Mogera insularis (Swinhoe, 1863)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6678191 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6671990 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0380B547-B64A-FF99-9F94-F771FB5AC1DD |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Mogera insularis |
| status |
|
Insular Mole
French: Taupe insulaire / German: Chinesischer Inselmaulwurf / Spanish: Topo insular
Other common names: Formosan Mole
Taxonomy. Talpa insularis Swinhoe, 1863 View in CoL , “Island of Formosa (China)” (= Taiwan).
Mogera insularis View in CoL has sometimes included M. latouchei from the continent as a synonym. Relationships between these two species are still uncertain, but M. latouche: is smaller and likely represents a distinct species. Taxonomic status of hainana described from Mount Wuzhi, Hainan Island, China, 1s also controversial and considered here to be subspecies of M. in-
sularis. In Taiwan, geographical variation in size was observed. Mogera insularis View in CoL from lowlands in northern and central Taiwan is larger than M. insularis View in CoL from mountains and southern Taiwan. This geographical variation might be affected by availabilities of suitable habitats among localities. Two subspecies recognized.
Subspecies and Distribution.
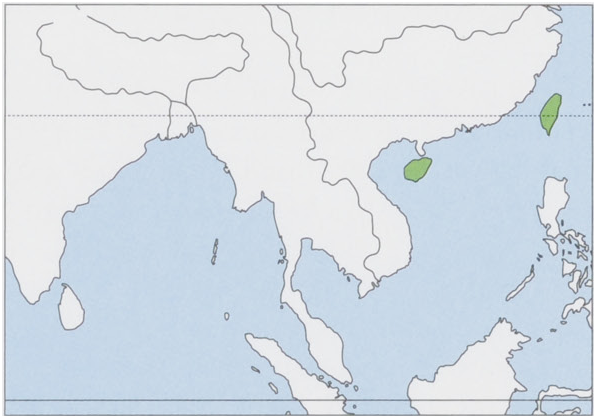
M.i.insularisSwinhoe,1863—Taiwan.
M. i. hainana Thomas, 1910 — Hainan I (China). View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 112-139-5 mm, tail 6-5-11-5 mm, hindfoot 15-5-17 mm; weight 42-725 g. Tail is 4-9-8-8% of head-body length. The Insular Mole is small, and tail is usually shorter than hindfoot. Pelage varies in color from dark brown to slate above and tawny brown or dark gray below. Skull is small and characterized by broad rostrum. Upper incisor row is V-shaped and projects forward. Dental formula is 13/2, C1/1,P4/4,M 3/3 (x2) = 42. There are 7 cervical, 13-14 thoracic, 5-6 lumbar, 6 sacral, and 11 caudal vertebrae. Chromosomal complement has 2n = 32 and FNa= 54 or 56.
Habitat. Fruit farms, abandoned cultivated fields, riverbanks, and forests from near sea level to elevations of 2000-2500 m. In high mountains, Insular Moles might have been confused with Kano’s Moles (M. kanoana).
Food and Feeding. Insular Moles eat earthworms, insects, and insect larvae.
Breeding. One pregnant Insular Mole with four fetuses was collected in March.
Activity patterns. The Insular Mole is fossorial and lives in underground tunnels.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red Last.
Bibliography. Abe (1995), Kawada (2016), Kawada, Oda et al. (2010), Kawada, Shinohara et al. (2007), Lin Liangkong & Motokawa (2014), Lin Liangkong et al. (2002), Motokawa, Lin Liangkong et al. (2001).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.