Lasioglossum (Leuchalictus) occidens ( Smith, 1873 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4044.4.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AC09A256-A83D-46B7-A71D-E84B5ABFD138 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6108235 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0204411B-FFC1-C851-41C5-FB26FC0EF8D2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lasioglossum (Leuchalictus) occidens ( Smith, 1873 ) |
| status |
|
Lasioglossum (Leuchalictus) occidens ( Smith, 1873) View in CoL
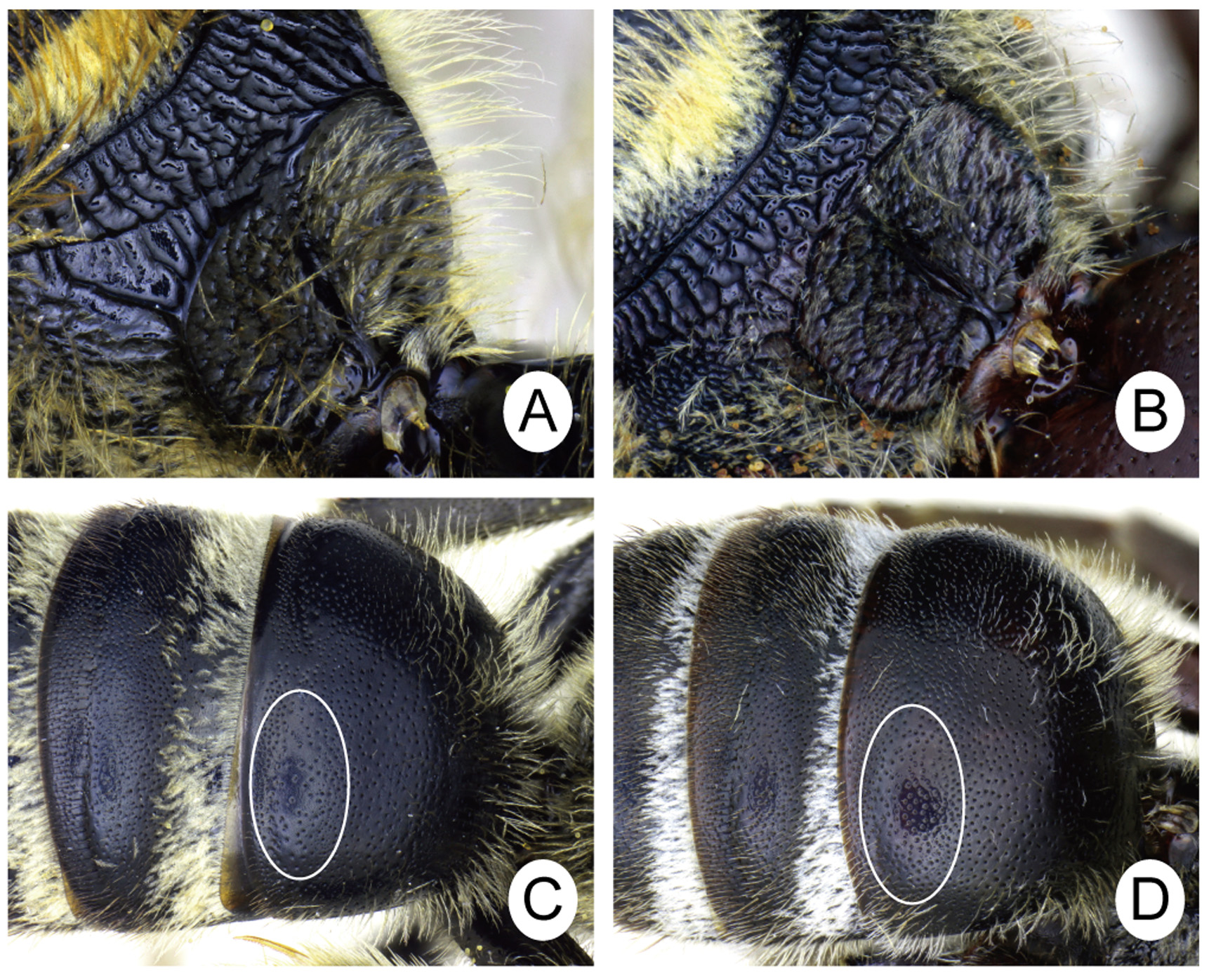
Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4. A, B, E, F D, 5D, 6A, 6C, 8B
Halictus occidens Smith 1873: 200 [Holotype: Natural History Museum, London, United Kingdom, ♀, type locality = Hiogo (Hyogo Pref)., Japan]; Cockerell 1909: 315 [in key].
Halictus quadraticollis Vachal 1903: 129 [Holotype: Muséum National d’ Histoire Naturelle, Paris, France, ♀, type locality = Japan]. Synonymy by Blüthgen (1926b: 348).
Lasioglossum (Lasioglossum) koreanum Ebmer 1978b: 309 View in CoL [Holotype: Hungarian Natural History Museum, Budapest, Hungary, ♂, type locality = Pyongyan, North Korea]. Synonymy by Pesenko (2006: 156).
Lasioglossum (Lasioglossum) occidens: Sakagami & Tadauchi 1995: 188 View in CoL [♂, illustration]; Ebmer 1996: 275; Ebmer & Maeta 1999: 243 [♀, photograph], 246 [♀, photograph]; Murao 2011: 88–89 [♂, illustration]
Lasioglossum (Leuchalictus) occidens: Pesenko 2006: 140 View in CoL [in key], 141 [♂, illustration], 143 [♂, illustration], 145 [in key], 156–157.
Diagnosis. This species is similar to L. circularum Fan & Ebmer and L. formosae (Strand) from eastern Asia. It is separated from L. circularum by the integument of the female mesoscutum nearly smooth among punctures, the lateral and posterior surfaces of the female propodeum with sparse tomentose hairs, the tuft of hair on male S6 thick apically ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8. A – D ), and the gonostylus of male genitalia broad apically ( Pesenko 2006, Fig. 61); from L. formosae it can be separated by the lateral and oblique carinae of the posterior surface of the female propodeum, which are strongly developed ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6. A, B ), and the submedial patch of T1 with sparser PP in both sexes (IS = 3.5 d in maximum; white circle in Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6. A, B C). In contrast, in L. circularum , the integument of the female mesoscutum is distinct tessellate, the lateral and posterior surfaces of female propodeum are covered with dense tomentose hairs, the tuft of hairs on the male S6 is narrow apically ( Fig. 7A View FIGURE 7. A – D ), and the gonostylus is elongate, elliptical ( Pesenko 2006, Fig. 53); in L. formosae , the lateral and oblique carinae of the posterior surface of the female propodeum are weakly developed ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6. A, B ) and the submedial patch of T1 has denser PP in both sexes (IS = 2 d in maximum; white circle in Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6. A, B D).
Specimens examined. (n = 55) [ South Korea] GW: 1♀, Bougmyong-ri, Dongsan-myon, Chunchon-gun, 23. v. 1992 (O. Tadauchi, ELKU); 1♀, Guryrong, Chiaksan, National Park, N37°23’17’’, E128°1’10’’, 11. vi. 2013 (O. Tadauchi, ELKU); 1♀, Sangchangbong-ri, Gonggeunmyeon, Hoengseong-gun, 25. v. 2009 (H.S. Lee, QIA). Seoul: 1♀, Jeongreung, Seonbukgu, 5. x. 1984 (S.M. Kim, QIA); 1♀, Jin-gwannaedong, Eunpyeibggu, 7. ix. 2010 (H.S. Lee, QIA); Mt. Dobong-san, Dobonggu, 1♀, 23. ix. 1984 (G.S. Jang, QIA), 1♀, 7. x. 1984 (G.H. Kim, QIA), 1♀, 21. vii. 1992 (S.H. Lee, QIA). Incheon: 1♀, Mt. Mari-san, Ganghwado, Ganghwan-gun, 13. viii. 1995 (I.K. Lee, SNU). GG: Kwangnung, Pochon-gun, 1♀, 16–19. vii. 1992 (K. Morimoto, ELKU), 1♀, 16. vii. 1992 (K. Kanmiya, ELKU), 2♀, 18. vii. 1992 (O. Tadauchi & K. Kanmiya, ELKU); 1♀, Anyang arboretum, Anyang-si, 8. v. 1990 (SNU); Arboretum, Suwon, 2♀, 4. viii. 1999 (H.T. Kim, SNU), 1♀, 8. x. 2000 (J.K. Lee, SNU); 1♀, CALS, Suwon, 23. v. 1995 (J.S. Park, SNU); 1♀, Cheonggye, 21. viii. 1971 (SNU); 1♀, Deokjeokdo, Ongjin, 6. vii. 1981 (G.S. Jang, QIA); 1♀, Eommi-ri, Gwangju, 23. v. 1981 (Y.M. Seo, QIA); 1♀, Enugogae, Gwangju, 15. ix. 1984 (G.S. Lee, QIA); 1♀, Everland, Yongin, 13. vii. 2000 (Kim & Kim, SNU); 2♀, Hantaek arb., Yongin, 25. vii. 2001 (H.S. Lee, QIA); 1♀, Mt. Cheonma-san, 6. viii. 1984 (B.R. Park, QIA); 1♀, Mt. Gamak-san, Paju-si, 8. ix. 1984 (J.I. Kim, QIA); 2♀, Mt. Gwanggyo-san, Suwon, 24. ix. 1994 (Y.S. Son & W. Kim, SNU); 1♀, Mt. Jonghyeon-san, Yeoncheon-gun, 24. iv. 1997 (H.S. Lee, QIA); 2♀, Sanyang, Icheon, 17. viii. 1999 (H.S. Lee, QIA); 3♀, Seondu-ri, Gilsang, Ganghwa, 12. viii. 1991 (H.C. Park, QIA); 1♀, Suwon, 1. vi. 1983 (H.J. Lee, SNU). CN: 1♀, Ilam-ri, Seongyeonmyeon, Seosan-si, 20. v. 2006 (S.W. Park, QIA); 2♀, Mt. Gyerying-san, Gongju-gun, 11. vii. 1995 (H.S. Lee, QIA); 1♀, Mt. Gwangdeong-san, Cheonan, 16–18. vi. 1994 (J.M. Park, QIA). CB: 1♂, Mt. Sogni-san, 21. viii. 1974 (I. Kudo, ELKU). GN: 1♀, Samjeong-ri, Macheong-myon, Hamyang-gun, 9. v. 1991 (T. Saigusa, ELKU); 1♀, Yulgoksa temple, Sancheongmyeon, Snacheong-gun, 14. v. 2010 (H.S. Lee, QIA); 1♀, Jungsan-ri, Mt. Jiri-san, 30. vii. 1981 (J.I. Kim, QIA). JN: Chusan, Gwangyang-si, 1♀, 23. vii. 2001 (H.E. Kim, SNU), 6♀, 14. viii. 2002 (HS. Park, SNU); 1♀, Hwaeomsa temple, Gurye, 26. viii. 1970 (SNU); Mt. Baekun-san, Gwangyang, 1♀, 26. vi. 1994 (H.S. Lee, SNU), 1♀, 23. ix. 1996 (H.S. Lee, QIA); 1♀, Nohoeeup, Wando, 21. viii. 1982 (J.I. Kim, QIA); Piagol, Mt. Jiri-san, 1♀, 23. vi. 1987 (S.J. Ban, QIA), 1♀, 26. vii. 1999 (H.T. Kim, SNU). JJ: 2♀, Hachujado Is., Youngheung-ri, Chujamyeon, Jeju-si, 17. ix. 2010 (H.S. Lee, QIA).
Distribution. North Korea, South Korea (new record), Japan, China, Russian Far East, Taiwan.
Flight period in South Korea. Female: Aril to October. Male: August. In Japan, male flies from July to November (Murao 2014).
Flower records in South Korea. This species has been recorded from the the following eight plant species in six families: Araliaceae : Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. Et Maxim.) Maxim. Asteraceae : Cornus sp.; Coreopsis basalis (A.Dietr.) S.F. Blake ; Erigeron annuus (L.) Pers. Fabaceae : Lespedeza bicolor Turcz. Malvaceae : Hibiscus syriacus L. Oleaceae : Ligustrum japonicum Thunb. Rutaceae : Phellodendron amurense Rupr.
Biology. According to Miyanaga et al. (2012) the biology of this species is as follows: bivoltine and basically solitary; brood rearing period of the overwintered and first generation start from early May to mid June and early July to mid August, respectively (the overwintered generation dies before emerging the first one); nest structure type IIIa of Sakagami & Michener (1962); some nest reared in the greenhouse were composed of multiple females (both the overwintered and first generation); the task allocation of foraging activity of each multi-female nest between cohabitants was relatively distinct.
Comments. Lasioglossum koreanum was synonymized under L. occidens by Pesenko (2006) because of the subtle difference between these species. However, the synonymy based on this lack of morphological difference remained in doubt (Murao et al. 2014). In the present study, we compared a part of COI gene sequence between L. koreanum from South Korea and L. occidens from Japan. As a result, the pair-wise sequence divergence between these species was within the limits commonly considered to typical of single Lasioglossum species (0.8 % of 657 bp) ( Gibbs 2009; Sheffield et al. 2009). Lasioglossum occidens and L. koreanum are treated as a single species based on the lack of clear morphological and molecular differences.
Accession numbers of DNA sequence. LC 043129 View Materials , LC 043131 View Materials .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Lasioglossum (Leuchalictus) occidens ( Smith, 1873 )
| Murao, Ryuki, Lee, Heung-Sik & Tadauchi, Osamu 2015 |
Lasioglossum (Leuchalictus) occidens:
| Pesenko 2006: 140 |
Lasioglossum (Lasioglossum) occidens:
| Ebmer 1999: 243 |
| Ebmer 1996: 275 |
| Sakagami 1995: 188 |
Lasioglossum (Lasioglossum) koreanum
| Pesenko 2006: 156 |
| Ebmer 1978: 309 |
Halictus quadraticollis
| Bluthgen 1926: 348 |
| Vachal 1903: 129 |
Halictus occidens
| Cockerell 1909: 315 |
| Smith 1873: 200 |