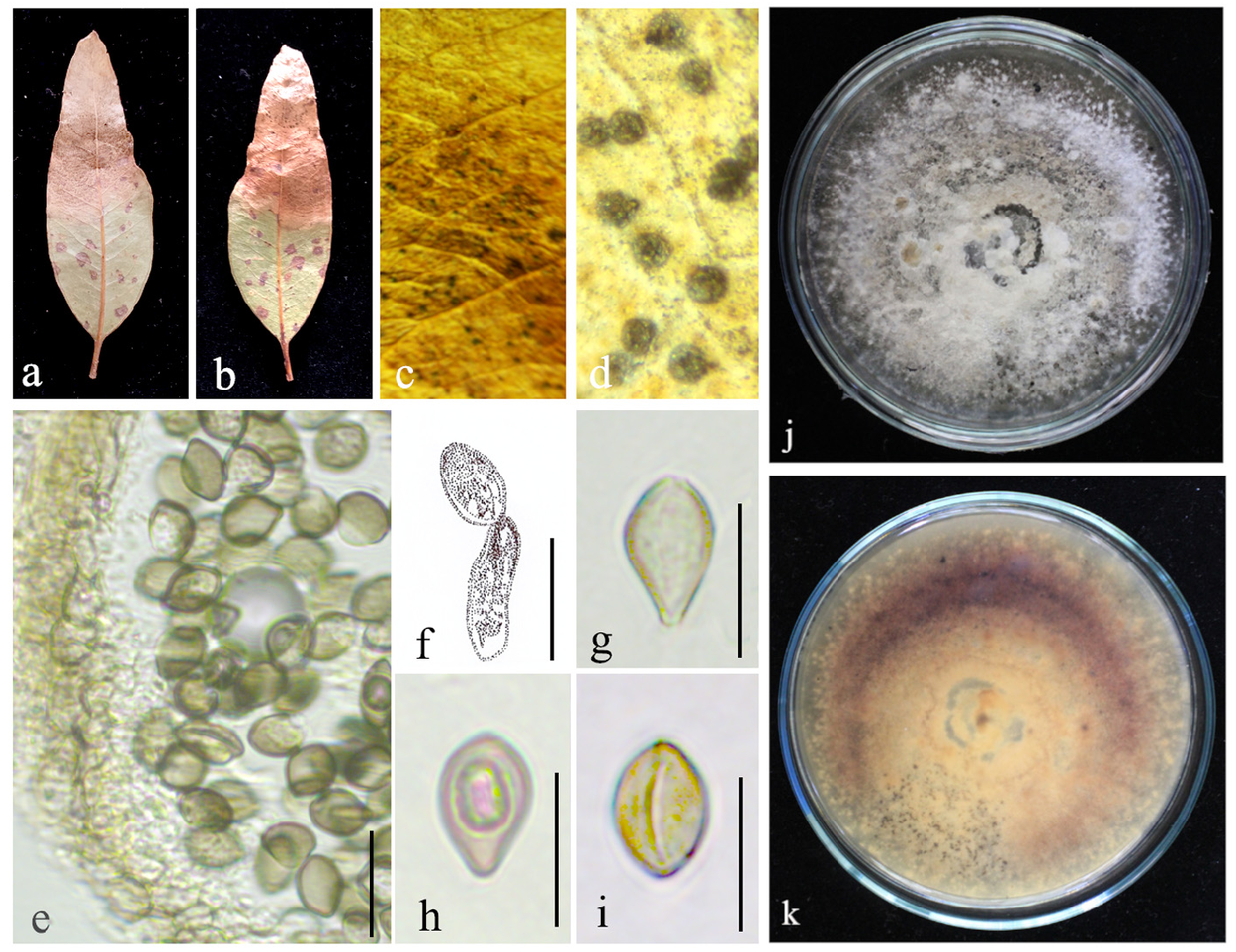
Pathogenic on leaves of E. camaldulensis View in CoL . Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: Conidiomata 80−140 μm long, 150−200 μm in diameter (n= 15), solitary or aggregated, globose, brown, and dark brown to black from the top. Conidioma wall consisting of 2–3 layers of hyaline textura prismatica and 4−5 layers of brown textura angularis cells. Conidiogenous cells 12–15 × 1–2 μm (x̄ = 13 × 2 μm, n = 20), annellidic, narrowing at the tip, smooth and hyaline. Conidia 10−13 × 3−6 μm (x̄ = 12 × 5 μm, n = 30), hyaline to pale brown, becoming dark brown at maturity, smooth, broadly ellipsoidal, both sides gradually tapering, smooth-walled, and multi-guttulate with one or two prominent guttules.
Culture characteristics: Colony on PDA reaching 25 mm diameter after seven days at 25 °C, colony circular, margin wavy, flat, velvety appearance, colony from above: pale pink to brown; reverse: light brown to dark brown.
Material examined: Sri Lanka, North Central Province, Polonnaruwa District, Aralaganwila , (Latitude 7.293889 Longitude 81.2109594) on leaves of E. camaldulensis , 5 th of May 2022, Rashika S. Brahmanage, RB-LP31, ( NIFSCC-RB-LP31 , UOCCC-RB-LP31 )
GenBank accession numbers: ITS = OR141147 , LSU = OR143784 , tef1-α = OR461287
Notes: Based on the morphological characteristics, our strain (NIFSMC-RB-LP31) is similar to the holotype of Coniella eucalyptorum (CBS 112640) collected from the leaves of Eucalyptus grandis × E. tereticornis hybrid ( Alvarez et al. 2016). According to multi-gene phylogeny (ITS, LSU, and tef1-α), our strain (NIFSMC-RB-LP31) clustered with other strains of C. eucalyptorum (CBS 111023, CBS 112640, CBS 114134, and MFLU 17-0675) with 100% ML and 1.00 PP bootstrap support ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). When comparing the ITS, LSU, and tef1-α gene regions, no base pair (0%) differences were observed between our strain (NIFSMC-RB-LP31) and the holotype of C. eucalyptorum (CBS 112640). Coniella eucalyptorum was previously recorded in Australia, Brazil, Chile, Indonesia, Malaysia, Mexico, Thailand, Venezuela, and Vietnam ( Hyde et al. 2020). Therefore, we identified our fungal collection as the first geographical record from Sri Lanka.
Pathogenicity assay
Results of the pathogenicity test showed that the RB-LP31 strain (identified as C. eucalyptorum ) can cause disease on only wounded host leaves. The initial symptoms were seen on wounded leaves after two to three days of inoculations with mycelial plugs ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 , e 1 – e View FIGURE 1 4). Small light-brown to brown lesions emerged at the inoculation site of the leaves. Subsequently, these lesions rapidly enlarged (diameter 2 – 5.5 cm) and transformed into brown to dark brown lesions after five days of inoculation. Symptoms continuously spread, and sparse white mycelia appeared on the lesions three days post-inoculation and subsequently spread throughout the host leaf. Initial symptoms were seen on wounded leaves treated with spore suspensions of C. eucalyptorum after 10–12 days of inoculation ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 , a 1 – a View FIGURE 1 4), and 1–3 cm lesions appeared after 16 days of inoculation. Non-wounded leaves inoculated with both spore suspensions and mycelial plugs showed no symptoms even after 16 days of inoculation ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 , b and f), similar to the negative control treatments ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 , c, d, g, and h). Based on the morphological characteristics, we identified the re-isolated fungus as C. eucalyptorum .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Coniella eucalyptorum (Crous & M.J. Wingf.) L.V. Alvarez & Crous, Stud. Mycol.
| Brahmanage, Rashika S., Wijayawardene, Nalin N., Nanayakkara, Chandrika M., Muthumala, Chaminda K., Wijesundara, Siril, Dai, Dong Q. & Ariyawansa, Kahandawa G. S. U. 2023 |
Coniella eucalyptorum (Crous & M.J. Wingf.) L.V. Alvarez & Crous, Stud. Mycol.
| L. V. Alvarez & Crous 2016: 15 |